Showing posts from category natural resources.
-
Paul Collier Discusses the Plundering of the Planet at the World Bank
›April 27, 2010 // By Dan Asin “Nature is something that is both vulnerable and valued,” Paul Collier said yesterday at the World Bank. “It is being mismanaged…what it has turned into is a series of environmental battles between environmentalists and economists.”
“Nature is something that is both vulnerable and valued,” Paul Collier said yesterday at the World Bank. “It is being mismanaged…what it has turned into is a series of environmental battles between environmentalists and economists.”
Collier was giving the first public presentation of of his new book, The Plundered Planet: Why We Must—and How We Can—Manage Nature for Global Prosperity. In it, he asserts that disputes between environmentalists and economists often arise from a fundamental misunderstanding on both sides about the unique qualities and purposes of “natural assets.” This misunderstanding, he says, has created a state of natural plunder. In Plundered Planet, Collier elucidates the ethical and economic considerations for the proper management of natural assets, how a greater understanding of natural assets and better environmental management can be achieved, and lessons for development.
Paul Collier will be joining ECSP for an in-depth discussion of Plundered Planet, economics, and development at the Wilson Center in June. Until then, for a more detailed look, check out the New Security Beat’s previous coverage of Collier’s book preview with Nancy Birdsall, president of the Center for Global Development, at the U.S. Institute of Peace. -
High Altitude Turbulence: Challenges to the Cordillera del Cóndor of Peru
›In 1998, Peru and Ecuador settled a long-running border dispute in the Cordillera del Cóndor mountain range that had killed and wounded dozens on both sides in 1995. In addition to pledging renewed cooperation on deciding the final placement of the border, the agreement, the Acta Presidencial de Brasilia, committed both sides to establishing extensive ecological protection reserves on both sides of the border: A peace park of sorts was born.
But now, indigenous groups fear that extractive industries in the area could threaten both the biodiversity and the ecological integrity of the forests and streams that they rely upon for their survival. They detail these charges in a new report, Peru: A Chronicle of Deception, and in a new video documentary, “Amazonia for Sale.”
Located on the eastern slopes of the Equatorial Andes, the area is a recognized global biodiversity hotspot with large areas of pristine montane habitat. In 1993-4, Conservation International led a biodiversity assessment trip to the area and identified dozens of species new to science. Their report, The Cordillera del Cóndor Region of Ecuador and Peru: A Biological Assessment, noted the “spectacular” biodiversity of the area, and its key role in the hydrological cycle linking the Andes with the Amazon.
Recognizing the region’s importance, the Acta Presidencial de Brasilia stipulated the need to create and update mechanisms to “lead to economic and social development and strengthen the cultural identity of native populations, as well as aid the conservation of biological biodiversity and the sustainable use of the ecosystems of the common border,” wrote Martin Alcade et al. in the ECSP Report.
Indigenous communities in Peru are accusing the Peruvian government of reneging on those promises by allowing extractive industries extensive access to the region. They charge that the government gave in to gold mining interests who want to reduce the size of the protected area in the Cordillera del Cóndor. They also claim that the Peruvian government is violating promises made to include indigenous peoples in the governance and management of the area.
Carefully managing extractive activities was a key priority for Peru and Ecuador when they negotiated an end to their border dispute. A management plan for the area with strong protection for key biodiversity areas was supposed to ensure everyone’s interests.
However, Peru’s current president, Alan Garcia, has been aggressive in promoting extractive industries in Peru,to the point of inciting significant popular opposition among many indigenous peoples. Less than a year ago, protests over oil exploration in Amazonian lowlands city of Bagua killed and wounded dozens of Peruvians. This violence followed years of social conflict over mining development in a number of communities in Peru’s Andean highlands.
Earlier this decade, Peru made some progress in resolving extractive disputes. But Garcia’s strong promotion of the extractive sector in the face of indigenous opposition, like we currently see in the Cordillera del Cóndor region, suggests years of confrontations to come.
