-
Reproductive Health an Essential Part of Climate Compatible Development
April 11, 2012 // By Sandeep BathalaMOREECSP was at London’s 2012 Planet Under Pressure conference following all of the most pertinent population, health, and security events.
At a panel on “climate compatible development” at this year’s Planet Under Pressure global change conference, Population Action International’s Roger-Mark De Souza was the lone voice to speak about demographics. He presented a detailed analysis of population trends, based on collaboration with the Kenya-based African Institute for Development Policy.
“The link between population dynamics and sustainable development is strong and inseparable – as is the link between population dynamics, reproductive health, and gender equality,” said De Souza. These linkages were emphasized by the UN at the International Conference on Population and Development, held in Cairo in 1994, as well as during the original Rio Conference on Environment and Development in 1992.
“Climate compatible development” is a novel development paradigm being developed by the Climate and Development Knowledge Network and defined as “development that minimizes the harm caused by climate impacts, while maximizing the many human development opportunities presented by a low emissions more resilient future.”
The key tenet of this development framework is an emphasis on climate strategies that embrace development goals and integrate opportunities alongside the threats of a changing climate. In this respect, climate compatible development is seen as moving beyond the traditional separation of adaptation, mitigation, and development strategies. It challenges policymakers to consider “triple win” strategies that result in lower emissions, better resilience, and development – simultaneously.
Although developed nations are historically the major contributors of greenhouse gases due to comparatively high levels of consumption, developing countries are the most vulnerable to consequences of climate change. Emerging evidence shows that rapid population growth in developing countries exacerbates this vulnerability and undermines resilience to the effects of climate change, said De Souza. Socioeconomic improvement will also increase the levels of consumption and emissions from developing countries.
“Meeting women and their partners’ needs for family planning can yield the ‘triple win’ strategy envisaged in the climate development framework,” De Souza said. “Meeting unmet family planning needs would help build resilience and strengthen household and community resilience to climate change; slow the growth of greenhouse gases; and enhance development outcomes by improving and expanding health, schooling, and economic opportunities.”
Decision makers engaged in climate change policy planning and implementation at local, national, and international levels should have access to evidence on population trends and their implications on efforts to adapt to climate change as well as the overall development process, De Souza said.
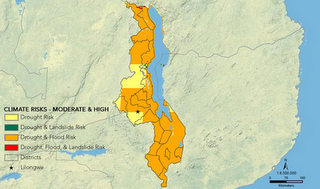
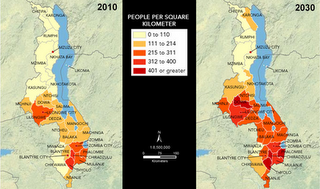
He presented new maps and analysis for Africa, particularly Malawi and Kenya, developed by PAI, building on earlier mapping work which identified 26 global population and climate change hotspots – countries that are experiencing rapid population growth, low resilience to climate change, and high projected declines in agricultural production.
“PAI’s work is a clear demonstration of how better decision making can be informed by the right analysis, in the right format, at the right time,” said Natasha Grist, head of research at the Climate Knowledge and Development Network.
“Most of the hotspot countries have high levels of fertility partly because of the inability of women and their partners to access and use contraception,” said De Souza. He continued:Investing in voluntary health programs that meet family planning needs could, therefore, slow population growth and reduce vulnerability to climate change impacts. This is especially important because women, especially those who live in poverty, are likely to be most affected by the negative effects of climate change and also bear the disproportionate burden of having unplanned children due to lack of contraception.
In conclusion, said De Souza, “global institutions and frameworks that support and promote climate compatible development can enhance the impact of their work by recognizing and incorporating population dynamics and reproductive health in their adaptation and development strategies.”
For full population-related coverage from the conference, see our “Planet 2012 tag.” Pictures from the event are available on our Facebook and Flickr pages, and you can join the conversation on Twitter (#Planet2012).
Sources: Climate and Development Knowledge Network, IPCC, Population Action International.
