-
Overlapping Crises: Gender-Based Violence, Maternal Mental Health, and COVID-19
›
According to the World Health Organization, 1 in 3 women in the world will experience physical or sexual violence during their lifetime. Intimate partner violence is the most common form of violence, impacting an estimated 641 million women worldwide. Lockdowns and disruptions in access to support services due to the COVID-19 pandemic have exacerbated the prevalence of gender-based violence (GBV).
-
Going Big on Climate: Opportunities and Challenges Facing the New Administration
›
“With climate change, we can make no small plans—we need to go big,” said Lieutenant General Wallace Gregson (ret.), former Assistant Secretary of Defense for Asian and Pacific Security Affairs, during a recent event co-hosted by the Environmental Peacebuilding Association and Wilson Center on opportunities and challenges facing the new administration relating to the environment, peace, and conflict.
-
Why Cities Matter
›
Do you remember a year ago when many of us traveled regularly? Do you remember the experience of flying into a major city somewhere in the world, picking up your bags in a modern airport (that probably functioned more efficiently than in the United States), and getting a vehicle to take you downtown? After leaving the airport, we would often drive past miles of informal settlements—self-built shelters unkindly called “slums” much of the time. We may have even found ourselves asking why local authorities “don’t do something” about them.
-
A Conversation with Marisa O. Ensor on Securitizing Youth and Youth’s Role in Peace and Security Agendas
› “I’ve been quite impressed by the wide diversity and complexity of young women’s and men’s engagement for peacebuilding and development often while confronting seemingly insurmountable challenges,” says Marisa O. Ensor, Adjunct Professor in the Justice and Peace Studies Program at Georgetown University, in this week’s Friday Podcast.
“I’ve been quite impressed by the wide diversity and complexity of young women’s and men’s engagement for peacebuilding and development often while confronting seemingly insurmountable challenges,” says Marisa O. Ensor, Adjunct Professor in the Justice and Peace Studies Program at Georgetown University, in this week’s Friday Podcast. -
Building Local Capacity for Zero-Waste in the Philippines: Q&A with Break Free From Plastic’s Former Asia-Pacific Coordinator Beau Baconguis
›
Large pollution can come in small packages. This is the case with the small plastic pouches, called sachets, that constitute a major source of the plastic waste crisis plaguing the Philippines, a country ranked third in the world for ocean plastic leakage. Filipino consumers throw away a staggering 163 million of these difficult-to-recycle plastic packets each day, which adds up to about 60 billion a year, enough to carpet 130,000 soccer fields.
-
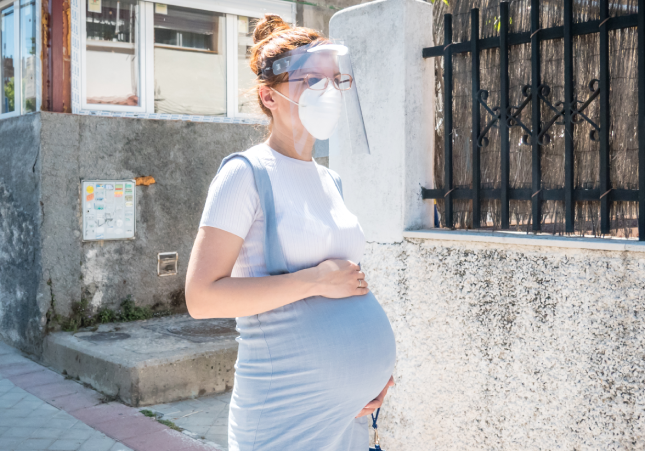
COVID-19’s Pregnancy Paradox: Greater Disease Risk but Lower Vaccine Priority
›
“Greater attention to pregnant patients as a unique population at higher risk of SARS-CoV-2 infection sequelae, is critical to preventing maternal and neonatal morbidity and mortality,” write the authors of a study in the American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology examining morbidity and mortality among pregnant women with COVID-19 in Washington state. The study found “markedly higher” hospitalization and fatality rates among this group compared with similarly-aged non-pregnant individuals.
-
Reviving Culture Through First Nations Midwifery
› “It’s more than just clinical care. It’s cultural. It’s connection to country. It’s connection to land. It’s all of those things that are important to the woman and family, kinship, babies,” says Mel Briggs, a First Nations midwife in Australia, speaking about the importance of Aboriginal midwifery in this week’s Friday Podcast. Like her great-grandmother, Briggs followed the call to midwifery and finds joy in helping women and families “create really healthy, chunky, fat babies.”
