-
Rear Admiral Morisetti Launches the UK’s “4 Degree Map” on Google Earth
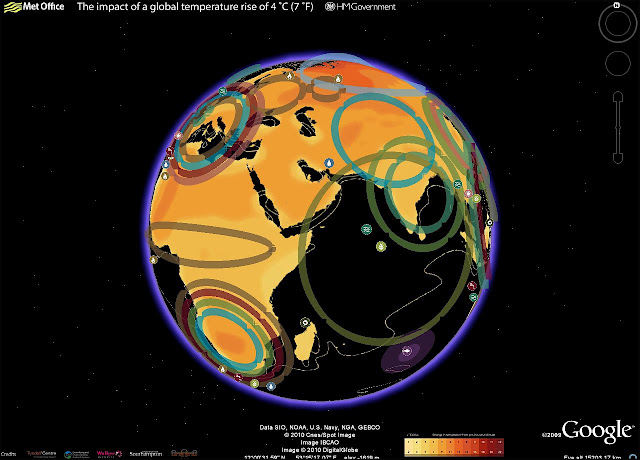
›Having had such success with the original “4 Degree Map” that the United Kingdom launched last October, my colleagues in the UK Foreign and Commonwealth Office have been working on a Google Earth version, which users can now download from the Foreign Office website.
This interactive map shows some of the possible impacts of a global temperature rise of 4 degrees Celsius (7° F). It underlines why the UK government and other countries believe we must keep global warming to below 2 degrees Celsius, compared to pre-industrial times; beyond that, the impacts will be increasingly disruptive to our global prosperity and security.
In my role as the UK’s Climate and Energy Security Envoy I have spoken to many colleagues in the international defense and security community about the threat climate change poses to our security. We need to understand how the impacts, as described in this map, will interact with other drivers of instability and global trends. Once we have this understanding we can then plan what needs to be done to mitigate the risks.
The map includes videos from the contributing scientists, who are led by the Met Office Hadley Centre. For example, if you click on the impact icon showing an increase in extreme weather events in the Gulf of Mexico region, up pops a video clip of the contributing scientist Dr Joanne Camp, talking about her research. It also includes examples of what the UK Foreign and Commonwealth Office and British Council are doing to increase people’s awareness of the risks climate change poses to our national security and prosperity, thus illustrating the FCO’s ongoing work on climate change and the low-carbon transition.
Rear Admiral Neil Morisetti is the United Kingdom’s Climate and Energy Security Envoy. -
‘The Plundered Planet’: A Discussion With Paul Collier
› Who owns the planet’s natural wealth found underwater, below ground, and in the air? How do we reconcile our use of these assets with that of future generations? Such questions are the subject of Oxford Professor Paul Collier’s latest book, The Plundered Planet: Why We Must–and How We Can–Manage Nature for Global Prosperity, which he discussed at a recent Wilson Center event.
Who owns the planet’s natural wealth found underwater, below ground, and in the air? How do we reconcile our use of these assets with that of future generations? Such questions are the subject of Oxford Professor Paul Collier’s latest book, The Plundered Planet: Why We Must–and How We Can–Manage Nature for Global Prosperity, which he discussed at a recent Wilson Center event.
The author of The Bottom Billion and Breaking the Conflict Trap, Collier called Plundered Planet “the most important book I’ve written.” Resources are a “one-shot game,” he said; if we waste them, they’re gone. The next 10-20 years are “vital” to preserving natural assets as new technologies for removing them proliferate. We’re sucking fish up like “hoovers,” he said, and a combination of technology and economic growth are rapidly pushing mineral extraction into the few remaining frontiers.
Because time is short, Collier hopes his work will bring economists and environmentalists together. He said the two groups are largely at each other “cat and dog,” yet their objectives–environmental preservation and economic development–are not fundamentally opposed. In fact, to overcome polarization and produce key policy decisions, development and conservation must become partners.
Becoming Custodians, Not Curators
Collier said resource plunder can take one of two forms: “Where the few expropriate what belongs to the many”; and “where nature is expropriated by the present generation and burned up rather than benefiting future generations.” Both forms of plunder not only impede development, but are also unjust, he said.
Unlike other assets–such as books or records, which are typically owned by their authors or artists–natural assets have no human creators. A system whereby “natural assets are owned by the people who are lucky enough to live on top of them” creates “staggering inequality,” said Collier. Instead, resources must be shared equally among all citizens of a nation, including those not yet born.
