-
Consumption and Global Growth: How Much Does Population Contribute to Carbon Emissions?
›July 6, 2011 // By Schuyler Null When discussing long-term population trends on this blog, we’ve mainly focused on demography’s interaction with social and economic development, the environment, conflict, and general state stability. In the context of climate change, population also plays a major role, but as Brian O’Neill of the National Center for Atmospheric Research put it at last year’s Society of Environmental Journalists conference, population is neither a silver bullet nor a red herring in the climate problem. Though it plays a major role, population is not the largest driver of global greenhouse gases emissions – consumption is.
When discussing long-term population trends on this blog, we’ve mainly focused on demography’s interaction with social and economic development, the environment, conflict, and general state stability. In the context of climate change, population also plays a major role, but as Brian O’Neill of the National Center for Atmospheric Research put it at last year’s Society of Environmental Journalists conference, population is neither a silver bullet nor a red herring in the climate problem. Though it plays a major role, population is not the largest driver of global greenhouse gases emissions – consumption is.
In Prosperity Without Growth, first published by the UK government’s Sustainable Development Commission and later by EarthScan as a book, economist Tim Jackson writes that it is “delusional” to rely on capitalism to transition to a “sustainable economy.” Because a capitalist economy is so reliant on consumption and constant growth, he concludes that it is not possible for it to limit greenhouse gas emissions to only 450 parts per million by 2050.
It’s worth noting that the UN has updated its population projections since Jackson’s original article. The medium variant projection for average annual population growth between now and 2050 is now about 0.75 percent (up from 0.70). The high variant projection bumps that growth rate up to 1.08 percent and the low down to 0.40 percent.
Either way, though population may play a major role in the development of certain regions, it plays a much smaller role in global CO2 emissions. In a fairly exhaustive post, Andrew Pendleton from Political Climate breaks down the math of Jackson’s most interesting conclusions and questions, including the role of population. He writes that the larger question is what will happen with consumption levels and technological advances:The argument goes like this. Growth (or decline) in emissions depend by definition on the product of three things: population growth (numbers of people), growth in income per person ($/person), and on the carbon intensity of economic activity (kgCO2/$). This last measure depends crucially on technology, and shows how far growth has been “decoupled” from carbon emissions. If population growth and economic growth are both positive, then carbon intensity must shrink at a faster rate than the other two if we are to slash emissions sufficiently.
Pendleton also brings up the prickly question of global inequity and how that impacts Jackson’s long-term assumptions:
Jackson calculates that to reach the 450 ppm stabilization target, carbon emissions would have to fall from today’s levels at an average rate of 4.9 percent a year every year to 2050. So overall, carbon intensity has to fall enough to get emissions down by that amount and offset population and income growth. Between now and 2050, population is expected to grow at an average of 0.7 percent and Jackson first considers an extrapolation of the rate of global economic growth since 1990 – 1.4 percent a year – into the future. Thus, to reach the target, carbon intensity will have to fall at an average rate of 4.9 + 0.7 + 1.4 = 7.0 percent a year every year between now and 2050. This is about 10 times the historic rate since 1990.
Pause at this stage, and take note that if there were no further economic growth, carbon intensity would still have to fall at a rate of 4.9 + 0.7 = 5.6 percent, or about eight times the rate over the last 20 years. To his credit, Jackson acknowledges this – as he puts it, decoupling is vital, with or without growth. Decoupling will require both huge innovation and investment in energy efficiency and low-carbon energy technologies. One question, to which we’ll return later, is whether and how you can get this if there is no economic growth.But Jackson doesn’t stop there. He goes on to point out that taking historical economic growth as a basis for the future means you accept a very unequal world. If we are serious about fairness, and poor countries catching up with rich countries, then the challenge is much, much bigger. In a scenario where all countries enjoy an income comparable with the European Union average by 2050 (taking into account 2.0 percent annual growth in that average between now and 2050 as well), then the numbers for the required rate of decoupling look like this: 4.9 percent a year cut in carbon emissions + 0.7 percent a year to offset population growth + 5.6 percent a year to offset economic growth = 11.2 percent per year, or about 15 times the historical rate.
To further complicate how population figures into all this, Brian O’Neill’s Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences article, “Global Demographic Trends and Future Carbon Emissions,” shows that urbanization and aging trends will have differential – and potentially offsetting – impacts on carbon emissions. Aging, particularly in industrialized countries, will reduce carbon emissions by up to 20 percent in the long term. On the other hand, urbanization, particularly in developing countries, could increase emissions by 25 percent.
