Showing posts from category environment.
-
Rich Thorsten on Water Sanitation, Population, and Urbanization in the Developing World
› “For the first time in human history, more than one half of the world’s population now lives in urban areas, and some of the largest and fastest growing population centers in the world – countries like India, China, parts of sub-Saharan Africa – are in areas where water resources are becoming more and more scarce,” said Water.org’s Rich Thorsten in a recent interview with ECSP.
“For the first time in human history, more than one half of the world’s population now lives in urban areas, and some of the largest and fastest growing population centers in the world – countries like India, China, parts of sub-Saharan Africa – are in areas where water resources are becoming more and more scarce,” said Water.org’s Rich Thorsten in a recent interview with ECSP.
Thorsten serves as director of international programs for Water.org, which partners with local communities, governments, and NGOs across Central America, South Asia, and Africa to bring improved water sanitation to at-need rural and urban populations. He emphasized that ensuring access to clean water has a number of positive spillover effects, ranging from improved prospects for economic development to greater social stability, since access to non-polluted water supplies removes one potential source of tension within and between communities.
Community Health
The greatest benefit of improved sanitation services, however, comes in the form of enhanced public health outcomes. “I would definitely say there is a strong correlation” between the two, Thorsten asserted. “Water and sanitation-related diseases are related to the deaths of at least 3.5 million people every year in the developing world – not to mention millions of hours and dollars that are lost to treating health problems and coping with health problems as a result of poor [water] access and hygiene practices.”
Thorsten said that community participation has been a key aspect of ensuring the sustainability of Water.org’s projects. To pave the way for continued gains in economic development and public health, he said they work alongside water users, engineers, and government officials in target communities to make those parties stakeholders in the infrastructure development process. Fostering a sense of community ownership of sanitation projects helps reduce the likelihood that infrastructure will fall into disrepair or disuse after the initial programming intervention has been conducted.
Given that improving water-sanitation access for the world’s poor is a key element of the UN Millennium Development Goals, Thorsten said he is pleased the subject seems to be attracting more attention within the policymaking and development communities. Despite the positive momentum, however, he acknowledged the fight to ensure clean-water access for the developing world will remain an uphill battle.
“When one considers that….about 2.6 billion people lack access to basic sanitation, that there’s more people in the world that have access to a cell phone than a pit latrine or a toilet, it’s still a very daunting task that will require a lot more investment, commitment, and attention in order to improve the situation for billions of people,” Thorsten said.
Sources: UN.
The “Pop Audio” series is also available as podcasts on iTunes. -
Alex Evans, Global Dashboard
Is it Time for Sustainable Development Goals?
›September 8, 2011 // By Wilson Center StaffThe original version of this article, by Alex Evans, appeared on Global Dashboard.
From MDGs to…SDGs? That’s one of the ideas swirling around in discussions ahead of the Rio 2012 sustainable development summit next year, anyway.
You can see the attraction. With less than a year to go, there are precious few concrete ideas on the table for what the summit might produce, especially in the area of “institutional framework for sustainable development,” one of two key themes for the event (sure, there’s much talk of a new World Environment Organization, but color me very unconvinced of the case for that). So might SDGs help to fill the gap?
Well, that would depend on what they cover. The government of Colombia has set out a proposal for SDGs that would cover various sectors – atmosphere, climate resilience, land degradation, sustainable agriculture, biotech, waste and so forth. This would mainly be about ‘reaffirming’ (that awful word – who, other than diplomats, ever ‘reaffirms’ anything?) commitments made at Rio 1992. But you have to wonder: important though delivery of existing commitments undoubtedly is, is ‘reaffirmation’ of stuff agreed 20 years ago really going to set any pulses racing outside the sustainable development priesthood?
Continue reading on Global Dashboard.
Sources: UN.
Image Credit: Adapted from UNSCD 2012 official logo. -
Watch: Don Lauro on How Integrated Development Deepens Community Involvement
›September 7, 2011 // By Schuyler Null Population, health, and environment (PHE) projects address an impressive range of issues – natural resource management, family planning, maternal and child health, water, sanitation, nutrition, and strengthening health systems – but perhaps their most important advantage is the level of community involvement elicited, said long-time PHE expert Don Lauro in an interview with ECSP.
Population, health, and environment (PHE) projects address an impressive range of issues – natural resource management, family planning, maternal and child health, water, sanitation, nutrition, and strengthening health systems – but perhaps their most important advantage is the level of community involvement elicited, said long-time PHE expert Don Lauro in an interview with ECSP.
“There’s a depth to these programs,” Lauro said. Tools like rural participatory appraisal allow communities to map out their problems and then come up with solutions on their own. “If you get deep enough, it becomes they who own the project, and I think that that’s your ultimate goal,” he explained. “You have a much greater prospect for sustainability of that effort, no matter what happens to the funding.”
