-
India’s Maoists: South Asia’s “Other” Insurgency
›July 7, 2010 // By Schuyler Null
The Indian government’s battle with Maoist and tribal rebels – which affects 22 of India’s 35 states and territories, according to Foreign Policy and in 2009 killed more people than any year since 1971 – has been largely ignored in the West. That should change, as South Asia’s “other” insurgency, fomenting in the world’s largest democracy and a key U.S. partner, offers valuable lessons about the role of resource management and stable development in preventing conflict.
-
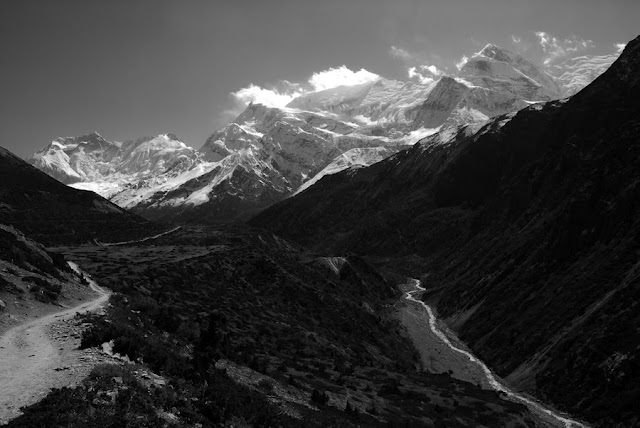
Is the Third Pole the Next Site for Water Crisis?
›July 1, 2010 // By Tara InnesThe Hindu-Kush Himalaya area may host future water crises as glaciers melt, population rapidly increases, and competition over scarce water resources intensifies, says a recent report from the Humanitarian Futures Programme at King’s College.
Himalayan glaciers – often called the “third pole” because they house the greatest volume of frozen water outside the polar regions – provide the headwaters for 10 major river systems in Asia. Despite clear evidence that the HKH glaciers are receding, recent controversy over the 2007 IPCC report has sidetracked the discussion from the degree of glacial melt and its impacts on the surrounding environment.
Glacial melt sends more water into the rivers in the rainy season, and less water in the dry season. This variability will increase both floods and droughts, which in turn can damage agriculture and create food shortages. Melting glaciers can also create “glacial lakes” that are prone to sudden bursting, causing disastrous flooding downstream (ppt).
According to The Waters of the Third Pole: Sources of Threat, Sources of Survival, climate change is already having significant impacts in the Himalayan region, intensifying natural disasters and the variability of the summer monsoon rains, and increasing the number of displaced people and government attempts to secure water supplies from its neighbors.
Rivers of People: Environmental Migrants
One of the major consequences, the report argues, could be “growing numbers of environmental migrants,” which the authors define as “people moving away from drying or degraded farmland or fisheries, and the millions displaced by ever-larger dams and river-diversion projects”—and including the Chinese government’s forced “‘re-location of people from ecologically fragile regions.”
Today, about 30 million (15 percent) of the world’s migrants are from the Himalayan region, the report says, warning that “in the next decade, should river flows reduce significantly, migration out of irrigated areas could be massive.” But the authors acknowledge that reliable estimates are rare – a problem pointed out in The New Security Beat.
However, it is clear that the region’s population is growing and urbanizing rapidly: By 2025, one-half of all Asians will live in cities, whereas one generation ago, the figure was one in 10. This incredible shift, says the report, places “some of the greatest pressures on water through increased demand and pollution.”
Water War or Water Peace?
The Waters of the Third Pole warns that growing scarcity could “raise the risk of conflict in a region already fraught with cross-border tensions.” While interstate tensions over water have been minimal to date, they could potentially increase in areas where significant percentages of river flow originate outside of a country’s borders – in 2005 Bangladesh relied on trans-boundary water supplies for 91 percent of its river flow, Pakistan for 76 percent, and India for 34 percent. Intra-state conflict is also expected to increase. The report notes, “In China alone, it has been reported that domestic uprisings have continued to increase in protest about water management or water-quality issues.”
