Showing posts from category Guest Contributor.
-
Where Have All the Malthusians Gone?
›Forget youth bulges and population bombs; lately, the population story has been all about the baby bust. The cover of this month’s Foreign Policy features “Old World: The graying of the planet – and how it will change everything,” by Phillip Longman, and author Ted Fishman recently appeared in The New York Times and on NPR to talk about his book, Shock of Gray: The Aging of the World’s Population and How It Pits Young Against Old, Child Against Parent, Worker Against Boss, Company Against Rival and Nation Against Nation. Nicholas Eberstadt covered similar issues in Foreign Affairs with his article, “The Demographic Future: What Population Growth – and Decline – Means for the Global Economy.”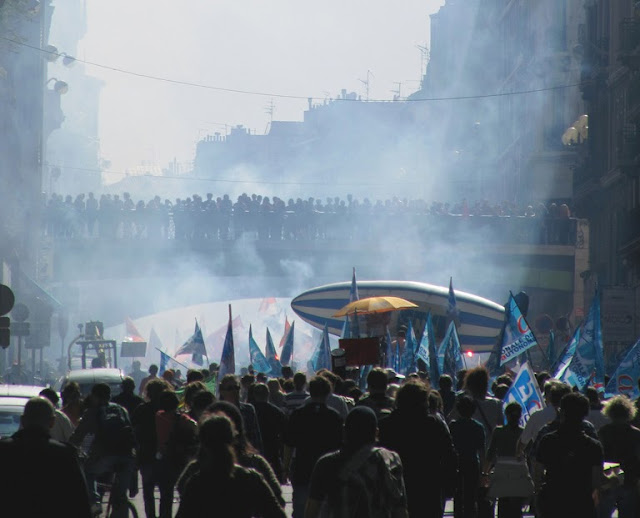
To the extent that policymakers take away a sense of urgency to reform retirement institutions and potentially reevaluate military strategy, the recent spate of publications about aging is useful. But policymakers should not be misled into thinking that the population tide has turned and resources for education, development, and family planning are no longer necessary. While global population growth is slowing, it has not stopped, and the political and economic consequences of continued growth and youthful age structures across most of the Global South will be dire.
A Population Bomb…of Old People
Eberstadt, Fishman, and Longman argue for the need to prepare for a future where there are large proportions of elderly dependents and relatively few workers to support them, and they chronicle the many challenges that may result, including political resistance. The October protests in France against raising the pensionable age from 60 to 62 — which, despite the hullabaloo, fall far short of the levels needed to improve France’s long-term economic position — are but one example of the reform resistance they warn about.
The concern is that while the Global North – Europe and Japan in particular – scramble to meet the needs of their older citizens and preserve the health of their economies, their powerful positions in the international system are at risk. As Fishman states, “It now looks as if global power rests on how willing a country is to neglect its older citizens.” China, a country on the cusp of aging, has thus far chosen neglect over meaningful investment, stoking more fear that the Global North may fall behind.
Though a focus on economic health is useful, other aspects of their arguments do a disservice, particularly those that start from the premise that the days of Malthusian angst over the planet’s ability to support a rapidly growing population are long gone.
Echoing Fred Pearce in his The Coming Population Crash and Our Planet’s Surprising Future, Longman argues without reservation that dangerous population growth is a thing of the past, and instead, the world faces a “population bomb…of old people.” He even goes so far as to claim that “having too many people on the planet is no longer demographers’ chief worry; now, having too few is.”
I have to ask: what demographers did he talk to? Articles published over the last year in the field’s top journals — Demography, Population and Development Review, and Population Studies — certainly explore low fertility, but they also cover a range of youth- and growth-related issues and topics such as mortality, teen parenthood, and immigration. And within the field of political demography in particular there is still quite a lot of attention being paid to the implications of population growth and youth bulges on civil conflict and human security. Even Foreign Policy, in which Longman’s article appears, publishes an annual Failed States Index that argues there is an important relationship between demographic pressure and state collapse.
As studies like the Failed States Index and the National Intelligence Council’s Global Trends project show, contrary to Pearce et al., carrying capacity arguments are not completely outmoded. Regardless of how extreme the impact of an aging population will be on developed nations in the near future (although the United States will almost certainly be less affected than others), in many parts of Africa, South Asia, and the Middle East, population growth is straining local water and land resources and creating instability — issues that will likely be exacerbated by climate change.
Geographic Bias
If there really is more attention being paid among demographers to low fertility it may well be due to institutional and geographic bias. After all, most of the funding for demography comes from Western nations concerned with their own decline. Likewise, all the top journals are American or European.
