-
U.S.-Mexico Cooperation on Renewable Energy: Building a Green Agenda
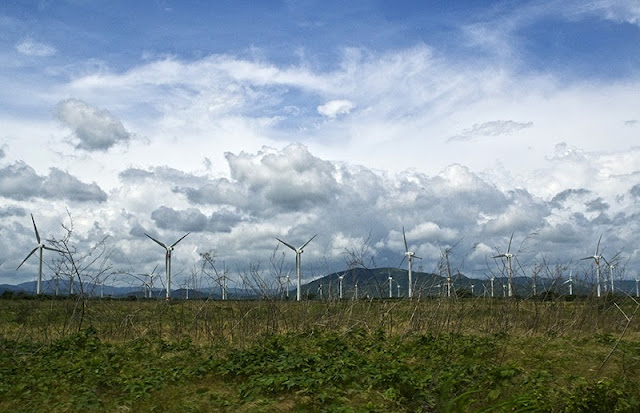
›Could joint green-energy development help improve relations between the United States and Mexico? Speakers at this spring’s launch of “Environment, Development and Growth: U.S.-Mexico Cooperation in Renewable Energies,” a report released by the Woodrow Wilson Center’s Mexico Institute, agreed that cooperating on renewable energy is a positive step. However, the panelists asserted that cooperation could be maximized by better harnessing Mexico’s renewable resources and by leveraging the economic complementarities that exist among the border states.
Mexico’s Green Energy Potential
Mexico has large untapped areas of geothermal, wind, and solar potential, according to Duncan Wood, author of the Wilson Center report and chair of the Department of International Relations at the Instituto Tecnologico Autonomo de Mexico (ITAM). Already, the country is the world’s third-largest producer of geothermal energy, and has large geothermal deposits in Baja California near major U.S. markets, such as San Diego and Los Angeles.
Mexico also offers great promise in wind power, with an estimated potential output of 1,800 to 2,400 megawatts for Baja California and 5,000 megawatts for southern Oaxaca state. Though Oaxaca is far from the U.S. border, it will soon be able to export electricity to U.S. markets, once Mexico’s mainland electrical grid is connected to the United States.
Wood also pointed out that Mexico is rich in solar energy, which could be marketed to the United States—particularly from the Baja California peninsula, which is the only part of the Mexican grid currently connected the United States. In biomass, he added, little investment has been made so far.
Opening New Avenues for Collaboration
With Mexico’s oil fields experiencing long-term and, in some cases, precipitous declines, the country is plotting a “future as a green nation,” shifting its policy focus toward alternative energy development, said Wood. In addition, Mexico’s renewable sector does have not the blanket prohibitions on private ventures that exist in the hydrocarbons sector, and regulatory adjustments over the past few administrations have enabled a more robust private stake in electricity generation and transmission.
A U.S.-Mexico taskforce on renewables was recently formed—an announcement timed to coincide with President Felipe Calderon’s April 2010 state visit to Washington—and there has been high-level engagement on the issue by both administrations. Collaboration between Mexico and U.S. government agencies through the Mexico Renewable Energy Program has enabled richer development of Mexico’s renewable resources while promoting the electrification and economic development of parts of rural Mexico. Joe Dukert, an independent energy analyst affiliated with the Center for Strategic & International Studies, pointed out that U.S.-Mexico collaboration on renewables is a little-acknowledged area of bilateral cooperation, and stressed the economic complementarities that exist between the two countries on the issue. He noted, for example, that Mexico was well-positioned to furnish power to help California meet its Renewables Portfolio Standard (RPS) by 2020.
Joe Dukert, an independent energy analyst affiliated with the Center for Strategic & International Studies, pointed out that U.S.-Mexico collaboration on renewables is a little-acknowledged area of bilateral cooperation, and stressed the economic complementarities that exist between the two countries on the issue. He noted, for example, that Mexico was well-positioned to furnish power to help California meet its Renewables Portfolio Standard (RPS) by 2020.
“Mexico can help them reach these [renewable energy] targets,” Dukert said. Yet at the same time, he said that Mexico needs to do more to enhance its profile as a renewable-energy supplier, and specifically suggested that energy attaches be assigned to the embassy and consulates.