However, the water-conflict link remains shaky within the scholarly community. As Dabelko recently told Diane Rehm about the region, “There are prospects for tensions, but quite frankly, water is difficult to [obtain] through war. It’s hard to pick it up and take it home.”
The report points out some areas in which water may actually pose an opportunity for regional cooperation rather than conflict, such as developing knowledge-sharing networks like the International Center for Integrated Mountain Development. The presence of such networks may help establish channels of communication and aid in diffusing other cross-border tensions. But the authors caution that “environmental cooperation generally lags far behind economic cooperation in the HKH region.”
The report concludes that policymakers must move the region higher on the humanitarian agenda; construct a framework for action that includes non-intrusive international support; and more thoroughly address knowledge and communication gaps.
Photo Credit: “Annapurna ways, Nepal,” courtesy of flickr user rakustow. -
U.S. Navy Task Force on Implications of Climate Change
›What about climate change will impact us? That’s the question the Navy’s Task Force Climate Change is trying to answer. Rear Admiral David Titley explains the task force’s objectives in this interview by the American Geophysical Union (AGU) at their recent “Climate Change and National Security” event on the Hill.
The task force is part of the military’s recent efforts to try to better understand what climate change will mean for the armed forces, from rising sea levels and ocean acidification to changing precipitation patterns. In the interview, Admiral Titley points out that for the Navy in particular, it is important to understand and anticipate what changes may occur since so many affect the maritime environment.
The Navy’s biggest near-term concern is the Arctic, where Admiral Titley says they expect to face significant periods of almost completely open ocean during the next two to three decades. “That has huge implications,” says Titley, “since as we all know the Arctic is in fact an ocean and we are the United States Navy. So that will be an ocean that we will be called upon to be present in that right now we’re not.”
Longer term, the admiral points to resource scarcity and access issues and sea level rise (potentially 1-2 meters) as the most important contributing factors to instability, particularly in places like Asia, where even small changes can have huge impacts on the stability of certain countries. The sum of these parts plus population growth, an intersection we examine here at The New Security Beat, is something that deserves more attention, according to Titley. “The combination of climate, water, demographics, natural resources – the interplay of all those – I think needs to be looked at,” he says.
Check out the AGU site for more information, including an interview with Jeffrey Mazo – whose book Climate Conflict we recently reviewed – discussing climate change winners and losers and the developing world (hint: the developing world are the losers).
Sources: American Geophysical Union, New York Times.
Video Credit: “What does Climate Change mean for the US Navy?” courtesy of YouTube user AGUvideos. -
Interview With Wilson Center Scholar Jill Shankleman: Could Transparency Initiatives Mitigate the Resource Curse in Afghanistan?
›June 25, 2010 // By Schuyler Null
In the wake of The New York Times article detailing a potential mineral bonanza in Afghanistan, Senators Ben Cardin and Dick Lugar earlier this week published an op-ed in support of a bill that would create “an international standard for transparency in law” by requiring oil, gas, and mining industries to report amounts paid for drilling/mining rights in their SEC filings. A similar program, albeit a voluntary one, already exists – the Extractive Industries Transparency Initiative (EITI). The senators, however, raised questions about the ability of EITI to ensure transparency and accountability of payments for future mining rights to Afghanistan’s government. Joining EITI was a “good first step,” they say, “but too many countries and companies remain outside this system.”