Though it is correct that most advanced industrial states are aging because of low fertility, for a large part of the world, population growth is still the number one issue. Declining fertility in most countries of the world means that populations are getting older, but this is not the same as saying they have a problem with aging. Between 1980 and 2010, the median age of the less developed countries, excluding China, rose from 19 to almost 25 and the world’s least developed countries saw a rise from 17 to 20 years. Median age in more developed countries, however, went from 32 to 40 — a level twice that of the least developed countries.
Many of the low-fertility countries Longman cites — Iran and Cuba, in particular — are exceptions among developing countries, rather than the rule. The UN Population Division estimates that sub-Saharan Africa will gain 966 million people by 2050 – more than the current population of all of Europe – and, as Richard Cincotta and I have both argued on this blog previously, the total fertility rate (TFR) projections used in those estimations are likely low. Rapid population growth in sub-Saharan Africa has already exacerbated many countries’ abilities to meet the growing needs of their populations, causing civil conflict and instability, and will continue to do so in the future.
Why is it Important to Get it Right?
Alarmism is useful when it grabs the attention of policymakers and a public that is overloaded with information, but it is also risky. Both Pearce and Longman take jabs at Paul Ehrlich because his “population bomb” never exploded. What they fail to note is that Ehrlich’s predictions could have proven right, except that he was successful at scaring a generation of policymakers into action. Funding towards population programs increased greatly in the wake of such research. If those of us who write about the dangers of aging are successful, perhaps we will be so lucky to look as foolish as Ehrlich one day.
If these warnings fall on deaf ears and policymakers do not act to reduce the burden of entitlements, certainly budgets will be strained beyond capacity and the dire future predicted by Fishman, Pearce, and Longman may well become a reality. On the other hand, if policymakers similarly disregard carrying capacity issues in the developing world, conflict and misery are sure to continue in these places and may well worsen.
Jennifer Dabbs Sciubba is the Mellon Environmental Fellow in the Department of International Studies at Rhodes College. She is also the author of a forthcoming book, The Future Faces of War: Population and National Security. Follow her on Twitter at @profsciubba for more on population-related issues.
Sources: Foreign Affairs, Foreign Policy, NPR, National Intelligence Council, The New York Times, Population Reference Bureau, Reuters, UN.
Photo Credit: Adapted from “Protest/Manifestation,” courtesy of flickr user lilicomanche. -
Blue Ventures’ Integrated PHE Initiative in Madagascar
›In the small coastal village of Andavadoaka, Madagascar, the village elders offer a bottle of rum and two cigarettes to their ancestors before the men and their sons launch their wooden dugout canoes into the sea. Leaning over the side, their masked faces scour the water for their prey.
Meanwhile, the women – with babies on back and spears in hand – set out on foot into the shallow waters. One probes a small hole with her spear, and a tentacle reaches out to grapple with it. After careful coaxing, she pulls out an octopus, kills it, and adds it to her collection, which she tows on a string behind her.
In total, more than 1,850 pounds of octopus are collected on the opening day of the octopus harvest, a seasonal occurrence in Velondriake, the Indian Ocean’s first locally managed marine area.
Velondriake, which means “to live with the sea,” stretches along more than 40 km of southwestern Madagascar’s coast. The region encompasses 25 villages and is home to more than 8,000 people of the Vezo ethnic group, who are almost entirely dependent on marine resources, such as octopus, fish, and mangrove forests, for subsistence and income. But these resources are quickly disappearing due in large part to over-harvesting.
Blue Ventures Conservation – the London-based NGO I work for – has been working in the area since 2003 to protect the region’s coral reefs and mangroves, as well as their biological diversity, sustainability, and productivity, while also improving the quality of life of the local community.
To this end, Blue Ventures helped the community create a series of coastal marine reserves. Several permanent reserves protect the biodiversity of the coral reefs and mangroves, and help fish populations recover; while nearly 50 temporary reserves have increased the productivity of the octopus and crab fisheries. Octopuses reproduce quickly and juveniles grow at a nearly exponential rate, so a brief harvesting hiatus can lead to significant increases in yield. Increased yields translate to increased profits – something greatly welcomed by the people of this impoverished region.
The people of the region are also reproducing quickly: the average total fertility rate in Velondriake is 6.7 children per woman, according to our data. On average women are only 15 years old when they first conceive. To compound this problem, a majority of the population is under the age of 15 – at or approaching reproductive age. At the current growth rate, the local population will double in only 10 to 15 years. The local food sources, already heavily depleted, barely feed the current population, let alone twice that amount. Without enabling these coastal communities to stabilize their population growth, efforts to improve the state of marine resources and the community’s food security are considerably hindered.
