-
Leona D’Agnes on Evaluating PHE Service Delivery in the Philippines
›“By reducing population growth, we are going to have a better chance of sustaining the gains of an environmental conservation project,” said Leona D’Agnes in this interview with ECSP. D’Agnes, a technical advisor to PATH Foundation Philippines, served as lead author on a research article published late last year in Environmental Conservation titled, “Integrated Management of Coastal Resources and Human Health Yields Added Value: A Comparative Study in Palawan (Philippines).” The study provided concrete statistical evidence that integrated development programming incorporating population, health, and the environment (PHE) can be more effective in lowering population growth rates and preserving critical coastal ecosystems than single-sector development interventions.
“What set this research apart from earlier work on integrated programming was the rigorous evaluation design that was applied,” said D’Agnes. “What this design aimed to do is to evaluate the integrated approach itself. Most of the previous evaluations that have been done on integrated programming were impact evaluations — they set out to evaluate the impact of the project.” This most recent research project, on the other hand, sought to evaluate the effectiveness of cross-sectoral interventions based on “whether or not synergies were produced,” said D’Agnes.
Although it took her team six years to generate statistically significant findings in Palawan, D’Agnes reports that the synergies of PATH Foundation Philippines’ PHE intervention took the form of reduced income poverty, a decreased average number of children born to women of reproductive age, and the preservation of coastal resources, which helped bolster the region’s food security.
Going forward, D’Agnes said, an integrated approach to environmental conservation should also prove appealing because of its cost effectiveness. “This has huge implications for local governments in the Philippines, where they are struggling to meet the basic needs of their constituents in the face of very small internal revenue allotments that they get from the central government,” she said. “They can really pick up on this example to see that at the local level, if somehow they can do this integrated service delivery that was done in the Integrated Population and Coastal Resource Management (IPOPCORM) model, that they’ll be able to achieve the objectives of both their conservation and their health programs in a much more cost-effective way, and, in the process, generate some other [positive] outcomes that perhaps they didn’t anticipate.”
D’Agnes expects the study’s results will prompt a fresh look at cross-sectoral PHE programming. “I hope that this evidence from this study will help to change the thinking in the conservation community about integrated approaches to conservation and development,” she said.
The “Pop Audio” series is also available as podcasts on iTunes. -
Rare Earths No More? Mineral Discoveries a Potential Game-Changer for East Asia
›July 7, 2011 // By Schuyler NullDiscoveries announced in a journal article over the weekend may prove a game-changer for global rare earth supplies and recent diplomatic maneuvering in East Asia between China, Japan, Vietnam, and the United States. A team of researchers from Japan’s Agency for Marine-Earth Science and Technology published findings in Nature Geoscience that indicate vast underwater reserves of rare earth minerals are scattered across a huge swath of the Pacific, including south and east of Japan. The U.S. Geological survey estimates current global reserves of rare earth minerals at about 110 million tons; Yasuhiro Kato, the lead author of the Japanese team, told Reuters that the sites surveyed could contain an additional 80 to 100 billion metric tons (yes, with a “b”) of the valuable resources.
The authors write that an “area of just one square kilometer, surrounding one of the sampling sites, could provide one-fifth of the current annual world consumption of these elements.” The team collected data from 78 sites in total, with the largest concentrations centered east of the Hawaiian and Polynesian islands (see a map of the surveyed areas here).
Resource Relationships
The discovery could prove crucial for Japan, as it has been seeking alternative sources of rare earth minerals after an embargo earlier this year by China, which controls 97 percent of the world’s current supply. The embargo (which China denied) was imposed in October of last year after the Japanese navy arrested the captain of a Chinese fishing boat, which was alleged to be encroaching on Japanese territorial waters. China’s response increased tensions across the region and produced a flurry of warnings in Washington over the security of U.S. supplies.
Although the embargo was later lifted, Japan and Vietnam reached an agreement for development of Vietnamese mines in November. The tensions sparked by the encounter also spread to the South China Sea where Chinese, Vietnamese, and Filipino forces have stepped up their jockeying over disputed and resource-rich waters to the highest levels in years. Vietnamese and Chinese naval forces recently held mirror exercises, and Filipino officials invoked a 1950-era defense pact with the United States. Chinese Vice Foreign Minister Cui Tiankai told reporters in June: “I believe the individual countries are actually playing with fire, and I hope the fire will not be drawn to the United States.”
Secretary of State Hillary Clinton called concerns over navigability and Chinese insistence on bilateral (as opposed to multilateral) negotiations in the South China Sea a matter of “national interest” for the United States last year.