Lauro recently visited the USAID-funded BALANCED Project in Tanzania as part of a wider look at integrated development projects. He emphasized that what exactly this integrated approach is called – be it PHE, HELP, or HELPS – is insignificant; what matters is that these disparate elements are combined. -
Karen Seto on the Environmental Impact of Expanding Cities [Part Two]
› “A lot of cities are trying to become green cities,” said Karen Seto in part two of an interview with ECSP about her recently published article, “A Meta-Analysis of Global Urban Land Expansion,” co-authored with Michail Fragkias, Burak Güneralp, and Michael K. Reilly. “I think one of the main policy implications of our study is that how a city urbanizes is critical, because one of the things we are finding is that urban land is growing faster than urban population, and in some cases it is growing much faster.”
“A lot of cities are trying to become green cities,” said Karen Seto in part two of an interview with ECSP about her recently published article, “A Meta-Analysis of Global Urban Land Expansion,” co-authored with Michail Fragkias, Burak Güneralp, and Michael K. Reilly. “I think one of the main policy implications of our study is that how a city urbanizes is critical, because one of the things we are finding is that urban land is growing faster than urban population, and in some cases it is growing much faster.”
Seto said that the cities with the best prospects for implementing green growth and expansion strategies “tend to focus on the low-hanging fruit,” such as planting trees or constructing buildings with green roofs. From the public’s perspective, these types of measures are relatively painless because they “don’t require changing people’s behavior.”
More challenging, said Seto, will be getting rapidly expanding cities to anchor future development around public-transit systems, especially given the changing lifestyle preferences of upwardly mobile urban populations across China and India, for whom private car ownership serves as an important status symbol.
Still, Seto said she is tentatively optimistic about city planners’ ability to grow cities in a sustainable fashion. “We’ve experienced this rapid growth of urban population and urban land areas, but we’re also seeing that over the next 20 years, according to the UN, we’re going to see even more people living in urban areas,” she said.
“We have this window of opportunity to really shape the way in which cities get developed, and I think that’s really one of the big messages of the study.”
Part one of Karen Seto’s interview is available here. The “Pop Audio” series is also available as podcasts on iTunes.
Sources: China Daily, USA Today. -
Karen Seto on the Environmental Impact of Expanding Cities [Part One]
› “When we think about the environmental impacts of rapid urbanization, we really need to unpack what we mean by ‘urbanization,’” said Karen Seto, an associate professor in Yale University’s School of Forestry and Environment Studies, in this interview with ECSP. “There is the demographic component, where more people are living in cities; there is economic urbanization, which is where livelihoods and economies are becoming more urban rather than rural; and then there is the land component – the conversion of land from agriculture and other ecosystems to become urban.”
“When we think about the environmental impacts of rapid urbanization, we really need to unpack what we mean by ‘urbanization,’” said Karen Seto, an associate professor in Yale University’s School of Forestry and Environment Studies, in this interview with ECSP. “There is the demographic component, where more people are living in cities; there is economic urbanization, which is where livelihoods and economies are becoming more urban rather than rural; and then there is the land component – the conversion of land from agriculture and other ecosystems to become urban.”
Seto is the lead author of a new article, “A Meta-Analysis of Global Urban Land Expansion” (with Michail Fragkias, Burak Güneralp, and Michael K. Reilly), which uses satellite imagery to help document the physical expansion of urban areas in developed and developing nations between 1970 and 2000.
Over that period, the population of cities in the developing world boomed. In 1970, there were roughly the same number of city dwellers in developed nations as in developing nations. By the mid-1990s, however, urban residents of the developing world outnumbered their developed-world counterparts by a factor of two to one. Since then, the gap has continued to grow.
According to the report, urban growth sprawled to cover nearly 60,000 square kilometers of previously non-urban areas during the last three decades of the twentieth-century. One of their most interesting finds, said Seto, was that “urban expansion has been occurring in low-elevation coastal zones more than it has been elsewhere.”
“Essentially what that means is that cities are growing precisely in areas that are highly vulnerable to the impacts of climate change, like sea level rise and storm surges,” she said.
Demography and the Environment
Seto acknowledged that many of the today’s discussions surrounding urbanization focus on the negative impacts for the environment and human security – among them the “loss of agricultural land, conversion of forests, biodiversity loss, changes in hydrology, and climate effects.” Ultimately though, she said, urbanization and its attendant land-use changes shouldn’t be viewed through a black-or-white lens.
“Certainly we think about the oncoming demographic transition of something like three billion more people living in cities,” Seto said, but “that means there’s a lot of efficiency to be gained, whether it is in education, energy, sanitation, or health – urbanization allows for opportunities for really efficient use of resources.”
