Showing posts from category minerals.
-
In Colombia, Rural Communities Face Uphill Battle for Land Rights
›November 14, 2011 // By Kayly Ober“The only risk is wanting to stay,” beams a Colombian tourism ad, eager to forget decades of brutal internal conflict; however, the risk of violence remains for many rural communities, particularly as the traditional fight over drugs turns to other high-value goods: natural resource rights.
La Toma: Small Town, Big Threats
In the vacuum left by Colombia’s war on drugs, re-armed paramilitary groups remain a threat to many rural civilians. Organized groups hold footholds, particularly in the northeast and west, where they’ve traditionally hidden and exploited weak governance. Over the past five years, their presence has increased while their aims have changed.
A recent PBS documentary, The War We Are Living (watch below), profiles the struggles of two Afro-Colombian women, Francia Marquez and Clemencia Carabali, in the tiny town of La Toma confronting the paramilitary group Las Aguilas Negras, La Nueva Generacion. The Afro-Colombian communities the women represent – long persecuted for their mixed heritage – are traditional artisanal miners, but the Aguilas Negras claim that these communities impede economic growth by refusing to deal with multinationals interested in mining gold on a more industrial scale in their town.
For over seven years, the Aguilas Negras have sent frequent death threats and have indiscriminately killed residents, throwing their bodies over the main bridge in town. At the height of tensions in 2010, they murdered eight gold miners to incite fear. Community leaders know that violence and intimidation by the paramilitary group is part of their plan to scare and displace residents, but they refuse to give in: “The community of La Toma will have to be dragged out dead. Otherwise we’re not going to leave,” admits community leader Francia Marquez to PBS.
La Toma’s predicament is further complicated by corruption and general disinterest from Bogota. Laws that explicitly require the consent of Afro-Colombian communities to mine their land have not always been followed. In 2010, the Department of the Interior and the Institute of Geology and Minerals awarded a contract, without consultation, to Hector Sarria to extract gold around La Toma and ordered 1,300 families to leave their ancestral lands. Tension exploded between the local government and residents.
The community – spurred in part by Marquez and Carabali – geared into action; residents called community meetings, marched on the town, and set up road blocks. As a result, the eviction order was suspended multiple times, and in December 2010, La Toma officially won their case with Colombia’s Constitutional Court. Hector Sarria’s mining license as well as up to 30 other illegal mining permits were suspended permanently. But, as disillusioned residents are quick to point out, the decision could change at any time.
“Wayuu Gold”
Much like the people of La Toma, the indigenous Wayuu people who make their home in northeast Colombia have also found themselves the target of paramilitary wrath. Wayuu ancestral land is rich in coal and salt, and their main port, Bahia Portete, is ideally situated for drug trafficking, making them an enticing target. In 2004, armed men ravaged the village for nearly 12 hours, killing 12, accounting for 30 disappearances, and displacing thousands. Even now, seven years later, those brave enough to lobby for peace face threats.
Now, other natural resource pressures have emerged. In 2011, growing towns nearby started siphoning water from Wayuu lands, and climate change is expected to exacerbate the situation. A 2007 IPCC report wrote that “under severe dry conditions, inappropriate agricultural practices (deforestation, soil erosion, and excessive use of agrochemicals) will deteriorate surface and groundwater quantity and quality,” particularly in the Magdalena river basin where the Wayuu live. Glacial melt will also stress water supplies in other parts of Colombia. The threat is very real for indigenous peoples like the Wayuu, who call water “Wayuu gold.”
“Without water, we have no future,” says Griselda Polanco, a Wayuu woman, in a video produced by UN Women.
The basic right to water has always been a contentious issue for indigenous peoples in Latin America – perhaps most famously in Cochabomba, Bolivia – and Colombia is no different: most recently 10,000 protestors took to the streets in Bogota to lobby for the right to water.
Post-Conflict Land Tenure Tensions
Perhaps the Wayuu and people of La Toma’s best hope is in a new Victims’ Law, ratified in June 2011, but in the short term, tensions look set to increase as Colombia works to implement it. The law will offer financial compensation to victims or surviving close relatives. It also aims to restore the rights of millions of people forced off their land, including many Afro-Colombian and indigenous peoples.
