-
The Business Case for Sustainable Development Is Real and Growing
›In 2000, the United Nations established the Millennium Development Goals (MDGs) with the goal of creating a global partnership for development. The formation of the MDGs created a foundation for collaboration and encouraged cross-sector partnerships to reduce poverty but also promote issues like environmental sustainability and gender equality. To carry on momentum from the MDGs, 17 Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) were established in 2015 to further encourage partnerships between civil society organizations, the private sector, academic institutions, and more. Increased private sector engagement in development is a major goal of the SDGs – and we would argue that it is crucial to their success.
-
Facing Floods, Social Entrepreneurs Push Chennai to Consider New Growth Strategy
›Before the 2015 floods that drowned Chennai, Pradeep John spent several years posting thorough and dutifully accurate updates and alerts on Twitter and Facebook as the Tamil Nadu Weatherman. An amateur meteorologist who developed considerable expertise in weather data and satellite imagery, John’s online followers relied on his crisp forecasts and advice.
-
Richard Choularton on 3 Steps to Avert the Famines We See Coming
› There has been great progress in anticipating famines in recent years, with most predicted six or more months ahead of time, says Richard Choularton, senior associate for food security and climate change at Tetra Tech, in this week’s podcast. But action to address their humanitarian impacts has lagged. Responses need to be more consistent and faster, he says, happening “almost without human intervention.”
There has been great progress in anticipating famines in recent years, with most predicted six or more months ahead of time, says Richard Choularton, senior associate for food security and climate change at Tetra Tech, in this week’s podcast. But action to address their humanitarian impacts has lagged. Responses need to be more consistent and faster, he says, happening “almost without human intervention.” -
With Network of River Watchers, Green Hunan Opens Second Front in China’s War on Pollution
›
“Made in China” products surround us, yet few consumers have anything more than a foggy idea of where in China their phones, computers, and other goods come from. Hunan Province in South Central China is not only the home of spicy food, but the world’s largest mines for non-ferrous metals used in many electronic devices. Nearly all the glass panels for Apple and Samsung smartphones are manufactured in Hunan as well. While this multibillion-dollar phone industry has been a boon for Hunan’s economy, it has also produced seriously polluted rivers and soil.
-
Displaced and Disrupted: Closing the Gaps in Maternal Health in Conflicts and Crises
›
Where violent conflict displaces people and disrupts societies, maternal and child health suffers, and such instability is widespread today. According to the UN Refugee Agency, there are 65.3 million forcibly displaced people, 21.3 million refugees, and 10 million stateless people over the world. In addition, more than 65 million people who are not displaced are affected by conflict.
-
Getting to Sustainable Palm Oil: A Hardware and Software Approach to a Market Problem
›
The palm oil sector is at a crossroads. Despite growing awareness of its massive effects on deforestation, the largely unregulated and decentralized industry has struggled to adopt, follow, and document rigorous sustainable sourcing standards.
-
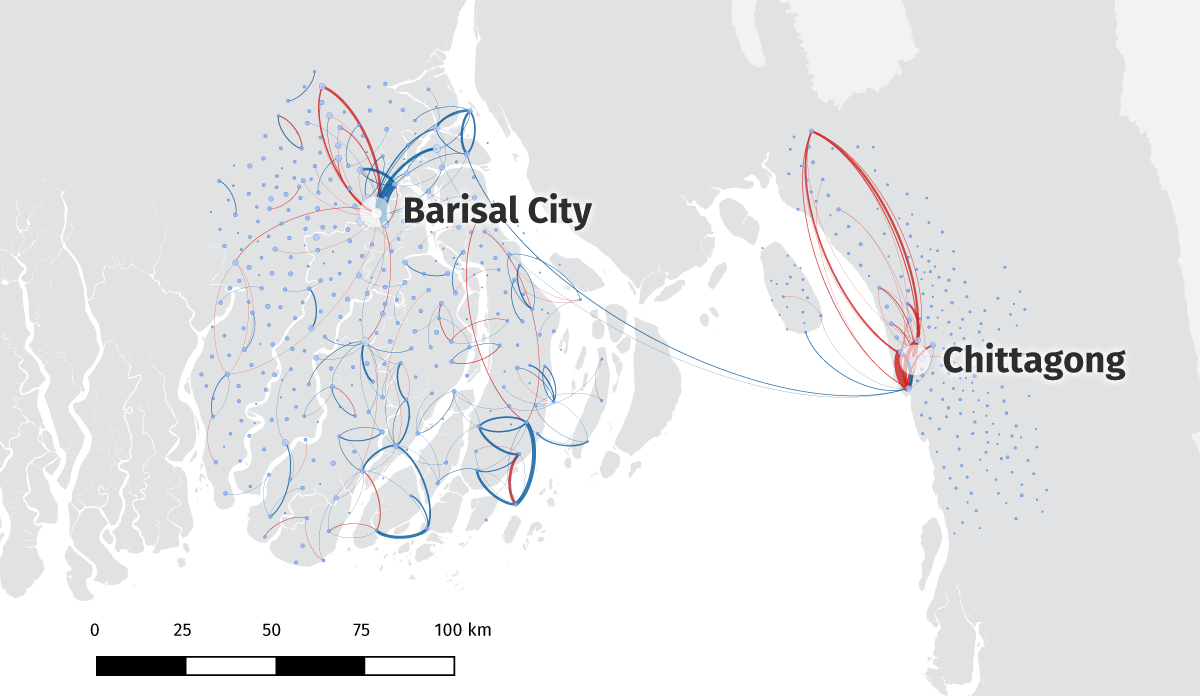
Mobile Phone Data Helps Identify Displaced People Faster, Cheaper, More Accurately
›If we are to avert the worst of climate change impacts, we need better tools for identifying patterns of displacement and migration around climate extremes. In vulnerable developing countries, increasingly frequent and intense storms will likely exacerbate current patterns of displacement and permanent migration. Displacement often leads to humanitarian crises in the short term and can derail progress toward development in the long term. Because of this dangerous potential, displaced persons and migrants are a common focus in humanitarian responses. However disaster responders must often “fly blind” without the benefit of current, accurate information about the worst-affected populations. To better respond to the impacts of climate change as they unfold, we will need more rapid, cost-effective, and accurate methods for identifying patterns of displacement and migration.
-
Tracking China’s “Foul and Filthy” Rivers With Citizen Science
›
Blackened rivers snake the ring roads of Beijing, carrying pollution and often smelly water from one end of the city to another. The most polluted of these have been dubbed “foul and filthy” rivers (黑臭河) by China’s Ministry of the Environment (MEP) and Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development (MOHURD). However, the government has decided to clean these up – and is enlisting the help of the public to do so.
Showing posts from category mobile technology.



 There has been great progress in anticipating famines in recent years, with most predicted six or more months ahead of time, says Richard Choularton, senior associate for food security and climate change at Tetra Tech, in this week’s podcast. But action to address their humanitarian impacts has lagged. Responses need to be more consistent and faster, he says, happening “almost without human intervention.”
There has been great progress in anticipating famines in recent years, with most predicted six or more months ahead of time, says Richard Choularton, senior associate for food security and climate change at Tetra Tech, in this week’s podcast. But action to address their humanitarian impacts has lagged. Responses need to be more consistent and faster, he says, happening “almost without human intervention.”