-
Backdraft: The Conflict Potential of Climate Mitigation and Adaptation
›The European Union’s biofuel goal for 2020 “is a good example of setting a target…without really thinking through [the] secondary, third, or fourth order consequences,” said Alexander Carius, co-founder and managing director of Adelphi Research and Adelphi Consult. While the 2007-2008 global food crisis demonstrated that the growth of crops for fuels has “tremendous effects” in the developing world, analysis of these threats are underdeveloped and are not incorporated into climate change policies, he said. [Video Below]
-
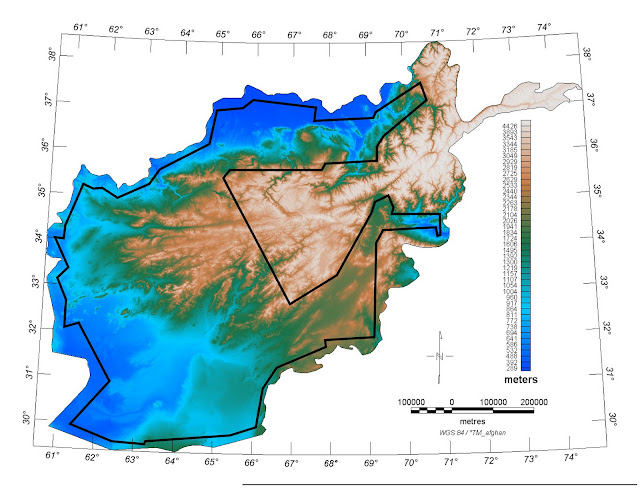
Afghanistan’s Mineral Wealth: Gold Mine, Curse, or Illusion?
›June 15, 2010 // By Schuyler NullAccording to The New York Times, U.S. officials have discovered a veritable bonanza of heavy metals and rare earth minerals in Afghanistan that have the potential “to fundamentally alter the Afghan economy and perhaps the Afghan war itself”:The previously unknown deposits — including huge veins of iron, copper, cobalt, gold and critical industrial metals like lithium — are so big and include so many minerals that are essential to modern industry that Afghanistan could eventually be transformed into one of the most important mining centers in the world, the United States officials believe.
Reaction to the announcement has been mixed, with both Foreign Policy and Wired bloggers expressing skepticism about the timing of the announcement – in the midst of a difficult period of the war – and pointing out that the “discovery” is old news.
Others have expressed hope that the find, worth an estimated $1 trillion, might provide an injection of much-needed capital into one of the world’s worst economies. Environmental security expert Saleem Ali of the University of Vermont told Public Radio International’s The World that “there’s an opportunity now for the country to develop outside of a predominantly drug-dependent economy and if properly managed the minerals could provide a catalyst for all kinds of other activities as well.”
Afghanistan’s rare earth minerals in particular might prove to be extremely valuable as global demand continues to grow for these critical components of renewable energy technology and advanced electronics. The New York Times reports that an internal Pentagon memo says Afghanistan has the potential to become the “Saudi Arabia of lithium”:Just this month, American geologists working with the Pentagon team have been conducting ground surveys on dry salt lakes in western Afghanistan where they believe there are large deposits of lithium. Pentagon officials said that their initial analysis at one location in Ghazni Province showed the potential for lithium deposits as large of those of Bolivia, which now has the world’s largest known lithium reserves.
The existence of mineral reserves in Afghanistan is not new news, nor is foreign interest in them (see our coverage of Chinese copper investments at Aynak earlier this year). But the size of these resources warrants attention and raises new questions about the possibility of the unstable country falling victim to the natural resource curse – remaining mired in poverty while generating billions of dollars for an elite few.
Mineral wealth has a long history of fueling conflict in unstable countries, such as Sierra Leone, Nigeria, and the Democratic Republic of Congo. The DRC’s mining laws – which, like Afghanistan’s, were designed by the World Bank – have not prevented violent struggle to control the country’s valuable resources, as described by John Katunga in ECSP Report 12.
How can Afghanistan’s newly discovered mineral resources be developed without funding insurgents or fueling new conflicts? USAID’s Minerals and Conflict Toolkit offers a start with a set of recommendations and discrete steps that development agencies should take to avoid exacerbating the links between mining, valuable resources, and violent conflict.
Stay tuned for more analysis on Afghanistan’s development, resource curse dynamics, and what this all means for the continuing conflict.
Sources: Foreign Policy, National Public Radio, The New York Times, Public Radio International, Wired.
Photo Credit: “Remote Sensing Survey 2006” courtesy of the U.S. Geological Survey. -
Political Rhetoric or Policy Reality? Tracking Trends in Environment, Peace, and Security
›May 21, 2010 // By Wilson Center StaffECSP Director Geoff Dabelko lectures at UC Irvine’s Sustainability Seminar Series.