Johanna Mendelson Forman, a senior associate with the Americas Program at the Center for Strategic & International Studies, emphasized the linkages connecting climate change, energy, and economic development. Forman warned that Mexico’s inadequate energy stocks are a problem for the United States, adding that “energy poverty is a real issue in Mexico.” Energy development and climate change—which are perceived as less polemical than other issues—are good entry points for a broader U.S.-Mexico dialogue, she remarked.
Robert Donnelly is a program associate with the Mexico Institute at the Woodrow Wilson Center.
Photo Credit: “Wind Mill Farm (Mexico),” courtesy of flickr user Cedric’s pics. Speaker photos by David Hawxhurst/Wilson Center. -
Don’t Cry for Me, Argentina: Why a Melting Arctic Needs Stronger Governance
›May 11, 2010 // By Schuyler NullThe Arctic Council, which helps broker economic and environmental agreements between the Arctic nations, needs a larger role in developing joint international policy, says Norway’s ambassador to Canada. Accelerating ice melt is expected to open the Arctic Ocean to seasonal ship traffic sometime between 2013 and 2030 – which analysts worry will lead to disputes over newly accessible oil and gas reserves.
The Arctic Council was founded in 1996 to “provide a means for promoting cooperation, coordination and interaction among the Arctic States” – Canada, Greenland, Finland, Iceland, Norway, Sweden, Russia, the United States, as well as some Arctic indigenous communities are all members. According to the U.S. Geological Survey, the Arctic may contain up to 90 billion barrels of oil (more than the known reserves of Nigeria, Kazakhstan, and Mexico combined) and 27 percent of the world’s known natural gas reserves, most of which is located offshore.
While rhetorical flare-ups over access to resources and accusations of militarization have occurred, to date the Arctic Council has been an effective mitigating body. However, the Council currently lacks a permanent secretariat and reliable funding.
Currently, any territorial disputes are handled under the U.N. Convention on the Law of the Sea (UNCLOS), while the Arctic Council mainly facilitates communication. However the United States has not yet ratified the Law of the Sea, despite concerted high-level efforts to do so.
Referring to the Arctic, Secretary of State Hillary Clinton recently told Congress that “the Law of the Sea provides commercial rights to the mining of what is in the seabed of the territories that are claimable under sovereignty provisions in the treaty,” and if the United States does not ratify it, “we will lose out, in economic and resource rights, in terms of environmental interests, and national security.”
While the National Intelligence Council predicts that a major armed conflict over the Arctic is unlikely in the near future, it suggests that “serious near-term tension could result in small-scale confrontations over contested claims.” A comprehensive agreement brokered by Arctic Council leadership and agreed upon by all members – like the Convention on the Protection of the Mediterranean Sea Against Pollution, and Protocols, which helps regulate commerce and environmental protections – would guarantee third-party moderation and alleviate the risk of an outstanding dispute erupting into real conflict.
The value of such an agreement is illustrated by the growing tension between Britain and Argentina over offshore oil rights around the Falkland Islands. Recent British drilling efforts, which have yielded a pocket of oil worth potentially an estimated $25 billion, provoked a furious response from Argentinean officials who have long disputed Britain’s claims to sovereignty, not only of the islands themselves, but of the seas around them.
Under UNCLOS, a nation is entitled to “explore and exploit” any natural resources within 200 nautical miles of their shores and in certain circumstances can apply for an extension to 350 nautical miles. By these definitions, there is considerable overlap in British and Argentinean claims, which the Law of the Sea alone is unable to resolve.
In a statement reported by the Times Online last week, Foreign Minister Jorge Taiana said that “Argentina energetically refutes what is an illegal attempt to confiscate non-renewable natural resources that are the property of the Argentine people.”
In an earlier bid to slow development, Argentinean President Cristina Fernandez de Kirchner announced in February that any ship coming to or from the disputed islands would have to be granted a permit in order to pass through Argentinean waters, effectively threatening blockade.
The sovereignty of the Falkland Islands has remained a disputed topic for Argentina since the loss of the Falkland Islands War in 1982, made worse by recent financial woes at home and the country’s lack of domestic oil reserves.