Photo Credit: Sean Peoples/Wilson Center; Maps: Population Action International. -
Reading Radar
Natural Resource Management, Climate Change, and Conflict
In Climate Change and Conflict: Lessons From Natural Resource Management, a new report from the Danish Institute for International Studies, authors Mikke Funder, Signe Marie Cold-Ravnkilde, Ida Peters Ginsborg, and Nanna Callisen Bang, review literature on how natural resource management, climate change, and conflict interact on the local, national, and transboundary levels, from which they offer lessons for development policymakers and programmers. Since natural resource management is “strongly related” to how climate change and conflict interact, they write, a better understanding of how natural resource management has taken conflict prevention and resolution into account would benefit development work aimed at mitigating climate change’s “multiplier effect” on conflict. Recommendations include working on as local a level as possible; working with and strengthening existing customary and legal conflict resolution frameworks; and coordinating development efforts across sectors so that policymakers and programmers can minimize the risk of unintentionally causing or aggravating conflict.MORE
In his March 2012 Transatlantic Academy paper, “The Geostrategic Implications of the Competition for Natural Resources: The Transatlantic Dimension,” François Heisbourg analyzes the strategic implications of emerging trends affecting the global energy marketplace, including climate change and scarcity. Whereas Europe and the United States shaped energy markets in the 19th and 20th centuries, respectively, there is no comparable leader in the 21st century marketplace, writes Heisbourg, nor is it clear that one will emerge. Instead, there will be a growing number of influential countries, like Brazil, India, and China, that will have an impact as both consumers and producers. That said, the Persian Gulf will remain geopolitically important given its dominance of the oil market, giving reason for the United States, Europe, India, and China to actively pursue cooperation in the Gulf in order to minimize the risk of future energy crises, Heisbourg concludes.Topics: Africa, Brazil, China, climate change, conflict, development, energy, environment, Europe, India, Middle East, natural resources, Reading Radar, U.S. -
Guest Contributor
Responses to JPR Climate and Conflict Special Issue: Steve Lonergan (University of Victoria)
MORE
The relationship between climate change and conflict has been discussed for over two decades but most of the evidence of the link between the two has been anecdotal, drawing on extreme climate scenarios. The authors featured in the January special issue of the Journal of Peace Research devoted to climate change and conflict are therefore to be commended for their detailed investigations into a possible causal relationship between the two.
-
Guest Contributor
Responses to JPR Climate and Conflict Special Issue: François Gemenne (Sciences Po)
MORE
If you want a government to address something, make it a defense issue. No need to hold a PhD in political science to know that governments tend to give the highest priority to issues that involve national security interests – one can complain and whine about it, but that’s the way it is.
-
Guest Contributor
Responses to JPR Climate and Conflict Special Issue: Solomon Hsiang (Princeton University) and Todd G. Smith (University of Texas, Austin)
MORE
A January special issue of the Journal of Peace Research brings together a new collection of evidence on a subject that has been a mainstay of the environmental security agenda: the links between climate and conflict.
-
Food Security in a Climate-Altered Future, Part Two: Population Projections Are Not Destiny
March 20, 2012 // By Kathleen MogelgaardMORERead part one, on the food-population-climate vulnerability dynamics of Malawi and other “hotspots,” here.
Too often, discussions about future food security make only a passing reference to population growth. It is frequently framed as an inevitable force, a foregone conclusion – and a single future number is reported as gospel: nine billion people in 2050. But adhering to a single path of future population growth misses the opportunity to think more holistically about food security challenges and solutions. Several recent food security reports illustrate this oft-overlooked issue.
Accounting for Population a Challenge
Oxfam International’s Growing a Better Future: Food Justice in a Resource-Constrained World is a thorough and fascinating examination of failures in our current food system and future challenges related to production, equity, and resilience. It reports newly-commissioned research, carried out by modelers at the Institute of Development Studies, to assess future agricultural productivity and food prices given the anticipated impacts of climate change.
