-
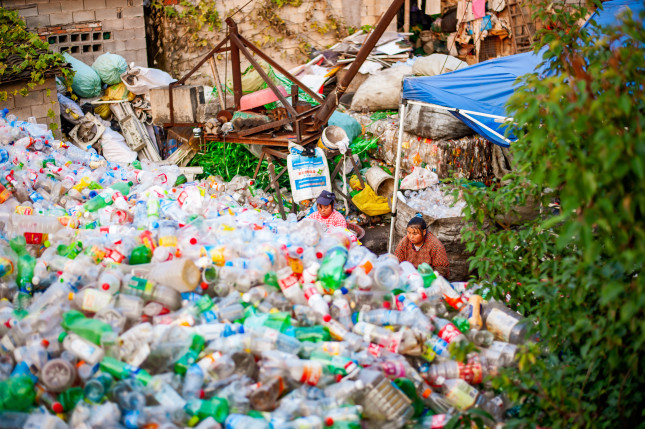
Delivering a Solution to the World’s Ocean Plastic Problem
›
In 2017, the Green Volunteer League of Chongqing, an environmental NGO, filed a suit against China’s three biggest food delivery companies—Meituan, Baidu, and Ele.me—for damaging the environment by generating excessive waste. Specifically, these three e-commerce platforms provided consumers with single-use chopsticks that consumed 6,700 trees every day as well as massive amounts of plastic containers, bags, and utensils. Today, over 400 million Chinese are regular users of food delivery. Since summer 2019, daily app use for Meituan was over 30 million orders, generating 100 million plastic containers every day—enough to carpet 360 football fields.
-
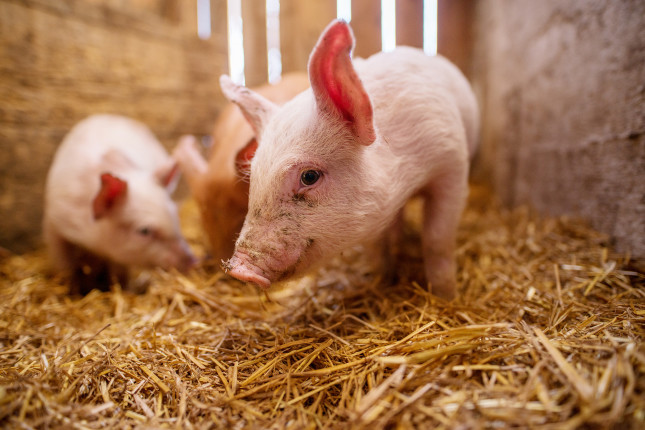
Pig Disease is Creating a Mountainous Solid Waste Problem
›
On a rainy July afternoon in 2017, I was in Jinhua, China, a city just south of Shanghai, to visit a pig farm. This was not just any pig farm—the Mebolo farm grows pigs that become the prized Jinhua Hams, a Chinese delicacy for nearly 1500 years. Long before Italians produced prosciutto and the Spanish their Jamón serrano ham, Marco Polo discovered Jinhua ham in the 13th century and brought ham-making techniques back to Europe.
-
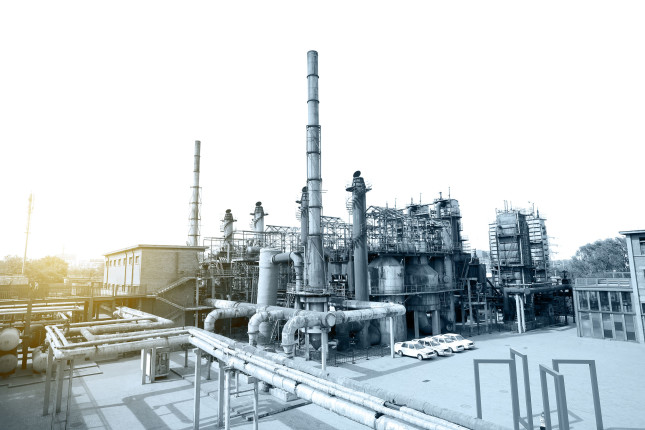
Black Coal to White Trash
›
Coal has long been China’s “black gold,” supplying over half of the nation’s electricity. Yet as coal’s energy share decreases due to domestic action to reduce air pollution and greenhouse gas emissions, a new coal industry is emerging. In China’s arid northwest, eight plants are pulverizing coal chunks and “cooking” coal powder into something more valuable than power—or maybe even gold. These coal conversion plants, soon numbering over 20, churn out chemicals to produce plastic.
-
Geoff Dabelko and Sharon Burke on Environmental Peacebuilding in an Era of Great Power Competition
› United States and China are on the road to war, said Senior Advisor of New America’s Resource Security Program, Sharon Burke in this week’s Friday Podcast. “And if you’re an environmental peacebuilder and you’re not thinking about that, you might want to,” she added. She spoke with Geoffrey Dabelko, Professor at Ohio University and Senior Advisor to ECSP, at the first ever International Conference on Environmental Peacebuilding in October 2019 at the University of California, Irvine. It’s a war we can’t afford, said Burke. “But we’re not doing anything to avoid it at the moment, in my opinion, other than deterrence.”