But “some armed groups – which still occupy much of the stolen land – have already tried to undermine the process,” reports the BBC. “There are fears that they will respond violently to attempts by the rightful owners or the state to repossess the land.”
Rhodri Williams of TerraNullius, a blog that focuses on housing, land, and property rights in conflict, disaster, and displacement contexts, wrote in an email to New Security Beat that there are many hurdles in the way of the law being successful, including ecological changes that have already occurred:Perhaps the biggest obstacle is the fact that many usurped indigenous and Afro-Colombian territories have been fundamentally transformed through mono-culture cultivation. Previously mixed ecosystems are now palm oil deserts and no one seems to have a sense of how restitution could meaningfully proceed under these circumstances. Compensation or alternative land are the most readily feasible options, but this flies in the face of the particular bond that indigenous peoples typically have with their own homeland. Such bonds are not only economic, in the sense that indigenous livelihoods may be adapted to the particular ecosystem they inhabit, but also spiritual, with land forming a significant element of collective identity. Colombia has recognized these links in their constitution, which sets out special protections for indigenous and Afro-Colombian groups, but has failed to apply these rules in practice. For many groups, it may now be too late.
As National Geographic explorer Wade Davis said at the Wilson Center in April, climate change can represent as much a psychological and spiritual problem for indigenous people as a technical problem. Unfortunately, as land-use issues such as those faced by Afro-Columbian communities, the Wayuu, and many other indigenous groups around the world demonstrate, there is a legal dimension to be overcome as well.
Sources: BBC News, Colombia Reports, International Displacement Monitoring Centre, PBS, Pulitzer Center on Crisis Reporting, UN Women. The War We Are Living, part of the PBS series Women, War, and Peace, was instrumental to the framing of this piece.
Image and Video Credit: “Countryside Near Manizales, Colombia,” courtesy of flickr user philipbouchard; The War We Are Living video, courtesy of PBS. -
Certification: The Path to Conflict-Free Minerals from Congo
›This summer, the Wilson Center’s Africa Program, in co-sponsorship with the Enough Project, assembled a panel of experts from American, British, and Congolese governments, private industry, and the NGO community to discuss the deplorable situation in the eastern Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC) involving conflict minerals and certification as a way forward.
After introductory remarks by Wilson Center President Jane Harman, Africa Program Director Steve McDonald introduced John C. Bradshaw, executive director of the Enough Project, who moderated the panel discussion. [Video Below]
Under Secretary of State Robert D. Hormats began by saying the “extremely traumatic” humanitarian situation in the restive areas of the eastern DRC requires “a bold, resolute, and morally inspired response by the United States and other countries.”
Sasha Lezhnev, policy consultant for the Enough Project, explained how the demand for tin, tantalum, tungsten, and gold – for use in batteries, circuit boards, and screens in computers and cellphones – are, in effect, driving the conflict in the DRC.
However, Ambassador to the United States from the DRC Faida Mitifu pointed out that a significant 70 percent of the economy in the eastern regions of the country depends on mining, thus any initiative would have to take into account the livelihoods of the people. In order to assist those communities while a process is formulated, Lezhnev called for targeted development projects in the most affected regions.
The Kimberley Process: A Potential Model?
“If we want to have a lasting impact, we’re going to need a certification process,” Lezhnev said, and we must learn lessons from the Kimberley Process (KP) in order to implement a suitable framework in the DRC.
Clive Wright, who served as the diplomatic negotiator for the KP and head of the foreign policy team for the British High Commission in Ottawa, described the intricacies of the process and its genesis. Under the provisions of the KP, the trade of rough diamonds is permissible, provided that there is a certificate from the country of origin and complementary legislation is in place in the importing country. This agreement was made through consultations and dialogue between the private sector and civil society.
Though successful in certain respects, Wright listed several shortcomings of the KP: it is not legally binding, therefore there are no levers to pull that compel government action; the process is void of an independent monitoring mechanism; and a consensus clause allows one government to block any action which clears the way for the status quo to prevail.
To implement a policy similar to the KP that guarantees legitimate minerals trade in the DRC, Under Secretary Hormats highlighted four key actors that have critical roles independently and collaboratively: 1) regional governments; 2) industry; 3) civil society; and 4) the U.S. government.