What do you think? Is infinite growth possible? If so, how do you reconcile that with its effects on “spaceship Earth?” Do you rely on technology to improve efficiency? Do you call it a loss and hope the benefits of growth are worth it?
Sources: Political Climate, Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, Prosperity Without Growth (Jackson). -
Nepal to East Africa: Population, Health, and Environment Programs Compared
›“Practice, Harvest and Exchange: Exploring and Mapping the Global, Health, Environment (PHE) Network of Practice,” by the University of Rhode Island’s Coastal Resources Institute and the USAID-supported BALANCED Project, explores the successes and challenges of their global population, health, and environment (PHE) network (with a heavy presence in East Africa). In order to increase support of the nascent PHE approach, the network seeks to shorten the “collaborative distance” between “PHE champions,” so they can develop a stronger body of evidence for the links between population, health, and the environment. In their analysis, the authors write that the network has facilitated the development of independent, information-sharing relationships between “champions.” However, they also observed shortfalls in the network, such as its limited reach into less technologically advanced yet more biodiverse regions, its bias toward BALANCED meet-up event participants, and its exclusion of those experts unlikely to be included in published works. In “Linking Population, Health, and the Environment: An Overview of Integrated Programs and a Case Study in Nepal” from the Mount Sinai Journal of Medicine, Sigrid Hahn, Natasha Anandaraja, and Leona D’Agnes provide both a broad survey of the structure and content of programs using the PHE method and an in-depth case study of a successful initiative in Nepal. Hahn et al. praise the Nepalese program for simultaneously addressing deforestation from fuel-wood harvesting, indoor air pollution from wood fires, acute respiratory infections related to smoke inhalation, as well as family planning in Nepal’s densely populated forest corridors. “The population, health, and environment approach can be an effective method for achieving sustainable development and meeting both conservation and health objectives,” the authors conclude. In particular, one benefit of cross-sectoral natural resource and development programs is the inclusion of men and adolescent boys typically overlooked by strictly family planning programs.
In “Linking Population, Health, and the Environment: An Overview of Integrated Programs and a Case Study in Nepal” from the Mount Sinai Journal of Medicine, Sigrid Hahn, Natasha Anandaraja, and Leona D’Agnes provide both a broad survey of the structure and content of programs using the PHE method and an in-depth case study of a successful initiative in Nepal. Hahn et al. praise the Nepalese program for simultaneously addressing deforestation from fuel-wood harvesting, indoor air pollution from wood fires, acute respiratory infections related to smoke inhalation, as well as family planning in Nepal’s densely populated forest corridors. “The population, health, and environment approach can be an effective method for achieving sustainable development and meeting both conservation and health objectives,” the authors conclude. In particular, one benefit of cross-sectoral natural resource and development programs is the inclusion of men and adolescent boys typically overlooked by strictly family planning programs. -
Irene Kitzantides
In FOCUS Coffee and Community: Combining Agribusiness and Health in Rwanda
›June 29, 2011 // By Wilson Center StaffDownload FOCUS Issue 22: “Coffee and Community: Combining Agribusiness and Health in Rwanda,” from the Wilson Center.
Rwanda, “the land of a thousand hills,” is also the land of 10 million people, making it the most densely populated country in Africa. Rwandans depend on ever-smaller plots of land for their food and livelihoods, leading to poverty, soil infertility, and food insecurity. Could Rwanda’s burgeoning specialty coffee industry hold the key to the country’s rebirth, reconciliation, and sustainable development?
In the latest issue of ESCP’s FOCUS series, author Irene Kitzantides describes the SPREAD Project’s integration of agribusiness development with community health care and education, including family planning. She outlines the project’s successes and challenges in its efforts to simultaneously improve both the lives and livelihoods of coffee farmers and their families. -
Watch: Demographic Security 101 With Elizabeth Leahy Madsen
›June 27, 2011 // By Schuyler Null“Today we are in an era of unprecedented demographic divergence, with population trends moving simultaneously in different directions. Some countries are beginning to experience population decline, while others continue to grow rapidly,” says Elizabeth Leahy Madsen, formerly the senior research associate at Population Action International (PAI). In this primer video from ECSP, Madsen explains how global demographic trends affect economic development, national security, and foreign policy.
-
Women in Agriculture: Closing the Gender Gap for Development and World Hunger
›June 22, 2011 // By Kellie FurrProviding women with equal access to productive resources and opportunities may be the key to bolstering the struggling global agricultural sector and feeding communities living in extreme hunger, according to the UN Food and Agriculture Organization’s (FAO) latest State of Food and Agriculture report, which this year is sub-titled, “Women in Agriculture: Closing the Gender Gap for Development.”
