-
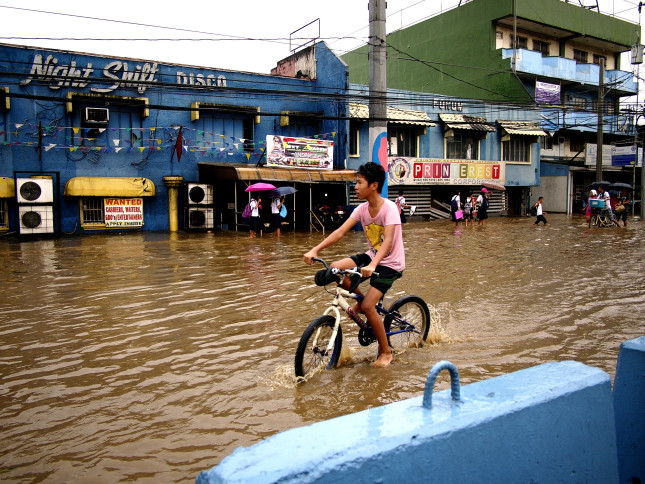
COVID-19 Adds to Challenges of Curbing Child Marriage
›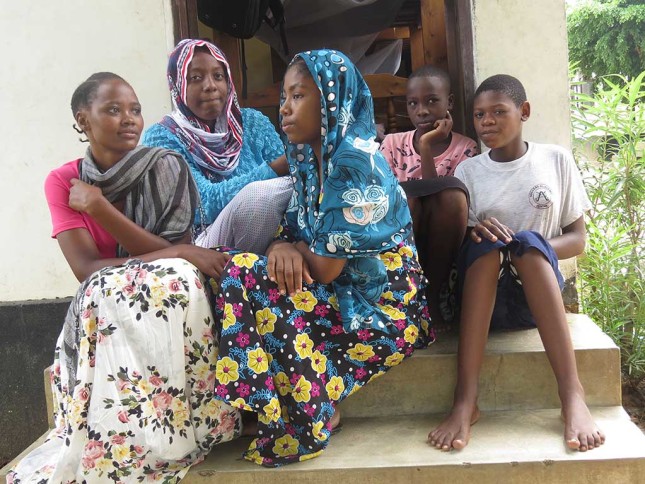
When Mwanahamisi Abdallah’s mother announced plans to marry her off to a stranger, the 14-year-old Tanzanian girl burst into tears. She had no desire to marry—especially after learning the man already had three wives. Remembering advice from a teacher, she phoned authorities to intervene. They blocked the wedding and eventually delivered Mwanahamisi from her village in southeastern Lindi region to a girls’ shelter in Dar es Salaam.
-
Earth Intel: Enhancing Researcher-Practitioner Partnerships to Address Eco-Security Challenges
›
“One of the most important accomplishments of the MEDEA program was to convince the intelligence community that near-term climate change is important for national security,” said D. James Baker, former Administrator of the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) and member of the MEDEA Program, at a panel at the American Geophysical Union’s virtual 2020 Fall Meeting. Organized by ISciences LLC’s Tom Parris, CASE Consultants International’s Eileen Shea, and Columbia University’ Robert Chen, the panel focused on how to build an effective knowledge-to-action enterprise that helps policymakers and society respond to emerging eco-security challenges. (See below for links to short, pre-recorded videos panelists shared prior to the panel to inform the discussion.)
-
The Climate and Ocean Risk Vulnerability Index: Measuring Coastal City Resilience to Inform Action
›Guest Contributor // January 26, 2021 // By Jack Stuart, Sally Yozell, Miko Maekawa & Nagisa Yoshioka
As the climate crisis continues to worsen, climate finance remains a fraction of what is needed. The Climate Policy Initiative estimates that $579 billion was spent on average on climate finance in 2017/18. This includes domestic and international investment from both the public and private sectors towards climate mitigation and adaptation actions. Of this amount, only $30 billion—five percent—was allocated for climate adaptation. This amount stands in stark contrast to $180 billion, which the Global Commission on Adaptation estimates is needed every year to build resilience to current and future climate impacts. This catastrophic funding gap is intensifying climate security threats and elevating the vulnerability of people across the world, particularly in coastal urban centers.
-
The Third Wave of Environmental Peacebuilding
›
For most of 2020, news, politics, policy, and research in the United States and abroad were dominated by the challenges posed by COVID-19, a rapidly unfolding global pandemic unprecedented in scale and cost. For much of the world, however, COVID-19 in fact competed with many other highly destructive events including a cascade of environmental disasters. Swarms of locusts pushed much of the Horn of Africa into or close to famine; 30 severe storms including Hurricanes Iota and Eta battered the Atlantic coasts; some 4 million acres of forest burned to the ground in California, doubling the previous high reached in 2018; typhoons ravaged the Philippines; floods overwhelmed parts of Indonesia; and many regions around the world experienced devastating heat waves. In addition to disaster patterns, the trends in violent state conflict were equally alarming, reaching their highest level since the end of World War II, according to a 2020 report on conflict trends from PRIO. In the most violent conflicts, in Syria and Yemen, the impacts of war have been amplified and complicated by the impacts of drought and years of environmental mismanagement.
