-
How Women’s Leadership Has Uniquely Shaped the Environmental Movement
›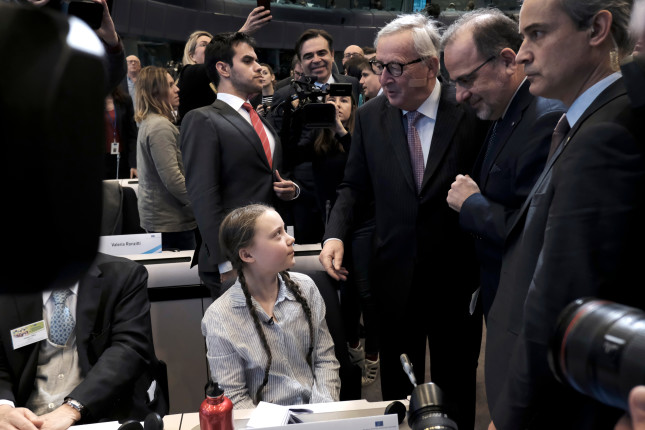
At first glance Greta Thunberg, a Swedish teenager, seems a very unlikely candidate to become arguably the world’s best known environmental activist. Yet despite her youth and lack of advanced degrees or political authority, she has inspired millions of people to join in the effort to combat climate change. Certainly Thunberg is unique in her global reach, but even a cursory history of women’s environmental leadership reveals countless women operating far outside the bounds of conventional government, yet making a meaningful impact.
-
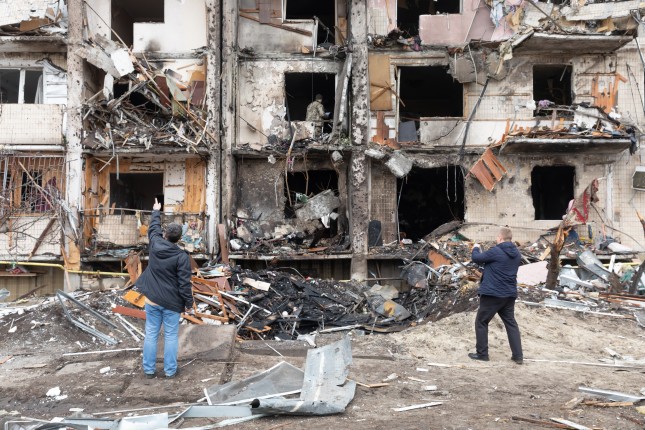
The Environmental Dimensions of the Russian Invasion of Ukraine
›March 4, 2022 // By Wilson Center Staff
Today, the Environmental Peacebuilding Association published an open letter, signed by 902 individuals and 156 organizations from more than 75 countries, to express solidarity with the people of Ukraine in the face of Russia’s invasion and shine a light on some of the environmental risks posed by the invasion that have both short and long-term implications. Below is an excerpt of that letter.
-
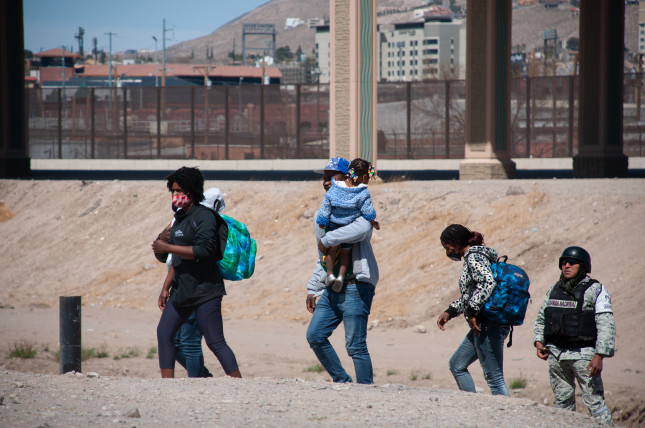
Tethering to Human Rights in the Pushes and Pulls of Human Mobility
›“In the movement toward complex solutions, at the heart of it all we’re talking about individuals with their own complex issues as they are moving through different scenarios,” said Shanna McClain, Disasters Program Manager with the National Atmospheric and Space Administration, at last month’s International Conference on Environmental Peacebuilding. The panel discussion, “Resource Implications of Human Mobility and Migration,” focused on what data shows—and doesn’t show—are the complex linkages between climate, conflict, and mobility. Panelists discussed how more integrated programming and policy actions are needed to make migration safe, orderly, and voluntary, and how to keep human rights at the center of the complex processes.
-
The Lasting Effects of the COVID-19 Pandemic on Women’s Work, Health, and Safety (New Report)
›
While the COVID-19 pandemic has affected the lives of many around the world, its effects on women have been particularly devastating. Even before the pandemic, women are highly affected by violence. Since the pandemic, rates of gender-based violence have risen, while uptake of critical health services have decreased. Women, especially low-income women, women of color, and migrant women, are also more likely to work in jobs that are underpaid, undervalued, and unprotected, and they comprise the majority of the frontline or “essential” workforce, which includes grocery and food retail workers, health care workers, and care workers.