“Women are farmers, workers, and entrepreneurs, but almost everywhere they face more severe constraints than men in accessing productive resources, markets, and services,” write the authors. “This ‘gender gap’ hinders their productivity and reduces their contributions to the agriculture sector and to the achievement of broader economic and social development goals.”
Barriers to Productivity
Globally, women comprise 43 percent of the agricultural labor force, ranging from 20 percent in Latin America to 50 percent in southeastern and eastern Asia and sub-Saharan Africa, according to the report. But despite their significant global presence, female farmers face gender-specific constraints that hinder access to productive resources, financial support, information, and services required to be viable and competitive. “The yield gap between men and women averages around 20 to 30 percent, and most research finds that the gap is due to differences in resource use,” write the authors.
Generally, women are more likely than men to hold lower-wage, part-time, or seasonal positions and tend to get paid less even when they are more qualified. Furthermore, domestic and occupational lines are blurred for women, who are often not compensated for work that is closely related to domestic food preparation. Most significantly for agricultural productivity, women across the developing world often lack access to quality land, sometimes being barred from land ownership. This ban precludes female farmers from exercising managerial discretion over farming activities, such as entering contract farming agreements. Women also generally own less livestock and contract for less labor – two crucial assets for marketable agricultural production in many developing countries. Moreover, because of insufficient land and resources, women farmers are also more vulnerable to climate shocks.
Resource barriers for female farmers extend to education, finance, and technology as well. The authors observe that “female household heads in rural areas are disadvantaged with respect to human capital accumulation in most developing countries, regardless of region or level of economic development,” which represents a historical bias against females in education. Despite notable success observed in finance projects involving female farmers, gender bias exists in the financial system, which prevents women from bearing initial financial risk in order to increase long-term productivity gains. Sources of gender bias in the financial sector include legal barriers, cultural norms, lack of collateral, and institutional discrimination by public and private lenders. Due to the aforementioned lack of credit, labor, and education, women farmers are deficient in all aspects of technology, such as the acquisition of new equipment, information about new seed varietals and animal breeds, pest control measures, and management techniques.
Global Implications
Closing the gender gap could have profound implications for easing world hunger. According to the FAO, approximately 925 million people are currently undernourished, most of whom live in developing countries. If women were given all the inputs and support as men, agricultural output could increase by 2.5 to 4 percent in developing countries, potentially reducing the world’s hungry by 100 to 150 million people. “This report clearly confirms that the Millennium Development Goals on gender equality (MDG 3) and poverty and food security (MDG 1) are mutually reinforcing,” FAO Director-General Jacques Diouf argues in his introductory remarks.
Increasing the economic viability of women farmers may also translate into better infant and child health indicators – when women control additional income, they tend to allocate more of their earnings toward the health and well-being of their children. Closing the agricultural gap is “a proven strategy for enhancing the food security, nutrition, education, and health of children,” Diouf asserted. “Better fed, healthier children learn better and become more productive citizens. The benefits would span generations and pay large dividends in the future.”
Finally, the FAO notes that in addition to reducing child mortality rates, increasing female education and economic prosperity helps lower fertility rates, which over time increases human capital and can help drive a demographic transition towards lower dependency rates and higher per capita growth.
Closing the Gender Gap
“The conclusions are clear,” write the authors:1) Gender equality is good for agriculture, food security, and society; and
Though they note that “no simple ‘blueprint’ exists for achieving gender equality in agriculture,” the authors do recommend some basic principles to the development community, including working towards eliminating discrimination against women under the law, strengthening rural institutions and making them gender-aware, freeing women for more rewarding and productive activities, building the human capital of women and girls, bundling interventions, improving the collection and analysis of sex-disaggregated data, and making gender-aware agricultural policy decisions.
2) Governments, civil society, the private sector and individuals, working together, can support gender equality in agriculture and rural areas
Recognizing that “women will be a pivotal force behind achieving a food secure world,” the U.S. Agency for International Development (USAID) has actually launched initiatives aimed directly at closing the gender gap. The Feed the Future initiative, announced last spring, includes a heavy focus on gender equity and integration with small-scale farming initiatives. For example, the Office of Women in Development is supporting a three-year project in Liberia, “Integrated Agriculture for Women’s Empowerment,” that aims to train and support 1,500 small farmers in Lofa county, two-thirds of whom are women. And in Rwanda, USAID helped the Ministry of Agriculture and Animal Resources – headed by Dr. Agnes Kalibata – develop a national investment plan, which has been successful in bringing in donor support.