“It’s more than just clinical care. It’s cultural. It’s connection to country. It’s connection to land. It’s all of those things that are important to the woman and family, kinship, babies,” says Mel Briggs, a First Nations midwife in Australia, speaking about the importance of Aboriginal midwifery in this week’s Friday Podcast. Like her great-grandmother, Briggs followed the call to midwifery and finds joy in helping women and families “create really healthy, chunky, fat babies.” -
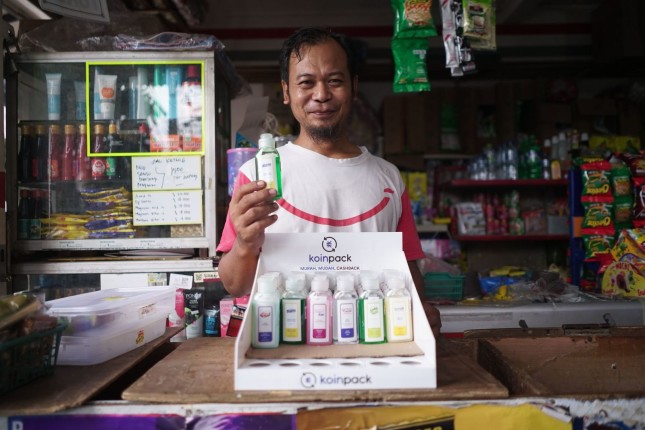
The Circular Business Models Behind Indonesia’s Reuse Revolution
›China Environment Forum // Guest Contributor // March 4, 2021 // By Dieuwertje Nelissen & Tauhid PandjiWaste banks are a cornerstone of Indonesia’s waste reduction efforts. Seeking to prevent plastic waste from getting burned or choking waterways, communities establish these places for people to bring plastic waste to be recycled. It only took a few months to see tangible results at the Bumi Daya Bersih waste bank in West Jakarta. In addition to collecting and sorting waste, the waste bank community is also contributing to waste prevention. A number of regular waste bank customers have started bringing empty plastic packaging that’s not intended to be recycled (yet) but instead refilled with high-quality home and body care products.
Showing posts from category *Main.



 “I’ve been quite impressed by the wide diversity and complexity of young women’s and men’s engagement for peacebuilding and development often while confronting seemingly insurmountable challenges,” says Marisa O. Ensor, Adjunct Professor in the Justice and Peace Studies Program at Georgetown University, in this week’s Friday Podcast.
“I’ve been quite impressed by the wide diversity and complexity of young women’s and men’s engagement for peacebuilding and development often while confronting seemingly insurmountable challenges,” says Marisa O. Ensor, Adjunct Professor in the Justice and Peace Studies Program at Georgetown University, in this week’s Friday Podcast.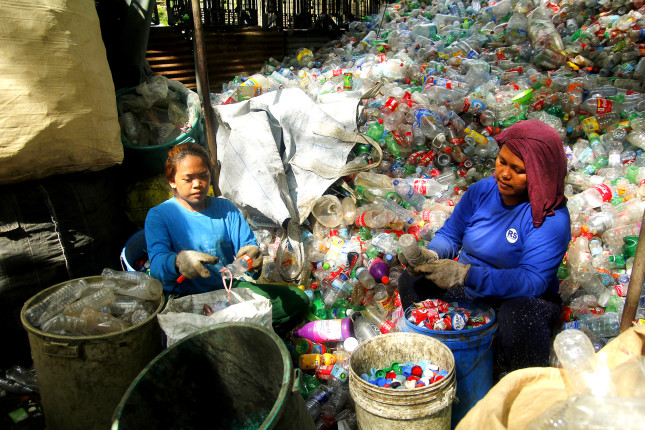

 “It’s more than just clinical care. It’s cultural. It’s connection to country. It’s connection to land. It’s all of those things that are important to the woman and family, kinship, babies,” says Mel Briggs, a First Nations midwife in Australia, speaking about
“It’s more than just clinical care. It’s cultural. It’s connection to country. It’s connection to land. It’s all of those things that are important to the woman and family, kinship, babies,” says Mel Briggs, a First Nations midwife in Australia, speaking about 


