-
Simon Zadek, Project Syndicate
Age Against the Machine
›September 21, 2012 // By Wilson Center StaffThe original version of this article, by Simon Zadek, appeared on Project Syndicate.
The elderly are a crucial link in the chain that binds generations and sustains civilized society. Today, however, older people are largely considered to be out of touch with the modern, technology-driven world, and incapable of paying their own way. But much evidence shows otherwise: If aging were framed as an economic opportunity, the growing number of older people worldwide could become modernity’s gift, rather than society’s burden.
-
Modeling Demographic Dividends, Fertility, and Income in Developing Countries
› The poorest households gain the least when countries reap the demographic dividend, according to a preliminary draft of a new study by four Harvard School of Public Health researchers. In “Microeconomic Foundations of the Demographic Dividend,” authors David Bloom, David Canning, Günther Fink, and Jocelyn Finlay write that 18 years of Demographic Health Surveys (DHSs) from 60 developing countries show that while declining fertility rates and dependency ratios can lead to rising incomes on a nationwide level, sub-nationally those trends occur unevenly and mostly benefit wealthier households. Poorer households, meanwhile, are likelier to see slower fertility declines, delaying the economic gains that can result from demographic transitions, and increasing inequality. Importantly, the authors emphasize that the study reflects “the early stages of the demographic transition”; long-term economic effects of fertility decline, they write, “remain ambiguous.”
The poorest households gain the least when countries reap the demographic dividend, according to a preliminary draft of a new study by four Harvard School of Public Health researchers. In “Microeconomic Foundations of the Demographic Dividend,” authors David Bloom, David Canning, Günther Fink, and Jocelyn Finlay write that 18 years of Demographic Health Surveys (DHSs) from 60 developing countries show that while declining fertility rates and dependency ratios can lead to rising incomes on a nationwide level, sub-nationally those trends occur unevenly and mostly benefit wealthier households. Poorer households, meanwhile, are likelier to see slower fertility declines, delaying the economic gains that can result from demographic transitions, and increasing inequality. Importantly, the authors emphasize that the study reflects “the early stages of the demographic transition”; long-term economic effects of fertility decline, they write, “remain ambiguous.”
-
Al Jazeera Maps Water Flashpoints Around the World
›Historically, the concept of “water wars” – inter-state wars fought solely over water – has been fairly unsubstantiated. But continued population growth, accelerating development, and environmental changes are making water more scarce and in turn increasing the chances of related tensions and violence. To illustrate the growing role water plays in tensions around the world, Al Jazeera has put together a map linked to a series of stories they’ve done on water “flashpoints.”
-
Michael D. Lemonick, Climate Central
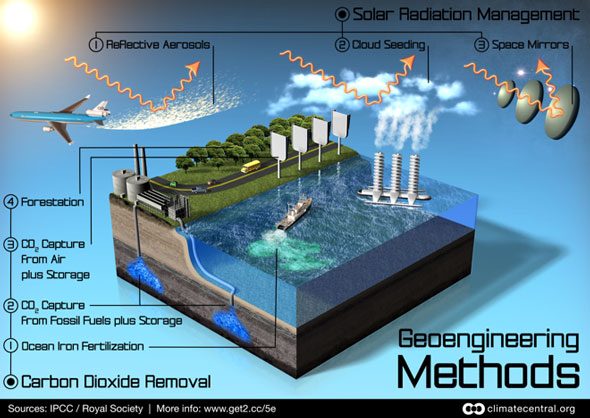
Geoengineering Faces Dilemma: Experiment or Not?
›September 18, 2012 // By Wilson Center Staff
The original version of this article, by Michael D. Lemonick, appeared on Climate Central.
In May, a team of British scientists abruptly canceled an experiment they had been planning for nearly two years. The Stratospheric Particle Experiment for Climate Engineering, or SPICE, was intended to test ways of injecting tiny particles of sulfur dioxide into the upper atmosphere, with the eventual goal of filtering out sunlight to cool the Earth in the face of global warming. The main reason given for the cancellation was a potential patent dispute over some of the technology involved.
-
The Challenges and Benefits of Addressing Young Adolescent Reproductive Health
›There are 1.2 billion adolescents (ages 10 to 19) in the world today, accounting for 17 percent of the global population. They are the largest youth cohort in history, and 90 percent live in the developing world. Within that broad age group, very young adolescents (ages 10 to 14) often fall through the cracks of international development work, especially when it comes to health, and reproductive health in particular.
-
Counting the World: UNFPA Highlights the Challenges of Census-Taking
›The United Nations biannual population projections are some of the most (if not the most) widely used numbers in demography. Researchers and policymakers alike rely on the figures to plan for present and future challenges. But few consider the story behind the statistics. Where does the data come from? The United Nations Population Fund (UNFPA) recently released a short documentary on conducting censuses in challenging environments, with a spotlight on Indonesia, Chad, the Palestinian Territories, Belarus, and Bolivia.
-
Ecological Footprint Accounting: Measuring Environmental Supply and Demand
›September 12, 2012 // By Kate Diamond
Twenty-five years have passed since the Brundtland Commission first brought sustainable development to international prominence. Today, the United Nations appears on track to replace the soon-to-expire Millennium Development Goals with “Sustainable Development Goals,” marking the extent to which the international community has embraced the concept. And yet, in spite of its prominence, a specific and measureable definition of sustainability remains lacking.
-
António Guterres, The New York Times
Why Mali Matters
›September 11, 2012 // By Wilson Center Staff
The original version of this op-ed, by António Guterres, appeared in The New York Times.
For many people, Timbuktu has long represented the essence of remoteness: a mythical, faraway place located on the boundaries of our collective consciousness. But like many of the myths associated with colonialism, the reality is very different.
 A Publication of the Stimson Center.
A Publication of the Stimson Center.