Showing posts from category environmental security.
-
Emily Gertz, Momentum Magazine
U of M’s ‘Momentum’ on Water Scarcity, Population, and Climate Change
›December 20, 2010 // By Wilson Center StaffExcerpted from the original article, “Water Tight,” by Emily Gertz in the University of Minnesota’s Momentum magazine.
The next time you stop off at a pub for a quick bite, think about this: It took around 630 gallons of water to make your burger. Your pint of beer used around 20 gallons. Manufacturing your blue jeans and t-shirt drank up about 1,218 gallons of water: 505 and 713 gallons, respectively.
Total: nearly 1,900 gallons of water – and that’s without fries on the side.
These quantities are the “water footprint” of each product: the total amount of freshwater used in its manufacture, including producing the ingredients.
For many products, that footprint is Paul Bunyan–sized: With water seemingly cheap and plentiful, there has been little incentive to try to keep it small.
But today, that’s changing. Even though much of the water we use for growing food and making products is replenished by natural hydrological cycles, freshwater will be less reliable and available in the coming century. Population growth is increasing both demand for water and pollution of potable supplies. At the same time, climate change is disrupting historical precipitation patterns, shrinking freshwater sources such as glaciers and snowpack, and creating unprecedented droughts and floods.
According to an analysis published in Nature in September 2010, the freshwater supplies of most of the world’s population are at high risk.
“If you look at the global distribution of people and the global distribution of threat levels to human water security, the places with the highly threatened water security represent about 80 percent of the world population, over four billion people,” says study co-author Peter McIntyre, assistant professor at the University of Wisconsin’s Center for Limnology.
In the United States, a 2010 analysis by the consulting firm Tetra Tech for the Natural Resources Defense Council found that more than 1,100 counties – fully two-thirds of all counties in the lower 48 states – will contend with higher water risk by 2050 due to climate change alone. Fourteen states can expect extremely serious problems with freshwater supply, including Florida, Mississippi, New Mexico, and California.
It’s not surprising, then, that businesses are increasingly considering their corporate water footprint. They encounter water risk – and opportunities to reduce it – at many stages of their operations, from growing crops to running retail stores. Factoring such risks into their present and future planning is helping companies present themselves as good environmental stewards to the public, and potentially reduce risks to their earnings from water scarcity.
“It’s often said that water is going to be the oil of the 21st century, in the sense of becoming an ever-more scarce commodity,” McIntyre says. “In the grand scheme of things, you can live without oil, but you can’t live without water. Water is fundamental for all life. And that’s certainly true for business as well.”
Continue reading on Momentum.
Sources: Natural Resources Defense Council, Nature.
Photo Credit: Adapted from “Lake Hume at 4%,” courtesy of flickr user suburbanbloke. -
Demographic Security Comes to the Hill
›December 16, 2010 // By Hannah Marqusee“We are now in an unprecedented era of demographic divergence,” said Population Action International’s Elizabeth Leahy Madsen at a September briefing held by Congressman John Tierney’s Subcommittee on National Security and Foreign Affairs and Congressman Russ Carnahan’s Subcommittee on International Organizations, Human Rights and Oversight.
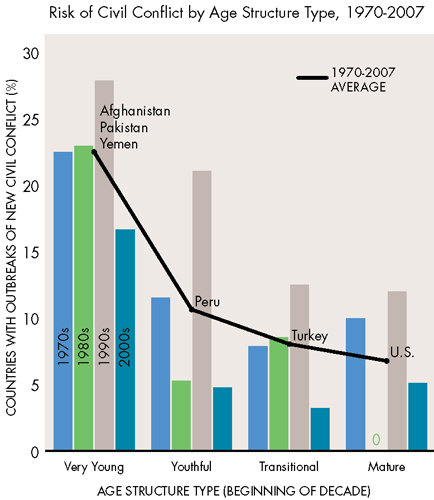
Eighty percent of the world’s conflicts occur in places where 60 percent or more of the population is under 30, and 90 percent of countries with young populations have weak governments, said Chairman Tierney in his opening remarks. He said that while such demographic trends “appear to be issues for the future…it is important that we start this dialogue today, so that we can make steps to address [them].” ECSP Director Geoff Dabelko and the Stimson Center’s Richard Cincotta joined Madsen on the panel titled, “The Effects of Demographic Change on Global Security,” at the Capitol Visitor Center.