United States and China are on the road to war, said Senior Advisor of New America’s Resource Security Program, Sharon Burke in this week’s Friday Podcast. “And if you’re an environmental peacebuilder and you’re not thinking about that, you might want to,” she added. She spoke with Geoffrey Dabelko, Professor at Ohio University and Senior Advisor to ECSP, at the first ever International Conference on Environmental Peacebuilding in October 2019 at the University of California, Irvine. It’s a war we can’t afford, said Burke. “But we’re not doing anything to avoid it at the moment, in my opinion, other than deterrence.” -
Population, Climate, and Politics—A New Phase is Emerging
› For some time, it has been clear that a global population imbalance is emerging. High income countries, including nearly all of the Americas, Europe, and most of East and parts of South and Southeast Asia, have seen a dramatic, sustained fall in fertility. Already, this is resulting in shrinking labor forces and the oldest mean age populations seen in history. At the same time, the low income countries and even some lower middle-income countries—mainly in Africa but also in Central America, the Middle East, and parts of South and Southeast Asia—continue to have relatively high fertility. This is now, and even more in the coming decades, producing fast-growing labor forces and relatively young populations.
For some time, it has been clear that a global population imbalance is emerging. High income countries, including nearly all of the Americas, Europe, and most of East and parts of South and Southeast Asia, have seen a dramatic, sustained fall in fertility. Already, this is resulting in shrinking labor forces and the oldest mean age populations seen in history. At the same time, the low income countries and even some lower middle-income countries—mainly in Africa but also in Central America, the Middle East, and parts of South and Southeast Asia—continue to have relatively high fertility. This is now, and even more in the coming decades, producing fast-growing labor forces and relatively young populations. -
Where Do the Plastic Miners Go When the “Mine” Disappears?
›
Usually after dinner, Mr. Ma would take off his shirt, shut the door, and begin work making plastic pellets from scrap. But tonight, he sits in his darkened yard staring at two SUV-sized plastic processing machines and a bundle of colorful scrap plastic. No lights are on, no machines grind, and no familiar theme song of CCTV-1 plays in the background. Walking through other villages in Wen’an County, more men meander around their yards filled with the same idle processing machines and mini-mountains of scrap plastic. Most have never studied English, but they are fluent in the language of plastics, sprinkling words like ABS, PP, and PVC into their conversations. They are the owners of small plastic scrap recycling workshops that were once booming—but are now silent.
-
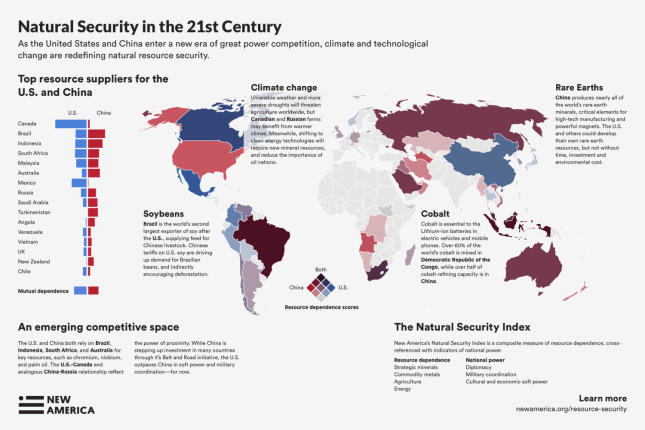
Great Power Resource Competition in a Changing Climate: New America’s Natural Security Index
›Late last year, Reuters reported that the U.S. Defense Department plans to fund mining and processing operations for rare earth elements—a class of minerals for which China dominates the global market, producing over 80 percent of the world’s supply. In the past, China has restricted exports of rare earths, and recently threatened to do so again. Even with a phase one trade deal hammered out between the United States and China, natural resources are likely to remain a point of geopolitical tension.
-
China’s Risky Gamble on Coal Conversion
›China Environment Forum // Choke Point // January 9, 2020 // By Richard Liu, Zhou Yang & Xinzhou Qian
At the September 2019 United Nations General Assembly (UNGA) Climate Summit, the U.S. delegation, under the shadow of intended withdrawal from Paris, did not volunteer a speaker. Attention instead focused on China. As the world’s largest carbon emitter, China was poised to assert leadership on the climate crisis. However, perhaps lacking the sibling rivalry pressure that brought the U.S. and China together in 2014 on a joint climate agreement, State Councilor and Foreign Minister Wang Yi offered no new commitments: no carbon tax, no increased investment in renewables, and no announcement to set a more ambitious coal consumption cap.
Showing posts from category China.




 United States and China are on the road to war, said Senior Advisor of New America’s
United States and China are on the road to war, said Senior Advisor of New America’s  For some time, it has been clear that a global population imbalance is emerging. High income countries, including nearly all of the Americas, Europe, and most of East and parts of South and Southeast Asia, have seen a dramatic, sustained fall in fertility. Already, this is resulting in shrinking labor forces and the oldest mean age populations seen in history. At the same time, the low income countries and even some lower middle-income countries—mainly in Africa but also in Central America, the Middle East, and parts of South and Southeast Asia—continue to have relatively high fertility. This is now, and even more in the coming decades, producing fast-growing labor forces and relatively young populations.
For some time, it has been clear that a global population imbalance is emerging. High income countries, including nearly all of the Americas, Europe, and most of East and parts of South and Southeast Asia, have seen a dramatic, sustained fall in fertility. Already, this is resulting in shrinking labor forces and the oldest mean age populations seen in history. At the same time, the low income countries and even some lower middle-income countries—mainly in Africa but also in Central America, the Middle East, and parts of South and Southeast Asia—continue to have relatively high fertility. This is now, and even more in the coming decades, producing fast-growing labor forces and relatively young populations.