The Japanese team’s discovery has the potential to significantly impact the power dynamics behind these tensions. China has used its rare earth monopoly to pressure Japan and the United States, which in turn may have also helped embolden its recent more aggressive maritime policies. If the new rare earth discoveries prove viable, that calculus could change considerably.
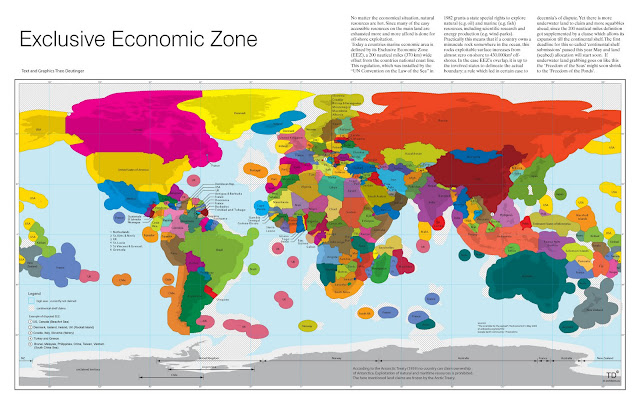
However serious questions remain: Many of the discoveries lie outside of established exclusive economic zones, so who has the rights to mine them? They’re also between 11,500 and 20,000 feet below the surface – how long before we have the technologies to extract them at an industrial scale? And how safe – both for humans and the environment – will those processes be? Aboveground rare earth mines are some of the most damaging to the environment – part of the claimed reason China curbed overall exports earlier this year, which drove up global prices and drew the ire of the World Trade Organization.
For more on the importance of rare earth minerals to the defense and electronics industries, see New Security Beat’s “Rare Earth: A New Roadblock for Sustainable Energy?” and “Reading Radar: The Mineral Security of the United States.” For more on the exclusive economic zones map, see “Eye on Environmental Security: Natural Resource Frontiers at Sea;” and on the South China Sea and what it reveals about future diplomatic fault lines between the United States and China, see “U.S. v. China: The Global Battle for Hearts Minds and Resources.”
Sources: Asia Sentinel, The Atlantic, BBC, Government Accounting Office, Nature Geoscience, The New York Times, Reuters, Tech News Daily, U.S. Department of State.
Photo Credit: Adapted from “USS Mustin underway in the Pacific Ocean,” courtesy of flickr user Official U.S. Navy Imagery, and “Exclusive Economic Zone,” used with permission courtesy of Theo Deutinger and TD Architects. -
Rosemarie Calvert, Center for a Better Life
Winning Hearts and Minds: An Interview with Chief Naval Officer Admiral Gary Roughead
›May 23, 2011 // By Wilson Center StaffThe original version of this article, by Rosemarie Calvert, appeared in the Center for a Better Life’s livebetter magazine.
Few people understand “smart” power as well as Chief Naval Officer (CNO) Admiral Gary Roughead. To this ingenious, adept leader of the world’s largest and most powerful navy, it’s not just about military strategy or political science; it’s about heart. It’s about the measure of a man with regard to honor, courage and commitment. And, it’s about appreciation and respect for the natural world. As one of the U.S. Defense Department’s most powerful decision-makers, Roughead has helped mold a new breed of sailor who understands that preventing war is just as important as winning war – that creating partners is more important than creating opponents. Add mission mandates such as humanitarian assistance, disaster relief, and environmental stewardship, and it’s clear why Roughead and his brand of smart power are having a profound impact on international peace, national security, and natural security.
Engendering Environmental Advocacy
“You don’t live on the ocean and not love it. My appreciation for the environment came from a very early age – from just loving to be on the water. It’s something that’s had a very strong impact on me,” explains Roughead, who grew up in North Africa where his father worked in the oil business. He and his family lived along an uninhabited area of coastline where his father’s company built a power plant and refinery to process and transport Libya’s huge oil field finds to offshore tankers.
“We were the first people to move there; I was still in grammar school. The beauty in being the first was that the coastline was absolutely pristine. Even before school, I would get up and go skin diving. There were beautiful reefs, and fish were everywhere. The vegetation was just incredible. The company built an offshore loading area a few miles off the beach with 36-inch pipes pumping crude oil out to where these big supertankers would come in. Back then, there wasn’t a high regard for the environment, so when storms would kick-up and ships got underway in a hurry, they would just cast them off and all that oil would go into the ocean.