Regional Governments
Governments in the region face considerable challenges, said Hormats, as rebel groups trade across borders and evade efforts to rein in the commerce of precious gems, minerals, and arms. The states surrounding the Great Lakes – including Uganda, Rwanda, Burundi, Zambia, Kenya, and the DRC – have coalesced around these issues and developed a plan that will require effective coordination to ensure credibility. Some countries have already established traceability schemes, which are crucial for states that share borders with the DRC, since smuggling is incessant.
With regard to rebel factions, Kinshasa has occasionally participated in joint operations with the governments of Rwanda and Uganda “to stabilize [and] contain the activities of armed groups,” said Ambassador Mitifu. Progress, though slow, has also been made in demilitarizing the mining areas in the Kivu provinces as well as Maniema and in weakening the Congrès National pour la Défense du Peuple’s (CNDP) parallel administration.
The government in Kinshasa has made significant steps toward a certification framework and taken punitive action against military personnel who have engaged in illicit trade, said Ambassador Mitifu. She outlined the efforts the Kabila administration has made to address the issue, including initiatives to put in place a credible certification system so that clean minerals can be exported. In conjunction with MONUSCO – the UN peacekeeping mission in the DRC – the Congolese government has introduced centers where miners can bring their products and feed them into a legitimate supply chain. Finally, Kinshasa is working closely with the private sector, international organizations, and local NGOs to minimize fraud and enhance cooperation. Nevertheless, governance and corruption represent a formidable roadblock in the implementation of any certification process.
Industry Responsibility
Tim Mohin, the director of corporate responsibility for Advanced Micro Devices – one of the largest semiconductor manufacturers in the world – argued that industry can positively influence the supply chain by creating conflict-free smelter programs and a due diligence bulwark where anyone along the supply chain can trace their resources back to a certified smelter.
Customers, Mohin said, are going to have to insist that businesses comply with this tracking system. Under Secretary Hormats agreed with this sentiment, saying that companies that look into the origin of their minerals send a powerful message to the region and the world. He also expressed hope that “companies [would] work to find ways to adhere to legislation [Dodd-Frank] and honor their obligations to their shareholders without shunning the region’s minerals entirely.”
The most difficult stretches along the supply chain are getting buy-in from the miners and the smelters; overcoming the constraints of socio-economic realities on the ground and geo-politics; and the lack of a sustainable tracing system that spans the spectrum of the supply chain. In addition to shored-up U.S. involvement, Mohin called for increased public-private sector partnerships with incentives reminiscent of the Fair Trade system, development aid to assist displaced people, and enhanced security for artisanal miners and their businesses.
Civil Society and Government
Hormats commended the pivotal role civil society has played and must continue to play in highlighting the humanitarian issues at stake, as governments and companies have been only “dimly aware of the link between human rights abuses and the minerals trade.” Furthermore, Wright encouraged civil society’s participation because it serves as a “great policeman” that monitors the bad behavior of governments, especially when the allure of profiteering seeps into deliberations. Moving forward on boosting security for civil society on the ground in the Congo will be essential.
The U.S. government, Hormats asserted, has to do its part to support initiatives on the table to create conflict-free supply chains. If more revenue is invested in legitimizing supply chains, a substantial portion of the problem would be solved. USAID and the State Department are working with civil society to take action against those responsible for illegitimate trade and exacerbating the conflict. Of course there remains work to be done, but as Under Secretary Hormats indicated “this is the most significant moral issue of our time.”
Derek Langford is a program assistant with the Wilson Center’s Africa Program.
Photo Credit: “Aerial View of Camps for People Displaced by Conflict,” courtesy of flickr user United Nations Photo. -
Conflict Minerals in the DRC: Still Fighting Over the Dodd-Frank Act, One Year Later
›August 11, 2011 // By Schuyler Null
One year after the Dodd-Frank Act passed Congress with a provision that was aimed at preventing the sourcing of “conflict minerals” by SEC-registered companies, backlash seems to be growing over the impact of the measure, particularly on artisanal miners in the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC).