In August 2007, Blue Ventures launched its Population, Health, & Environment (PHE) program as a weekly family planning clinic in Andavadoaka, which provided access to ingestible and injectable birth control options, as well as condoms. The clinic increased the village’s contraceptive prevalence rate (CPR) from 9.4 percent to 36.3 percent, and the Velondriake region’s CPR from 11.0 percent to 15.1 percent, in its first two years. (CPR data for the third year is not yet available, but should be notably higher, especially at the regional level.)
In 2009, Blue Ventures opened two more clinics and began holding quarterly outreach clinics in all Velondriake villages. We started offering long-acting, reversible contraceptive options, including Implanon and IUDs. Most recently, we have implemented a community-based distributor (CBD) program to provide wider access to contraceptives around the region, particularly for villagers that could not easily reach one of the clinic sites. These expansions paid dividends: the number of patients increased almost four-fold between the second and third years, with a cumulative total for all three years of just under 1,700 patients.
Recently, the PHE program began a partnership with the UN Population Fund (UNFPA), becoming the first PHE project to receive support from the UNFPA within Madagascar. The UNFPA funds will allow us to add new regional clinics; launch a behavior change campaign, including a regional theater tour and educational events; and further develop the CBD program.
UNFPA’s support of this initiative represents an important endorsement of Blue Ventures’ integrated approach to the challenges of marine sustainability, food security, reproductive health, and population growth. Funding applications to focus on improving maternal and infant health and to conduct a full health-needs assessment of the Velondriake region are pending.
In taking a population, health, and environment approach, Blue Ventures creates synergies that allow for the more effective achievement of health and conservation outcomes. Through providing family planning and health options – services the community really wants – Blue Ventures generates more support for all of its other initiatives, such as conservation and aquaculture programs.
This integrated multi-pronged approach also helps speed up the move towards a more sustainable future. By empowering and enabling couples to take control of their fertility, couples are able to have the size family they want. The use of family planning helps lower the population growth rate, and lower growth rates decrease pressures on natural resources. Decreased pressures on natural resources lead to healthier ecosystems; healthier ecosystems mean more natural resources available; and more resources lead to healthier families.
Through recognizing this inextricable link between communities, their health, and the environment they live in, Blue Ventures hopes to preserve not just the local coral reefs and mangroves, but the Vezo seafaring lifestyle. This way, the sons on the boats and the babies on the women’s backs may still have enough octopus and fish to harvest when they take their own children out to sea.
Matthew Erdman is the PHE coordinator for Blue Ventures. For more information about Blue Ventures’ PHE activities, please contact phe@blueventures.org, or visit their website at www.blueventures.org.
Photo Credit: Adapted from “07,” courtesy of Blue Ventures. -
Rape, Resource Management, and the UN in Congo: What Can Be Done?
›Rape as a weapon of war is not unique to the Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC), but the scope and degree to which it occurs in this part of the world, especially in the resource-rich eastern provinces – an epicenter of violence during the war – is alarming and unprecedented.
Walikale, the site of a recent scourge of rapes and violence is not unlike several other cities and villages in the Kivus and in the DRC in general. Rich in both tin and gold, Walikale is beset by a convergence of several opposing military factions: the rebel Congrès National pour la Défense du Peuple, (CNDP), whose members have supposedly been reintegrated into the official Congolese army; the FARDC, who have been accused of crimes as egregious as those committed by rebel armies; the Rwandan FDLR; Tutsi rebel factions; and numerous other smaller rebel groups and non-Congolese military groups.
The raping of more than 300 women, children, and men that occurred between July 31 and August 2 in the area of Walikale and the village of Ruvungi has made international news headlines and caused an uproar about the role and responsibilities of the United Nation mission in the DRC – MONUSCO (formerly MONUC) – and their capacity to actually keep the peace. UN peacekeepers, stationed about 30 kilometers away from the attacks, were reportedly aware of rebel activity in the area, but were not aware of the mass raping until after the crimes had been committed. Officials went on a fact-finding mission several days later once the rapes were reported by the International Medical Corps. Some, however, argue that officials should have acted differently, dispatching peacekeepers to the Walikale area as soon as they were made aware of rebel activity.
UN workers and other international organizations may have known about the rapes while they were occurring, and in retrospect the international community can criticize their inaction during the perpetration of this massive atrocity, but there are larger questions that loom: Why has the DRC become the “rape capital of the world?” And what can we do to enable UN peacekeeping forces to actually keep the peace?