-
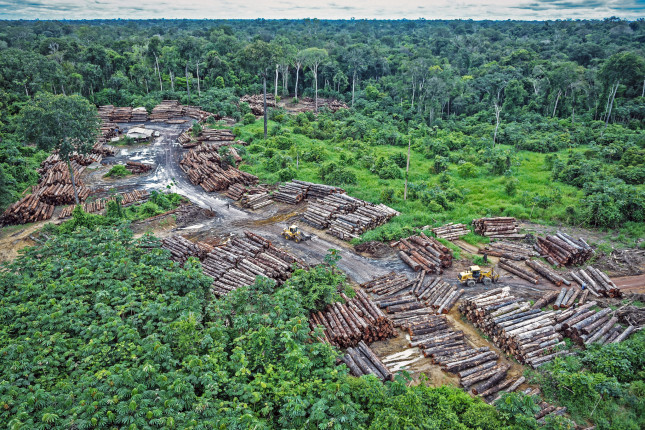
Climate Change Front and Center in U.S. and Brazil Relations in Biden-Bolsonaro Era
›
As the warm relationship between U.S. President Donald Trump and Brazil President Jair Bolsonaro comes to an end with the former’s electoral defeat in November 2020, the next two years (Bolsonaro is up for reelection in 2022) could prove to be strenuous for the bilateral relations of the two largest economies in the Western Hemisphere. President-elect Biden has signaled that combatting climate change will be a priority in his administration. Now, without the cover of a U.S. administration that denies climate change, Brazil could become further isolated in international environmental politics. All of this complicates the political realities for President Bolsonaro, whose political survival depends on maintaining his coalition of fanatical supporters, the agricultural sector, and former and current members of the military. Still, given U.S. concerns about Chinese influence in the region, the Biden-Bolsonaro relationship could prove to be low-key and practical.
-
Putting a Lid on Fish Boxes and Other Foamed Polystyrene Marine Debris
›Where the murky brown waters of the Pearl River meet the opaque green South China Sea, a trail of floating plastic debris is gathered by the currents as they flow past Macao, Shenzhen, and Hong Kong. I first noticed this floating litter while standing on the deck of a research vessel in 2017, scanning the waves off the western coast of Lantau island for signs of Indo-Pacific humpback dolphins as part of a monitoring program run by the Hong Kong Dolphin Conservation Society. A glimpse of these rare animals was often overshadowed by the foamed polystyrene pollution (also known as expanded polystyrene (EPS) or by the proprietary name Styrofoam) from fish boxes and fishing buoys. And this was not just a problem in the water; as we conducted surveys between Hong Kong’s islands, we passed beaches covered in white plastic, strewn along the shoreline like snow.
-
How We Misunderstand the Magnitude of Climate Risks – and Why That Contributes to Controversy
›
For years, analysts have disputed the extent of climate change’s role in conflict. But the nature of climate risks can stifle those looking to define them.
The Syrian civil war has raged for almost a decade now, and in the climate security community it can feel as if we’ve spent at least that long arguing about its causes. For every claim about the impact of extreme drought in the lead up to 2011, there’s been blowback, with some scholars arguing that the climate angle has been exaggerated at the expense of other causes of the conflict. And for every argument about rural-to-urban migration, there have been suggestions that its impact in precipitating protests has been overstated. Amid some overly forceful media assertion about the significance of climate change—and valid fears that invoking the environment might be seen as absolving guilty parties, despite efforts to highlight the regime’s ultimate culpability—climate security analysts have struggled to fully pinpoint climate’s precise contribution to the conflict. Cue uncertainty, controversy, and sometimes fierce academic polemics.
-
Michael Standaert, Ensia
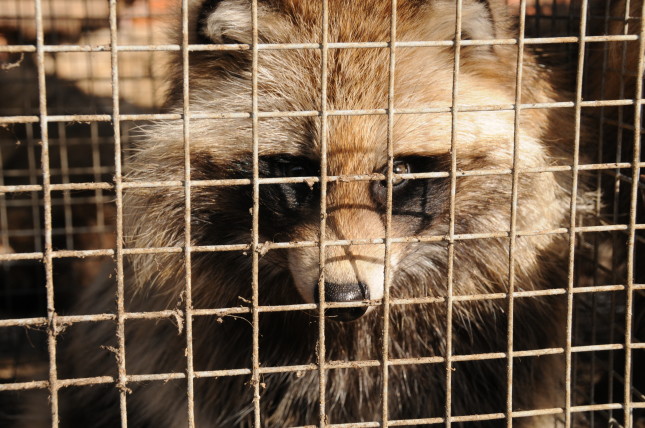
How effective are China’s attempts to reduce the risk of wildlife spreading disease to humans?
›
Nearly a year ago, somewhere in China, a previously unknown virus made its way from a wild animal into a human host. There it found not only a hospitable home, but also an opportunity to spread trillions of copies of itself, eventually replicating to become the global Covid-19 pandemic.
That outbreak, now having infected more than 46 million people around the world, has been the impetus for a series of actions taken by the Chinese government to — in theory — get a handle on zoonotic disease outbreaks now and in the future.
Showing posts from category Guest Contributor.