Yet sharing nature’s wealth with generations to come does not mean leaving all fish in the sea, all trees on land, or all minerals underground. “We are not curators of natural artifacts,” Collier said. “We’re custodians of natural value.”
For the one billion people living in poverty, the development of natural resources can provide a path toward development, growth, and better lives, Collier argued, when properly and justly managed.
Filling the Gaps in Governance
Why have we largely plundered, rather than invested in, our resources thus far? What can be done to change the current principles of resource management? Collier’s short answer: governance.
For the poor countries in the “bottom billion,” Collier said the “broken decision chain” must be mended. The chain has six steps:- Discovering natural assets;
- Avoiding appropriation by a few at the expense of the many;
- Ensuring local inhabitants receive generous compensation for unavoidable environmental damage;
- Consuming in a way that benefits both the present and the future;
- Investing in the absorptive capacity of government; and
- Investing in domestic development.
Igniting a Movement
“There is no substitute…for building a critical mass of informed opinion,” Collier said. While technology enables plunder, it also creates a way for people to share knowledge at tremendous speeds and with wide audiences. The challenge, he said, “is to ignite the information transformation process.” A shift from plunder to sustainable management of transnational and developing country resources is a historic opportunity to benefit the world’s poor. “If these resources are harnessed for sustained development,” he said, “they can drag themselves decisively from poverty to prosperity.” The window of opportunity, however, is closing. -
Urbanization, Climate Change, and Indigenous Populations: Finding USAID’s Comparative Advantage
›May 26, 2010 // By Kayly Ober “Part of the outflow of migrants from rural areas of many Latin American countries has settled in remote rural areas, pushing the agricultural frontier further into the forest,” writes David López-Carr in a recent article in Population & Environment, “The population, agriculture, and environment nexus in Latin America.” In a May 4 presentation at the LAC Economic Growth and Environment Strategic Planning Workshop in Panama City, Panama, he discussed how to integrate family planning and environmental services in rural Latin America.
“Part of the outflow of migrants from rural areas of many Latin American countries has settled in remote rural areas, pushing the agricultural frontier further into the forest,” writes David López-Carr in a recent article in Population & Environment, “The population, agriculture, and environment nexus in Latin America.” In a May 4 presentation at the LAC Economic Growth and Environment Strategic Planning Workshop in Panama City, Panama, he discussed how to integrate family planning and environmental services in rural Latin America.
Latin America is one of the most highly urbanized continents in the world, with an average of 75 percent of the population living in cities. However, “there are two Latin Americas,” said López-Carr at the workshop, which was sponsored by the Woodrow Wilson Center’s Environmental Change and Security Program and Brazil Institute, as well as the U.S. Agency for International Development. Largely developed countries like Chile, Argentina, and Uruguay are close to 90 percent urbanized, while Guatemala, Ecuador, and Bolivia are about 50 percent. In less urbanized countries, rural-rural migrants in search of agricultural land remain a major driving force behind forest conversion, he said.
Between 1961 and 2001, Central America’s rural population increased by 59 percent, said Lopez-Carr. The increasing density of the rural population had a negative impact on forest reserves: a 15 percent increase in deforestation totaling some 13 million hectares.
“Rural areas of Latin America still have high fertility rates but (unlike much of rural Africa, for example) also have a high unmet demand for contraception, meaning that improved contraceptive availability would likely result in a rapid and cost-effective means to reduce population pressures in priority conservation areas,” he said. Additionally, remote rural areas with high population growth rates tend to be associated with indigenous populations located in close proximity to protected forests.
For example, in Guatemala, communities surrounding Sierra de Lacandon National Park have, since 1990, grown by 10 percent each year, with birthrates averaging eight children per woman. Larger communities and larger households have led to agricultural expansion, which infringes on the park and accelerates deforestation in one of the most biologically diverse biospheres in the world, said López-Carr.
Based on these demographic and environmental trends, López-Carr suggested USAID’s work in the region should focus on rural maternal and child health, and education – especially for girls. Not only does USAID already invest in such programs, but they only cost pennies per capita and could reduce the number of rural poor living in Latin American cities by tens of millions.