More than two months after these crimes were perpetrated, rapes are no doubt still occurring across the region. The UN has declared that militias will be charged for the crimes in Walikale, arrests have already been made, and there are people doing good work to help the victims of sexual crimes after the fact. But despite these efforts and the ongoing presence of MONUSCO and efforts to integrate and train the FARDC as a legitimate army that protects the citizens of the country, sexual violence against civilians, and especially against women, has continued at an outrageous level.
The mandate of MONUSCO, carried over in part from its predecessor, MONUC, is to both protect civilians and backstop the efforts of the FARDC – a sometimes conflicting mandate. Designed to keep the peace and monitor the implementation of the ceasefire agreement, to “facilitate humanitarian assistance and human rights monitoring, with particular attention to vulnerable groups including women, children and demobilized child soldiers” (emphasis added), the UN mission has clearly not been able to successfully fulfill this mandate, even after almost 12 years on the ground. While the UN charter does not explicitly include the word “peacekeeping,” and there are those who argue that it is not properly structured to act as a peacekeeping body, the UN has more than 60 peacekeeping missions under its belt since its first mission in 1948 and the DRC is its largest ever. Still, the weak record of success of MONUC and of its successor MONUSCO together with the unreliability of the FARDC does not inspire confidence for the safety or security of civilians in the DRC.
Why the rapes continue and why neither MONUSCO nor the Congolese authorities are unable to stop them are complicated questions. Explanations range from political complications preventing peacekeepers from becoming involved in day-to-day human security to a simple lack of mission resources. The rapes in Walikale occurred in an area with abundant tin deposits and some of the largest gold mines in the country. The DRC, and the east in particular, is ripe with resources, and historically, underdeveloped regions characterized by such a heavy concentration of natural resources are often more cursed than they are blessed. The competition over resources and violence spurred by an unequal distribution of rents is perhaps part of the reason for such intense violence; it does not, however, explain why rape has become a weapon of choice, why women have become a target of war crimes in general, or why the level of violence against women in the DRC in particular has risen to such a horrifying level.
Justine Lindemann is program assistant with the Africa Program at the Woodrow Wilson Center.
Sources: AFP, AFRICOM, AllAfrica, BBC, Congo Siasa, IPS News, The New York Times, Panzi Hospital of Bukavu, UN, UN Office of the High Commissioner for Human Rights, VII Photo Agency.
Photo Credit: “Congo kivu,” courtesy of flickr user andré thiel. -
Youth on Fire at UN Climate Talks in Tianjin
›For the past week, as part of the Adopt a Negotiator program, I got the chance to observe many of the negotiations of the latest UN Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC) intersessional meeting that took place in Tianjin, China. In many ways it was rather humdrum. I observed as negotiators debated changing agendas and the mandate of contact groups rather than the issues themselves, and made many of the same, tired position speeches again and gain.
When controversial issues did rise to the fore, they felt like more of the same old, same old: arguments between China and the United States about who is doing more to stall the talks and who should make legally binding emissions cuts; developed countries carving enormous loopholes into the LULUCF; the greenhouse gas inventory sector covering emissions and removals of greenhouse gases resulting from land use. But the dry nature of the talks concealed the more important truth – that the negotiators are not just discussing acronyms, but human lives, which could be catastrophically altered due to the effects of climate change.
The Adopt a Negotiator program is supported by the Global Campaign for Climate Action, a group of young people from countries around the world who come to the UNFCCC meetings to track the delegations from their own countries and share what is happening at the negotiations through social networking tools (be sure to check out our blogs).
If the UN climate talks fail, and if countries cannot muster the political will to make substantial economy-wide changes and greenhouse gas emissions continue unabated, the results for the poorest and most vulnerable people on the planet will be catastrophic.
Last week was the first time that I have ever experienced any kind of UN negotiation first hand, and some of what I saw was incredibly depressing. Mitigation efforts are especially in danger, as disagreements primarily between the United States and China about who should agree to emissions cuts and international reporting and verification requirements sharpened and intensified.
But there were many bright spots as well. Negotiators are very close to making the final decisions about an international architecture for technology transfer to help the most vulnerable and poorest countries adapt to the effects of climate change and mitigate greenhouse gas emissions. They also spent the week narrowing and refining draft text with regards to climate finance and an international architecture to disburse “Green Funds,” and hopefully will be able to make final decisions at COP-16 in Cancun this November 29th through December 10th. These steps are small examples of potential good news for the people who will suffer, and are most likely already suffering, from climate change’s global impacts.