Although tensions in the Arctic region are low now, a changing environment and increased competition for energy resources may lead to similar disputes in the polar region – a strong argument for strengthening multilateral institutions like the Arctic Council and UNCLOS sooner rather than later.
Video Credit: “2008 Arctic Sea Ice Minimum w/overlay” courtesy of Flickr user NASA Goddard Photo and Video. -
Deepwater Horizon Prompts DOD Relief Efforts, Questions About Energy Security
›May 6, 2010 // By Schuyler NullAs the crippled Deepwater Horizon oil rig continues to spew an estimated 210,000 gallons of crude oil a day into the Gulf of Mexico, the Department of Defense has been asked to bring its considerable resources to bear on what has become an increasingly more common mission – disaster relief.
British Petroleum has requested specialized military imaging software and remote operating systems that are unavailable on the commercial market in order to help track and contain the spill.
In addition, the Coast Guard has been coordinating efforts to burn off oil collecting on the ocean’s surface and thousands of National Guard units have been ordered to the Gulf coast to help erect barriers in a bid to halt what President Obama called “a massive and potentially unprecedented environmental disaster,” as the oil slick creeps towards the coast.
As shown by these calls and the ongoing earthquake relief effort in Haiti, the military’s ability to respond to large-scale, catastrophic natural (and manmade) disasters is currently considered unmatched. The first Air National Guard aircraft was on the ground in Haiti 23 hours after the earthquake first struck, and DOD’s Transportation Command was able to begin supporting USAID relief efforts almost immediately. The Department of Defense also spearheaded American relief efforts after the 2004 tsunami and played a critical role in providing aid and security in New Orleans after Hurricane Katrina.
The Pentagon’s four-year strategic doctrine, the Quadrennial Defense Review (QDR), released earlier this year, predicts that such humanitarian missions will become a more common occurrence for America’s military, as the world grapples with the destabilizing effects of climate change, population growth, and competition over finite energy resources. Some experts see this expansion of the military’s portfolio as an essential part of a “hearts and minds” strategy, while others are critical of the military’s ability to navigate the difficulties of long-term reconstruction.
The QDR also highlights DOD’s efforts to reduce the need for oil – and thus deepwater oil rigs – in the first place.
The DOD as a whole is the largest consumer of energy in the United States, consuming a million gallons of petroleum every three days. In accordance with the QDR, Pentagon leaders have set an ambitious goal of procuring at least 25 percent of the military’s non-tactical energy requirement from renewable sources by 2025. The Air Force – by far the Pentagon’s largest consumer of petroleum – would like to acquire half of its domestic jet fuel requirement from alternative fuels by 2016 and successfully flight-tested a F/A-18 “Green Hornet” on Earth Day, using a blend of camelina oil and jet fuel.
At a speech at Andrews Air Force Base in March, President Obama lauded these efforts as key steps to moving beyond a petroleum-dependant economy. However, at the same event, he announced the expansion of off-shore drilling, in what some saw as a political bone thrown to conservatives. Since the Deepwater Horizon incident, the administration announced a temporary moratorium until the causes of the rig explosion and wellhead collapse have been investigated.
Cleo Paskal, associate fellow for the Energy, Environment, and Development Programme at Chatham House, warns that without paying adequate attention to the potential effects of a changing environment on energy infrastructure projects of the future – like the kind of off-shore drilling proposed for the Gulf and Eastern seaboard – such disasters may occur more frequently.
In an interview with ECSP last fall, Paskal pointed out that off-shore oil and gas platforms in the Gulf of Mexico were a prime example of how a changing environment – such as increased storm frequency and strength – can impact existing infrastructure. “Katrina and Rita destroyed over 400 platforms, as well as refining capacity onshore. That creates a global spike in energy prices apart from having to rebuild the infrastructure.”
The Department of Defense has demonstrated – in policy, with the QDR, and in action – that it can marshal its considerable resources in the service of renewable energy and disaster relief. But given the scope of today’s climate and energy challenges, it will take much more to solve these problems.