Given the strong links between population density and deforestation in Latin America, expanding access to family planning would also be a smart investment in forest conservation and climate mitigation, López-Carr concluded.
Source: Population Reference Bureau.
Photo Credit: Dave Hawxhurst, Woodrow Wilson Center. -
Coffee and Contraception: Combining Agribusiness and Community Health Projects in Rwanda
›“Population pressures and diminishing land holdings – due to high fertility rates, war and genocide, and subsequent migration – have caused a rapid decrease in the forested and protected areas and increased soil infertility and food insecurity” in Rwanda, USAID’s Irene Kitzantides told a Wilson Center audience.
Kitzantides, a population, health, and environment advisor and global health fellow, said “the population is projected to reach over 14 million by 2025” – nearly one-third more than today, due to the country’s high fertility rate of nearly 5.5 children per women–which could continue to negatively impact forests and food supplies.
In response to these challenges, USAID supported the Sustaining Partnerships to Enhance Rural Enterprise and Agribusiness Development (SPREAD) Project. SPREAD uses an integrated population-health-environment (PHE) approach to develop the coffee agribusiness and bring family planning, HIV/AIDS, and reproductive health services to coffee workers.
Combining income generation with health services was thought an effective way to “fulfill the overall SPREAD goal of improving lives and livelihoods,” said Kitzantides.
A SPREADing Mandate: Integrating Health and Agribusiness
SPREAD follows USAID’s PEARL I and II Projects, which focused exclusively on agricultural development. Coffee is still at the center of SPREAD’s activities, with $5 million of the project’s $6 million USAID budget earmarked for agricultural development.
However, a broader mandate to include health services emerged after recognition that greater income alone does not ensure greater quality of life. The additional health funding leverages SPREAD’s already established relationships with farming cooperatives to bring health services to traditionally underserved rural communities.
“We really tried to build on the existing assets of the cooperative,” said Kitzantides. “We also really tried to complement local and national public health policy and partners.”
The integration of health with agricultural goals, and the use of already established in-country health programs, has made SPREAD extremely cost-effective, with HIV/AIDS prevention education costing less than $2 per person.
Examples of SPREAD’s integrated work include:Combined health and agricultural lessons: Kitzantides and her colleagues trained nearly 400 animateurs de café, cooperative employees running the agricultural education programs, to incorporate public health objectives into their activities. Combining health and agricultural education into one session takes advantage of workers already trained during previous USAID programs. The combination also attracts more male participants, who traditionally shunned HIV/AIDS, family planning, and reproductive health campaigns and services.
Radio programming: SPREAD worked with the agricultural radio program Imbere Heza (“Bright Future”) to incorporate health messaging at the end of each program.
 Mobile clinics: SPREAD works with cooperatives and local health centers to bring convenient services to farmers when they gather at sales or processing stations during harvests.
Mobile clinics: SPREAD works with cooperatives and local health centers to bring convenient services to farmers when they gather at sales or processing stations during harvests.Community theater: SPREAD hires local theater groups to perform skits on health. The farming communities “really love community theater and always ask for it,” said Kitzantides.

In its relatively short existence, SPREAD’s health activities have reached over 120,000 people with HIV/AIDS prevention messages; nearly 90,000 with messages discussing family planning/reproductive health; and almost 40,000 about maternal and child health. The project counts 347 women as new users of family planning services.
Lessons learned – which will be examined in more detail in an upcoming issue of Focus – include the importance of using community-based approaches to overcome perceived social barriers; the advantages of integrating cross-cutting activities at the outset of a program; and the need for strong monitoring and evaluation systems to measure the effort’s outcomes. Jason Bremner of the Population Research Bureau said PHE projects such as SPREAD go “beyond what the health sector itself can do and find new ways of reaching underserved remote populations.” He presented a soon-to-be-released PRB map plotting the location of more than 40 PHE projects in Africa.
Jason Bremner of the Population Research Bureau said PHE projects such as SPREAD go “beyond what the health sector itself can do and find new ways of reaching underserved remote populations.” He presented a soon-to-be-released PRB map plotting the location of more than 40 PHE projects in Africa.
The success of SPREAD and similar projects demonstrates the potential for PHE approaches to bring reproductive health and family planning services to rural areas, Bremner noted, but there is still much work to be done to scale up this integrated approach – and to document its successes.