Youth Bulges and National Security
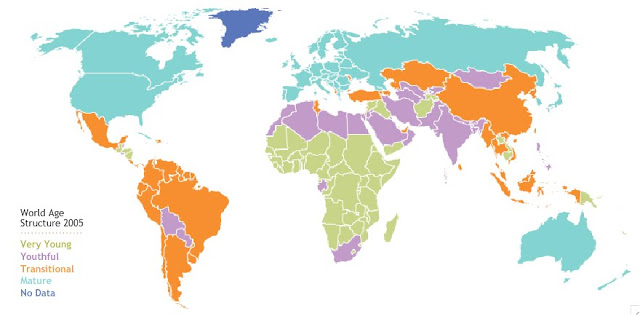
The countries of greatest security threat to the United States are also those with the youngest age structures and rapidly increasing populations, said Madsen. By next year, the world’s population will have reached seven billion, with 95 percent of that growth occurring in the developing world.
Large youthful populations can be a source of national strength because they provide innovation and manpower, said Dabelko, but without significant investment they may also contribute to state instability. When there are often few opportunities to obtain a job or an education for young people, there are low “opportunity costs” to joining a rebel group, said Madsen.
State instability can be affected by youth bulges, shifting religious or ethnic compositions, or food and water insecurity, but age-structural transitions are the strongest indicator of state performance, said Cincotta. Despite conventional wisdom, there is actually little evidence to link state failure with premature adult mortality due to AIDS or a high male-to-female ratio, he added.
It is not only developing countries with high fertility rates that face demographic difficulties, Cincotta noted. Countries such as Japan and Germany will soon have reached a “post-mature” age structure in which their aging populations and comparatively small workforces will tax state institutions and threaten economic stability.
Population Policies: Using “Soft Tools” to Improve National Security
Recently, leaders in the U.S. government have been paying increased attention to the linkages between demography and security through the “three Ds:” diplomacy, development, and defense. In 2008, the National Intelligence Council’s Global Trends 2025 included demographic assessments to analyze security trends, and this year, the National Security Strategy featured demographic trends along with the environment and other non-traditional areas.
Dabelko said that while this growing recognition signals progress, the “hard tools” of the traditional security community must be bolstered with “soft tools” commonly used by the international aid community, such as female empowerment, education, health services and youth employment.
Madsen argued that empowering the 215 million women with an unmet need for family planning worldwide through increased funding for voluntary family planning programs is a cost-effective way to shape population trends and ultimately reduce security threats.
“Demography is not destiny,” said Madsen. “Family planning has been an unsung signature of U.S. foreign assistance for decades.”
Similarly, Cincotta said that policies should help states transition out of youth bulges, and help countries with aging populations reform social institutions to protect older people.
Dabelko added that while progress has been made in acknowledging the linked nature of population trends and national security, there is significant room for improvement. Pointing to the successes of integrated population, health, and environment (PHE) programs, which provide environmental conservation and family planning services simultaneously, he called for similar programs to address population dynamics and conflict prevention. Long-term solutions call for coordinated resources and integrated strategies, he said.
Read the speakers’ full remarks: Chairman John F. Tierney, Richard Cincotta, Geoff Dabelko, and Elizabeth Leahy Madson (slides).
Sources: Guttmacher Institute, Population Action International, National Intelligence Council.