The real challenge to achieving environmentally sustainable urban development, said Seto, is thoughtful city planning: “How we configure ourselves has a big impact on the environment, so it is not the issue of just whether we are urbanizing – the form in which we urbanize [also] has a huge impact.”
Part two of Karen Seto’s interview is available here. The “Pop Audio” series is also available as podcasts on iTunes.
Sources: Population Reference Bureau, UNFPA. -
Certification: The Path to Conflict-Free Minerals from Congo
›This summer, the Wilson Center’s Africa Program, in co-sponsorship with the Enough Project, assembled a panel of experts from American, British, and Congolese governments, private industry, and the NGO community to discuss the deplorable situation in the eastern Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC) involving conflict minerals and certification as a way forward.
After introductory remarks by Wilson Center President Jane Harman, Africa Program Director Steve McDonald introduced John C. Bradshaw, executive director of the Enough Project, who moderated the panel discussion. [Video Below]
Under Secretary of State Robert D. Hormats began by saying the “extremely traumatic” humanitarian situation in the restive areas of the eastern DRC requires “a bold, resolute, and morally inspired response by the United States and other countries.”
Sasha Lezhnev, policy consultant for the Enough Project, explained how the demand for tin, tantalum, tungsten, and gold – for use in batteries, circuit boards, and screens in computers and cellphones – are, in effect, driving the conflict in the DRC.
However, Ambassador to the United States from the DRC Faida Mitifu pointed out that a significant 70 percent of the economy in the eastern regions of the country depends on mining, thus any initiative would have to take into account the livelihoods of the people. In order to assist those communities while a process is formulated, Lezhnev called for targeted development projects in the most affected regions.
The Kimberley Process: A Potential Model?
“If we want to have a lasting impact, we’re going to need a certification process,” Lezhnev said, and we must learn lessons from the Kimberley Process (KP) in order to implement a suitable framework in the DRC.
Clive Wright, who served as the diplomatic negotiator for the KP and head of the foreign policy team for the British High Commission in Ottawa, described the intricacies of the process and its genesis. Under the provisions of the KP, the trade of rough diamonds is permissible, provided that there is a certificate from the country of origin and complementary legislation is in place in the importing country. This agreement was made through consultations and dialogue between the private sector and civil society.
Though successful in certain respects, Wright listed several shortcomings of the KP: it is not legally binding, therefore there are no levers to pull that compel government action; the process is void of an independent monitoring mechanism; and a consensus clause allows one government to block any action which clears the way for the status quo to prevail.
To implement a policy similar to the KP that guarantees legitimate minerals trade in the DRC, Under Secretary Hormats highlighted four key actors that have critical roles independently and collaboratively: 1) regional governments; 2) industry; 3) civil society; and 4) the U.S. government.
Regional Governments
Governments in the region face considerable challenges, said Hormats, as rebel groups trade across borders and evade efforts to rein in the commerce of precious gems, minerals, and arms. The states surrounding the Great Lakes – including Uganda, Rwanda, Burundi, Zambia, Kenya, and the DRC – have coalesced around these issues and developed a plan that will require effective coordination to ensure credibility. Some countries have already established traceability schemes, which are crucial for states that share borders with the DRC, since smuggling is incessant.
With regard to rebel factions, Kinshasa has occasionally participated in joint operations with the governments of Rwanda and Uganda “to stabilize [and] contain the activities of armed groups,” said Ambassador Mitifu. Progress, though slow, has also been made in demilitarizing the mining areas in the Kivu provinces as well as Maniema and in weakening the Congrès National pour la Défense du Peuple’s (CNDP) parallel administration.
The government in Kinshasa has made significant steps toward a certification framework and taken punitive action against military personnel who have engaged in illicit trade, said Ambassador Mitifu. She outlined the efforts the Kabila administration has made to address the issue, including initiatives to put in place a credible certification system so that clean minerals can be exported. In conjunction with MONUSCO – the UN peacekeeping mission in the DRC – the Congolese government has introduced centers where miners can bring their products and feed them into a legitimate supply chain. Finally, Kinshasa is working closely with the private sector, international organizations, and local NGOs to minimize fraud and enhance cooperation. Nevertheless, governance and corruption represent a formidable roadblock in the implementation of any certification process.
Industry Responsibility
Tim Mohin, the director of corporate responsibility for Advanced Micro Devices – one of the largest semiconductor manufacturers in the world – argued that industry can positively influence the supply chain by creating conflict-free smelter programs and a due diligence bulwark where anyone along the supply chain can trace their resources back to a certified smelter.