Sustaining SPREAD
Kitzantides said it took several years to integrate health activities with the already established agricultural programs. Since USAID funding for the program is scheduled to end in 2011, she is uncertain that the time remaining will be enough for SPREAD’s health partners to develop the logistical and financial capacities to become self-sustaining. But SPREAD has changed attitudes and beliefs, two key objectives that do not require sustained funding.
“We used to talk about growing coffee, making money, buying material things like bikes – not about problems like malaria, HIV/AIDS, etc.,” said one SPREAD agricultural business manager during the program’s evaluation. “Someone could have 5 million Rwandan francs in the house but could suffer from malaria where medicine costs 500 Rwandan francs, due to ignorance. You have to teach people about production, you have to also think of their health to improve their lives.”
Photo Credits: Irene Kitzantides, courtesy David Hawxhurst; condom demonstration, courtesy Nick Fraser; community theater group, courtesy SPREAD Health Program; Jason Bremner, courtesy David Hawxhurst. -
Challenges Found in ‘The Places We Live’
›May 18, 2010 // By Julien KatchinoffThe work of photographer Jonas Bendicksen provided the inspiration for a research paper competition organized by the Woodrow Wilson Center’s Comparative Urban Studies Project, the Cities Alliance, the International Housing Coalition, USAID, and the World Bank. At “The Places We Live: Slums and Urban Poverty in the Developing World,” four of the winning papers (out of 200 entries) were critiqued by urbanization policy experts. The authors focused on critical issues facing the world’s rapidly urbanizing centers, including service delivery, the challenge of political cleavages, redevelopment mechanisms, sanitation, and citizen participation in urban development.
The competition was established to “tap into the academic community and encourage … a younger generation of academics…to think about the challenges of rapid urbanization and the needs of slum dwellers and what we can do about it,” said USAID’s Jessica Tulodo. “It is the central issue that we are going to be grappling with for the coming decades and beyond. How do we not just address the challenges, but harness the opportunities of urban growth and how do we ensure that the larger population of urban poor can benefit and participate?”
“This is an effort to rekindle a stronger debate between the academic community and policymakers. I think that’s desperately absent, particularly in this field,” said Christopher Williams, the U.S. Representative of UN-HABITAT.
All Politics Are Local: Urban Services in Zambia
In her case study of the shanty compounds on the periphery of Lusaka, Zambia, Danielle Resnick investigates how the ruling government — through “development initiatives” — suppresses political opposition and controls weaker economic and political factions. The difficult relationship between local service delivery and inter-party politics is endemic in many African countries, where local municipalities are often run by opposition parties.
Christopher Williams, in his review, praised Resnick’s work for capturing the intricacies and complexity of rapid urbanization in Zambia and beyond, noting that it offered a “scathing” critique of direct budget assistance by foreign donors.
“Land Sharing”: A New Approach for Slums in Southeast Asia
Paul Rabe’s “Land Sharing in Phnom Penh and Bangkok: Lessons From Four Decades of Innovative Slum Redevelopment Projects in Two Southeast Asian ‘Boom Towns'” examines the emerging issue of land conflict in redeveloping urban areas and innovative solutions such as land sharing. Sometimes called a “win-win-win,” land sharing through multi-use agreements based on maximized utility can help to mediate the needs of slum dwellers, private developers, and municipal governments.
Rabe found that land sharing has several limitations, including programmatic delays, muted benefits for stakeholders, and limited deployments. “In retrospect,” he said, “the institutional setting [for land sharing] is not mature enough to accommodate a fairly complex redevelopment procedure.”
If donors and civil society groups are willing to brave a complex and highly politicized environment, land sharing may be an innovative option for those looking to quell redevelopment conflict. Robin Rajack of the World Bank said it was critical for the future sustainability of growing urbanization, as improving the ability of the urban poor to navigate difficult land tenure changes may foster urban economic growth.
Maintaining Sanitation, Building Community in India
In “Desired Outcomes, Unexpected Processes: Two Stories of Sanitation Maintenance in Erode Tenements, India,” Sai Balakrishnan asks why, “within the same municipality, are residents of some tenements more willing to contribute towards septic tank maintenance than others?” Her analysis of two communities in the state of Tamil Nadu in Southern India finds that asset ownership, embedded and accessible politicians, and political patronage did not improve maintenance of sanitation infrastructure. Instead, the critical factors were the spatial proximity of infrastructure, bundling of water and sanitation services, and “street-level bureaucrats.”