Image Credits: “World Age Structure 2005” and “Risk of Civil Conflict by Age Structure Type, 1970-2007,” courtesy of Population Action International. -
Rebuilding Stronger, Safer, Environmentally Sustainable Communities After Disasters
The GRRT Toolkit for Humanitarian Aid
›Natural disasters present an immediate humanitarian crisis but are also an opportunity to rebuild societies to be more resilient and environmentally sustainable than they were before. The “Green Recovery and Reconstruction Training Toolkit” (GRRT), created by World Wildlife Fund (WWF) and the American Red Cross and launched at the Wilson Center on November 19, will help future humanitarian efforts integrate principles of environmental conservation into their disaster recovery strategies. This strategic partnership has been “an incredible effort and marriage between organizations that have different operating styles, different approaches to situations,” said WWF Chief Operating Officer Marcia Marsh. While implementing the GRRT may not be easy, “we need integrated solutions for integrated problems,” said Erika Clesceri, bureau environmental officer at USAID.
A Critical Partnership
In the midst of a crisis, humanitarian workers on the ground often do not have the time, skills, or funding to incorporate environmental concerns into relief efforts, said Robert Laprade, senior director for emergencies and humanitarian assistance at CARE. Humanitarian workers are “going a hundred miles an hour, they’re going on adrenaline and they’re there to save people’s lives – and the environment is just of secondary importance,” he said.
But “environmental sustainability is critical to the achievement of long-lasting recovery results,” said Roger Lowe, senior vice president of communications at American Red Cross. The Red Cross Principles of Conduct state that “relief aid must strive to reduce future vulnerabilities to disaster as well as meeting basic needs” and “avoid long-term beneficiary dependence upon external aid,” he said.
From Damnation, Purgatory, and Armageddon to Redemption
For many crisis-stricken regions, lack of an emphasis on environmental sustainability during disaster recovery efforts can mean “damnation in the present, purgatory in the near future, and Armageddon in the long term,” said Peter Walker, director of the Feinstein International Center at Tufts University. Stress on the environment caused by climate change or unsustainable resource consumption can often contribute to conflict, he explained.
In Darfur, “the environmental change was part and parcel of what led to that conflict,” Walker said. At one time an “environmental Eden” of diverse ecological zones, Darfur gradually became an environment that could not support a society of livestock herding. As the environment changed, some former herders became salaried, armed gunmen, known as the Janjaweed who felt they faced “a choice of no choice,” Walker said, to either “die as pastoralists or become pariahs as mercenaries.”
The challenge for humanitarian aid organizations is to not only help communities recover from disasters, but help them adapt to future environmental stress caused by globalization, climate change, or other factors. “If you cannot adapt,” Walker said, “that’s going to lead to violence.” To avoid aid dependency or resurgence in conflict it is critical to integrate environmental sustainability into disaster relief efforts from the beginning, he said:We used to believe that our world in the aid business was divided between relief on the left and long-term development on the right, and one would gradually go into the other in this relief-development continuum. But the reality is that you have a significant population – a population of millions of people – who are effectively trapped in a form of aid purgatory. They’re basically on a drip feed. Humanitarian assistance does not get you forward, it keeps you alive.
The GRRT offers organizations guidelines for implementing integrated disaster relief to provide a sustainable solution. While every crisis is different, the GRRT’s guidelines should be as applicable to “flooding in Boston as they are to flooding in Aceh,” said Walker.
Implementing Integrated Solutions
Securing funding for this integrated approach will be a challenge, as a significant portion will go towards staffing and training people on the ground, said Clesceri. A stand-alone, dedicated budget for environmental issues within humanitarian assistance programs must “be fought and re-fought for on a continual basis,” she said.
Local partnerships are essential. “Replicate” should be “stricken from the lexicon,” said Marsh. “You can’t replicate, and this toolkit isn’t meant to be a one-size-fits-all.” Instead, she said, the goal of the GRRT is to “create very practical approaches with communities.”
The key to helping communities recover from disasters is to form the kinds of strategic partnerships demonstrated by WWF and the American Red Cross in the creation of the GRRT. “Interdisciplinary groups are always, in my mind, going to get you a better solution in the end, but the risk is that they take more time…but it’s absolutely worth it,” she said.
Photo Credit: “Dark Clouds from Haiti’s Hurricane Tomas Loom over Camps,” courtesy of flickr user United Nations Photo. -
An Integrated Climate Dialogue
COP-16 Cancun Coverage Wrap-up
›December 13, 2010 // By Schuyler NullAfter focused last-minute negotiations, the UNFCCC COP-16 parties meeting in Mexico finally reached an agreement on a package being called “The Cancun Agreements” on Saturday. One of the most important impacts of the agreement (also referred to as the “balanced package”) is the establishment of a green climate fund which will help developing countries adapt to and mitigate the effects of climate change.