Tom Deligiannis is adjunct faculty member at the UN-mandated University for Peace in Costa Rica, and an associate fellow of the Institute for Environmental Security in The Hague.
Photo Credit: “El vuelo del condor, acechando a su presa,” courtesy of flickr user Martintoy. -
Book Review: ‘Global Warring: How Environmental, Economic, and Political Crises Will Redraw the World Map’ by Cleo Paskal
›April 9, 2010 // By Rachel Posner As record-breaking snowstorms blanketed Washington, D.C. this winter, I took advantage of the citywide freeze to read Cleo Paskal’s new book, Global Warring: How Environmental, Economic, and Political Crises Will Redraw the World Map. In it, Paskal makes a compelling case for why the West should care about the geopolitical shifts—already underway—that will be exacerbated by climate change.
As record-breaking snowstorms blanketed Washington, D.C. this winter, I took advantage of the citywide freeze to read Cleo Paskal’s new book, Global Warring: How Environmental, Economic, and Political Crises Will Redraw the World Map. In it, Paskal makes a compelling case for why the West should care about the geopolitical shifts—already underway—that will be exacerbated by climate change.
Paskal eloquently explains the science behind climate change in layman’s terms, breaking down incredibly complex issues and drawing connections across seemingly disparate challenges, such as rising food prices, degrading energy infrastructure, and growing water scarcity. She is a skilled storyteller, using memorable vignettes (and at times even humor) to effectively illustrate these climate-related complexities.
But what truly sets Paskal’s book apart from a number of recent works on this topic is her ability to elucidate the major power shifts that are directly related to today’s climate and resource stresses. “Environmental change is the wild card in the current high-stakes game of geopolitics,” she writes (p. 249). Such natural resource stresses will only become more pronounced in the future.
Global Warring highlights a number of key challenges and opportunities that could take the United States and other Western nations by surprise if they don’t change policies now to secure their positions as major global powers.
Impacts of Environmental Change: Like the developing world, the United States and other Western nations will suffer from extreme weather events and the broader effects of environmental change. However, the United States has “institutional, regulatory, political, and social” weaknesses that affect its “ability to absorb the stress of repeated, costly, and traumatic crises,” including its expensive, aging infrastructure, writes Paskal (p. 40). For example, while the country will face more Hurricane Katrinas, the U.S. military is still not adequately prepared to address such domestic environmental disasters.
Transportation Routes and Trade: The Northwest Passage—the sea route that connects the Atlantic and Pacific Oceans through North American waterways—is a highly coveted trade route that will become all the more valuable as Arctic ice continues to melt in the years ahead. Already the United States, Canada, Russia, China, and even the European Union are engaged in a geopolitical chess game for control of the Arctic. Each is staking a claim to the natural resources below the surface, new shipping routes, and strategic chokepoints. According to Paskal, if the West wants to remain “a major force in the twenty-first century,” the United States and the EU should help Canada secure its claim to the Northwest Passage. This way, Canada could protect its borders and “talk to other countries, including Russia, on a more equal basis about creating and jointly using facilities like search, rescue, and toll stations, and on methods of speeding legitimate, safe shipping and exploration in the northern waters,” she writes (p. 125).
New Power Dynamics and Partnerships for China, India, and the West: China and India are two of the world’s fastest growing economies and each are taking on new roles in Asia and beyond. But could climate change and environmental challenges stem their growth, or will these “powerhouse” countries prove resilient? As the global power balance begins to shift toward Asia, Paskal sees India as the “swing vote” that might shape the future of geopolitics for the next long while” by aligning itself with Russia and China and potentially marginalizing the West (p. 185). Alternatively, the West could finally acknowledge India as an equal partner—for example, by strengthening civilian nuclear cooperation—and thus help foster stability over the long term. Stresses on natural resources, now and in the future, will only increase the importance of strong alliances and geopolitical partnerships.
