Yearly archive for 2011.
Show all posts
-
Michael Kugelman, Huffington Post
Pakistan’s Biggest Threats May Not Be What You Think They Are
›August 30, 2011 // By Wilson Center StaffThe original version of this article, by Michael Kugelman, appeared on the Huffington Post.
The most troubling news to emerge from Pakistan in recent days has little to do with militancy or other headline-grabbing scourges that afflict the country. Rather, it relates to a new Oxfam report’s finding that more than a third of the country’s population – about 60 million people – is undernourished.
Pakistan may well be convulsed by extremist violence; according to Pakistani estimates, it has killed or injured 30,000 in recent years. Yet contrary to what U.S. media coverage may suggest, this is not the greatest threat to the Pakistani people.
Numerous candidates contend for this dubious honor. One, underscored by Oxfam, is hunger. Even before last year’s devastating floods, which destroyed more than 2 million hectares of arable land, the World Food Program estimated that 77 million Pakistanis were going hungry. Another is water insecurity, one of Pakistan’s biggest killers. With a third of Pakistanis lacking access to clean water, no wonder waterborne illness claims the lives of 1.2 million Pakistanis per year – and 630 children every day. Lack of education also tops the list. More than 40 million of Pakistan’s 70 million school-age children (those between the ages of 5 to 19) are not in school. And then there is Pakistan’s energy crisis. Due to power shortfalls, some Pakistanis suffer outages for as long as 20 hours per day – crippling industry and bringing misery to millions of households. All of this is compounded by state corruption, which constrains access to these precious resources and services.
Continue reading on Huffington Post.
Sources: Business Recorder, Oxfam International, PBS, World Food Program.
Michael Kugelman is a program associate with the Wilson Center’s Asia Program.
Photo Credit: “People returning home as soon as the water recedes enough,” courtesy of flickr user DFID – UK Department for International Development. -
‘Dialogue’ TV: Revisiting Mr. Y and “A National Strategic Narrative”
›“We are, what I would call, very non-linear thinkers,” said U.S. Navy Captain Wayne Porter about the white paper he co-authored with U.S. Marine Colonel Mark Mykelby, “A National Security Narrative,” launched by Woodrow Wilson Center President Jane Harman at the Center in April. “We’re almost incapable of restricting ourselves to defense and security in isolation from a much larger perspective,” he told Dialogue TV.
“I think maybe that’s why Admiral Mullen has kept me around – I can offer a perspective that maybe he wouldn’t get from conventional strategists or from conventional planners,” said Porter, who served three out of four tours with the current chairman of the Joint Chiefs of Staff as a special assistant for strategy.
Dialogue host John Milewski sat down with Captain Porter and Robert Litwak, director of International Security Studies and vice president for programs at the Wilson Center, for a discussion about the white paper – published under the pseudonym “Mr. Y” (echoing George Kennan’s seminal “X” article) – and its contention that the United States should move away from an outmoded Cold War-era model of containment, deterrence, and control towards a “strategy of sustainability.”
The narrative has been well received, Porter said: “I think there is an appreciation that it’s a very complex strategic environment that we live in now and that maybe we need to re-look at all of the tools that we could use as a nation to pursue our enduring national interest.”
Inflection Points in History
“The timing of such conversations is cyclical,” said Litwak. “The original ‘X’ article emerged from the end of the Second World War and the advent of the Soviet threat, which required a new conception of international relations that Kennan articulated, as well as the National Security Act of 1947 to line up the U.S. government with this new environment.”
There have also been periods of concern about American decline. “I think what one sees in the current era are both of those trends coming together,” Litwak said:The system is changing – it’s a debatable proposition that the United States is in decline – but we see in the international system rising powers, notably China, as well as transnational trends that are beyond the sovereign control of any single state, which have called into question the nature of the international system…as well as a sense that…there’s something qualitatively different about this recession than the typical economic, cyclical recession and that has to do with the domestic sources of American strength.
These conditions, as well as the source of argument – coming from the military – combined to give particular resonance to the piece, Litwak said.
The Information/Globalization Age
“I think the thing that has changed materially to us is that the information age has brought about an awareness that our environment is completely interconnected,” Porter said. “There’s a complexity to this that can’t be analyzed linearly, that has to have new tools applied.”
“I’d honestly characterize it as significant as the Enlightenment in the 1600s,” he said.