-
Environmental Cooperation for Peacebuilding in Sierra Leone
›Sierra Leone’s decade-long civil war led to a complete collapse of environmental management in the country, according to Oli Brown, an environmental affairs officer with the UN Environment Programme (UNEP). Speaking at the Wilson Center last month, Brown highlighted the country’s current environmental conditions and how they have evolved since the war ended in 2002, while also outlining UNEP’s support for rebuilding the country’s natural resource governance.
Despite its wealth of natural resources, Sierra Leone is plagued by high unemployment, a massive gap between the poor and wealthy, and extreme poverty – 70 percent of the population lives on $1.00 a day. The country is still “very fragile,” said Brown; the poor distribution of resources is partly responsible for the current problems facing the country.
Sierra Leone’s environmental future and prospects for improving its natural resource governance depend on the answers to three key questions, said Brown:
The first 5 to 10 years after a civil war are a critical time for peacebuilding efforts, Brown emphasized. Natural resources can help in this peace building process, but countries must recognize the value of their natural resources, and establish policies that are sustainable – environmentally, economically, and socially.- How can the countries bountiful natural resources be shared more equitably?
- How can the countries natural resources improve local livelihoods and provide jobs?
- How can the war’s legacies be properly addressed while minimizing their negative impact?
Potential in Abundance: Agriculture, Minerals, Fisheries, and Tourism
Today, agriculture – including rice, palm oil, and sugar cane – accounts for 50 percent of Sierra Leone’s GDP, but current production methods are extremely inefficient, said Brown. Farmers use slash-and-burn clearing techniques to grow crops with zero consideration for the environmental effects, a practice which has led to a high level of deforestation. Only four percent of the country’s original forest cover remains, he said.
As part of its plan, Sierra Leone’s government is actively seeking large-scale investment in agricultural products for export. However, access to land development is complicated by the fact that more than 100 different chiefs control land and leasing rights around the country.
Additionally, some fear that companies investing in Sierra Leone may be exploiting the situation to achieve maximum profit without providing local development benefits, such as employment.
Water is also crucial to agriculture development, but Sierra Leone’s government does not know how much they have, said Brown, so they cannot properly plan for addressing the needs of their people. Reforming the sector is critical, as palm oil and sugar cane in particular have great potential for increasing the country’s GDP.
Sierra Leone also has an abundant supply of minerals: Diamonds, iron, rutile, gold, and oil currently account for about 20 percent of GDP and approximately 250,000 jobs, said Brown.
The planned Tonkolili iron mine will be the largest of its type built over the past 20 years anywhere in the world. If successful, the mine could double Sierra Leone’s GDP, he said. But the government must monitor these mining operations to ensure that the environmental damage does not undermine the economic benefits, said Brown. For example, rutile mining without proper safety precautions has produced acid lakes, he said, some of which have been measure with a PH level of 3.7 or greater.
While fishing operations in Sierra Leone make up only 10 percent of GDP, fish provide 80 percent of the animal protein consumed in the country’s households. However, lack of regulation and enforcement has left the door open for rampant illegal and unregulated fishing, said Brown, which has depleted local fish stocks and reduced the size of fish that are caught threatening the country’s food security.
On a more positive note, environmental tourism could be a potential source of sustainable revenue. The large chimpanzee population and the national parks could be strong tourist draws. However, the country must overcome its “blood diamonds” stigma in order to take advantage of its potential.
UNEP is seeking to help Sierra Leone’s government develop its environmental regulations and planning, said Brown, such as ways to measure and regulate water usage. The regulation of agriculture, minerals, fisheries, and tourism industries will be vital steps toward helping Sierra Leone build a sustainable economy and a sustainable peace.
Sources: Awoko Newspaper, Delegation of the European Union to Sierra Leone, Infinity Business Media, The Oakland Institute, UNDP, USAID.
Photo Credit: “mining57,” courtesy of flickr user thehunter1184. -
Beyond Supply Risks: The Conflict Potential of Natural Resources
›While the public debate about resource conflicts focuses on the risk of supply disruptions for developed countries, the potentially more risky types of resource conflict are usually ignored. As part of a two-year research project on behalf of the German Federal Environment Agency, adelphi and the Wuppertal Institute for Climate, Energy, and Environment have analyzed the risks of international conflict linked to natural resources in a series of reports titled Beyond Supply Risks – The Conflict Potential of Natural Resources.