But both the modeling work and the report text utilize a single projection for population growth: the UN’s 2008 medium variant projection of 9.1 billion by 2050 (which has since been revised by the UN up to 9.3 billion). Early on, the report does recognize some degree of uncertainty about this number: “Greater investment in solutions that increase women’s empowerment and security – by improving access to education and health care in particular – will slow population growth and achieve stabilization at a lower level.” But such investments do not appear in the report’s overall recommendations or Oxfam’s food security agenda. This is perhaps a missed opportunity, since the range of possibilities for future population growth is wide: the UN’s low variant for 2050 is 8.1 billion, and the high variant is 10.6 billion.
Food Security, Farming, and Climate Change to 2050: Scenarios, Results, and Policy Options is another frequently-cited report published by the International Food Policy Research Institute in 2010. In recognizing that economic growth and demographic change have important implications for future food security, IFPRI researchers modeled multiple scenarios for the future: an “optimistic” scenario which embodies high GDP growth and low population growth, a “pessimistic” scenario with low GDP growth and high population growth, and a “baseline” scenario which incorporates moderate GDP growth and the UN’s medium population projection. Each of these scenarios was then combined with five different climate change scenarios to better understand a range of possible futures.
Using different socioeconomic scenarios enabled researchers to better understand the significance of socioeconomic variables for future food security outcomes. The first key message from the report is that “broad-based economic development is central to improvements in human well-being, including sustainable food security and resilience to climate change.” This focus on economic development is based in part on the “optimistic scenario,” which counts on high GDP and low population growth (translating to high rates of per capita GDP growth).
Unfortunately, the socioeconomic scenario construction for this analysis doesn’t allow for an independent assessment of the significance of slower population growth, since high population growth is paired only with low GDP and lower population growth is paired only with high GDP. Therefore, none of the report’s recommendations includes reference to reproductive health, women’s empowerment, or other interventions that would contribute directly to a slower population growth path.
Expanding the Conversation to Better Inform Policy
Without a more nuanced treatment of population projections in technical analysis and popular reporting on food security, decision-makers in the realm of food security may not be exposed to the idea that population growth, a factor so critical in many areas where food security is already a challenge, is a phenomenon that is responsive to policy and programmatic interventions – interventions that are based on human rights and connected to well-established and accepted development goals.
There are some positive signs that this conversation is evolving. A new climate change, food security, and population model developed by the Futures Group enables policymakers and program managers to quickly and easily assess the impact of slower population growth on a country’s future food requirements and rates of childhood malnutrition. In the case of Ethiopia, for example, the model demonstrates that by 2050, a slower population growth path would make up for the caloric shortfall that is likely to arise from the impact of climate change on agriculture and would cut in half the number of underweight children.
And recently, we’ve begun to see some of this more nuanced treatment of population, family planning, and food security linkages in a riveting, year-long reporting series (though perhaps unfortunately named), Food for 9 Billion, a collaboration between American Public Media’s Marketplace, Homelands Productions, the Center for Investigative Reporting, and PBS NewsHour.
In January, reporter Sam Eaton highlighted the success of integrated population-health-environment programs in the Philippines, such as those initiated by PATH Foundation Philippines, that are seeing great success in delivering community-based programs that promote food security through a combination of fisheries management and family planning service delivery. Reporting from the Philippines in an in-depth piece for PBS NewsHour, Eaton concluded:So maybe solving the world’s food problem isn’t just about solving the world’s food problem. It’s also about giving women the tools they want, so they can make the decisions they want – here in the world’s poorest places.
Making clear connections of this nature between population issues and the most pressing challenges of our day may be the missing link that will help to mobilize the political will and financial resources to finally fully meet women’s needs for family planning around the world – an effort that, if started today, can have ongoing benefits that will become only more significant over time. Integrating reproductive health services into food security programs and strategies is an important start.