Over the past 25 plus years, the understanding of environment and security links has evolved to reflect changing threat and opportunity scenarios. Today, “environmental security” has become a popular phrase used to encompass everything from oil exploration to pollution controls to corn subsidies.
While environmental advocates and security actors remain wary of each other’s focus, means, and ends, both scholars and policymakers are working to better understand these linkages and respond to them. Today, the wide range of potential climate change impacts is re-energizing broader debates over human security that suggest redefining security beyond purely militaristic terms.
At the same time, the traditional security community’s increased concern with climate change (and the social reactions it may produce) has helped garner wider attention. The number of U.S. and overseas policy responses is dizzying. In this lecture–part of the Sustainability Seminar Series at the UC-IrvineCenter for Unconventional Security Affairs–the Wilson Center’s Geoff Dabelko highlights key environmental security policy developments and situates today’s initiatives within a context of nearly three decades of efforts.
Video courtesy of OpenCourseWare at University of California, Irvine. -
As Somalia Sinks, Neighbors Face a Fight to Stay Afloat
›May 14, 2010 // By Schuyler NullThe week before the international Istanbul conference on aid to Somalia, the UN’s embattled envoy to the country, Ahmedou Ould-Abdallah, warned the Security Council that if the global community “did not take the right action in Somalia now, the situation will, sooner or later, force us to act and at a much higher price.”
The UN High Commission for Refugees (UNHCR) also issued strong warnings this week. Deputy High Commissioner Alexander Aleinikoff said in Geneva, “The displacement crisis is worsening with the deterioration of the situation inside Somalia and we need to prepare fast for new and possibly large-scale displacement.”
But the danger is not limited to Somalia. The war-torn country’s cascading set of problems – criminal, health, humanitarian, food, and environmental – threaten to spill over into neighboring countries.
A Horrendous Humanitarian Crisis
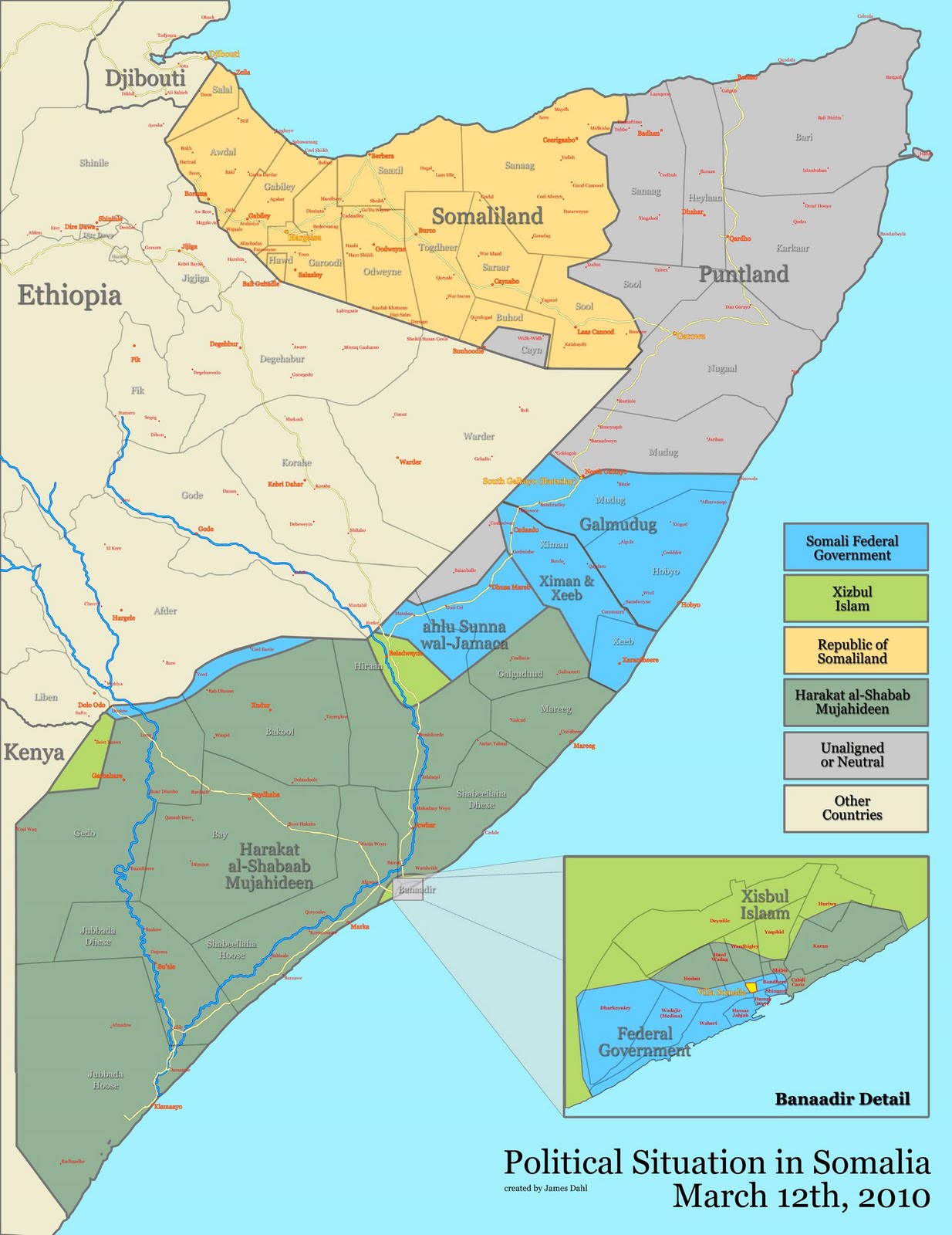
The UN- and U.S.-backed Transitional Federal Government (TFG) controls only parts of Mogadishu and small portions of central Somalia, while insurgent group Al Shabab controls nearly the entire south. The northern area is divided into semi-autonomous Somaliland and Puntland, which also fall outside of the transitional government’s control.