For more on the green fund as well as the integration of gender, population, development, and even a little bit of security in the broader climate dialogue, see The New Security Beat’s coverage of Cancun below.- Interview with Karen Hardee: Climate-Proofing Development
- Pop Audio: From Cancun: Roger-Mark De Souza on Women and Integrated Climate Adaptation Strategies
- Guest Contributor Alex Stark: From Cancun: Getting a Climate Green Fund
- The Number Left Out: Bringing Population Into the Climate Conversation
Kicking off our coverage was an email interview with Karen Hardee, visiting fellow with the Population Reference Bureau, on “climate-proofing” development. Hardee gives a brief overview of the UN National Adaptation Programmes of Action system and the current state climate adaptation integration in international development. She points out that one of the enduring positives from COP-15 was a renewed focus on financing tools that has permeated to the top levels of the UN.
Hardee also touched on the nascent but largely unfulfilled connection between population growth and resilience, noting that “of the first 41 programs submitted to the UNFCCC…37 noted that population growth exacerbated the effects of climate change, but only six explicitly stated that meeting an unmet demand for RH/FP should be a key priority for their adaptation strategy and only two proposed projects that included RH/FP.”
Next, Population Action International’s Roger-Mark De Souza was kind of enough to speak with us briefly over the phone from the conference itself, providing a run-down on a PAI-sponsored side event focusing on empowering women in climate debates.
“When you look at the negative impacts of climate change, the impacts on the poor and the vulnerable – particularly women – increase, so investing in programs that put women at the center is critical,” De Souza said.
Leaving gender issues, like child and maternal health and education, out of deliberations like those COP-16 are missed opportunities to get more “power for your peso,” he said.
Alex Stark, formerly of CNAS and now with the Adopt a Negotiator program in Cancun, provided an update and a strong argument for one of the most critical elements of the “balanced package” that many are hoping will come out of Cancun – the establishment of an international fund to help pay for adaptation and mitigation programs in developing countries.
Stark provides an insight into some of the chatter on the floor at COP-16 and also outlines the moral, development, and security advantages to supporting a green fund, pointing out that “by managing displacement, migration, and violent conflict driven by the effects of climate change, such as water scarcity, climate change adaptation can help bolster international security and stability.”
“Within the UN process itself,” she writes, “a robust, well-run, equitable green fund would help rebuild the trust lost between developed and developing countries at Copenhagen last year.”
Lastly, Bob Engelman, of the Worldwatch Institute, provides a broad argument for more inclusion of a key variable in climate debates – population (and not in the Ted Turner mold). He enumerates the common pitfalls of population debates, from sensitivities about personal choices to squeamishness about sexuality and reproductive health, and just plain gender bias.
But despite these barriers, says Engelman, population – and not just growth but demographics too – matters in the climate debate and therefore needs to be part of the conversation (an argument he makes more comprehensively in a new report, Population, Climate Change, and Women’s Lives). Echoing De Souza, he concludes by pointing out that although the discussion may be difficult, the solution is relatively simple: “On population, the most effective way to slow growth is to support women’s aspirations.”
“As societies, we have the ability to end the ongoing growth of human numbers – soon, and based on human rights and women’s intentions,” Engelman said. “This makes it easy to speak of women, population, and climate change in a single breath.”
Sources: Population Action International, Slate, UN Framework Convention on Climate Change, The Washington Post, Worldwatch Institute.
Photo Credit: Adapted from “Trees Dead on Shore of Timor-Leste Lake,” courtesy of flickr user United Nations Photo; Roger-Mark De Souza, courtesy of David Hawxhurst/Wilson Center; “Will you back a climate fund?,” courtesy of flickr user Oxfam International; and “Met Office Climate Data – Month by Month (September),” courtesy of flickr user blprnt_van. -
Bringing Cambodia Back from the Brink: An Audio Interview with Suwanna Gauntlett
›December 10, 2010 // By Hannah MarquseeThree decades after the Khmer Rouge regime wiped out an estimated 1.7 million people – one fifth of Cambodia’s total population – the environment and Cambodian people are still feeling the effects.