Unfortunately, negotiators are already in agreement that the only bright spots that we are likely to see at COP-16 are small items such as these. Almost no one believes that there is any chance that countries will agree on a final, legally binding text to reduce carbon emissions, and negotiators have instead pushed off this decision until the next Conference of the Parties (COP) in South Africa in 2011. Instead, the near-universal buzz at the conference was about a “balanced package.” Although the phrase in reality means something slightly different to everyone who uses it, it is generally understood to refer to a set of decisions on issues like climate finance, technology transfer, initiatives to cut back on deforestation, and putting some of the decisions made under the Copenhagen Accord into legally binding text, like “fast start” finance measures to the developing world.
In many ways the Tianjin session was itself a “balanced package” – a set of interactions and experiences that was both deeply discouraging and incredibly uplifting. One of the personally uplifting moments for me was having the honor of delivering a short intervention on the first day of the opening plenary on behalf of youth NGOs around the world (known as YOUNGOs). In the words I read, which had been drafted by a group of Chinese youth, all the particulars of policy were stripped away and the only thing that remained was the frustration – and also the hopes – of young people around the world (those who will actually experience the effects of climate change well within their lifetimes if UNFCCC negotiators don’t work harder to reach a consensus).
Through the disappointments of Copenhagen to the slow-moving intersessionals throughout this year, many pundits have cynically declared the UNFCCC process dead. This is certainly not the case. But if they are truly serious about saving the planet from climate change’s most serious impacts, negotiators will certainly have to work harder in Cancun.
Alex Stark is a Program Assistant at the Friends Committee on National Legislation, working on the Peaceful Prevention of Deadly Conflict Program. She attended the Tianjin negotiations as part of the Adopt a Negotiator team.
Photo Credit: Adapted from “COP11_lo,” courtesy of Neil Palmer and flickr user CIAT – International Center for Tropical Agricultu. -
Tracking the End Game: Sudan’s Comprehensive Peace Agreement
›
The next nine months are critical for Sudan. The 2005 Comprehensive Peace Agreement (CPA) sets January 9, 2011, as the date when southern Sudanese will vote on secession or unity, and the people of disputed Abeyei will vote on whether to be part of North or South Sudan. Between now and July 2011, when the provisions of the CPA come to an end, we could see the birth of the new country of South Sudan—or a return to a North-South war if the referendum is stalled, botched, or disputed. (Few currently expect that a unity vote will create the “New Sudan” envisioned by the late John Garang.)
-
Tackling Youth Unemployment, Instability in Kenya
›Today, Kenya’s youth unemployment rate stands at 65 percent, among the highest in the world. Three in five unemployed Kenyans are 15 – 35 years old. The situation is exacerbated by a shrinking economy, political instability, and pervasive income inequality.
Significantly, youth are engaged in the informal sector, which is largely unregulated and subjects workers to low earnings and long hours, without any formal contract. Suffering under a slow-growing economy, youth, whether well educated or uneducated, have increasingly turned to crime and violence, serving as watu wa mkono (handymen) to the ruling elite and intimidating and harassing their political opponents.Violence during Kenya’s disputed 2007 elections left approximately 1,133 people dead and 650,000 displaced from their land. Many of these atrocities were committed by youth, for sums as low as $6. With the 2012 elections fast approaching, Kenya risks renewed violence if its daunting youth unemployment rate is not properly addressed.
Against this backdrop, the Kenyan government has established the Youth Enterprise Development Fund (YEDF) and Kazi kwa Vijana (KKV), which means “jobs for youth,” to boost employment and entrepreneurship among people 18 to 35 years old.
Through YEDF, groups of up to 12 people can submit a business plan and apply for funding, as well as other services such as training, mentorship, and market access. The fund also connects youth with local and international job markets. KKV facilitates access to temporary, labor-intensive jobs for generally low wages, and also offers some business training.
Given the high poverty levels among youth in Kenya, temporary jobs can help young people learn the marketable skills they need to find decent work. But it’s not a long-term solution, as these low-paying jobs can also trap people in poverty, making crime and violence seem like the only viable exit.
Kenya would do well to learn from other countries’ efforts, where similar programs have long existed. For example, Italy’s Imprenditorialita Giovanile, or “Young Entrepreneurs’ Company,” and the UK’s Prince Trust exist solely to support young people’s start-up businesses.