“Certainly we’ve thought in silos and debates have been too often compartmentalized,” Litwak said. “One of the strengths of this piece is that it is truly synthetic – working across the continuum of instruments of power – and talks in a really powerful way about how hard power…has its place, but that the non-military dimensions of American power have been neglected.”
But, Porter said, it’s important to focus on being proactive, rather than reactive:The thing that bothered us most about the strategies that we see every day in our jobs on our side of the river and across the river is that they are almost universally based on anticipating and countering known risk and threat, and our sense is that we have entered an age in which we need to overcome that sense of fear and seize the opportunity to shape the environment of the future as opposed to simply being resilient to it.
As Litwak points out, Secretaries Gates (now former) and Clinton – in the form of the Quadrennial Defense Review, Quadrennial Diplomacy and Development Review, and numerous speaking engagements – have both called for closer integration between State and Defense, more resources for non-military levers of power, and more holistic concepts of security. But unfortunately the greater integration called for in these documents remains unrealized.
Dialogue is an award-winning co-production of the Woodrow Wilson International Center for Scholars and MHz Networks that explores the world of ideas through conversations with renowned public figures, scholars, journalists, and authors. The show is also available throughout the United States on MHz Networks, via broadcast and cable affiliates, as well as via DirecTV and WorldTV (G19) satellite.
Find out where to watch Dialogue where you live via MHz Networks. You can send questions or comments on the program to dialogue@wilsoncenter.org. -
Certification: The Path to Conflict-Free Minerals from Congo
›This summer, the Wilson Center’s Africa Program, in co-sponsorship with the Enough Project, assembled a panel of experts from American, British, and Congolese governments, private industry, and the NGO community to discuss the deplorable situation in the eastern Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC) involving conflict minerals and certification as a way forward.
After introductory remarks by Wilson Center President Jane Harman, Africa Program Director Steve McDonald introduced John C. Bradshaw, executive director of the Enough Project, who moderated the panel discussion. [Video Below]
Under Secretary of State Robert D. Hormats began by saying the “extremely traumatic” humanitarian situation in the restive areas of the eastern DRC requires “a bold, resolute, and morally inspired response by the United States and other countries.”
Sasha Lezhnev, policy consultant for the Enough Project, explained how the demand for tin, tantalum, tungsten, and gold – for use in batteries, circuit boards, and screens in computers and cellphones – are, in effect, driving the conflict in the DRC.
However, Ambassador to the United States from the DRC Faida Mitifu pointed out that a significant 70 percent of the economy in the eastern regions of the country depends on mining, thus any initiative would have to take into account the livelihoods of the people. In order to assist those communities while a process is formulated, Lezhnev called for targeted development projects in the most affected regions.
The Kimberley Process: A Potential Model?
“If we want to have a lasting impact, we’re going to need a certification process,” Lezhnev said, and we must learn lessons from the Kimberley Process (KP) in order to implement a suitable framework in the DRC.
Clive Wright, who served as the diplomatic negotiator for the KP and head of the foreign policy team for the British High Commission in Ottawa, described the intricacies of the process and its genesis. Under the provisions of the KP, the trade of rough diamonds is permissible, provided that there is a certificate from the country of origin and complementary legislation is in place in the importing country. This agreement was made through consultations and dialogue between the private sector and civil society.
Though successful in certain respects, Wright listed several shortcomings of the KP: it is not legally binding, therefore there are no levers to pull that compel government action; the process is void of an independent monitoring mechanism; and a consensus clause allows one government to block any action which clears the way for the status quo to prevail.
To implement a policy similar to the KP that guarantees legitimate minerals trade in the DRC, Under Secretary Hormats highlighted four key actors that have critical roles independently and collaboratively: 1) regional governments; 2) industry; 3) civil society; and 4) the U.S. government.
Regional Governments
Governments in the region face considerable challenges, said Hormats, as rebel groups trade across borders and evade efforts to rein in the commerce of precious gems, minerals, and arms. The states surrounding the Great Lakes – including Uganda, Rwanda, Burundi, Zambia, Kenya, and the DRC – have coalesced around these issues and developed a plan that will require effective coordination to ensure credibility. Some countries have already established traceability schemes, which are crucial for states that share borders with the DRC, since smuggling is incessant.