The Pol Pot regime’s policy of agrarian collectivization dramatically reorganized land ownership and relocated millions from urban to rural areas. The ensuing decades of Vietnamese occupation and civil war further changed Cambodia’s workforce, dislocating millions.
The “Khmer Rouge regime increased the destruction of natural resources exponentially,” Suwanna Gauntlett, founder and CEO of Wildlife Alliance, told ECSP in this interview. Today, 78 percent of Cambodia’s 14.5 million people live in rural areas, according to the World Bank, nearly all of whom work as subsistence farmers. These rural households account for almost 90 percent of Cambodia’s poor and 36 percent of the total population in 1997.
“These Forests Were Silent”
When Wildlife Alliance arrived in Cambodia in 2000, “these forests were silent,” Gauntlett said. “You couldn’t hear any birds, you couldn’t hear any wildlife and you could hardly see any signs of wildlife because of the destruction.”
In one village, Chi Phat, Gauntlett noted how years of slash-and-burn agriculture had left a “circle of death” around the village as farmers gradually encroached further into the forest.
Cambodians have compensated by turning from traditional subsistence farming to illegal logging, wildlife trafficking, slash-and-burn agriculture, mining, and other unsustainable development (with significant Chinese investment). This has contributed to food and water insecurity, rapid deforestation, habitat loss, and species extinctions. In 1990, 73 percent of Cambodia’s land was covered by forest. By 2007, that number had dropped to 57 percent. Cambodia’s 146 threatened plant and animal species have also felt the effects of this loss. The Indochinese tiger, native to Cambodia, is now thought to have less than 30 individuals remaining in the entire country.
Integrated Solutions
Focusing on the Cardamom mountain range – Cambodia’s largest remaining intact forest – Wildife Alliance established several community-based agriculture and ecotourism programs to help villagers escape the “vicious circle” of poverty and environmental destruction. Ten years later, “there’s been tremendous progress in the geographic areas of our projects,” said Gauntlett.
In another village, Sovanna Baitong, Wildlife Alliance’s community agriculture program has raised the incomes of some residents to over $200 a month when the national poverty level is $200 a year, Gauntlett said. Today this village has a school, a clinic that provides health care and family planning, and a micro-credit fund. This is all managed by the community leaders, 30 percent of whom are women.
Ten years ago, “it was a mess,” Gauntlett said. “It’s amazing to see the difference.”
However, in parts of the country where Wildlife Alliance does not operate, deforestation continues at an alarming pace, often fueled by Chinese and other foreign investment. In some parts of the country, “deforestation has led to very severe water shortages,” including villages where people have to walk up to 20 kilometers for water because “there is no more underground water,” said Gauntlett. This has troubling implications for Cambodian security, particularly with aggressive hydrological development of the Upper Mekong continuing in China and Laos.
“I’m afraid that’s what’s going to happen throughout Cambodia – that this water shortage will lead to food shortage [which] will lead to civil unrest,” Gauntlett said.
Sources: BBC, Cambodian Genocide Program, The Washington Post, Wildlife Alliance, World Bank, WWF, UNEP.
Photo Credit: “Farmer at Sovanna Baitong” and “Suwanna Gauntlett” Courtesy of Wildlife Alliance. -
David Lawson, Wildlife Conservation Society
Afghanistan’s Non-Confrontational Conservation
›December 7, 2010 // By Wilson Center Staff
Excerpt from the Center for a Better Life:
Afghanistan is more than war and turmoil; it has a long and colorful history, strong cultures and a stunning landscape. It has enormous biodiversity, as it sits at the crossroads of what biologists call “biological realms.” The country, therefore, has plants and animals that also occur in Europe, northern Asia, India, south Asia and Africa. It has nine species of wild cats, which is the same as the whole of sub-Saharan Africa, as well as an estimated 800 plant species that occur nowhere else in the world. In other words, Afghanistan is worth attention in terms of its biodiversity alone.These natural resources are also critically important from the people’s perspective. After 30 years of conflict, more than 80 percent of Afghanistan’s population relies directly on natural resources for their livelihood. Most of the inhabitants are rural and desperately poor by world standards. Child mortality is the highest in the world, and their infrastructure is mostly broken down and inoperable. The economy is donor-dependent, and the Afghan government is still in its infancy. Outside the capital of Kabul, governance sometimes seems non-existent. As a result, movement away from the major population centers can be very risky due to the presence of various insurgent groups.