But the civil war is only one part of what Ould-Abdallah called a “horrendous” humanitarian crisis.
According to the UN, 3.2 million Somalis rely on foreign assistance for food – 43 percent of the population – and 1.4 million have been internally displaced by war. Another UN-backed study finds that approximately 50 percent of women and 60 percent of children under five are anemic. Most distressing, the UN Security Council reported in March that up to half of all food aid sent to Somalia is diverted from people in need by militants and corrupt officials, including UN and government employees.
Because of the country’s large youth bulge – 45 percent of Somalia’s population is under the age of 15 – food and health conditions are expected to get much worse before they get better. In the 2009 Failed States Index, Somalia ranks as the least stable state in the world and, along with Zimbabwe, has the highest demographic pressures.
Islamic Militants and the Battle for the High Seas
Yet the West continues to focus on the sensational pirate attacks on Somalia’s coast. The root cause of these attacks is not simply lawlessness say Somali officials, instead, they began partly as desperate attempts to stop foreign commercial fleets from depleting Somalia’s tuna-rich, lawless shores. A 2006 High Seas Task Force reported that at any given time, “some 700 foreign-owned vessels are engaged in unlicensed and unregulated fishing in Somali waters, exploiting high value species such as tuna, shark, lobster and deep-water shrimp.”
The transitional government opposes the fishermen-turned-pirates, but can do little to stop them. Al Shabab has thus far allowed pirates to operate freely in their territory. Their tacit approval may be tied to reports that the group has received portions of ransoms in the past.
Another hardline Islamist group, Hizbul Islam, recently took over the pirate safe haven of Haradhere, allegedly in response to local pleas for better security, but the move may simply have been part of an ongoing struggle with Al Shabab for control of pirate ransoms and port taxes – one of the few sectors of the economy that has remained lucrative.
“I can say to you, they are not different from pirates — they also want money,” Yusuf Mohamed Siad, defense minister with Somalia’s TFG, told Time Magazine.