Back in Malawi, just before we turned off the highway to the Lilongwe airport, I asked the taxi driver to pull over in front of a big billboard. We both smiled as we looked at the huge government-sponsored image of a woman embracing an infant. The billboard proclaimed: “No woman should die while giving life. Everyone has a role to play.” Exactly. The reproductive health services that save women’s lives are the same services that can slow population growth and bring food security within closer reach. -
USAID’s New Climate Strategy Outlines Adaptation, Mitigation Priorities, Places Heavy Emphasis on Integration
February 29, 2012 // By Kathleen MogelgaardMOREIn January, the U.S. Agency for International Development released its long-awaited climate change strategy. Climate Change & Development: Clean Resilient Growth provides a blueprint for addressing climate change through development assistance programs and operations. In addition to objectives around mitigation and adaptation, the strategy also outlines a third objective: improving overall operational integration.
The five-year strategy has a clear, succinct goal: “to enable countries to accelerate their transition to climate-resilient low emission sustainable economic development.” Developed by a USAID task force with input from multiple U.S. agencies and NGOs, the document paints a picture of the threats climate change poses for development – calling it “among the greatest global challenges of our generation” – and commits the agency to addressing both the causes of climate change and the impacts it will have on communities in countries around the world.
These statements are noteworthy in a fiscal climate that has put development assistance under renewed scrutiny and in a political environment where progress on climate change legislation seems unlikely.
Not Just Challenges, But Opportunities
To make the case for prioritizing action on climate change, the strategy cites climate change’s likely impact on agricultural productivity and fisheries, which will threaten USAID’s food security goals. It also illustrates the ways in which climate change could exacerbate humanitarian crises and notes work done by the U.S. military and intelligence community in identifying climate change as a “threat multiplier” (or “accelerant of instability” as the Quadrennial Defense Review puts it) with implications for national security.
Targeted efforts to address climate change, though, could consolidate development gains and result in technology “leap-frogging” that will support broader development goals. And, noting that aggregate emissions from developing countries are now larger than those from developed countries, the strategy asserts that assisting the development and deployment of clean technologies “greatly expands opportunities to export U.S. technology and creates ‘green jobs.’”
In addition to providing a rationale for action, the strategy provides new insights on how USAID will prioritize its efforts on climate change mitigation and adaptation. It provides a clear directive for the integration of climate change into the agency’s broader development work in areas such as food security, good governance, and global health– a strong and encouraging signal for those interested in cross-sectoral planning and programs.
Priorities Outlined, Tough Choices Ahead
President Obama’s Global Climate Change Initiative, revealed in 2010, focuses efforts around three pillars: clean energy, sustainable landscapes, and adaptation. USAID’s climate strategy fleshes out these three areas, identifying “intermediate results” and indicators of success – such as the development of Low Emission Development Strategies in 20 partner countries, greenhouse gas sequestration through improved ecosystem management, and increasing the number of institutions capable of adaptation planning and response.
In laying out ambitious objectives, however, the authors of the strategy acknowledge constrained fiscal realities. The strategy stops short of identifying an ideal budget to support the activities it describes, though it does refer to the U.S. pledge to join other developed countries in providing $30 billion in “fast start financing” in the period of 2010 to 2012 and, for those USAID country missions that will be receiving adaptation and mitigation funding, establishes “floors” of $3 million and $5 million, respectively.
The final section of the strategy lists over thirty countries and regions that have already been prioritized for programs, including Bangladesh, India, Kenya, Malawi, and Peru. But “we are unable to work in every country at risk from climate change impacts or with the potential for low carbon sustainable growth,” the strategy asserts. An annex includes selection criteria to guide further funding decisions, including emission reduction potential, high exposure to physical climate change impacts, a suitable enabling environment, coordination with other donors, and diplomatic and geographic considerations.
“Integration” Central to Strategy
The concept of integration figures prominently throughout the 27-page document. For those of us working in the large and growing space where the global challenges of climate change, food security, health, livelihoods, and governance overlap, this attention is heartening. While it may sometimes seem simply fashionable to pay lip service to the idea of “breaking out of stovepipes,” the strategy identifies concrete ways to incentivize integration.