Photo Credit: “Deepwater Horizon,” courtesy of flickr user U.S. Coast Guard. U.S. Air Force Tech. Sgt. Joe Torba of the 910th Aircraft Maintenance Squadron, which specializes in aerial spray, prepares to dispatch aircraft to a Gulf staging area. -
DOD Measures Up On Climate Change, Energy
›May 5, 2010 // By Schuyler Null“As Congress deliberates its role, DOD is moving ahead steadily on a broad range of energy and climate initiatives,” says former Senator John Warner in a recent Pew report, Reenergizing America’s Defense: How the Armed Forces Are Stepping Forward to Combat Climate Change and Improve the U.S. Energy Posture.
The military as a leader and catalyst for renewable energy was a key focus of the recently released Quadrennial Defense Review (QDR), which for the first time included consideration of the effects of climate change and excessive energy consumption on military planning:Assessments conducted by the intelligence community indicate that climate change could have significant geopolitical impacts around the world, contributing to poverty, environmental degradation, and the further weakening of fragile governments. Climate change will contribute to food and water scarcity, will increase the spread of disease and may spur or exacerbate mass migration.
According to the Pew report, the Department of Defense has set a goal of producing or procuring at least 25 percent of its non-tactical electric energy needs from renewable sources by 2025. Highlights of the service’s efforts include:
The Pew report offers a generally favorable appraisal of the military’s response to the “twin threats of energy dependence and climate change” and the progress made towards reaching federal energy mandates. However, the authors let slide that the overwhelming amount of DOD energy usage is tied to tactical consumption, which has been given inadequate attention thus far (consider that the senior Pentagon official overseeing tactical energy planning was only just appointed, although the position has existed since October 2008).- The U.S. Navy’s “Great Green Fleet” carrier strike group, which will run entirely on alternative fuels and nuclear power by 2016;
- The construction of a 500-megawatt solar facility in Fort Irwin, California by the U.S. Army which will help the base reach ‘net-zero plus’ status;
- The goal of acquiring 50 percent of the U.S. Air Force’s aviation fuels from biofuel blends by 2016;
- The U.S. Marine Corps’ 10×10 campaign to develop a comprehensive energy strategy and meet ten goals aimed at reducing energy and water intensity and increasing the use of renewable electric energy by the end of 2010.
Interest in this field has grown quickly, as evidenced by the more than 400 people gathered at the launch of the latest report from the Center for New American Security (CNAS), Broadening Horizons: Climate Change and the U.S. Armed Forces – a big increase from the 50 or so at CNAS’ first natural security event in June 2008.
The CNAS study, much like the Pew report, breaks down the military’s efforts by service, but the study’s authors – including U.S. Navy Commander Herbert E. Carmen – thankfully provide more specific recommendations for what could be done better.
Based on research, interviews, and site visits, the study offers geographically specific recommendations for each of the Unified Commands, as well as seven broad recommendations for DOD as a whole:
“While we believe there is still much work ahead, there is a growing commitment to addressing energy and climate change within the DOD,” said USN Commander Carmen in the report:- In light of its implications for the global commons, ensure that DOD is included in the emerging debate over geoengineering.
- Urge U.S. ratification of the UN Convention on the Law of the Sea in order to provide global leadership and protect U.S. and DOD interests, especially in the context of an opening Arctic sea.
- Eliminate the divided command over the Arctic and assign U.S. Northern Command (NORTHCOM) as the supported commander.
- The U.S. government should make an informed decision about constructing nuclear reactors on military bases and provide clear policy guidelines to DOD.
- Congress and DOD should move away from the “cost avoidance” structure of current renewable energy, conservation, and efficiency practices in order to reward proactive commanders and encourage further investment.
- All of the services should improve their understanding of how climate change will effect their missions and capabilities; e.g. migration and water issues may impact Army missions, a melting Arctic, the Navy.
- The Air Force should fully integrate planning for both energy security and climate change into a single effort.
Indeed, in our conversation with officials in the Office of the Secretary of Defense for Policy, it was clear that, in developing the climate change and energy section of the 2010 QDR, the Department of Defense has developed a nascent, intellectual infrastructure of civilian and military professionals who will continue to study the national security implications of climate change, and, we hope, will continue to reevaluate climate change risks and opportunities as the science continues to evolve.