However, the FAO report does not offer specific feedback on programs like Feed the Future, which is arguably a crucial component of a truly comprehensive assessment on the current state of agriculture. Though they write that the State of Food Agriculture series is intended to simply be “science-based assessments of important issues,” the infancy of these food security efforts and the immediacy of the problems examined (see recent food price instability) creates an excellent opportunity for critical input. “Women in Agriculture” offers perhaps the most comprehensive report on the gender gap and development to date, but more specific critiques on the current efforts of USAID and others might make more of an impact in a field where the issues at play have been fairly clearly enumerated many times before.
Sources: Food and Agriculture Organization, The Hunger Project, International Fund for Agricultural Development, Population Action International, USAID.
Photo Credit: Adapted from “Ngurumo Village-Ntakira (Kenya),” courtesy of flickr user CGIAR Climate. -
New Oxfam Report Tackles Broken Food System
›June 17, 2011 // By Ramona Godbole“The global food system is broken,” reads a new report from Oxfam International. While much of Growing a Better Future: Food Justice in a Resource-Constrained World essentially reviews the major factors that contribute to food insecurity, Oxfam’s call to transform the food system is certainly timely, given this year’s high food prices (blamed in part for inflaming popular revolts in the Middle East) and fears of another global food crisis.
Despite producing enough food for everyone, one in seven people globally face chronic under-nutrition and almost one billion people are food insecure. Hunger is concentrated within rural areas in developing countries, and within families, women are often disproportionally affected, having serious implications for maternal and child health.
“We face three interlinked challenges in an age of growing crisis: feeding nine billion without wrecking the planet; finding equitable solutions to end disempowerment and injustice; and increasing our collective resilience to shocks and volatility,” write the authors of the report.
A “Perfect Storm” for Hunger
If current trends continue, population growth, natural resource scarcity, and climate change will put increasing stress on the food system in the future and create a “perfect storm” for more hunger, says Oxfam.
In the short term, oil price hikes, extreme weather, and speculative trading in markets have caused food prices to rise. With global population slated to grow to 9.1 billion and the global economy projected to be three times as big, demand for food may increase by as much as 70 percent by 2050. Food scarcity will also be deeply affected by the depletion of other natural resources including water, oil, and land.
According to the report’s predictions, child malnutrition levels in sub-Saharan Africa are expected to grow by 8 million by 2030. This estimate is before taking into account the effects of climate change, which could reduce agricultural yields by 20 to 30 percent in sub-Saharan Africa by 2080. The latest UN Population Division projections over that same time period predict an additional two billion people will be living in the region.
The Broken Food System
Up until now, many governments in developed countries have either ignored rising food prices or made it worse by imposing trade restrictions or encouraging the production of biofuels, says Oxfam. Thirty to fifty percent of all food grown is wasted, at least in part, as the result of poor consumer and business practices in rich countries, write the authors, and national governments are not doing enough to address climate change and manage scarce resources, especially water.
Another major challenge that contributes to global hunger is equitable access to land, technology, and markets, says Oxfam. In Guatemala, for example, less than eight percent of agricultural producers hold almost 80 percent of the land, and in developing countries, despite sharing an equal or larger burden of the work, women account for only 10 to 20 percent of landowners. Large companies, rather than local farmers, make the majority of decisions regarding key resources such as land, water, seeds, and infrastructure, while ignoring the technological needs of small-scale farmers.
“Growing a Better Future”
The report concludes that “from the failing food system to wider social and ecological challenges, the dominant model of development is hitting its limits.” The authors recommend three ways to effectively reduce hunger and fix the broken food system:1) Make food security a top priority for national and international governing bodies;
To make this a reality, write the authors, governments must invest in climate adaptation, disaster risk reduction, and social protection, while international governance of trade, food aid, financial markets, and climate change must work to reduce risks of future shocks and respond quickly and effectively when shocks do occur. The policies and practices of both governments and businesses should support the needs and interests of small-scale farmers, ensuring access to natural resources, technology, and markets.
2) Support small-scale food producers in developing countries; and
3) Set clear global targets for the equitable distribution of scarce resources.