With regard to rebel factions, Kinshasa has occasionally participated in joint operations with the governments of Rwanda and Uganda “to stabilize [and] contain the activities of armed groups,” said Ambassador Mitifu. Progress, though slow, has also been made in demilitarizing the mining areas in the Kivu provinces as well as Maniema and in weakening the Congrès National pour la Défense du Peuple’s (CNDP) parallel administration.
The government in Kinshasa has made significant steps toward a certification framework and taken punitive action against military personnel who have engaged in illicit trade, said Ambassador Mitifu. She outlined the efforts the Kabila administration has made to address the issue, including initiatives to put in place a credible certification system so that clean minerals can be exported. In conjunction with MONUSCO – the UN peacekeeping mission in the DRC – the Congolese government has introduced centers where miners can bring their products and feed them into a legitimate supply chain. Finally, Kinshasa is working closely with the private sector, international organizations, and local NGOs to minimize fraud and enhance cooperation. Nevertheless, governance and corruption represent a formidable roadblock in the implementation of any certification process.
Industry Responsibility
Tim Mohin, the director of corporate responsibility for Advanced Micro Devices – one of the largest semiconductor manufacturers in the world – argued that industry can positively influence the supply chain by creating conflict-free smelter programs and a due diligence bulwark where anyone along the supply chain can trace their resources back to a certified smelter.
Customers, Mohin said, are going to have to insist that businesses comply with this tracking system. Under Secretary Hormats agreed with this sentiment, saying that companies that look into the origin of their minerals send a powerful message to the region and the world. He also expressed hope that “companies [would] work to find ways to adhere to legislation [Dodd-Frank] and honor their obligations to their shareholders without shunning the region’s minerals entirely.”
The most difficult stretches along the supply chain are getting buy-in from the miners and the smelters; overcoming the constraints of socio-economic realities on the ground and geo-politics; and the lack of a sustainable tracing system that spans the spectrum of the supply chain. In addition to shored-up U.S. involvement, Mohin called for increased public-private sector partnerships with incentives reminiscent of the Fair Trade system, development aid to assist displaced people, and enhanced security for artisanal miners and their businesses.
Civil Society and Government
Hormats commended the pivotal role civil society has played and must continue to play in highlighting the humanitarian issues at stake, as governments and companies have been only “dimly aware of the link between human rights abuses and the minerals trade.” Furthermore, Wright encouraged civil society’s participation because it serves as a “great policeman” that monitors the bad behavior of governments, especially when the allure of profiteering seeps into deliberations. Moving forward on boosting security for civil society on the ground in the Congo will be essential.
The U.S. government, Hormats asserted, has to do its part to support initiatives on the table to create conflict-free supply chains. If more revenue is invested in legitimizing supply chains, a substantial portion of the problem would be solved. USAID and the State Department are working with civil society to take action against those responsible for illegitimate trade and exacerbating the conflict. Of course there remains work to be done, but as Under Secretary Hormats indicated “this is the most significant moral issue of our time.”
Derek Langford is a program assistant with the Wilson Center’s Africa Program.
Photo Credit: “Aerial View of Camps for People Displaced by Conflict,” courtesy of flickr user United Nations Photo. -
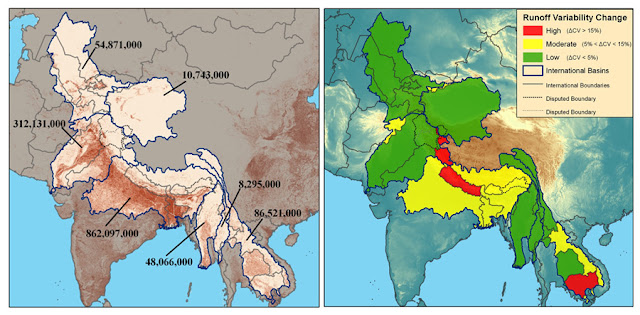
Redrawing the Map of the World’s International River Basins
›Understanding why conflict over water resources arises between nations begins with a solid understanding of the geography of international river basins. Where are the basins? How big are they? How many people live there? Who are the riparian nations, and what is the significance of each to the basin?
-
What’s in a Name? Watch Don Lauro on PHE, HELP, and HELPS
› Population, health, and environment (PHE) expert Don Lauro has worked on integrated projects for decades as a scholar, an implementer, a donor, and an evaluator. He recently visited the USAID-funded BALANCED Project in Tanzania as part of a wider look at this integrated approach. In an interview with ECSP, Lauro said the effort “made me think more broadly…about this area that we call population, health, and environment and what’s really in a name like that.”
