-
Changing Cities: Climate, Youth, and Land Markets in Urban Areas
›The number of urban slum dwellers worldwide is staggering. According to UN-Habitat, 827.6 million people live in slums around the world. Despite meeting a Millennium Development Goal to significantly improve the lives of at least 100 million slum dwellers by 2020, the total number of people living in these areas still increased by 55 million between 2000 and 2010. By 2020, the world slum population is projected to reach 889 million. With the majority of people now living in cities, urban priorities are synonymous with human security and environmental sustainability and must be accounted for in the global development agenda.
-
Farzaneh Roudi for the Middle East Program
Iran Is Reversing Its Population Policy
›Excerpted below is the introduction by Farzaneh Roudi. The full report is available for download from the Wilson Center’s Middle East Program.
Once again, the Iranian government is reversing its population policy – its fertility policy, to be more precise. Alarmed by the country’s rapidly aging population, Iran’s Supreme Leader Ayatollah Ali Khamenei is now calling on women to procreate and have more children, and the Iranian Minister of Health and Medical Education Marzieh Vahid Dastjerdi has recently said, “The budget for the population control program has been fully eliminated and such a project no longer exists in the health ministry. The policy of population control does not exist as it did previously.”
-
Coming of Age: Reason for Optimism in Burma’s Turn Towards Democracy
›
Burma (also known as Myanmar), a country plagued by internal political turmoil and direct or tacit military rule since 1962, had its first general elections in 50 years in 2010 and long-time jailed opposition leader Aung San Suu Kyi won a seat in the National Assembly, but questions remain as to how much power the military is willing to cede. Demography provides reason for hope that this turn towards democracy is more than temporary.
-
Linking Extreme Weather Events to Climate Change
›Specifically attributing a particular weather event to climate change has been difficult – as one famous analogy goes, it’s like determining which of Mark McGwire’s home runs were because of steroids and which weren’t. But climate attribution science is slowly becoming more accurate and accepted. In “Explaining Extreme Events of 2011 From a Climate Perspective,” a new study appearing in July’s Bulletin of the American Meteorological Society, editors Thomas C. Peterson, Peter A. Stott, and Stephanie Herring provide a review of six extreme weather events from last year and offer “some illustrations of a range of possible methodological approaches” to the process of attribution. Among their conclusions, the editors note that, due to climate change, the extreme heat and drought that suffocated Texas in 2011 was 20 times more likely to occur than 40 years earlier. However, the devastating floods that swept across Thailand last year are blamed on a number of other non-climatic factors.
-
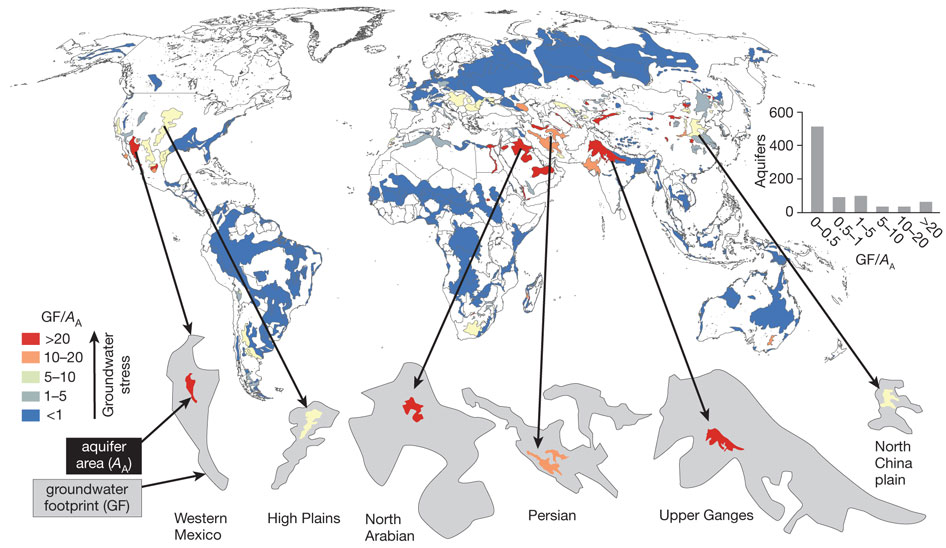
Stress Levels of Major Global Aquifers Revealed by Groundwater Footprint Study
›In the “first spatially explicit comparison of groundwater use, availability, and environmental flow for aquifers globally,” a new article in Nature finds that the “size of the global groundwater footprint is currently about 3.5 times the actual area of aquifers.” An aquifer’s footprint is the theoretical size it would need to be to sustainably support use at its current rate, so groundwater footprints being much larger than their corresponding aquifers is a sign of overuse.