A holistic view of national security that includes energy and environment, as well as demographic and development inputs, continues to gain traction as an important driver in DOD policy and planning.
Photo Credit: “Refueling at FOB Wright” courtesy of Flickr user The U.S. Army. -
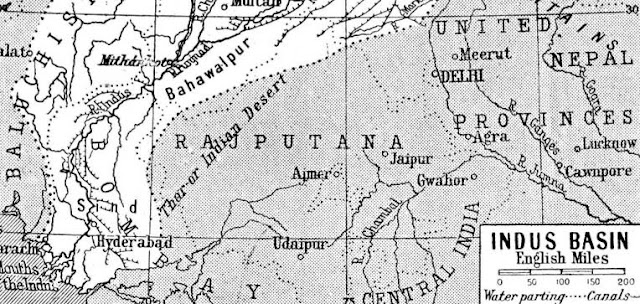
Parched and Hoarse, Indus Negotiations Continue to Simmer
›April 30, 2010 // By Julien KatchinoffBrewing conflicts over water in South Asia are not new to the readers of the New Security Beat. Violence due to variations in the monsoon season , high tensions over water and energy diplomacy, and pressures stemming from mismanaged groundwater stocks in the face of burgeoning population growth have all been reported on before.
The latest addition to this thread is disappointingly familiar: escalating tensions between Pakistan and India over the Indus river basin. Pakistan views Indian plans to construct the Nimoo-Bazgo, Chutak, and Kishanganga power plants as threatening the crucial water flows of an already parched nation according to objections voiced by the Pakistani Water Commission at the annual meeting of the Indus Water Commission in March. As a result, all efforts to reach an agreement on India’s plans for expanded hydroelectric and storage facilities in the basin’s upstream highlands failed.
In a recent editorial in the Pakistani newspaper The Dawn , former Indus River System Authority Chairman Fateh Gandapur claimed that new construction amounts to a clear violation of the Indus Water Treaty (IWT):“India is building large numbers of dams …on the rivers Indus, Jhelum, Chenab, Ravi, Sutlej and Beas, including on their tributaries in Indian-administered Kashmir. Together, these will have the effect of virtually stopping the perennial flow of water into Pakistan during a period of six to seven months that include the winter season. Not only will this be a blatant violation of the IWT and international laws on water rights of lower riparian areas, it will also amount to making Pakistan dry and, in the future, causing water losses that will deprive this country of its rabi and kharif crops. Our part of Punjab, which has a contiguous canal irrigation system that is amongst the largest in the world, will be turned into a desert.”
Gandapur’s fears, shared by many in Pakistan, are borne out of the desperate situation in which many of their compatriots live. As noted in Running on Empty: Pakistan’s Water Crisis, a report by the Wilson Center’s Asia program, water availability in the country has plummeted from about 5,000 cubic meters (m3) per capita in the early 1950s to less than 1,500 m3 per capita today–making Pakistan the most water stressed country in Asia. With more than 90% of these water flows destined for agricultural use, only 10% remains to meet the daily needs of the region’s booming population. This harmful combination of low supplies and growing demand is untenable and in Karachi results in 30,000 deaths–the majority of which are children–from water-borne illnesses each year.
This harmful combination of low supplies and growing demand is untenable, and may be get worse before it gets better, as Pakistan’s population is projected to almost double by 2050. At an upcoming conference at the Wilson Center, “Defusing the Bomb: Pakistan’s Population Challenge,” demographic experts on Pakistan will address this issue in greater detail.
Recent talk of ‘water wars’ and ‘Indian water jihad’ from Hafiz Muhammad Saeed, the founder of Lashkar-e-Taiba and head of Jamaat-ud-Dawah, have played upon popular sentiments of distrust and risk inflaming volatile emotions, the South Asian News reports.
Harvard’s John Briscoe, an expert with long-time ties to both sides of this dispute, sees such statements as the inevitable result of the media-reinforced mutual mistrust that pervades the relationship of the two nations and plays on continued false rumors of Indian water theft and Pakistani mischief. “If you want to give Lashkar-e-Taiba and other Pakistani militants an issue that really rallies people, give them water,” he told the Associated Press.