Rising Sea Levels in the Pacific Ocean: Most Americans and other Westerners are not terribly concerned about the welfare of the small-island nations in the Pacific whose entire existence is threatened by sea-level rise. Paskal rightfully draws our attention to the ambiguous state of the international law of the sea, which leaves much of this region up for grabs when sea levels rise and coastlines change. “At stake is access to fisheries, sea-lanes in relatively calm waters, control over regional security, unknown underwater resources, geostrategic advantage, and geopolitical political leverage,” she writes (p. 214). China has already gone to great lengths to secure its control over the Pacific, and if it continues to be successful, the United States will risk losing influence in the region.
Throughout all of these cases, Paskal weaves in a discussion of the growing and strategically significant practice of “nationalistic capitalism.” For example, she describes how China’s state-owned companies work with their government to “advance national strategic interests,” often signing bilateral deals that “cut out the open market and overtly link much-needed resources to wide-ranging agreements on other goods and services, including military equipment” (p. 94-5). As China and other nationalistic capitalist countries expand their reach into the resource-rich regions of Africa and Latin America, fewer resources (like food and fuel) will be available in the open market. For the United States and other “free market” nations, this practice could lead to higher prices and increased competition for business and political alliances.
Overall, Global Warring is an excellent read that I would recommend to friends and colleagues, especially those tracking long-range global trends and promoting farsighted policies. I appreciated Paskal’s recurring call for abandoning short-term expediency in U.S. decision-making in favor of a longer-term approach. Paskal shows how over time the United States’ short-term interests are creating major vulnerabilities that will be worsened by environmental stresses in the future.
The book’s only notable shortcoming is its skewed geographic scope. Paskal focuses heavily on North America and Asia, particularly China and India, and only briefly mentions Africa, Latin America, the Middle East, and Australia. Obviously, a book about the shift of major world powers would concentrate on the most influential players, but these other regions are worthy of greater consideration given their critical natural resources, demographic trends, and ongoing climate adaptation efforts.
Regardless of how the climate changes, the environmental trends described in Global Warring are already manifesting as geopolitical realities that will dramatically affect the United States. As Paskal says, “Countries that want internal stability, influence over allies, control over sea-lanes, and access to critically important resources better start planning now (p. 235).
Rachel Posner is a fellow in the Energy and National Security Program at the Center for Strategic and International Studies (CSIS). Previously, she has served as the assistant director of the CSIS Global Water Futures Project; research associate with the CSIS Global Strategy Institute; and Brent Scowcroft Award Fellow with the Aspen Strategy Group. -
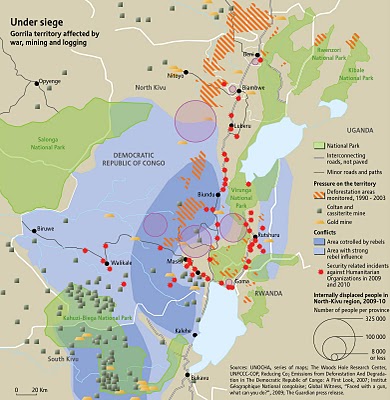
Guerrillas vs. Gorillas in the Congo Basin
›Gorillas could disappear from the Congo basin in the next 10-15 years, according to a new report issued by the United Nations and Interpol. The Last Stand of the Gorilla – Environmental Crime and Conflict in the Congo Basin places responsibility for the decline of gorilla populations in the Democratic Republic of the Congo and its surrounding region squarely on the shoulders of resource-hungry militants, who poach gorilla bushmeat to feed hungry soldiers and mine workers and sell in local markets. Militants extract timber, charcoal, diamonds, and other resources to raise funds for arms, reducing gorilla territory.
Yet another rationale is retaliation against park rangers who attempt to limit their illegal activities within national parks. In the process, park rangers have found themselves, their parks, and their endangered charges targets of militant groups seeking to plunder and traffic goods through protected areas. “In Virunga Park alone, 190 park rangers have been killed in the last 15 years,” notes the report, which is also available in an interactive e-book edition.