Resource extraction, transportation, and processing can create considerable crises and increase the risk of conflicts in producing and transit countries. This phenomenon – widely referred to as the “resource curse” – impacts consuming countries only if it leads to shortages and higher prices. However, in the producing and transit countries it can have much wider destabilizing effects – from increasing corruption to large-scale violent conflict. In addition, the extraction, processing, and transportation of resources often create serious environmental risks. Overexploitation, pollution, and the degradation of ecosystems often directly affect the livelihoods of local communities, which can increase the potential for conflict.
The eight reports that comprise Beyond Supply Risks explore plausible scenarios over the next two decades, focusing on four case studies: copper and cobalt in the Democratic Republic of Congo; the Nabucco natural gas pipeline project across Southern Europe and Turkey; lithium in Bolivia; and rare earth minerals in China.
Lithium in Bolivia
Bolivia possesses the world’s largest known lithium deposits, a potentially important resource for the development of electric vehicles. While the development of Bolivia’s lithium reserves could provide major economic benefits for one of the poorest countries in Latin America, our analysis identifies two main potential risks of conflict.
First, the environmental consequences of developing industrial-scale lithium production might have negative effects on the livelihoods of the local population. The local population in the lithium-rich department of Potosí has shown that it is capable of organizing itself effectively in defense of its interests, and past resource conflicts have turned violent, making a conflict-sensitive approach all the more important.
Second, the Bolivian economy is largely dependent on natural resources, and consequently is susceptible to price shocks. At present, this risk is primarily associated with natural gas. But lithium production, if developed, might be subject to the same dynamics, which could potentially destabilize the political system.
For consuming countries, these conflicts threaten supplies of lithium only if local protests or broader destabilization were produce bottlenecks in the supply chain.
Rare Earths and China
Like lithium, rare earths are likewise essential for some new technologies. China’s well publicized monopoly on 97 percent of the global production spurred a heated debate on the security of supply of strategic minerals. While our case study identifies supply risks for consuming countries, it also outlines some of the conflict risks China might face internally.
First, local populations could protest against the severe ecological impact of rare earth mining and production. In addition, conflicts might arise if those who profit from economic development (entrepreneurs or regional power-holders) undermine the traditional centralized party structures and expand their own influence.
International conflicts over access to Chinese rare earth resources, while they dominate the headlines, do not appear to be the dominant risk. Instead, internal political tensions could result in a weakened China that is not able to exploit its monopoly position for foreign policy gains. Or the government could enter into multilateral agreements and thus avoid a confrontational approach towards consumer nations.
Ultimately, the actual rate of diffusion of environmental technologies and the development of new technologies remain the key factors in determining whether relative shortages in global supply of rare earths will in fact occur. If industrialized nations and emerging economies commit to the same technologies to attain climate policy goals, international resource governance and coordinated promotion of (environmental) technology will also play a role in preventing conflict and crisis over rare earths.
The Way Forward
The series concludes with five recommendations to mitigate the risks of future resource conflicts:- Introduce systematic policy impact assessments to understand how policy goals and strategies, especially in regard to climate and environmental policy, interact with resource conflict risks.
- Increase the transparency of raw material markets and value creation chains to prevent extreme fluctuations in prices and improve information on markets, origins, and individual players.
- Improve the coherence of raw material policy by linking raw material policies with security, environmental, and development policies.
- Demand and promote corporate social responsibility along the whole value chain.
- Increase environmental and social sustainability as a means of strengthening crisis and conflict prevention by systematically taking into account social and conflict-related aspects in the resource sector.
The individual reports from the project can be downloaded here:- Conflict Risks (GERMAN only)
- Supply and demand (GERMAN only)
- Case Study: Nabucco Pipeline (GERMAN only)
- Case Study: Congo
- Case Study: Bolivia
- Case Study: China
- Conflict Resolution Strategies (GERMAN only)
- Summary and Recommendations
Sources: Government Accounting Office.