Customers, Mohin said, are going to have to insist that businesses comply with this tracking system. Under Secretary Hormats agreed with this sentiment, saying that companies that look into the origin of their minerals send a powerful message to the region and the world. He also expressed hope that “companies [would] work to find ways to adhere to legislation [Dodd-Frank] and honor their obligations to their shareholders without shunning the region’s minerals entirely.”
The most difficult stretches along the supply chain are getting buy-in from the miners and the smelters; overcoming the constraints of socio-economic realities on the ground and geo-politics; and the lack of a sustainable tracing system that spans the spectrum of the supply chain. In addition to shored-up U.S. involvement, Mohin called for increased public-private sector partnerships with incentives reminiscent of the Fair Trade system, development aid to assist displaced people, and enhanced security for artisanal miners and their businesses.
Civil Society and Government
Hormats commended the pivotal role civil society has played and must continue to play in highlighting the humanitarian issues at stake, as governments and companies have been only “dimly aware of the link between human rights abuses and the minerals trade.” Furthermore, Wright encouraged civil society’s participation because it serves as a “great policeman” that monitors the bad behavior of governments, especially when the allure of profiteering seeps into deliberations. Moving forward on boosting security for civil society on the ground in the Congo will be essential.
The U.S. government, Hormats asserted, has to do its part to support initiatives on the table to create conflict-free supply chains. If more revenue is invested in legitimizing supply chains, a substantial portion of the problem would be solved. USAID and the State Department are working with civil society to take action against those responsible for illegitimate trade and exacerbating the conflict. Of course there remains work to be done, but as Under Secretary Hormats indicated “this is the most significant moral issue of our time.”
Derek Langford is a program assistant with the Wilson Center’s Africa Program.
Photo Credit: “Aerial View of Camps for People Displaced by Conflict,” courtesy of flickr user United Nations Photo. -
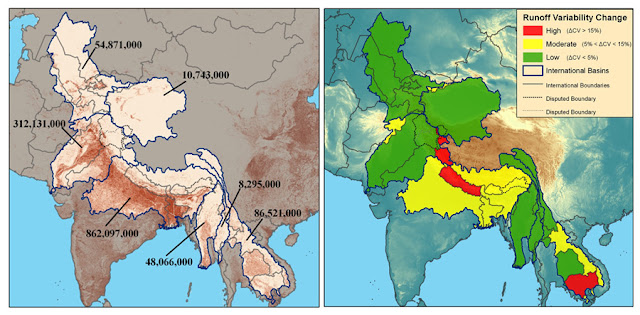
Redrawing the Map of the World’s International River Basins
›Understanding why conflict over water resources arises between nations begins with a solid understanding of the geography of international river basins. Where are the basins? How big are they? How many people live there? Who are the riparian nations, and what is the significance of each to the basin?
-
What’s in a Name? Watch Don Lauro on PHE, HELP, and HELPS
› Population, health, and environment (PHE) expert Don Lauro has worked on integrated projects for decades as a scholar, an implementer, a donor, and an evaluator. He recently visited the USAID-funded BALANCED Project in Tanzania as part of a wider look at this integrated approach. In an interview with ECSP, Lauro said the effort “made me think more broadly…about this area that we call population, health, and environment and what’s really in a name like that.”
Population, health, and environment (PHE) expert Don Lauro has worked on integrated projects for decades as a scholar, an implementer, a donor, and an evaluator. He recently visited the USAID-funded BALANCED Project in Tanzania as part of a wider look at this integrated approach. In an interview with ECSP, Lauro said the effort “made me think more broadly…about this area that we call population, health, and environment and what’s really in a name like that.”
“We commonly say PHE, and we all know what we’re talking about,” Lauro said of the population and development community, “but when you look deeply into these projects – or even not so deeply – you see that there’s other things going on as well.”
For example, Lauro pointed to the focus on livelihoods that many PHE programs have: “In the project I saw in Tanzania, there were many microcredit groups on the ground – mostly women – taking small loans for developing little enterprises that they had, like baking bread, raising bees, buying a cow…little enterprises to make their lives a little bit better.”
“Some people don’t use the term ‘PHE’…maybe it’s a ‘HELP’ project; that is health, environment, livelihoods, and population,” Lauro said. “Other people would say it’s maybe something even longer, ‘HELPS’ – health environment, livelihoods, population, and sustainability (or ‘security’ – Ed.).” When he was at the Wilson Center, Gib Clarke coined the “HELP” term in ECSP’s FOCUS Issue 20, arguing that livelihoods is such a critical component that it ought to be more formally recognized.
But, said Lauro, “on the ground they don’t use these terms – they say things like, ‘this is a healthy community program’ or ‘this is a green community program.’”
“I think it’s very important for us to realize what happens on the ground is lot different, and maybe more real, than how we talk about it.”