-
Hans Rosling on Religion, Babies, and Poverty
›“I’m going to talk about religion. But it’s a broad and very delicate subject, so I have to limit myself. Therefore I will limit myself to only talk about the links between religion and sexuality…I will talk on what I remember as the most wonderful – it’s the moment when the young couple whispers, ‘tonight, we are going to make a baby,’” said Hans Rosling, the eclectic Swedish doctor and statistician known for his Gapminder tool, in a TedxSummit presentation in April.
-
Taking On Domestic Violence in Post-Conflict Liberia
›Liberia is a case study in post-conflict violence against women, said panelists at the Wilson Center on July 24. “Confined merely to performing household chores and childrearing duties, from early childhood, women and girls have been socialized into subservience and powerlessness and acceptance of domestic abuse as a norm,” Annette Kiawu, deputy minister for research and technical services at the Liberian Ministry of Gender and Development, told the audience. [Video Below]
Kiawu was joined by Pamela Shifman of the Novo Foundation and Esther Karnley and Elisabeth Roesch of the International Rescue Committee (IRC). They discussed the prevalence of domestic violence in Liberia after the 14-year civil war, which ended in 2003.
Violence Stemming from Changing Norms
Kiawu pointed to women’s changing roles in Liberia as a source of household tension. She noted that women are increasingly “demanding a greater role in household decision making,” which some men see as “encroachment on their sphere of influence.”
“According to the LDHS [Liberia Demographic and Health Survey], the persistence of domestic violence is directly linked to the increased status of women on the one hand and men’s [perception] of loss of power and authority on the other,” she said. Some men’s urge to assert dominance is exacerbated by higher levels of alcohol abuse and a tendency towards violence learned during the civil war.
There has been legislation against gender-based violence – including the Rape Amendment Act, also known as the “revised rape law,” the Revised Gender-Based Violence Action Plan, and the African Union Protocol – as well as action plans and community-based groups meant to decrease the rate of domestic violence, like the Gender-Based Violence Network, an initiative designed to increase community ownership of domestic violence issues and improve response at the grassroots level. But despite these advances, Kiawu stressed that there still is a long way to go, saying that increased funding and coordination between domestic and international agencies and the Liberian government is necessary to have a real impact on the lives of the “countless women” whose lives are threatened by domestic violence.
Making Reality Match Rhetoric
Pamela Shifman agreed that domestic violence prevention programs need more funding. “So often in conflict-affected settings we hear that we need to address other issues first…that domestic violence is a back-burner issue,” she said. Domestic violence is often perceived to be “not that serious” when compared to other issues in conflict-prone and post-conflict countries.
But Shifman argued that divorcing domestic violence from other types of violence is problematic. “Violence in the home normalizes violence in the street, normalizes violence in the community, and normalizes violence by the state,” she said.
NoVo is one of the few private organizations which prioritizes domestic violence and gender equity, Shifman said, but she asserted that all humanitarian organizations should devote time and money to these issues, saying that “if we ignore domestic violence, all of the other investments we make to improve the quality of life for communities will suffer.”
Empowering women can have significant results for the whole community. Shifman remarked that “investing in women is smart economics,” citing studies which suggest directing funds towards women “pays off at huge levels” for women’s families and communities. But when women experience violence, “their potential is thwarted,” she said. “They suffer, their families suffer, their community suffers, the entire nation suffers.”
Programs targeting domestic violence need greater awareness, more long-term commitment, and more funding, she said. “We don’t expect that violence is going to end overnight – no deep-seated social problem will be solved that quickly,” she said. “In order to make a dent in improving the lives of girls and women and ending violence against girls and women, we need more direct funding” from private and public sources.
“To put it bluntly, I think the reality needs to match the rhetoric,” Shifman concluded.