Photo Credit: “Potosí: miners in darkness,” courtesy of flickr user Olmovich. -
Rare Earths No More? Mineral Discoveries a Potential Game-Changer for East Asia
›July 7, 2011 // By Schuyler NullDiscoveries announced in a journal article over the weekend may prove a game-changer for global rare earth supplies and recent diplomatic maneuvering in East Asia between China, Japan, Vietnam, and the United States. A team of researchers from Japan’s Agency for Marine-Earth Science and Technology published findings in Nature Geoscience that indicate vast underwater reserves of rare earth minerals are scattered across a huge swath of the Pacific, including south and east of Japan. The U.S. Geological survey estimates current global reserves of rare earth minerals at about 110 million tons; Yasuhiro Kato, the lead author of the Japanese team, told Reuters that the sites surveyed could contain an additional 80 to 100 billion metric tons (yes, with a “b”) of the valuable resources.
The authors write that an “area of just one square kilometer, surrounding one of the sampling sites, could provide one-fifth of the current annual world consumption of these elements.” The team collected data from 78 sites in total, with the largest concentrations centered east of the Hawaiian and Polynesian islands (see a map of the surveyed areas here).
Resource Relationships
The discovery could prove crucial for Japan, as it has been seeking alternative sources of rare earth minerals after an embargo earlier this year by China, which controls 97 percent of the world’s current supply. The embargo (which China denied) was imposed in October of last year after the Japanese navy arrested the captain of a Chinese fishing boat, which was alleged to be encroaching on Japanese territorial waters. China’s response increased tensions across the region and produced a flurry of warnings in Washington over the security of U.S. supplies.
Although the embargo was later lifted, Japan and Vietnam reached an agreement for development of Vietnamese mines in November. The tensions sparked by the encounter also spread to the South China Sea where Chinese, Vietnamese, and Filipino forces have stepped up their jockeying over disputed and resource-rich waters to the highest levels in years. Vietnamese and Chinese naval forces recently held mirror exercises, and Filipino officials invoked a 1950-era defense pact with the United States. Chinese Vice Foreign Minister Cui Tiankai told reporters in June: “I believe the individual countries are actually playing with fire, and I hope the fire will not be drawn to the United States.”
Secretary of State Hillary Clinton called concerns over navigability and Chinese insistence on bilateral (as opposed to multilateral) negotiations in the South China Sea a matter of “national interest” for the United States last year.
The Japanese team’s discovery has the potential to significantly impact the power dynamics behind these tensions. China has used its rare earth monopoly to pressure Japan and the United States, which in turn may have also helped embolden its recent more aggressive maritime policies. If the new rare earth discoveries prove viable, that calculus could change considerably.
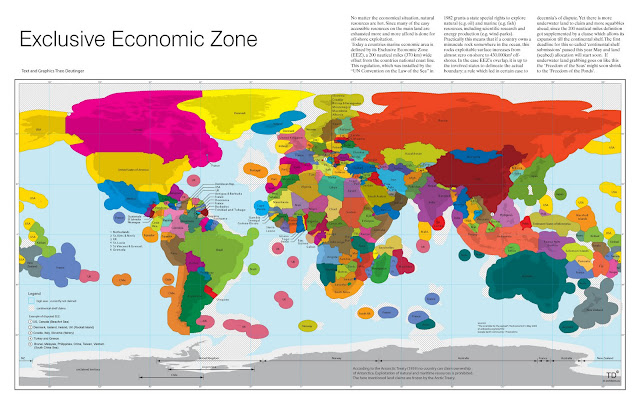
However serious questions remain: Many of the discoveries lie outside of established exclusive economic zones, so who has the rights to mine them? They’re also between 11,500 and 20,000 feet below the surface – how long before we have the technologies to extract them at an industrial scale? And how safe – both for humans and the environment – will those processes be? Aboveground rare earth mines are some of the most damaging to the environment – part of the claimed reason China curbed overall exports earlier this year, which drove up global prices and drew the ire of the World Trade Organization.
For more on the importance of rare earth minerals to the defense and electronics industries, see New Security Beat’s “Rare Earth: A New Roadblock for Sustainable Energy?” and “Reading Radar: The Mineral Security of the United States.” For more on the exclusive economic zones map, see “Eye on Environmental Security: Natural Resource Frontiers at Sea;” and on the South China Sea and what it reveals about future diplomatic fault lines between the United States and China, see “U.S. v. China: The Global Battle for Hearts Minds and Resources.”