Population, health, and environment (PHE) expert Don Lauro has worked on integrated projects for decades as a scholar, an implementer, a donor, and an evaluator. He recently visited the USAID-funded BALANCED Project in Tanzania as part of a wider look at this integrated approach. In an interview with ECSP, Lauro said the effort “made me think more broadly…about this area that we call population, health, and environment and what’s really in a name like that.”
“We commonly say PHE, and we all know what we’re talking about,” Lauro said of the population and development community, “but when you look deeply into these projects – or even not so deeply – you see that there’s other things going on as well.”
For example, Lauro pointed to the focus on livelihoods that many PHE programs have: “In the project I saw in Tanzania, there were many microcredit groups on the ground – mostly women – taking small loans for developing little enterprises that they had, like baking bread, raising bees, buying a cow…little enterprises to make their lives a little bit better.”
“Some people don’t use the term ‘PHE’…maybe it’s a ‘HELP’ project; that is health, environment, livelihoods, and population,” Lauro said. “Other people would say it’s maybe something even longer, ‘HELPS’ – health environment, livelihoods, population, and sustainability (or ‘security’ – Ed.).” When he was at the Wilson Center, Gib Clarke coined the “HELP” term in ECSP’s FOCUS Issue 20, arguing that livelihoods is such a critical component that it ought to be more formally recognized.
But, said Lauro, “on the ground they don’t use these terms – they say things like, ‘this is a healthy community program’ or ‘this is a green community program.’”
“I think it’s very important for us to realize what happens on the ground is lot different, and maybe more real, than how we talk about it.” -
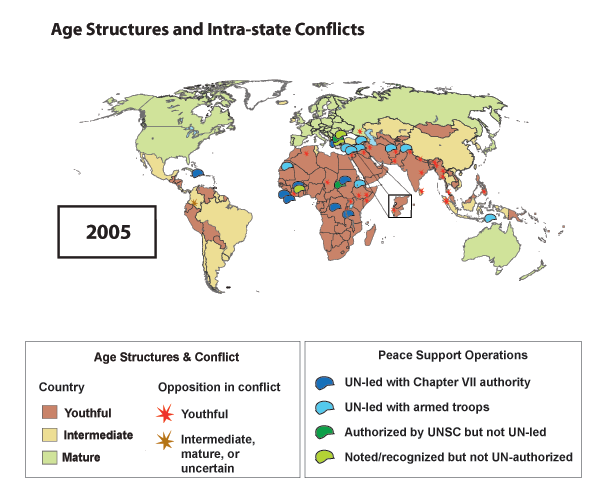
Youth Bulge and Societal Conflicts: Have Peacekeepers Made a Difference?
›August 22, 2011 // By Richard CincottaUntil recently, the question of which countries are at the most risk of violent societal conflict could be answered with a terse, two-part response: “the young and the war-torn.” This simple characterization regarding youth and conflict worked well, until the first decade of the 21st century. The proportion of youthful countries experiencing one or more violent intrastate conflicts declined from 25 percent in 1995 to 15 percent in 2005. What’s behind this encouraging slump in political unrest? One hypothesis is that peace support operations (PSOs) – peacekeepers, police units, and specialized observers that are led, authorized, or endorsed by the United Nations – have made a difference.
From the 1970s through the 1990s, more than 90 percent of all societal conflicts broke out in countries with a youthful age structure – a population with a median age of 25 years or less. And wherever civil and ethnic wars emerged, they tended to persist. The average societal conflict that began between 1970 and 1999 continued without a one-year break in battle-associated fatalities for about six years. Some – including the Angolan civil war, Northern Ireland’s “Troubles,” Peru’s war against the Shining Path, and the Afghan civil war – endured for decades. In contrast, inter-state conflicts that began between 1970 and 1999 lasted, on average, less than two years (see the UCDP/PRIO Conflict Database).
