Yearly archive for 2010.
Show all posts
-
In Kampala, African Leaders Discuss Maternal Health While Attacks Renew Concern over Somalia
›July 19, 2010 // By Schuyler NullLeaders from 49 African countries are meeting today in Kampala, Uganda, at the start of a scheduled week-long African Union (AU) summit on maternal and child health. Uganda is a fitting location, as it faces some of the toughest health and demographic challenges in Africa, including a very young and rapidly growing population and poor maternal health services. However, with the memory of last week’s twin bomb blasts still fresh, peace and security issues will surely be on the agenda as well.
Somalia’s lead insurgency group, Al Shabab, took responsibility for the attacks in Kampala, which killed more than 70 people. Al Shabab’s first prominent cross-border attack is only the latest sign that Somalia’s issues – which also include a very young and rapidly growing population – are starting to spill over its borders. For more on Somalia’s deepening crisis and its effects on the East African region, see New Security Beat’s recent analysis: “As Somalia Sinks, Neighbors Face a Fight to Stay Afloat.”
Sources: AP, Washington Post.
Photo Credit: Adapted from “Ugandan African Union contingent in Mogadishu, Nov. 25, 2007” courtesy of flickr user david axe. -
Local Case Studies of Population-Environment Connections
›“The role of intergenerational transfers, land, and education in fertility transition in rural Kenya: the case of Nyeri district” in Population & Environment by Karina M. Shreffler and F. Nii-Amoo Dodoo, explores the reasons for a dramatic and unexpected decline in fertility in rural Kenya. In one province, total fertility rate (TFR) declined from 8.4 to 3.7, from 1978 to 1998. The study found numerous contributing factors for this decline, which occurred more quickly and earlier than demographers expected, but land productivity seemed to be the primary motivator. A growing population and the tradition of dividing family land among sons made continuing to have large families unrealistic for these Kenyan families. “Family planning is, therefore, not the primary causal explanation for limiting the number of children, but rather serves to help families attain their ideal family sizes,” the authors conclude. Also in Population & Environment, “Impacts of population change on vulnerability and the capacity to adapt to climate change and variability: a typology based on lessons from ‘a hard country,’” by Robert McLeman, explores the potential for human communities to adapt to climate change. The article centers on a region in Ontario that is experiencing changes in both local climatic conditions and demographics. The study finds that demographic change can have both an adverse and positive effect on the ability of a community to successfully adapt to climate change and highlights the importance of social networks and social capital to a community’s resilience or vulnerability. McLeman also presents a new typology that he hopes will “serve the purpose of drawing greater attention to the degree to which adaptive capacity is responsive to population and demographic change.”
Also in Population & Environment, “Impacts of population change on vulnerability and the capacity to adapt to climate change and variability: a typology based on lessons from ‘a hard country,’” by Robert McLeman, explores the potential for human communities to adapt to climate change. The article centers on a region in Ontario that is experiencing changes in both local climatic conditions and demographics. The study finds that demographic change can have both an adverse and positive effect on the ability of a community to successfully adapt to climate change and highlights the importance of social networks and social capital to a community’s resilience or vulnerability. McLeman also presents a new typology that he hopes will “serve the purpose of drawing greater attention to the degree to which adaptive capacity is responsive to population and demographic change.”
SpringerLink offers free access to both these articles through August 15. -
‘Dialogue Television’ Interviews Paul Collier
›Watch below or on MHz Worldview
According to last week’s guest on Dialogue, restoring environmental order and eradicating global poverty have become the two defining challenges of our era. The environmental horror unfolding in the Gulf of Mexico illustrates just how difficult it is to balance economic progress and protection of the planet. It provides an alarming example of how the search for resources and profit can lead to the plunder of nature. Host John Milewski speaks with Oxford University economist Paul Collier on his latest book, The Plundered Planet: Why We Must and How We Can Manage Nature for Global Prosperity. Scheduled for broadcast starting June 30th, 2010 on MHz Worldview channel.
Paul Collier is professor of economics and director of the Center for the Study of African Economies at Oxford University. Formerly, he served as director of development research at the World Bank. He is the author of several books, including the award-winning The Bottom Billion.