The rising tensions have echoed strongly throughout the region. For the first time in its 25-year history, the South Asian Association for Regional Cooperation (SAARC) has raised the water issue (long thought to be a major political impediment and contributor to SAARC’s stagnation) among its members during its meeting this week. “I hope neighbors can find ways to compartmentalize their differences while finding ways to move forward. I am of course referring to India and Pakistan,” said Maldives President Mohammed Nasheed, during his address on Wednesday. “I hope this summit will lead to greater dialogue between (them.)”
Prime ministers Manmohan Singh and Yousuf Raza Gilani heeded the calls and responded with a hastily arranged in-person meeting on the sidelines of the SAARC conference. The emerging agreement targeted a comprehensive set of issues, including water and terrorism, and, while unsurprisingly weak on action, set a path upon which the nations can begin to move forward. Speaking about the agreement’s significance, Indian Foreign Secretary Nirumpama Rao told the Los Angeles Times, “There’s been a lot of soul-searching here. We need to take things forward. This is good for the two countries and good for the region.”
The fragile détente faces great hurdles in the months to come, especially if rainfall remains scarce as forecasters predict. Already, local communities in India and Pakistan are venting frustrations over water shortages. On Thursday, just one day after the agreement between Prime ministers Singh and Gilani, several Bangalore suburbs staged protests at the offices of the local water authorities, complaining loudly about persistent failures of delivery services to produce alternative arrangements for water provision despite regular payments by local citizens. Whether local civil action ultimately helps or hinders bilateral water cooperation between India and Pakistan will be interesting to track in the near future and we at the New Security Beat look forward to continuing to engage with readers on the latest developments.
Photo Credit: Mahe Zehra Husain Transboundary Water Resources Spring 2010 -
World Bank President: Climate Policy Is Not “One-Size-Fits All”
› Speaking at the Woodrow Wilson Center yesterday, World Bank President Robert Zoellick said the financial crisis indicated that developed countries should listen to developing countries, but not out of “charity or solidarity: It is self-interest.”
Speaking at the Woodrow Wilson Center yesterday, World Bank President Robert Zoellick said the financial crisis indicated that developed countries should listen to developing countries, but not out of “charity or solidarity: It is self-interest.”
His prepared remarks, “The End of the Third World? Modernizing Multilateralism for a Multipolar World,” notably included a section on climate change:Take climate change: The danger is that we take a rule book from developed countries to impose a one-size-fits-all model on developing countries. And they will say no.
Climate change policy can be linked to development and win support from developing countries for low carbon growth but not if it is imposed as a straitjacket.
This is not about lack of commitment to a greener future. People in developing countries want a clean environment, too.
Developing countries need support and finance to invest in cleaner growth paths. 1.6 billion people lack access to electricity. The challenge is to support transitions to cleaner energy without sacrificing access, productivity, and growth that can pull hundreds of millions out of poverty.
Avoiding geo-politics as usual means looking at issues differently. We need to move away from the binary choice of either power or environment. We need to pursue policies that reflect the price of carbon, increase energy efficiency, develop clean energy technologies with applications in poorer countries, promote off-grid solar, innovate with geothermal, and secure win-win benefits from forest and land use policies. In the process, we can create jobs and strengthen energy security.
The developed world has prospered through hydro electricity from dams. Some do not think the developing world should have the same access to the power sources used by developed economies. For them, thinking this is as easy as flicking a switch and letting the lights burn in an empty room.
While we must take care of the environment, we cannot consign African children to homework by candlelight or deny African workers manufacturing jobs. The old developed country prism is the surest way to lose developing country support for global environment goals. -
Energy Is a “Constraint on Our Deployed Forces”: DOD DOEPP Nominee Sharon Burke
›March 24, 2010 // By Wilson Center Staff“I believe right now that energy is a vulnerability and constraint on our deployed forces,” said Department of Defense nominee and CNAS Vice President Sharon Burke yesterday morning at her confirmation hearing before the Senate’s Armed Services Committee. She described the tremendous cost—in lives, capital, and operational flexibility—of meeting the current fuel needs of troops in Afghanistan. Leading DOD’s efforts to account for the “full cost and full burden of energy,” she said, will be one of her priorities if she is confirmed.