-
Hydropolitics in the Russian – Ukrainian Conflict
›
It’s telling that one of the first actions that Russian forces took in their invasion of Ukraine was to blow up a dam on the North Crimean Canal (NCC), allowing water to flow back into Crimea. The current war being waged by Russia in Ukraine has its origins in fractured and contested political history, but there are also key natural resource security questions which often go overlooked. While there are established debates about the extent to which natural resources contribute to conflict, the current conflagration exemplifies a rare use of water as a means of direct leverage in a military standoff. Regardless of the outcome of the conflict, the tensions between Russia and Ukraine over the NCC illustrate the need to consider the role of natural resources—and access to them—in broader diplomatic efforts.
-
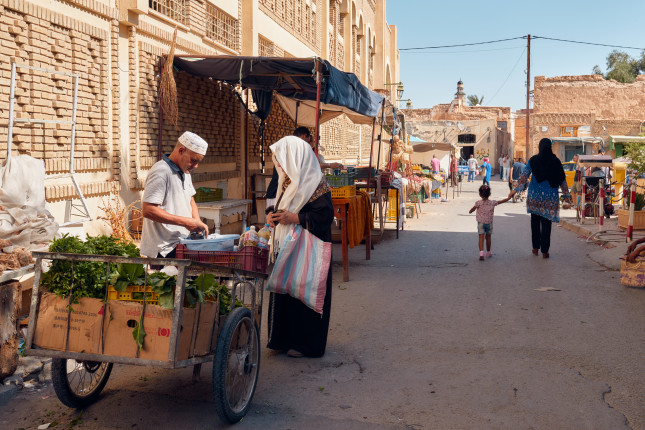
Migrating to Adapt to Climate Change, Tunisians Lose Their Way of Life
›
“After a series of poor harvests, limited rainfall, and an increase in the price of fertilizer, farm work has become unprofitable,” said Lazher, a fellah (agricultural laborer) from Tataouine in the rural south east of Tunisia. The 45-year-old had worked the land for half his life, even dropping out of school early to support his young family. However, when I met Lazher in December 2021, he was making the final arrangements to migrate to Tunisia’s capital, Tunis, in search of better job opportunities. Now, with diminishing local opportunities for agricultural work and few local companies that might hire unemployed laborers, Lazher secured work in one of Tunis’s many dried fruit shops called hamas.
-
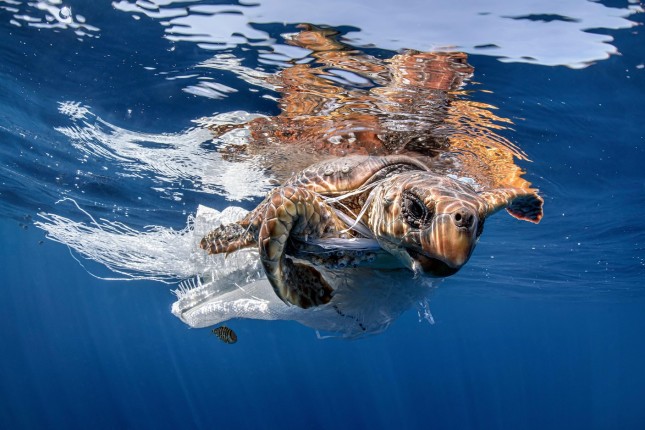
UN Meeting Sets Sights on Global Plastics Treaty
›
In Nairobi this month, the world’s governments will discuss the path towards the first global treaty to tackle plastic pollution. But with multiple proposals on the table, the scope and ambition of a potential treaty hangs in the balance.
-
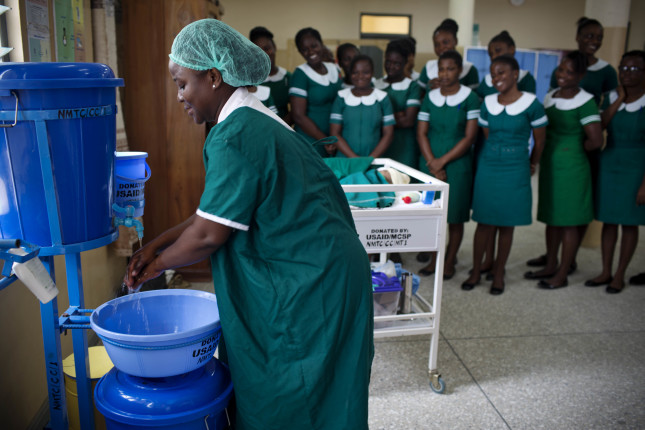
No Progress Without Quality: Why Quality of Care Matters
›
Evidence shows that in low- and middle-income countries, the expansion of health coverage or access to care has not always reduced overall mortality, said Dr. Patricia Jodrey, Child Health Team Lead in the Office of Maternal and Child Health and Nutrition at the U.S. Agency for International Development (USAID). “However, the analysis also showed that when countries have progressed in improving the quality of their health systems, the survival rate tends to improve,” she said.
Showing posts from category *Main.