Note: A QuickTime plug-in may be required to launch the video. -
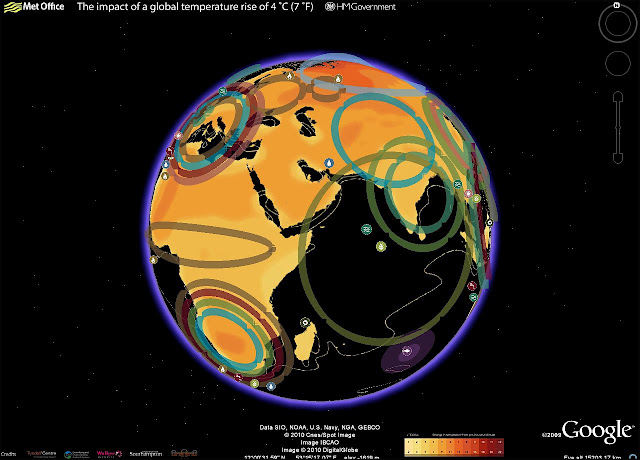
Rear Admiral Morisetti Launches the UK’s “4 Degree Map” on Google Earth
›Having had such success with the original “4 Degree Map” that the United Kingdom launched last October, my colleagues in the UK Foreign and Commonwealth Office have been working on a Google Earth version, which users can now download from the Foreign Office website.
This interactive map shows some of the possible impacts of a global temperature rise of 4 degrees Celsius (7° F). It underlines why the UK government and other countries believe we must keep global warming to below 2 degrees Celsius, compared to pre-industrial times; beyond that, the impacts will be increasingly disruptive to our global prosperity and security.
In my role as the UK’s Climate and Energy Security Envoy I have spoken to many colleagues in the international defense and security community about the threat climate change poses to our security. We need to understand how the impacts, as described in this map, will interact with other drivers of instability and global trends. Once we have this understanding we can then plan what needs to be done to mitigate the risks.
The map includes videos from the contributing scientists, who are led by the Met Office Hadley Centre. For example, if you click on the impact icon showing an increase in extreme weather events in the Gulf of Mexico region, up pops a video clip of the contributing scientist Dr Joanne Camp, talking about her research. It also includes examples of what the UK Foreign and Commonwealth Office and British Council are doing to increase people’s awareness of the risks climate change poses to our national security and prosperity, thus illustrating the FCO’s ongoing work on climate change and the low-carbon transition.
Rear Admiral Neil Morisetti is the United Kingdom’s Climate and Energy Security Envoy. -
DRC’s Conflict Minerals: Can U.S. Law Impact the Violence?
›July 13, 2010 // By Schuyler NullApple CEO Steve Jobs, in a personal email posted by Wired, recently tried to explain to a concerned iPhone customer the complexity of ensuring Apple’s devices do not use conflict minerals like those helping to fund the civil war in the Democratic Republic of Congo. However much one might be tempted to pile on Apple at the moment, Mr. Jobs is on to something with regard to the conflict minerals trade – expressing outrage and raising awareness of the problem is one thing but actually implementing an effective solution is quite another.
As finely articulated in a number of recent articles about conflict minerals in the DRC (see the New York Times, Guardian, and Foreign Policy for example), the Congo is, and has been for some time, a failed state.
Although a ceasefire was signed in 2003, fighting has continued in the far east of the country around North and South Kivu provinces, home to heavy deposits of tin, gold, coltan, and other minerals. The remote area is very diverse ethnically and has seen clashing between government troops and various militias from the Congo itself as well as encroachments by its neighbors Rwanda, Uganda, and Burundi. Referred to as “the Third World War” by many, there are by some accounts 23 different armed groups involved in the fighting, and accusations of massacres, rampant human rights abuses, extortion, and pillaging are common. According to the UN Special Representative on Sexual Violence in Conflict, “there is almost total impunity for rape in the Congo,” and a survey by the International Rescue Committee puts the estimated dead from preventable diseases, malnutrition, and conflict in the area at over five million over the past decade (or 45,000 deaths a month).