While not exactly novel or ground-breaking ideas, these reforms certainly are lofty and the report avoids sugarcoating issues of food security, directly calling out governments and the private sector for their role in supporting food injustice. But, some argue that simpler solutions, like promoting fertilizers and new technologies among poor farmers, might be more effective at fighting malnutrition. Others question the validity of the reports assertion that the average food prices will more than double in the next 20 years.
Despite criticisms, this report and the corresponding GROW campaign will hopefully help further highlight the importance of food security and the need to move towards a more sustainable future.
Image Credit: “Thriving in Africa,” courtesy of flickr user Gates Foundation. -
Shall the Religious Inherit the Earth?
›
“The world as a whole is getting more religious,” said Professor of Politics at the University of London Eric Kaufmann, speaking at the Wilson Center for the launch of his latest book, Shall the Religious Inherit the Earth? Due to their consistently higher birthrates, religious fundamentalists may reverse the tide of secularism within the next century, he said. [Video Below]
-
Pakistan’s Population Bomb Defused?
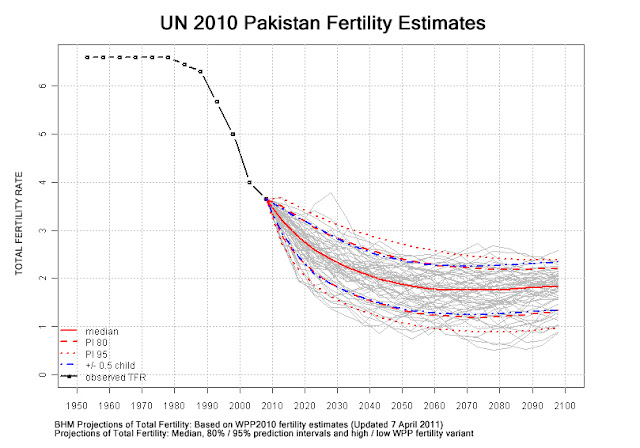
›What is going on over at the UN Population Division? In response to The New Security Beat’s post on the UN’s sub-Saharan projections, Ed Carr of USAID recently highlighted what appears to be gross overestimations in the 2010 population revision for Ghana. Yet in the case of Pakistan, the opposite is seemingly at play – the projections appear to wildly (and unrealistically) underestimate population numbers for the coming decades.
The 2008 revision’s mid-variant estimate for Pakistan in 2050 was 335 million people. The new revision projects only about 275 million by that year. Even the new high-variant estimate (314 million) falls below the earlier mid-variant projection. Furthermore, the constant-fertility variant estimate for 2050 has fallen from 450 million to under 380 million.
What gives? Thanks to some helpful staff at the Population Division and Population Action International’s Elizabeth Leahy Madsen (who helped translate the UN’s demographic-ese for this non-specialist), I can only conclude that the UN has decided to hedge its bets that Pakistan’s fertility rates will fall, simply because its South Asian neighbors (and other nations) have followed this trajectory.
If so, I believe this assumption is spurious. As reported in the Wilson Center’s recent book on Pakistan’s population challenges, though Pakistan’s fertility rate is in decline, it is falling at a considerably slower pace than that of its neighbors, and the rate of decrease has slowed considerably over the last decade. The country’s total fertility rate (TFR) today is just under four, considerably above the replacement level rate (2.1).
By many indications, Pakistan’s TFR does not figure to fall quickly anytime soon. Pakistan’s maternal and reproductive health sector is deeply troubled, with family planning services either of poor quality or nonexistent – particularly in rural areas. Many rural women are obliged to travel on average 50 to 100 kilometers to obtain such services. Meanwhile, the status of Pakistani women is dreadful; female literacy is estimated to stand at only 44 percent (some places it as low as 35 percent), while women’s labor participation rates barely approach 20 percent. Not surprisingly, Pakistan’s contraceptive prevalence rate is quite low (30 percent), while its rate of unmet need for family planning is high (25 percent).
With all of Pakistan’s problems, improving access to family planning is simply not a front-burner issue for Islamabad (in fact, as our book notes, demography on the whole is largely neglected in Pakistan), which makes the 2010 revision’s projections all the more questionable.
The UN is expected to release details on the methodology behind its basic assumptions in the coming weeks; here’s hoping for some clarity. (Editor’s note: As Liz Madsen points out, there’s also a white paper on the new probabilistic model to sift through, if you’re prepared for some heavy reading.)
Michael Kugelman is a program associate for the Asia Program at the Woodrow Wilson Center.
Chart Credit: Modification of projections of total fertility based on Bayesian hierarchical model, courtesy of the UN Population Division.
Showing posts from category population.