Reviewer Bob Buckley of the Rockefeller Foundation asked if future research could incorporate empirical data on the costs of sanitation problems for communities, “beyond the visuals,” which could provide a deeper understanding of the difficulty of delivering services in urban slums.
Gaming Community Participation in Argentina
Josh Lerner’s “What Games Can Teach Us about Community Participation: Participatory Urban Development in Rosario’s Villas” reveals the results of his six months of fieldwork in the slums of Rosario, Argentina. Although urban redevelopment can produce conflict–especially when combined with vast inequities in economic and political power–Lerner found that taking a game theory approach to difficult land-use decisions helped to “enhance the quality of community participation, by making it more attractive, active, and effective, and making decisions fairer and more transparent.”
William Corbett of Cities Alliance warned that if developing countries cannot effectively deal with the chaotic informality of land tenure and urban development, “gangs with guns will do it for you”– particularly when urban change and resource or land scarcity provokes competition for limited resources.
Photo Credits: “Christopher Williams, Danielle Resnick; Moynahan Boardroom” courtesy of David Hawxhurst.
-
Philippines’ Bohol Province: Elin Torell Reports on Integrating Population, Health, and Environment
›For 10 years, I have been working on marine conservation in Tanzania with the University of Rhode Island’s Coastal Resources Center. As part of that effort, I’ve helped forge links between HIV/AIDS prevention in vulnerable fishing communities and marine conservation. However, family planning and reproductive health (FP/RH) were relatively new to me. But a recent study tour of an integrated Population, Health, and Environment (PHE) program in the Philippines helped me understand that combining family planning services and marine conservation can help reduce overfishing and improve food security.
Together with developing country representatives from seven African and Asian countries, I spent two weeks in February visiting three PHE learning sites and a marine protected area in Bohol province in the central Philippines, as part of a South-to-South study tour sponsored by the USAID-funded BALANCED Project, for which I work. The tour focused on the activities of the 10-year-old Integrated Population and Coastal Resource Management Initiative (IPOPCORM) project, which is run by PATH Foundation Philippines, Inc. (PFPI).
IPOPCORM has garnered a wealth of lessons learned and best practices to share with PHE newbies like me. Its integrated programs train people to be community-based distributers (CBDs) of contraceptives and PHE peer educators, as well as work with local and regional government officials to build support for family planning as a means to improve food security.
I was most impressed with the ways in which PFPI identifies and cultivates dynamic and motivated local leaders–men, women, and especially youth–to reach out to the members of their community who are highly dependent on marine resources for their survival. My Tanzanian colleagues and I would like to foster the volunteer spirit and “can do” attitudes we experienced through our work in East Africa. (Similar PHE peer educators are successfully working in Ethiopia’s Bale Mountains, as reported by Cassie Gardener in a previous edition of the “Beat on the Ground.”
My favorite part of the tour was a trip to the Verde Island Passage to see PFPI’s efforts in this fragile hotspot. The insights my Tanzanian colleagues and I gained from talking to the field practitioners in the Verde Islands helped us refine our ideas for translating some of the PHE techniques used in the Philippines to the Tanzanian cultural context, including an action plan for strengthening our existing PHE efforts with CBDs and peer educators.
Thanks to the study tour, I now have a better understanding of how to address population pressures in the context of conservation. Overall, my Tanzanian colleagues and I were inspired by the successes we saw firsthand and hope to emulate them to some degree in our own projects.
Elin Torell is a research associate at the Coastal Resources Center at the University of Rhode Island. She is the manager of CRC’s Tanzania Program and coordinates monitoring, evaluation, and learning within the BALANCED project. -
City Living: World Health Day 2010 Focuses on Urban Health
›April 7, 2010 // By Julien KatchinoffCelebrating World Health Day, the World Health Organization, with its partners around the globe, today launched an initiative for healthly lives in urban settings, through the theme “1000 Cities, 1000 Lives.” “We are at a critical turning point in history where we can make a difference,” said Dr Ala Alwan, assistant director-general for noncommunicable diseases and mental health.