“Fast forward about five years, and the last time I went skin diving I didn’t see a living thing. The vegetation was dead. At that time I was visiting my folks on summer leave from the Naval Academy. There were periods when I would skin dive and then surface after being down about 35-40 feet, and my lungs would be ready to burst. I’d look up, having moved from my original location, and see this massive oil slick. And, I’d go, ‘Oh gosh…no!’ But, you didn’t have any choice. I would come home and actually have to clean the oil off with kerosene because it was caked on me.
“I saw and experienced environmental devastation, and it had an effect on me. Being at sea all the time – I love going to sea and seeing everything about it – drove me to the views I have. I really do think there’s compatibility between the Navy and the environment. We have things we must accomplish, but we can do them cleanly and responsibly. That’s what we’ve tried to demonstrate to those who have different views – that there has to be compatibility between the two.”
Continue reading on the Center for a Better Life.
Rosemarie Calvert is the publisher and editorial director of livebetter magazine and director of the Center for a Better Life.
Photo Credit: Adapted from “USS Nitze underway with ships from U.S. Navy, Coast Guard and foreign navies,” courtesy of flickr user Official U.S. Navy Imagery. -
David Biello, Momentum Magazine
Coping with Change: Climate Adaptation Today
›May 2, 2011 // By Wilson Center StaffThe original version of this article, by David Biello, appeared in the University of Minnesota’s Momentum Magazine.
The view from space offers a clarity about our changing planet less visible from the ground: spring thaw coming sooner year after year, the iconic snows of Kilimanjaro and glaciers across the globe dwindling – and a great green wall of vegetation spreading across the region just south of Africa’s Sahara Desert.
This arid expanse, known as the Sahel, stretches from the Atlantic Ocean to the Red Sea. It has undergone a remarkable transformation since farmers in nations across the region began to allow trees to grow amidst their crops.
In some places it was by accident, as seeds sprouted from manure spread as fertilizer in Niger. In others it was by design, such as the “green dam” against the desert started in Algeria in 1971. But the result has been the same: improved harvests of millet, sorghum, and other staple crops in a region gripped by perennial drought.
Such “agroforestry” boosts yields by returning vital nutrients to the soil in the form of decaying leaves, shading crops from the harshest sun, and recharging underground water reserves. The trees also provide an additional source of income: wood for fires and construction. And they have another even more important benefit: They may help some of the poorest farmers in the world adapt to climate change – while potentially removing as much as 50 billion metric tons of carbon dioxide from the atmosphere, according to agronomist Dennis Garrity, head of the Nairobi-based World Agroforestry Centre.
“The transformation of agriculture into agroforestry is well underway,” Garrity says. “Agricultural systems incorporating trees increase overall productivity and incomes in the face of more frequent droughts, and agroforestry systems provide much greater carbon offset opportunities than any other climate mitigation practice in agriculture.”
Climate change is already worse than anticipated by the UN Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. Extreme precipitation events, such as last spring’s flooding in Nashville, Tenn., or last winter’s drought in China, have become more frequent. Sea ice extents have reached record lows in the Arctic. And 2010 marked the end of the hottest decade in recorded history.
Not only that, but the 0.7-degree-Celsius uptick in global average temperatures we’ve seen so far is only half the warming that can be expected from the concentrations of greenhouse gases already in the atmosphere, according to a 2010 report from the U.S. National Research Council. And as warming continues, according to the NRC report, the world can expect (among other things) a drop in the yield of cereal crops due to higher temperatures, an increase in heavy rainfall, and a rise in ocean levels.
In other words, whatever measures might be adopted to reduce emissions of greenhouse gases, the world will still need to adapt to a changing climate. Indeed, that process has already begun.
Continue reading on the University of Minnesota’s Momentum Magazine site.
Photo Credit: Deep in the Sahel, the dwindling Lake Chad borders Niger, Chad, and Nigeria. Courtesy of flickr user NASA Goddard Photo and Video. -
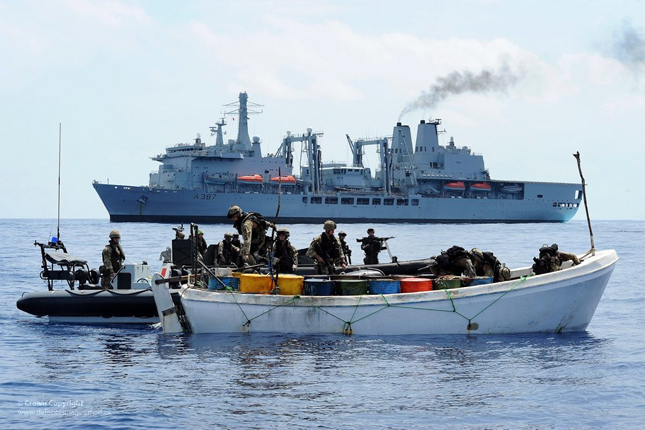
Shannon Beebe, Los Angeles Times
Somali Piracy Shows How an Environmental Issue Can Evolve Into a Security Crisis
›March 14, 2011 // By Wilson Center Staff
It has become apparent that real piracy is far different from the lighthearted subject sometimes portrayed in popular culture, and the problem is growing much worse. Besides the tragic cost in lives, the United States, many other nations, and NATO spent roughly $2 billion combined last year to safeguard the busy international sea lanes off the Horn of Africa from Somali pirates. According to the International Maritime Bureau, “hijackings off the coast of Somalia accounted for 92 percent of all ship seizures last year,” and the price tag does not include the costs of reallocating critical military resources.