Like Kenya’s efforts, these two programs provide training and mentoring to young people. However, they also have autonomy from their respective governments, which gives them freedom to operate without political interference and burdensome bureaucracy. Services are delivered by highly competent, successful entrepreneurs, who inspire youth to become entrepreneurs, not as an alternative to joblessness, but as a genuine career path with financial reward and work satisfaction. Through these programs, youth have managed to start and sustain viable businesses, and attain financial independence and stability.
Compared to these cases, Kenya’s KKV and YEDF fall short. Their activities overlap, and their objectives are too broad, which makes them unachievable within a reasonable timeframe.
They are also constrained by heavy government control. The prime minister’s office oversees KKV, while the Ministry of Sports and Youth Affairs manages YEDF. As a consequence, the programs are burdened by politics rather than buoyed with professionalism.
The tendency to treat youth as a homogenous group could isolate some young people who cannot fulfill YEDF’s requirements, such as a business development plan, a registered group, or an existing bank account. The rules should be more flexible and needs-based in order to benefit some of the needy and illiterate youth who require more rigorous training and support to succeed.
Finally, the programs’ near-sighted focus on temporary employment is but a bandage; Kenya needs long-term strategies to enable youth to access more rewarding and productive work.
Fundamentally, the problem requires properly planned, well-structured, and broad-based programs, and so far the government seems to be tinkering at the superficial level without a long-term, comprehensive plan. Accelerating economic growth is central to creating employment opportunities for youth, as well as providing market-driven education, training, and life skills.
In order to make a smooth transition to adulthood, young people require decent work and the ability to actively contribute to economic and political development and stability. Short of this, youth will remain at the margin of the economy, to serve as the violent watu wa mkono in 2012 and beyond.
Margaret Wamuyu Muthee is Programs Manager for Kenya’s University of Nairobi Center for Human Rights and Peace, and is currently an Africa Program Scholar at the Woodrow Wilson Center.
Photo Credit: Adapted from “Promulgation,” courtesy of flickr user ActionPixs (Maruko). -
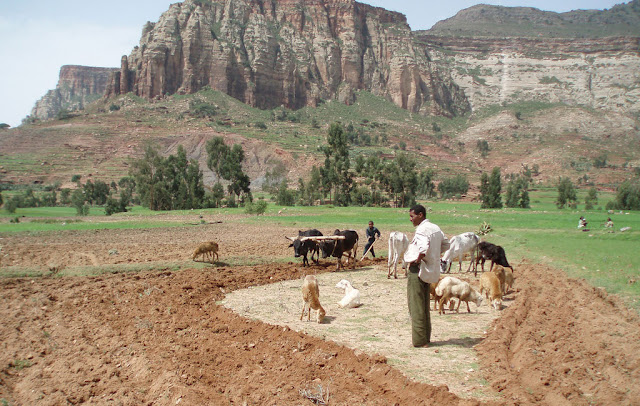
Ethiopian Case Study Illustrates Shortcomings of “Land Grab” Debate
›The lines have been drawn in the “land grab” debate: Will foreign investors displace small, local land-holders, damaging the environment with exploitive practices? Or will a combination of infrastructure investment and employment opportunities lead to a virtuous development cycle?
Recent reports suggest that the former is more likely than the latter (e.g., see the Oakland Institute, GRAIN, and the Food and Agriculture Organization). In each case, the proposed antidote is the typical wish-list: Boost institutional capacity to ensure that agreements are honored, environmental and labor regulations are observed, and local populations are given a stake in the process.
While it incorporates a broader swath of data and country case studies, the recent World Bank report, “Rising Global Interest in Farmland: Can It Yield Sustainable and Equitable Results?” largely recycles this tired diagnosis, as noted recently by Michael Kugelman on The New Security Beat.
But the two months we spent in the Amhara and Oromia regions of Ethiopia, surveying smallholders and profiling large-scale commercial farms, left us with a different impression. After completing 1,200 pages of surveys on smallholder livelihood strategies and farm management practices with 120 local farmers, as well as six profiles of private investors’ farms, we identified several key points that these reports missed.
Strong Laws Don’t Always Scare Investors Away
The World Bank report focuses on the belief that countries with weak institutions attract predatory investors, who use lack of oversight to their advantage by exploiting local populations, abusing regulations, etc. Ethiopia, however, has high institutional capacity relative to other African nations, yet still receives enormous land investment.
Every commercial farm we profiled received yearly visits from multiple regional and federal agencies investigating regulatory compliance. Moreover, two of the farms had been sold to their current owners because the previous business ventures failed to observe the terms of their business proposals. These terms included bringing certain amounts of foreign exchange into the country and hitting export targets.