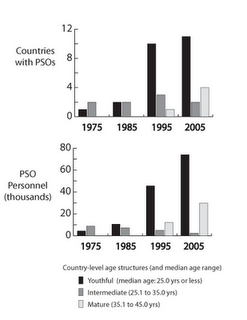
Taking on Intra-State Conflicts Beginning in the early 1990s, however, there was a marked expansion in size and number of PSOs deployed in the aftermath of societal warfare, which appears to have dampened the persistence of some conflicts and prevented the reemergence of others. The annual number of active PSOs deterring the re-emergence of societal conflict jumped from just 2 missions during 1985 to 22 in 2005. In contrast, those led, authorized, or endorsed by the UN to maintain cease-fire agreements between neighboring states during that same period only increased from three active missions to four. By 2009, nearly 100,000 peacekeepers were stationed in countries that had recently experienced a societal conflict. About 70 percent were deployed in countries with a youthful population (see Figures 2A and B). Why the sudden expansion in use of PSOs?
Beginning in the early 1990s, however, there was a marked expansion in size and number of PSOs deployed in the aftermath of societal warfare, which appears to have dampened the persistence of some conflicts and prevented the reemergence of others. The annual number of active PSOs deterring the re-emergence of societal conflict jumped from just 2 missions during 1985 to 22 in 2005. In contrast, those led, authorized, or endorsed by the UN to maintain cease-fire agreements between neighboring states during that same period only increased from three active missions to four. By 2009, nearly 100,000 peacekeepers were stationed in countries that had recently experienced a societal conflict. About 70 percent were deployed in countries with a youthful population (see Figures 2A and B). Why the sudden expansion in use of PSOs?
According to William Durch and Tobias Berkman, this upsurge was less a change of heart or modification of a global security strategy and more an outcome of the unraveling web of Cold War international relations. Before the 1990s, the majority of PSOs were United Nations-led operations that were mandated to monitor or help maintain cease-fires along mutual frontiers. Because insurgents were typically aligned with either the Soviets or a Western power, Security Council authorization to mediate a societal conflict was difficult to secure.
This situation changed with the breakup of the Soviet Union and the initiation of PSOs by regional organizations, including operations by the Economic Community of West African States (ECOWAS) in Liberia and Sierra Leone and the NATO-led Kosovo Force in 1998-99.
Demographic Forecasting
What do national demographic trends suggest for the demand for PSOs over the next two decades? For societal conflict, political demographers foresee that the demand for PSOs will continue to decline among states in Latin America and the Caribbean – with the exception of sustained risk in Guatemala, Haiti, Bolivia, and Paraguay. Similarly, demand for peacekeeping is expected to continue to ebb across continental East Asia.
Gauged by age structure alone, the risk of societal warfare is projected to remain high over the coming two decades in the western, central, and eastern portions of sub-Saharan Africa; in parts of the Middle East and South Asia; and in several Asian-Pacific island hotspots – Timor-Leste, Papua New Guinea, the Philippines, and Solomon Islands. But even in some countries that are losing their youthful blush, domestic political relations could turn out less rosy than this simple age-structural model forecasts.
In other words, there are roadblocks to a “demographic peace.” Among them is an increasing propensity for a specific demographic configuration of ethnic conflict: warfare between state forces and organizations that recruit from a minority that is more youthful than the majority ethnic group. Examples of these conflicts include the Kurds in Turkey, the Shiites in Lebanon, the Pattani Muslims in southern Thailand, and the Chechens of southern Russia.
However, this twist on the youth bulge model of the risks of societal conflict is a discussion for another installment on New Security Beat. Suffice it to say that when political demographers look over the UN Population Division’s current demographic projections, they see few signs of either the waning of societal warfare, or the withering of the current level of demand for PSOs.
Richard Cincotta is a consultant on political demography for the Wilson Center’s Environmental Change and Security Program and demographer-in-residence at The Stimson Center.
Sources: PRIO, The Stimson Center, UN Population Division.
Chart Credit: Data courtesy of the UN Population Division 2011, PRIO, and Durch and Berkman (2006). Arranged by Richard Cincotta. -
IRP and TIME Collaborate on Indonesia’s Palm Oil Dilemma
›“Everything the company does goes against my conscience. But the question remains, who should work from the inside to inform everyone? Who should be pushing that these things are right, these things are acceptable, and these things are not?” says Victor Terran, in this video by Jacob Templin for TIME and the International Reporting Project (IRP). Templin traveled to Indonesia as part of IRP’s Gatekeeper Editor program in May 2011.