A Toxic ThreatInitially the pirates claimed one of their goals was to ward off “mysterious European ships” that were allegedly dumping barrels of toxic waste offshore. UN envoy Ould-Abdallah told Johann Hari of The Independent in 2009 that “somebody is dumping nuclear material here. There is also lead, and heavy metals such as cadmium and mercury – you name it.” After the 2005 tsunami, “hundreds of the dumped and leaking barrels washed up on shore. People began to suffer from radiation sickness, and more than 300 died,” Hari reports.
Finnish Minister of Parliament Pekka Haavisto, speaking to ECSP last year, urged UN investigation of the claims. “If there are rumors, we should go check them out,” said the former head of the UN Environment Program’s Post-Conflict Assessment Unit:I think it is possible to send an international scientific assessment team in to take samples and find out whether there are environmental contamination and health threats. Residents of these communities, including the pirate villages, want to know if they are being poisoned, just like any other community would.
To date, there has been no action to address these claims.
Drought, Deforestation, and Migration
While foreign entities may have been exploiting Somalia’s oceans, the climate has played havoc with the rest of the country. Reuters and IRIN report that the worst drought in a decade has stricken some parts of the interior, while others parts of the country face heavy flooding from rainfall further upstream in Ethiopia.
Land management has also broken down. A 2006 Academy for Peace and Development study estimated that the province of Somaliland alone consumes up 2.5 million trees each year for charcoal, which is used as a cheaper alternative to gas for cooking and heating. A 2004 Somaliland ministry study on charcoal called the issue of deforestation for charcoal production “the most critical issue that might lead to a national environmental disaster.”
West of Mogadishu, Al Shabab has begun playing the role of environmental steward, instituting a strict ban on all tree-cutting – a remarkable decree from a group best known for their brutal application of Sharia law rather than sound governance.
The result of this turmoil is an ever-increasing flow of displaced people – nearly 170,000 alone so far this year, according to the Washington Post – driven by war, poverty, and environmental problems. The burden is beginning to weigh on Somalia’s neighbors, says the UNHCR.
The Neighborhood Effect
One of the largest flows of displaced Somalis is into the Arabian peninsula country of Yemen – itself a failing state, with 3.4 million in need of food aid, 35 percent unemployment, a massive youth bulge, dwindling water and oil resources, and a burgeoning Al Qaeda presence.
In testimony on Yemen earlier this year, Assistant Secretary of State Jeffrey Feltman said that the country’s demographics were simply unsustainable:Water resources are fast being depleted. With over half of its people living in poverty and the population growing at an unsustainable 3.2 percent per year, economic conditions threaten to worsen and further tax the government’s already limited capacity to ensure basic levels of support and opportunity for its citizens.
Other neighboring countries face similar crises of drought, food shortage, and overpopulation – Ethiopia has 12 million short of food, Kenya, 3.5 million, says Reuters. UNHCR reports that in Djibouti, a common first choice for fleeing Somalis, the number of new arrivals has more than doubled since last year, and the country’s main refugee camp is facing a serious water crisis.
A Case Study in Collapse
The ballooning crises of Somalia encompass a worst-case scenario for the intersection of environmental, demographic, and conventional security concerns. Civil war, rapid population growth, drought, and resource depletion have not only contributed to the complete collapse of a sovereign state, but could also lead to similar problems for Somalia’s neighbors – threatening a domino effect of destabilization that no military force alone will be able to prevent.
Speaking at a naval conference in Abu Dhabi this week, Australian Vice Admiral Russell Crane told ASD News that, “The symptoms (piracy) we’re seeing now off Somalia, in the Gulf of Aden, are clearly an outcome of what’s going on on the ground there. As sailors, we’re really just treating the symptoms.”
Sources: Academy for Peace and Development, AP, ASD News, Carnegie Endowment for International Peace, Christian Science Monitor, Foreign Policy, High Seas Task Force, Independent, IRIN, New York Times, Population Action, Population Reference Bureau, Reuters, Telegraph, Time, UN, US State Department, War is Boring, Washington Post.
Photo Credits: “Don’t Swim in Somalia (It’s Toxic)” courtesy of Flickr user craynol and “Somalia map states regions districts” courtesy of Wikimedia Commons.
Showing posts from category environmental security.