Ethiopia attracts investors for other reasons. Official documents tout the diversity of its micro-climates, but we suspect investors are more likely drawn by a lease rate roughly 100x lower per hectare than the African average.
Given the emphasis on boosting institutional capacity as a means to ensure positive development outcomes, it’s too bad that the World Bank didn’t choose to conduct one of its case studies on Ethiopian commercial farms. Such a study could provide grounds for discussing what investment governed by stronger institutions would look like.
An Incomplete Paradigm
The potential for population displacement (with or without compensation), job creation, and infrastructure development is a well known and well studied paradigm. The World Bank report investigates the occurrence of these phenomena in its case studies, and the results are unsurprising: Sometimes things go OK and sometimes they go badly. This same story emerges in studies of foreign investments of all stripes: logging, oil and natural gas extraction, precious mineral mining, among others.
A more inventive analysis of land grabs could yield meaningful findings, however. Investors and smallholders are engaged in the same activity — farming — and in the case of cereal farms, they are producing the same crops. The resulting overlap allows for a multitude of creative interactions between smallholders and investors that should receive more attention.
Two of the investors we interviewed used these creative interactions to promote their business plans to regional development authorities. One farm sold certified seed to local farmers; another imported an irrigation system new to the region and plans to introduce it to the broader community. They each rented farm equipment to smallholders and held demonstration days to discuss farming techniques and new crop types with community members. One had already introduced new crops to the adjacent village via an “outgrowing” scheme and was exporting smallholder products from the farm, thus diversifying livelihoods for local farming households.
These are, of course, anecdotal accounts. But they suggest a broader point: More attention must be given to “secondary” benefits like technology and knowledge transfers, outgrowing or renting schemes, and informal interactions. Given the unique attributes of large-scale commercial investment in the agricultural sector, which continues to provide most Ethiopians’ livelihoods, these secondary benefits are the mechanism through which livelihoods seem most likely to be transformed. In this case, the preoccupation with displacement, formal compensation, jobs created, and infrastructure development only leads to generalized and ineffective analysis.
Our smallholder surveys and commercial farm profiles point to one conclusion: The commercial farms in our sample that engaged most fully in those creative interactions will generate substantial benefits for local populations over the next 5-10 years (quantitative analysis to be published in our final report this spring). The particular interactions taking place between these smallholders and commercial farms directly alleviate the primary constraints to smallholder livelihoods identified by our survey, such as lack of mechanization, lack of access to inputs, and inability to generate cash through sale of crops.
It’s far from clear that the World Bank analysis would have captured this reality in Ethiopia given its limited focus. Ideas like outgrowing receive scant attention, and are usually only discussed in hypothetical terms or in parentheticals – a trend the World Bank report unfortunately continued.
Incorporate Case Studies and Put Livelihoods First
So while our limited analysis may not enable us to speak broadly about the effects of commercial farming, we can offer two observations.
First, the creative arrangements that accompany the introduction of commercial farming must be front and center of any study. The study should be grounded in an understanding of the livelihood constraints faced by local populations, followed by an analysis of the types of interactions between commercial farms and smallholders that may affect those constraints, including not only traditional effects, such as displacement and employment, but also atypical impacts, such as improved seed distribution and technology demonstration.
Second, since Ethiopia has enough institutional capacity to be selective when choosing commercial investors (and to ensure they adhere to the terms), it embodies a number of principles the promoted by the World Bank report. Ethiopian Prime Minister Meles Zenawi views large-scale private farms as one piece of a broader commercialization effort to revolutionize smallholder agriculture, as described in the government’s development plan, PASDEP. This effort is in keeping with the report’s basic recommendation that host governments ensure that investment is compatible with domestic needs.
Understanding the phenomenon of large-scale land acquisitions should be at the top of the international research agenda. The effects on livelihood security and food security (in both developed and developing countries), as well as the potential contributions to resource conflicts, place such land deals among the most consequential recent trends in the international arena.
We believe a new framework must be brought to the analysis of land grabs. To effectively implement this framework, important but overlooked cases, such as we found in Ethiopia, should be included in future studies.
Nathan Yaffe and Laura Dismore are students at Carleton College, who just returned from researching commercial farming in Ethiopia. They can be reached at yaffen@carleton.edu and dismorel@carleton.edu.