At a recent event in Washington, DC on this terrible conflict (see Natural Security for an excellent summary), DRC Ambassador Faida Mitifu expressed her hope to the audience and panel (including U.S. Under Secretary of State Robert Hormats) that they would not limit themselves to “just talking.” Hosts John Pendergast and Andrew Sullivan of the NGO Enough Project hope to address the demand side of Congo’s mineral trade by pushing Congress to pass the Conflict Minerals Trade Act, which would require U.S. companies to face independent audits to certify their products are conflict mineral-free.
But Laura Seay, of Texas in Africa and the Christian Science Monitor, is dubious of this proposal, pointing out that:Without the basic tools of public order in place and functioning as instruments of the public good in the DRC, the provisions of this bill are likely to work about as well as the Kimberley Process Certification Scheme does in weak states that lack functioning governmental institutions – which is to say, not at all.
The Kimberely Process (KP) is a certification scheme that is supposed to stem the flow of “blood diamonds” that support corrupt regimes and fuel human rights abuses. But the KP’s governing body has recently reached a crisis of action over whether or not to punish Zimbabwe for alleged abuses, with one diamond magnate even claiming, according to IRIN, that “corrupt governments have turned the KP on its head – instead of eliminating human rights violations, the KP is legitimizing them.”
The problem with international transparency schemes like the Kimberely Process, the proposed Conflict Minerals Act, or even EITI, is that at the very least, a functioning government – if not a beneficent one – is needed to enforce regulations at the source. In the DRC’s case, not only does the government have little to no authority over the affected areas, but the mining militias are smuggling their loot, on foot in some cases, directly into neighboring countries anyway. By the time they reach U.S. companies (if ever – Americans are not the only consumers in the world), conflict minerals have passed hands so many times that proving their provenance is next to impossible.
Then there is the question of whether or not cutting off the militias, rogue military officials, and government forces from conflict mineral monies would even end violence in the region in the first place. Certainly many armed groups gain a great deal from their illegal mining activities (as do some locals), but is it the root cause of their discontent? In the best case scenario where mining revenues are actually decreased, would that really convince the remnants of the Hutu Interahamwe, fleeing retribution from the now majority-Tutsi Rwandan government, to suddenly put down their weapons? How about the Mai Mai, who are fighting the Hutu incursion into their homeland?
I for one find that hard to believe. Stopping the conflict mineral trade from afar is very difficult, if not impossible, and even if we could end the trade, it would not necessarily stop the suffering. Illegal mining does play a large part in supporting rebel groups, but to address the human security problems that have so horrified the world, international attention ought to first be turned toward improving governance mechanisms in the Congo and rethinking the troubled UN peacekeeping mission (how about more involvement out of U.S. AFRICOM too?). The failure of the current UN mission is well documented, but withdrawing the largest peacekeeping force in the world in the face of continued violence, including the recent death of Congo’s most famous human rights activist under suspicious circumstances, seems more likely to cause harm than good.
Would passing the Conflict Minerals Act make Apple consumers feel better? Perhaps. But that’s not the point. Environmental security measures that prevent the DRC’s tremendous mineral wealth from being used to fund conflict can only make an impact if the government has some measure of accountable control over the area. To make a real difference in east Congo, human security must first be addressed directly and forcefully.
Sources: BBC, Christian Science Monitor, Daily Beast, Human Rights Watch, IPS News, IRIN News, International Rescue Committee, Enough Project, Foreign Policy, GlobalSecurity.org, Globe and Mail, New York Times, Share the World’s Resources, Southern Times, Times Online, UN, Wired.
Image Credit: “Minerals and Forests of the DRC” from ECSP Report 12, courtesy of Philippe Rekacewicz, Le Monde diplomatique, Paris, and Environment and Security Institute, The Hague, January 2003. -
An “Aye” for an “Aye”: Everyone Has a Right to Be Counted
›July 12, 2010 // By Kayly Ober Around the world, countries from Afghanistan to Papua New Guinea to the United States are taking part in their decadal census, leading the UN Population Fund (UNFPA) to select the theme “Everyone Counts” for World Population Day 2010, which was celebrated on July 11.