Conflict with local communities also frequently leads to the slaughter of the gorillas and loss of their habitats. Displaced people and refugees also compete with gorillas for land. In several cases, gorillas facing shrinking natural domains have satisfied their appetites in banana plantations, and local farmers have struck back.
Strengthening Law Enforcement
Not all, however, is dire. The report finds several success stories stemming out of transboundary law enforcement collaboration and recommends increased training and support for local and international law enforcement groups. “The gorillas are yet another victim of the contempt shown by organized criminal gangs for national and international laws aimed at defending wildlife,” said David Higgins, Interpol’s Environmental Crime Programme Manager. “The law enforcement response must be internationally coordinated, strong, and united, and Interpol is uniquely placed to facilitate this.”
Law enforcement in the Congo Basin faces an uphill battle, in part due to conditions present in peace agreements between guerillas and the Congolese government. Removing vehicle checkpoints from important border crossings was key to the insurgents agreeing to peace. While these agreements reduced violence, they have created a highway for illegal exports. This trade props up the militant groups and undercuts the chances for peace on a regional scale. It is an example of how large remaining quantities of automatic weapons and turns to poaching by ex-militants can render post-conflict environments even more damaging to local wildlife than war itself.
Toward Coexistence
In some locations, conflicts between gorillas and local farmers are disappearing with the construction of natural barriers and as local populations realize the potential of ecotourism to generate greater revenue from thriving gorilla populations than collapsing ones. Greater international coordination and local commitment, however, are necessary. Turning threatening competition into beneficial cooperation is possible.
Tara Innes is a PhD student at the University of Maryland, studying conflict-environment linkages.
Photos: Gorilla, courtesy Flickr user mrflip; Gorilla Territory Affected by War, Mining, and Logging courtesy UNEP/GRID-Arendal. -
Copper in Afghanistan: Chinese Investment at Aynak
›Will new investments by the Metallurgical Corporation of China (MCC) in the Aynak copper mine break Afghanistan out of its poverty trap? Will future revenues from the subsoil assets in Logar Province bring peace and stability to the ongoing conflict?
The U.S. Institute of Peace brought together expert panelists to discuss the pitfalls and possibilities related to the Aynak contract. Discussed were current uncertainties in investment plans, future risks related to mine operations, how the various stakeholders of the Aynak project can be more engaged in the process, as well as the planned reinvestment of economic benefits within the broader economy.
Alone, the Aynak Copper Mine’s multi-billion dollar reserves will not bring about security, but its success can be a gateway to future development. According to Lorenzo Delesgues, co-director of Integrity Watch Afghanistan, however, there is also a chance that this conflict-ridden region will find the mines a catalyst for more disputes. According to Delesgues, the potential negative impacts on the surrounding communities and the environment “can be exacerbating factors that might create even more insecurity than what you already have in that area.”Delesgues suggested that certain programmatic alterations needed to be considered by the MCC and the Afghan government to leverage local sustainable economic development beyond Aynak. For Delesgues, local communities need better information about mining’s environmental and employment impacts to improve their decision-making abilities, as many common social and environmental protections are lacking from the current MCC mining plans and activities. An environmental impact assessment, for example, has not yet been carried out, leading to concerns that on-going exploration activities may harm the local environment and downstream populations. To prevent future disputes, Integrity Watch Afghanistan recommends strengthening project monitoring processes and greater public communication and consultation with key stakeholders.
Gary McMahon, senior mining specialist at the World Bank, believes that Afghanistan is in a good position to benefit from the Aynak copper mines. Local employment generation and the MCC’s stated commitment to provide educational, health, and housing services to employees all offer promise for development. There are also contractual obligations for a power plant that will supplement a portion of Kabul’s current demand and the construction of a railway system through Afghanistan, which will extend from China to Tajikistan, and strengthen existing Afghan trade networks.