Terran is a resident of a village west of Borneo in the Kalimatan province, where he works as a field supervisor for one of the largest palm oil companies in Indonesia. Although the industry has supplied his village with much-needed employment and economic development, he worries that the influx of jobs has come at the expense of the health of the forests, agriculture, and clean rivers that sustain his village. “It’s not just about the money,” he says. “Will they sincerely keep the regulations and be fair to our community?”
An Industry with a Checkered Past
Terran’s skepticism of the industry is justified – palm companies, such as Sinar Mas, have a nasty track record of “abusing local labor and pilfering forests” for what they call “liquid gold,” says Templin.
Greenpeace released a report, “How Sinar Mas is Pulping the Planet,” in 2010 that alleged that Sinar Mas cut down important wildlife preserves, illegally planted on peat lands, and that these actions resulted in the release of considerable amounts of carbon into the atmosphere and loss of critical wildlife habitat.
As a result, the company lost major contracts with Unilever, Kraft, and Nestle. Sinar Mas CEO Franky Widjaya tells Templin that the company is taking definitive steps to prevent such instances from happening again, but that change will not happen overnight.
Akhir bin Man, a manager for another palm oil company, PT Kal, says he does not want to experience a public relations nightmare similar to Sinar Mas, so his company is seeking certification from the internationally recognized Roundtable on Sustainable Palm Oil (RSPO). The RSPO certification requires PT Kal to conserve nearly half of its land, use safer pesticides, and negotiate profit-sharing agreements with villagers.
Global Benefits
“These are not only vast forest landscapes which are home to species such as orangutans, elephants, and rhinos, but they’re also some of the globally most important reservoirs of carbon,” Adam Tomasek, director of the WWF Heart of Borneo Initiative, tells Templin.
Due to the wide-scale implications of disrupting such a substantial carbon sink, Tomasek and his colleagues see the destruction of these habitats as not just a local problem: “Sustainably managing the forest and carbon stocks that they contain here in Indonesia is not only important locally, not only important regionally, but an extremely important critical in the global approach to dealing with climate change,” he says.
Resisting the Juggernaut
Recognizing the inherent value of their natural resources, some villages are fighting to keep palm companies off of their land. Pak Bastarian is the head of such a village: “In my opinion, [palm] plantations are only owned by certain groups of people, and they don’t necessarily bring prosperity,” he tells Templin.
Bastarian is a reformed environmentalist whose hesitance toward the palm industry is a by-product of his own experiences – in the 1990s he worked for years running a timber company that illegally cut down trees. “I don’t know how many trees I cut down…a countless number.” Now, he uses his elected power to preserve trees like the ones he once cut down.
However, keeping the companies out of his village is an uphill battle, Templin explains. Bastarian says he faces mounting pressure from governmental officials, who make threats, and many villagers, who would rather have the jobs. He tells Templin that he even received bribes from PT Kal (an accusation they deny).
Bastarian’s position may cost him though – with elections right around the corner, he said does not know how much longer he can keep the palm companies out.
“My worry is that if our forests are cleared, our children will not be able to see what protected wood looks like, or what protected animals look like,” he tells Templin. When the palm oil companies first came, he chose to wait and see how the other villages fared before allowing them to come in. “To this day,” he says, “I’ve never changed my mind.”
Video Credit: “Indonesia’s Palm Oil Dilemma: To Cash In or Fight for the Forests?,” courtesy of the International Reporting Project. -
Deborah Mesce, Behind the Numbers
Kenya’s New Data Website Puts the Ball in Media’s Court
›The original version of this article, by Deborah Mesce, appeared on PRB’s Behind the Numbers blog.
The Kenya government took a bold step toward transparency a few weeks ago when it fired up its Open Data website and posted loads of data in a format that makes the information easily understood by the average person. The data sets include national census statistics as well as government spending, and the government promises more data to come. This is a boon for journalists willing to wade into the numbers to examine what’s going on in their country and hold their government accountable. I’m waiting now to see how they will use this new tool.
We always hear that information is power, but that works only if the information is used. Lots of information begins as numbers, statistics, and data sets, with lots of good stories tucked away in there to be found by the journalist willing to go the extra mile, examine the numbers, and do the math. In many developing countries, the information – numbers, statistics, data sets – isn’t easily accessible, if it is available at all. Governments keep a tight hold on it, or if it’s made available, the average person would be hard pressed to make heads or tails out of it.
Continue reading on Behind the Numbers.
Image Credit: Open Data.