And yet, what is seldom mentioned in newscasts and media is that the Afghans are proud and resilient. They want what everyone else wants: education for their children, healthcare for the young and elderly, and reliable livelihoods to support their families. Then they want to get on with their lives in their own unique, culturally diverse way, free of violence and conflict.
Understanding Cultures
Understanding these things is one reason why the Wildlife Conservation Society (WCS) has been successful in Afghanistan. When hearing of the Society’s field work in this war-torn country, most people are surprised. They wonder how, with its pressing problems, Afghanistan can afford the time, let alone the resources, to conserve its remaining wildlife and wild places. But this is one of the core strengths of WCS – to offer assistance in conserving natural resources at a practical level within a country in need, like Afghanistan. As one of the oldest conservation organizations in the world, with more than 100 years of field conservation experience, the Society has extensive seasoning under extreme circumstances. Currently, WCS has more than 600 projects in place with 3,000 staff; and, many of these projects are in the most remote areas of the world.
Since 2006, USAID has supported WCS’s work in Afghanistan within three geographical areas – the northeast in Badakhshan Province’s Wakhan District, Bamiyan’s central province and the eastern, forested Nuristan province. Experts chose these areas because they believed they held the largest numbers of untouched remaining wildlife; this presumption generally proved correct. Through the years, WCS has created trust by having conservation teams on the ground and working year-round with local communities. Similar trust has been established with the relevant ministries by WCS’ central office, located in Kabul, through continuous presence and assistance.
Results are impressive. More than seven pieces of environmental legislation were enacted; 10,000 Afghans received conservation training; the first biological surveys in 30 years were completed (which doubled as crucial skills development exercises for Afghan scientists); the first wildlife/domestic stock disease assessments were accomplished, with corresponding human health effects, plus many more exemplary achievements. One of the more intriguing results was WCS’ ability to build local governance in the most remote communities, thus connecting communities that had seen no real government representatives for years. This link extended to district authorities then to provincial authorities, and finally to the Kabul central government. This extension of Afghanistan’s rule-of-law is paramount because it improves governance, which is one of the more crucial strategic needs in the country today.
How was a non-governmental conservation organization able to contribute to governance and rule-of-law? It is simple. Wildlife conservation is usually a non-confrontational issue, and most people, when exposed to the process, take an active interest and express opinions. Rural people have grown up with and are surrounded by wildlife everyday; they have local knowledge and feel comfortable discussing how things have changed. They want to be empowered to make natural resource decisions in the areas in which they live. WCS staff encourages local people to discuss species protection with their local and provincial governments. In some instances, WCS workers have taken government officers into communities that cannot recall ever seeing a government official. These processes and contacts evolve and can be used as basis for non-conservation related discussion. These processes and relationships become the building blocks for extending governance and empowering local communities. And, the process works.
Continue reading on the Center for a Better Life.
David Lawson is the Wildlife Conservation Society Afghanistan country director.
Photo Credit: “Bamiyan Band-e-Emir,” courtesy of flickr user USAID Afghanistan. USAID and WCS have been working in the Band-e-Amir lakes region since 2006 to create a national park. -
International Responses to Pakistan’s Water Crisis
›December 6, 2010 // By Michael KugelmanExcerpt from the executive summary of the NOREF Policy Brief, via the Norwegian Peacebuilding Centre:
Pakistan faces a multidimensional water crisis that claims hundreds of thousands of lives every year. The root causes of the crisis are twofold:- Circumstantial, which are linked to poor water-resource management policies (including water-wasting flood irrigation);
- Structural, tied to factors deeply ingrained in politics and society such as the obsession with India, inequitable rural land-ownership and endemic water misgovernance (for example, exploitation of the rotational irrigation system to the detriment of the poor).