Photo Credit: Adapted from “P8060261,” courtesy of flickr user Ben Jarman. -
Environmental Security Along the U.S.-Mexico Border
›
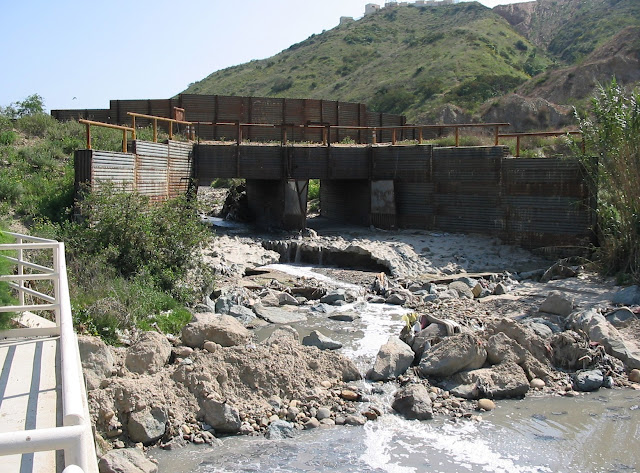
In 2005, the U.S. Department of Homeland Security (DHS) began the construction of a massive earthen, concrete, and metal security barrier along much of the U.S.-Mexico border, from the Pacific Ocean to the Gulf of Mexico.
Framing it as an issue of national security, DHS used provisions in the Real ID Act to waive environmental laws and citizen review for the controversial infrastructure project.
Unfortunately in Imperial Beach, California – my corner of the U.S.-Mexico border – the poorly engineered barrier has caused serious environmental mishaps and damage. In 2009 the Voice of San Diego reported that DHS circumvented numerous local and state laws in the course the barrier’s construction:Were it anyone else’s project, state regulators would’ve required irrigation to ensure that plants grew. But the federal government is responsible for the $59 million effort to complete and reinforce 3.5 miles of border fence separating San Diego and Tijuana. The Department of Homeland Security exempted itself from eight federal laws and any related state laws that would have regulated the project’s environmental impacts.
The Voice goes on to report that state water regulators also have no jurisdiction over the project since it has been exempted from the federal Clean Water Act.
“They did better engineering in 8th century China,” said Joe Sharkey of The New York Times, whom I took on a tour of the border, about the massive amphitheater of dirt that DHS dumped in Smuggler’s Gulch a few miles from the Pacific.
Ironically, while DHS has focused its efforts on the massive earthen and concrete wall, the agency has virtually ignored the tidal wave of polluted sewage water and garbage that flows across this section of the U.S.-Mexico border, a problem that makes the very people charged with safeguarding our security – border patrol agents and even Navy Seals – often unable to carry out their mission.
Over the past 20 years, border patrol agents have become ill from contact with the region’s polluted rivers, as well as the Pacific Ocean. In the Calexico-Mexicali region, border patrol agents worked directly with the Calexico New River Committee to clean up the New River – a drainage canal turned toxic hot spot.
Navy Seals based in Coronado, California, about 10 miles north of the U.S.-Mexico border, train in an area of the ocean that is directly impacted by polluted water flowing across the border from Mexico, bypassing the vaunted concrete and metal border barrier.
The organization I run, WiLDCOAST, is now working with U.S. agencies such as the International Boundary and Water Commission and the Environmental Protection Agency along with agencies in Mexico (e.g., CONANGUA and the state of Baja California) to reduce the threats to our military personnel and federal employees as well as border residents from cross-boundary pollution.
This cooperation has required a significant investment on the part of both the Mexican and U.S. governments in developing real solutions to our environmental security crisis on the border. Unfortunately the massive Berlin Wall-style barrier on our southern border is of little assistance in this effort.
Solving complex transboundary issues sometimes requires ignoring the cacophony of politics from distant capitals and instead working on the ground with colleagues from both nations who are experts in their shared geography. It appears the Obama administration is now slowly trying to repair some of the damage done to local communities, the cross-boundary relationship with Mexico, and our fragile shared environment.
But much more work and investment is needed to safeguard those we entrust to protect our security along the borderlands, as well as the residents of the region, from pollution that ignores international divisions and concrete walls. We must remember not only the national security component of our border-strengthening efforts but also the effect on human and environmental security as well.
Serge Dedina is the executive director of WiLDCOAST. He grew up and still lives on the U.S.-Mexico border in Imperial Beach, California. He is the author of Saving the Gray Whale and the forthcoming Wild Sea: Eco-Wars and Surf Stories From the Coast of the Californias.
Sources: Defenders of Wildlife, Environmental Protection Agency, University of Arizona, Voice of San Diego, WiLDCOAST.
Photo Credit: Serge Dedina.