Perspectives from the Field: Social Isolation
Esther Karnley described the results of interviews conducted with Liberian women, both survivors of domestic violence and fellow community members. She found that a key reason women stay in abusive relationships is financial dependence. “Most of them said, ‘it’s because we depend on the men for everything… we don’t have any money, we are not empowered financially, we depend on the men for everything. Because of that, we remain in that relationship and we get killed.’”
She added that social isolation means that many women lack the resources to leave a relationship. “We are isolated socially, we don’t have access to services, we are all by ourselves,” they told her. Without support from friends, relatives, or organizations, it can be difficult to find the means to relocate.
Part of the problem in Liberia is the prevalence of informal education, especially Sande bush schools – schools run by a traditional women’s society designed to prepare girls for marriage, teaching them traditional housekeeping methods and culminating in female circumcision. Girls leave home to attend these traditional schools for several months, which severely curtails their access to formal education. Kiawu reported that “over 60 percent of girls attending Sande school drop out of regular school.” This means that “successive generations of young children, especially young girls, are expected to forgo formal education in favor of attending the Sande school.”
In addition to formal education, Karnley said financial empowerment and legislation holding perpetrators of domestic violence accountable for their actions would enable more women to leave abusive relationships.
Reaching Both Women and Men
Each of the panelists recognized that working against domestic violence requires comprehensive societal reforms. Karnley stressed that the impetus to begin working with men came from Liberian women. “Initially when we started working on GBV issues, we talked to women, and then the women came and said, ‘OK, you talk to us every day, and when we go home, we go and meet fire. Can you also talk to our men?’” In response, the IRC developed a 16-week program designed to change men’s behavior and views about violence and relationships. Karnley also mentioned a desire to reach out to the religious community to change the constant focus on the man as the head of a relationship to one based on love.
The Liberian government is also working with churches and mosques to change norms that encourage the subjugation of women, including work with a network of religious leaders known as Christian/Muslim United against SGBV (sexual and gender based violence). Kiawu said this organization emphasizes partnership within a marriage and teaching equality to children in the home. The panelists also mentioned additional efforts to increase the responsiveness and sensitivity of the police and judicial system to domestic violence issues, as well as the need for resources like safe houses to provide relief to survivors.
“The family, far from being off limits, has to be a priority for us in the humanitarian community as we help to rebuild nations where peace not only exists between nations, and among nations, and among communities, but among families,” Shifman contended. Kiawu agreed, adding that without interventions, violence and isolation prevent women “from taking advantage of opportunities that peace presents.”
Event Resources: Photo Credit: A woman prays during a Sunday morning service in Monrovia, courtesy of Bruce Strong/Newhouse School. -
Family Planning Saves Lives, Can Help Mitigate Effects of Climate Change
›Contraceptives prevented an estimated 272,040 maternal deaths in 2008, reducing worldwide maternal mortality by 44 percent, according to a recent paper by Saifuddin Ahmed, Qingfeng Li, Li Liu, and Amy O. Tsui, published in The Lancet. But the prevention of maternal deaths could have been even higher. The study, “Maternal Deaths Averted by Contraceptive Use: An Analysis of 172 Countries,” estimates that an additional 104,000 maternal deaths – many occurring in developing parts of Africa and South Asia – could have been averted simply by satisfying existing unmet need for contraception. In sub-Saharan Africa, for example, only 22 percent of women who are married or sexually active use contraception – a far cry from the 65 percent which the study suggests is the point at which maternal deaths avoided by contraceptive use begin to plateau. Not surprisingly, this has also yielded some of the highest regional fertility rates in the world.

Such high fertility rates are driving growing concerns about scarcity and capacity in the region, and how climate change might exacerbate already-difficult development hurdles. This nexus of issues was the subject of a recent policy brief by Population Action International and the African Institute for Development Policy, titled Population, Climate Change, and Sustainable Development in Africa. The brief points out that “a large share of Africa’s population lives in areas susceptible to climate variation and extreme weather events,” and that there is an inherent tension the continent faces as it seeks to balance high population growth with climate change-induced reductions in the availability of natural resources, like water and arable land. The authors urge policymakers, rather than focusing on environment, population, and health individually, to “connect population dynamics and climate change” to address their interlinked challenges together.
Showing posts from category *Blog Columns.