However, international responses must be measured. They should actively target the circumstantial causes but, at the same time, recognize that their ability to take on the structural ones is limited. While the international community can help mitigate the effects of the underlying structural drivers, Pakistan itself must take the ultimate steps to eliminate them.
Circumstantial causes can be addressed through international aid provision and international exchanges. Aid provision must be generous enough to meet Pakistan’s prodigious needs but modest enough to respect the country’s limited absorptive capacities. It should emphasize the restoration of infrastructure and distribution systems, be more responsive to the needs of Sindh and Baluchistan provinces, and be channeled through both government agencies and civil society.
Despite the challenges the international community faces in addressing the structural causes, opportunities do abound. These include embarking on back-channel diplomacy to bring Pakistan and India closer together and cooperative projects with Pakistanis to make water distribution more equitable. To be effective, international responses must target all affected parties and be sensitive to ground realities. They should also be mindful of indigenous success stories and the factors that bring about that success.
The full report, “International Responses to Pakistan’s Water Crisis: Opportunities and Challenges,” is available through the Norwegian Peacebuilding Centre.
Michael Kugelman is program associate with the Asia Program at the Woodrow Wilson International Center for Scholars.
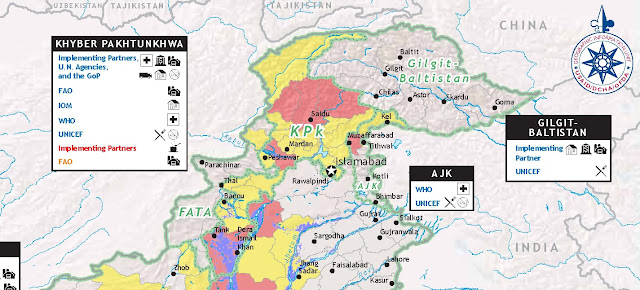
Image Credit: Adapted from “USG Humanitarian Assistance to Pakistan for Floods in FY 2010 and FY 2011 (as of 30 Nov 2010),” courtesy of USAID and ReliefWeb. -
Joydeep Gupta, ChinaDialogue
Nervous Neighbors: China-India Water Relations
›December 3, 2010 // By Wilson Center StaffExcerpted from the original article, “Nervous Neighbors,” on ChinaDialogue.net:
Only five rivers in the world carry more water than the Yarlung Zangbo, or Brahmaputra, as it is known when it reaches India. Only one carries more silt. Rising at a height of 5,300 meters in the Kailash range of the Middle Himalayas – an area holy to both Hindus and Buddhists – the river flows east through Tibet for 1,625 kilometers before taking a horseshoe bend, changing its name and flowing as the Brahmaputra into north-eastern India.
There, for 918 kilometers, it is both a lifeline, due to the water it carries, and a scourge, because of the floods it causes almost every year. It then takes a southward turn and flows into Bangladesh for 363 kilometers before it merges with the Ganges, together forming South Asia’s largest river, the Meghna, and flowing into the Bay of Bengal. This huge river, with its 25 large tributaries in Tibet and 105 in India, drains much of the eastern Himalayas.
As the world’s youngest mountain range, the Himalayas are particularly unstable – and so is the river. It has changed its course significantly at least once in the last 200 years, following a major earthquake. Smaller changes in course are common, wiping out farms and homes on one bank while depositing fertile silt on the other. Now humans are changing the course of this river: Chinese engineers have started to build the Zangmu hydroelectric power station in Lhoka prefecture, 325 kilometers from Lhasa, Tibet’s capital. The development has led to serious expressions of concern, particularly in India but also in China.
Continue reading on ChinaDialogue.net.
Joydeep Gupta is the project director (South Asia) of ChinaDialogue’s Third Pole Project.
Map Credit: Google Maps.