Around the world, countries from Afghanistan to Papua New Guinea to the United States are taking part in their decadal census, leading the UN Population Fund (UNFPA) to select the theme “Everyone Counts” for World Population Day 2010, which was celebrated on July 11.
Everyone has the right to be counted, because “censuses and population data play a critical role in development and humanitarian response and recovery,” said UNFPA Executive Director Thoraya Ahmed Obaid in her World Population Day message. Obaid added that “with quality data we can better track and make greater progress to achieve the Millennium Development Goals, and promote and protect the dignity and human rights of all people,” especially among vulnerable populations like women, girls, the poor, and the marginalized.
USAID similarly supports quality data collection, which it says plays a critical role in advancing voluntary family planning in the developing world. For the last 25 years, USAID has funded the Demographic and Health Surveys (DHS) program, which collaborates with national health ministries to collect data on family planning, child and maternal health, disease prevalence, and other health indicators.
This invaluable data is made freely available for public use, which can foster new research in the field and stimulate innovative approaches to addressing public health issues. Praising the DHS program, Gapminder Foundation Director Hans Rosling told a Wilson Center audience last year that “statistics should be the intellectual sidewalks of a society, and people should be able to build businesses and operate on the side of them.”
Accurate census counts are also important elements of “good governance, transparency and accountability,” said UN Secretary-General Ban Ki Moon in his World Population Day message. “Population data helps leaders and policy-makers to make informed decisions about policies and programmes to reduce poverty and hunger, and advance education, health and gender equality,” he said.
But no one is suggesting that coming up with reliable population data is an easy task. As Sean Peoples and Elizabeth Leahy point out in the May/June 2009 issue of World Watch magazine, issuing population projections can be a risky business:In the 2008 Revision of World Population Prospects, the UN Population Division projects that our planet will grow to 9.15 billion people by 2050. Yet this medium-variant projection is just one of several possible scenarios released in this latest round of number crunching. The low- and high-variant projections—7.96 billion and 10.5 billion, respectively—could instead become reality, given uncertainties in the developing world due to factors such as inconsistent data collection, weak health system infrastructure, and low government capacity.
The goal, then, is to make sure everyone counts. -
Stacy VanDeveer: Will Using Less Oil Affect Petrostate Stability?
›July 12, 2010 // By Schuyler NullIf we were to actually use less fossil fuel, what would happen to today’s petrostates? “If the oil revenues dry up or even decline a little bit you might have a real serious crisis,” said Stacy VanDeveer of the University of New Hampshire, during an interview with ECSP. We spoke to VanDeveer following his presentation at the Wilson Center event, “Backdraft: The Conflict Potential of Climate Mitigation and Adaptation.”
-
New Film Looks at Sub-Saharan Africa’s Unmet Need for Family Planning
›A new documentary film released recently by Population Action International brings attention to the plight of women across sub-Saharan Africa who lack access to basic reproductive health supplies, such as condoms and contraceptives. Funded with the support of the Reproductive Health Supplies Coalition, “Empty Handed” documents the unmet need for family planning services in the region, which has some of the world’s highest fertility rates.
PAI filmmaker Nathan Golon shot the film in Uganda earlier this year. The film’s focus on Ugandan women’s struggles in particular is with good reason, as the country has a well-documented history of providing insufficient family planning services. According to the CIA’s World Factbook, Uganda has the world’s second highest total fertility rate at 6.73 children per woman.
“Empty Handed” examines how a lack of family planning tools and services can lead to a slippery slope of unintended consequences, from unplanned pregnancies to the rampant spread of sexually transmitted diseases. The film revolves around interviews conducted with women who share common hardships as they try to access family planning from under-resourced local healthcare clinics, often traveling long distances only to find upon arrival that no contraceptives or condoms are available.
In addition to identifying past and current issues with reproductive healthcare access in sub-Saharan Africa, “Empty Handed” also puts forward some ideas for better meeting family planning needs of the more than 200 million women throughout the world without access to even basic contraception.
To watch the full film online, visit the “Empty Handed” website.
Sources: C.I.A., FHI, Population Action International, Reproductive Health Supplies Coalition