-
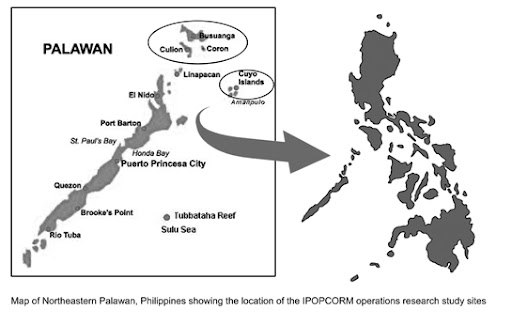
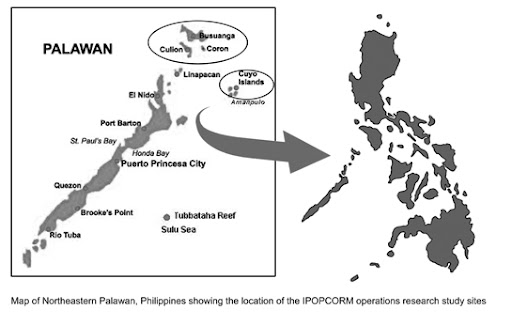
Joan Castro on Integrated Population and Coastal Resource Management in the Southern Philippines
› In the southern Philippines, the innovative IPOPCORM program “worked in areas where there is high…marine biodiversity, high population, and high population momentum, which means…about 40 percent of the population are 15 years and below,” Joan Castro told ECSP in this interview. Castro, the executive vice president of PATH Foundation Philippines, Inc., recently spoke at the Wilson Center on the state of integrated development efforts in her country and elsewhere.
In the southern Philippines, the innovative IPOPCORM program “worked in areas where there is high…marine biodiversity, high population, and high population momentum, which means…about 40 percent of the population are 15 years and below,” Joan Castro told ECSP in this interview. Castro, the executive vice president of PATH Foundation Philippines, Inc., recently spoke at the Wilson Center on the state of integrated development efforts in her country and elsewhere.
From 2000-2006, IPOPCORM (which stands for “integrated population and coastal resource management”) sought to integrate population, health, and environment (PHE) development efforts in Philippine communities. They had four primary objectives, said Castro: 1) improve the reproductive health of the community members; 2) improve management of the coastal resources; 3) increase knowledge of the linkages between population, health, and the environment; and 4) increase the capacity of community leaders to advocate for these links.
“The aspect of livelihoods was very essential,” said Castro, especially for empowering women in the communities. Through family planning services and micro-credit finance initiatives, women were able to better space their pregnancies and contribute to household incomes, she said. In addition, by establishing locally managed, marine protected areas, IPOPCORM increased the protection of high biodiversity zones and improved the likelihood that there will be enough fish to feed future generations.
The “Pop Audio” series is also available as podcasts on iTunes. -
Watch: Joan Castro on Resource Management and Family Planning in the Philippines
›January 27, 2011 // By Wilson Center Staff“Sixty-percent of Filipinos live in the coastal areas,” said Joan Castro, executive vice president of PATH Foundation Philippines, Inc., in an interview with ECSP, and dwindling fish stocks are an issue across the archipelago. “With increasing population, the food that goes on the table for a lot of families in these coastal communities was an issue, so food security was the theme of the IPOPCORM project.”
IPOPCORM (standing for “integrated population and coastal resource management”) was started in 2000 and ran for six years. It sought to address population, health, and the environment (PHE) issues together in rural, coastal areas of the Philippines.
“When we started IPOPCORM, there was really nothing about integrating population, health, and environment,” Castro said. IPOPCORM provided some of the first evidenced-based results showing there is value added to implementing coastal resource management and family planning in tandem rather than separately.
The PATH Foundation worked with local governments and NGOs to establish a community-based family planning system while also strengthening local resource management. The results showed a decrease in unmet need for family planning and also improved income among youth in the remote areas they worked in.