Since the first World Health Day 60 years ago, the world has seen a dramatic rural exodus. Today, more people live in urban areas than anywhere else. Providing healthy livelihoods for the urban poor is a challenge, as poverty-stricken urban centers face a number of health obstacles, from high child mortality rates, environmental pollution, and widespread disease, to a lack of access to basic water, sanitation, and health care.
“In general, urban populations are better off than their rural counterparts,” said WHO Director-General Margaret Chan. “They tend to have greater access to social and health services and their life expectancy is longer. But cities can also concentrate threats to health such as inadequate sanitation and refuse collection, pollution, road traffic accidents, outbreaks of infectious diseases and also unhealthy lifestyles.”
The 1000 Cities campaign hopes to encourage all cities to promote healthy activities during the week following World Health Day (4/7-4/11). Through a new website, the WHO is collecting profiles and pictures in an easy-to-navigate map. Notable activities include HIV/AIDS-awareness flashmobs, skateboarding and cycling competitions, car-free days, outdoor sports events, and dance performances, in cities as diverse as Mandalgobi, Mongolia; Bangalore, India; and Luanda, Angola.
The Wilson Center’s Environmental Change and Security Program and its Comparative Urban Studies Program have collaborated on urbanization events and publications that examine the strong and critical connections between healthy urban populations and environmental sustainability.
With proper attention paid to delivering population, health, and environmental services in our urban centers, it may be possible to leverage the benefits of higher urban densities—such as lower aid dispersion costs, communication access, infrastructure services, and fertile environments for ideas and productivity—to ensure urban sustainability for the future. -
A Tough Nut to Crack: Agricultural Remediation Efforts in Afghanistan
›April 5, 2010 // By Julien Katchinoff“It was pretty much a normal day in Afghanistan on Monday.
Though only earning a glancing mention in The New York Times, it is heartening to see a response to the environmental and economic loss of Afghanistan’s once abundant wild pistachio forests. As a result of wide-spread environmental mismanagement and war, the past 30 years have seen a dramatic decline in the wild pistachio woodlands native to Northwestern Afghanistan.
“A couple of civilian casualties caused by insurgents. More investigations into corrupt former ministers. The opening of six new projects in Herat Province by the Italians and the Spaniards, which are the NATO countries in the lead in western Afghanistan. All right, not six, projects, but two or three, and the Spanish announced a pistachio tree-growing program to replace poppies. Pistachios, poppies… maybe pine nuts will be next.”
— At War: An Airborne Afghan Folk Tale, Alissa J. Rubin, New York Times, April 1, 2010
In a 2009 survey of Afghanistan’s environmental challenges, UNEP found that, while in 1970 “the Badghis and Takhar provinces of northern Afghanistan were covered with productive pistachio forests and earned substantial revenue from the sale of nuts,” few remain as the forests have since succumbed to mismanagement, war, and illegal logging.
In this video by the Post-Conflict and Disaster Management Branch of UNEP, scenes of dusty and denuded hillsides clearly show that rural Afghan farmers in search of sustainable livelihoods have few options remaining.
The project mentioned in the New York Times is a recent foray into remediation efforts by a Spanish Provincial Reconstruction Team (PRT) that targets communities previously involved in the production of illegal drugs. In conjunction with the Spanish Agency of Coordination and Development (AECID), the Spanish PRT is working in over 13 sites in Baghdis province–a region once covered in pistachio trees–to help farmers transition to legal crops and restore the traditional pistachio forests to their former prominence. AECID joins the Afghan Conservation Corps (ACC), USAID, NATO and additional partners in promoting remediation projects to reverse deforestation.
Unfortunately, these programs face daunting obstacles, as pistachio and other traditional Afghan cash crops –such as raisins, figs, almonds and other nuts– require substantial re-investments of time, money, and infrastructure development. Furthermore, convincing desperate rural farmers to transition to nearly untested alternative crops is difficult when they are currently counting the days to the spring opium harvest.
Recently, eradication efforts targeting small-scale farms have abated, and increased attention is being paid to facilitating shifts toward new products through free seeds, loans, technical assistance, and irrigation investments. If successful, these projects will grant rural Afghan communities the ability to sustainably and legally provide for their families, providing long-term employment and returns for a region lacking in both money and hope for the future.
Video Credit: UNEP Video, “UNEP observes massive deforestation in Afghanistan” .
Showing posts from category livelihoods.