While the royalty rates established by the Afghan government in the Aynak contract on future mining revenue streams are unprecedented in the mining sector, McMahon fears that the revenue will solely follow international aid flows. “If all that happens is that fiscal revenues [from Aynak] replace foreign aid, the impacts are going to be way less,” says McMahon.
McMahon suggests that, moving forward, the Ministry of Mines and the National Environmental Agency’s capacities for monitoring and evaluation must be improved and strengthened. There also needs to be assurance that the local population gets a “fair share” of jobs and other opportunities, along with continuous consultation of the impact the mines are having on their social and environmental conditions.
In his concluding statements, Ishaq Nadiri, professor of economics at New York University and former senior economic advisor to Hamid Karzai, cautioned the audience about the weight that economics plays in the overall outcome of the Aynak Copper Mine. According to Nadiri, the objective in establishing the Aynak contract was to maximize national benefits. Nadiri offered hope that “the lack of security…[which] emanates from the highly chronic poverty of the country,” could find promising solutions in the wealth of Aynak.
Drafted by Michelle Neukirchen, edited by Julien Katchinoff.
Photo Credits: “River and Mountains of Logar,” courtesy of flickr user AfghanistanMatters and “Logar Province Shura,” courtesy of flickr user IsafMedia. -
Visualizing Natural Resources, Population, and Conflict
›Environmental problems that amplify regional security issues are often multifaceted, especially across national boundaries. Obtaining a comprehensive understanding of the natural resource, energy, and security issues facing a region is not fast or easy.
Fortunately, the Environment and Security Initiative (ENVSEC) has created highly informative, easy-to-understand maps depicting environmental, health, population, and security issues in critical regions.
Published with assistance from the United Nations GRID-Arendal, these maps offer policymakers and the public a snapshot of the complex topography of environmental security hotspots in Central Asia, Eastern Europe, Southeastern Europe, and the Southern Caucasus.
Some that caught our eye:
• Environmental Issues in the Northern Caspian Sea: Overlaying environmental areas and energy production zones, this map finds hydrocarbon pollution in sturgeon spawning grounds, seal habitats in oil and gas fields, and energy production centers and waste disposal sites in flood zones.
• Water Withdrawal and Availability in the Aral Sea Basin: Simple and direct, this combination map and graph contrasts water usage with availability in Turkmenistan, Uzbekistan, and Kazakhstan—which stand in stark comparison to the excess water resources of Tajikistan and Kyrgyzstan.
• Environment and Security Issues in Belarus: In addition to noting the parts of the country with poor water quality and potassium mining, the map also delineates wildfires that occurred in areas contaminated by the Chernobyl explosion, thus threatening downwind populations.
Maps: Illustrations courtesy of the Environment & Security Initiative. -
Monitoring Resources and Conflict
›
Is the “resource curse” inevitable? The Resource Conflict Monitor (RCM) produced by the Bonn International Center for Conversion (BICC) attempts to monitor the management, administration, and governance of natural resources in countries prone to resource-conflict dynamics by establishing an empirical measure of resource governance.
-
VIDEO – Juan Dumas on Natural Resources, Conflict, and Peace
›February 24, 2010 // By Michelle NeukirchenMediation and conflict resolution around natural resources require “long-term engagement, timely interventions, and lots of flexibility,” says Juan Dumas, senior advisor for the Fundación Futuro Latinoamericano in Quito, Ecuador. The Woodrow Wilson Center and the Fetzer Institute hosted Dumas for a roundtable event on Pathways to Peace: Stories of Environment, Health, and Conflict. In this interview with ESCP Director Geoff Dabelko, Dumas shares key lessons learned from his experience with his NGO that specializes in prevention and management of socio-economic conflicts around natural resources.
In order to overcome challenges posed by current funding procedures, the foundation has been trying to establish an “early-action fund” that would provide flexible funding to facilitate conflict resolution dialogue. “With the right capacities at the right time… you can make a difference… you can prevent the escalation of conflict into violence… and create a governance path for that conflict to be addressed in a different way,” Dumas says.