Today, Castro also serves as the PHE technical assistance lead of the Building Actors and Leaders for Advancing Community Excellence in Development (BALANCED) project – a USAID initiative transferring PHE know-how to regions of East Africa and Asia. -
Greater Than the Sum of Its Parts: Quantifying the Integration of Population, Health, and Environment in Development
›It makes intrinsic sense that integrated approaches working across development sectors are a good thing – especially when it comes to the complex issues facing people in developing countries and the environment in which they live. After all, integration avoids overlap and redundancies, and adds value to results on the ground. Yet, quantifying the benefit of integration has been difficult and to date, little on this topic has been published in the peer-reviewed literature.
Not anymore. Our article, “Integrated management of coastal resources and human health yields added value: a comparative study in Palawan (Philippines),” recently published in the journal Environmental Conservation, breaks new ground. Rigorous time-series data and regression analysis document evidence of different disciplines working together to produce synergies not obtainable by any one of the disciplines alone.
The article presents quasi-experimental research recently conducted in the Philippines that tested the hypothesis that a specific model of integration – one in which family planning information, advocacy, and service delivery were integrated with coastal resources management – yields better results than single-sector models that provide only family planning or coastal resources management services.
The study collected data from three island municipalities in the Palawan region of the Philippines, where the residents are dependent on coastal resources for their livelihoods. The integrated model was implemented in one municipality, while the single-sector models (one coastal resource management program and one reproductive health management program) were conducted in two separate municipalities.
The results of the study provide strong evidence that the integrated model outperformed the single-sector models in terms of improvements in coral reef and mangrove health; individual family planning and reproductive health practices; and community-level indicators of food security and vulnerability to poverty. Young adults – especially young men – at the integrated site were more likely to use family planning and delay early sex than at the sites where only family planning and reproductive health interventions were provided.
Coral reef health – as measured by a composite condition index – and mangrove health increased significantly at the integrated site, compared to the site where only coastal resource management interventions were provided. Data from the integrated site also showed a significant decline in the number of full-time fishers, as well as fewer people who knew someone that used cyanide or dynamite to fish – both factors that amplify a community’s vulnerability to food insecurity. Finally, the proportion of young people with income below the poverty threshold decreased by a significant margin in areas where the integrated population and coastal resources management (IPOPCORM) model was applied.
Let’s hope this research is just the beginning of a more thoughtful and effective approach to meeting multiple development goals in a lasting mannerEducational activities at the integrated site focused on illuminating the intrinsic relationship between fast-growing coastal communities in the Philippines and the diminishing health of the coral reefs and fisheries that they depend on for food and livelihoods. Community change agents, often fishermen and their families, talked to their neighbors and fellow fishers about the importance of planning and spacing families and establishing and respecting marine reserves to protect the supplies of food from the sea. They referred those interested in family planning to community-based social marketers of contraceptives or the nearest health center for other services.
These same community members also participated in activities to sustainably manage their coastal resources: working with local government officials to establish marine reserves, replant mangroves, serve as community fish wardens to patrol those reserves, test out alternative livelihoods such as seaweed farming, and start small businesses to diversify their income and reduce fishing pressure.
Development professionals should pay close attention to the conclusions of this study. In environmentally significant areas where human population growth is high, it will be difficult to sustain conservation gains without parallel efforts to address demographic factors and inequities in the distribution of health and family planning services. Integrating responses to population, health, and environment (PHE) issues provides an opportunity to address multiple stresses on communities and their environments and, as this study demonstrates, adds value in such a way that significantly improves community resilience and other outcomes.
This research allows those of us who believe strongly in integrating population, health, and environment programming to point to quantitative proof that the approach works. We now need to expand PHE programming to reach more people in other parts of the world where communities face a similar nexus of challenges. New initiatives have started taking the lessons from this research, applying them to new contexts in Africa and Asia, and scaling them up to reach many more in the Philippines.
Let’s hope this research is just the beginning of a more thoughtful and effective approach to meeting multiple development goals in a lasting manner in the places that need it most.Leona D’Agnes is the technical director of IPOPCORM, Joan Castro is the executive vice president of PATH Foundation Philippines Inc, and Heather D’Agnes is the Population, Health, Environment Technical Advisor in the U.S. Agency for International Development’s (USAID) Office of Population and Reproductive Health.
Sources: BALANCED, Link TV, PATH Foundation Philippines Inc., World Wildlife Foundation.
Image Credit: Philippines village (adapted) and municipalities map courtesy of PATH Foundation Philippines Inc.
Showing posts from category oceans.