“Integration of climate change into USAID’s development portfolio will not happen organically,” the strategy says. “Rather, it requires leadership, knowledge and incentives to encourage agency employees to seek innovative ways to integrate climate change into programs with other goals and to become more flexible in use of funding streams and administrative processes.”
To this end, USAID plans to launch a group of pilot activities. USAID missions must submit pilot program proposals, and selected programs will emphasize integration of top priorities within the agency’s development portfolio (including Feed the Future and the Global Health Initiative). Among other criteria, pilots must demonstrate buy-in from multiple levels of leadership, and will be selected based on their potential to generate integration lessons and tools over the next several years.
This kind of integration – the blending of key priorities from multiple sectors, the value of documented lessons and tools, the important role of champions in fostering an enabling environment – mirrors work carried out by USAID’s own population, health, and environment (PHE) portfolio. To date, USAID’s PHE programs have not been designed to address climate challenges specifically, and perhaps not surprisingly they aren’t named specifically in the strategy. But those preparing and evaluating integration pilot proposals may gain useful insights on cross-sectoral integration from a closer look at the accumulated knowledge of more than 10 years of PHE experience.
Population Dynamics Recognized, But Opportunities Not Considered
Though not a focus of the strategy, population growth is acknowledged as a stressor – alongside unplanned urbanization, environmental degradation, resource depletion, and poverty – that exacerbates growing challenges in disaster risk reduction and efforts to secure a safe and sufficient water supply.
Research has shown that different global population growth scenarios will have significant implications for emissions growth. New analysis indicates that the fastest growing populations are among the most vulnerable to climate change and that in these areas, there is frequently high unmet need for family planning. And we have also clearly seen that in many parts of the world, women’s health and well-being are increasingly intertwined with the effects of changing climate and access to reproductive health services.
In its limited mention of population as a challenge, however, the strategy misses the chance to identify it also as an opportunity. Addressing the linked challenges of population growth and climate change offers an opportunity to recommit the resources required to assist of the hundreds of millions of women around the world with ongoing unmet need for family planning.
The strategy’s emphasis on integration would seem to be an open door to such opportunities.
Integrated, cross-sectoral collaboration that truly fosters a transition to climate-resilient, low-emission sustainable economic development will acknowledge both the challenge presented by rapid population growth and the opportunities that can emerge from expanding family planning access to women worldwide. But for this to happen, cross-sectoral communication will need to become more commonplace. Demographers and reproductive health specialists will need to engage in dialogues on climate change, and climate specialists will need both opportunities and incentives to listen. USAID’s new climate change integration pilots could provide a new platform for this rare but powerful cross-sectoral action.
Kathleen Mogelgaard is a writer and analyst on population and the environment, and a consultant for the Environmental Change and Security Program.
Sources: FastStartFinance.org, International Energy Agency, Maplecroft, Population Action International, The White House, U.S. Department of Defense, USAID.
Photo Credit: “Displaced Darfuris Farm in Rainy Season,” courtesy of United Nations Photo.Topics: adaptation, Bangladesh, climate change, environment, food security, funding, gender, global health, India, Kenya, Malawi, natural resources, Peru, population, poverty, urbanization, USAID -
Dot-Mom // From the Wilson Center
Programming to Address the Health and Livelihood Needs of Adolescent Girls
MORE
“There are 750 million adolescent girls in the world today, and this is by far one of the world’s most marginalized and vulnerable demographics,” said Denise Dunning, the Public Health Institute’s program director for emergency contraception in Latin America during a February 2 panel at the Wilson Center. Dunning, who also leads the Adolescent Girls’ Advocacy and Leadership Initiative (AGALI), was joined by Margaret Greene, director of Greeneworks, and Jennifer Pope, the deputy director of sexual and reproductive health at Population Services International, to discuss how to better reach underserved adolescent girls in developing countries with health and livelihood programs.
 A Publication of the Stimson Center.
A Publication of the Stimson Center.