Sources: Asia Sentinel, The Atlantic, BBC, Government Accounting Office, Nature Geoscience, The New York Times, Reuters, Tech News Daily, U.S. Department of State.
Photo Credit: Adapted from “USS Mustin underway in the Pacific Ocean,” courtesy of flickr user Official U.S. Navy Imagery, and “Exclusive Economic Zone,” used with permission courtesy of Theo Deutinger and TD Architects. -
Annie Murphy, International Reporting Project
Mozambique Coal Mine Brings Jobs, Concerns
›May 31, 2011 // By Wilson Center StaffThe original version of this article, by Annie Murphy appeared on the International Reporting Project and NPR (follow the links for the accompanying audio track as well). Murphy appeared with three other IRP fellows at the Wilson Center on April 28 to talk about their experiences reporting abroad.
As developing countries grow, their need for raw materials grows, too.
This is the case for Brazil, a country that has much in common with the nation of Mozambique: Both have a mix of African and Portuguese influences; both are rich in natural resources; and both fought long and hard to throw off European colonialism.
Today, however, a Brazilian coal mine in Mozambique has some wondering what the energy demands of growing economies like Brazil really mean for African countries like Mozambique.
This coal mine in northwestern Mozambique is owned by the Brazilian company Vale — it’s a gaping, dark gray pit in the middle of a green, windswept savannah. Still under construction, it currently employees about 7,500 people.
Jose Manuel Guilengue, 23, a machine operator, says that he and a friend traveled 1,000 miles from the capital to get there, where they were both hired. That was a year ago. He now makes around $400 a month — which is more than four times the average salary in Mozambique.
According to the general manager overseeing construction, Osvaldo Adachi, this mine will produce about 11 million tons of coal each year, for at least three decades.
Continue reading and listen to the audio at the International Reporting Project.
Annie Murphy reported this story during a fellowship with the International Reporting Project (IRP). To hear more about Murphy and the IRP program, see the event summary for “Reporting on Global Health: A Conversation With the International Reporting Project Fellows.”
Photo Credit: Adapted from Mozambique, courtesy of flickr user F H Mira. -
Southern Africa, China, and “Sustainable Access”
The Mineral Security of the United States
›In a report titled “Elements of Security: Mitigating the Risks of U.S. Dependence on Critical Minerals,” author Christine Parthemore from the Center for a New American Security writes, “Growing global demand coupled with the mineral requirements necessary for both managing military supply chains and transitioning to a clean energy future will require not only clearer understanding, but also pragmatic and realistic solutions.” Minerals and rare earth elements such as lithium, gallium, and rhenium are critical elements for many defense technologies (e.g. jet engines, satellites, missiles, etc.) and alternative energy sources (batteries and wind turbines). Parthemore argues that U.S. policy should focus on preventing suppliers from exerting undue leverage (as China did in 2010), mitigating fiscal risk and cost overruns, reducing disruption vulnerability, and ensuring the United States is able to meet its growth goals in clean energy and other high-tech fields. In a report from the U.S. Air War College, author Stephen Burgess writes of the potential for conflict over competition for “strategic minerals” in five southern African states: South Africa, the Democratic Republic of the Congo, Zambia, Zimbabwe, and Namibia. The report, titled “Sustainability of Strategic Minerals in Southern Africa and Potential Conflicts and Partnerships,” states that growing industrial countries like China will compete, potentially aggressively, with the United States for sustainable access to elements such as chromium, manganese, cobalt, uranium, and platinum group metals. Burgess recommends that the United States become more engaged in southern Africa by providing development assistance to mining communities and developing strategic partnerships.
In a report from the U.S. Air War College, author Stephen Burgess writes of the potential for conflict over competition for “strategic minerals” in five southern African states: South Africa, the Democratic Republic of the Congo, Zambia, Zimbabwe, and Namibia. The report, titled “Sustainability of Strategic Minerals in Southern Africa and Potential Conflicts and Partnerships,” states that growing industrial countries like China will compete, potentially aggressively, with the United States for sustainable access to elements such as chromium, manganese, cobalt, uranium, and platinum group metals. Burgess recommends that the United States become more engaged in southern Africa by providing development assistance to mining communities and developing strategic partnerships.