“The committee and Congress have shown an acute interest in operational energy by creating this position,” said Burke, who would be the first person to serve as Director of Operational Energy Plans and Programs (DOEPP). “Sharon Burke has a deep understanding of the energy and climate change challenges facing the Department of Defense,” according to Geoff Dabelko, director of the Wilson Center’s Environmental Change and Security Program. “She would be able to hit the ground running if confirmed.”
Burke said that previous Congressional and presidential mandates have pushed DOD to improve the energy posture of its domestic facilities. She hopes to achieve similar successes in the operational arena. While she was reluctant to privilege any single solution, she suggested that more efficient weapon platforms and tactical vehicles, alternative fuels, and better business and acquisition processes could all be part of the mixture.
In response to a question from Senator Chambliss (R-GA) about climate change, Burke said, “I think the Quadrennial Defense Review (QDR) does a very good job laying out the proper role of the military forces.” The Wilson Center recently hosted a panel discussion on the QDR and the UK Defence Green Paper, at which the speakers repeatedly referred to the future DOEPP.
The nomination hearing largely avoided any tension concerning climate science and mitigation policies, focusing instead on military operations and ensuring the maximum effectiveness of U.S. forces. “My top priority would be mission-effectiveness,” Burke said. E&E; News reports Burke is expected to be confirmed.
Photo: Sharon Burke courtesy CNAS. -
Is the Melting Arctic a Security Challenge or Crisis? The View From Russia and Washington
›March 24, 2010 // By Geoffrey D. DabelkoIn his opening remarks at the Security Council of the Russian Federation’s meeting on climate change last week, Russian President Dmitry Medvedev framed climate change as a force for increased competition and “disputes between countries.” Unsurprisingly, he focused on the Arctic region and what he called the “inadmissible” and “unfair” threats to Russia’s access to the region’s resources:
We must not forget either that climate change can give rise not only to physical change, change in the nature around us, but can also see the emergence of disputes between countries over energy exploration and extraction, the use of marine transport routes, bioresources, and shortages of water and food resources. The countries bordering the Arctic region are already actively engaged in expanding their research, economic, and even military presence in the Arctic. Unfortunately, in this situation, we are seeing attempts to limit Russia’s access to exploring and developing Arctic energy deposits, which is inadmissible from a legal point of view and unfair in terms of our country’s geographical location and very history.
His reference to “shortages of water and food resources” fits squarely within the increasingly common view of climate change’s potential as a “conflict accelerant” (see, e.g., the U.S. Department of Defense’s 2010 Quadrennial Defense Review) or “threat multiplier” (as in CNA’s National Security and the Threat of Climate Change and statements from representatives of the UK and EU foreign offices).
But his Arctic comments sounded different than what I’ve been hearing in Washington. The Arctic rightfully gets a lot of attention for alarming rates of physical change, newly accessible resources, and potential new shipping routes. Yet remarks at a recent spate of Arctic climate and security discussions suggest officials in Washington view the geopolitical and trade issues more as “challenges” than “crises.”
For example, last month at the Stimson Center, and just yesterday at the Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Lab, the U.S. Navy’s director of Task Force Climate Change and oceanographer, Rear Admiral David Titley, used “challenge” rather than “crisis” to depict the security situation in the far North. At numerous panels, officials and experts expressed confidence that the Arctic Council and related institutions are forums robust enough to manage current and future disputes.
Ironically, one of those key institutions is UNCLOS, the Law of the Sea treaty, which has been ratified by 157 countries, but not the United States. U.S. military and civilian officials alike see ratification as a key step for the United States to represent its interests in these critical multilateral settings. Nevertheless, we can anticipate some knee-jerk demagoguery about the treaty ceding U.S. sovereignty to the United Nations, so the Senate is unlikely to take up the issue until after the fall 2010 elections.
I want to thank friend and colleague Alexander Carius, co-director of Adelphi Research, for calling President Medvedev’s speech to my attention.
Photo: Russian President Dmitry Medvedev, courtesy Flick user World Economic Forum
Showing posts from category energy.