-
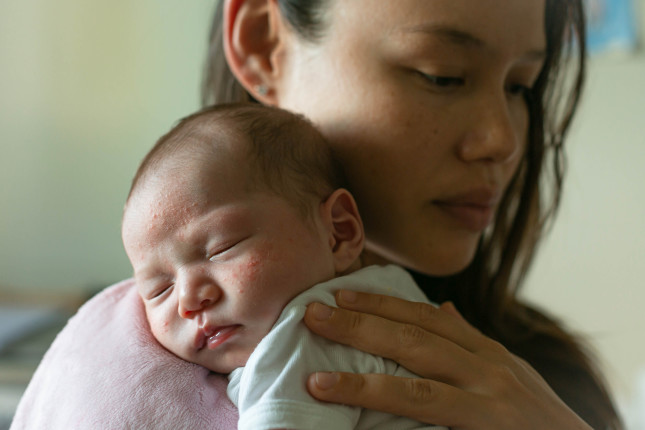
Seeing and Hearing Mothers: Uncovering Poor Perinatal Mental Health
›
Globally, 15 to 20 percent of women experience a perinatal mental health condition, said Sarah Barnes, Project Director of the Maternal Health Initiative at a recent event, held in partnership with the United Nations Population Fund (UNFPA), on mental health support for mothers in the perinatal period. Women are more likely to develop anxiety or depression in the year after giving birth than in any other time in their lives, with suicide and overdose the leading causes of death in the first year postpartum. “And yet, the prevention, early recognition, and treatment of perinatal mental health conditions is a challenge for many, if not most, healthcare systems across the world,” said Barnes.
-
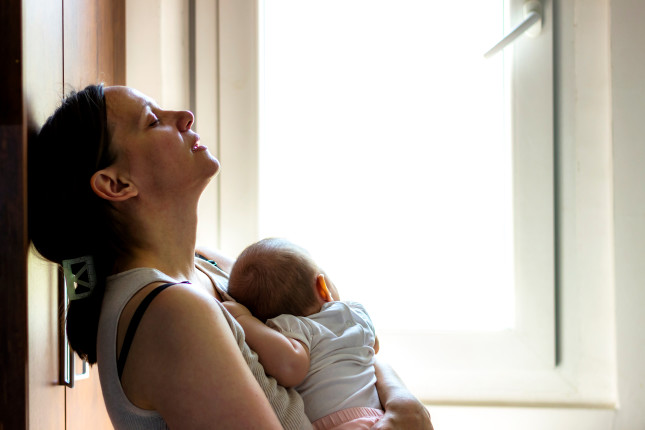
Respectful Maternity Care and Maternal Mental Health are Inextricably Linked
›
A positive birth experience is not a luxury, but a necessity, said Hedieh Mehrtash, consultant for the Department of Sexual and Reproductive Health and Research at the World Health Organization (WHO), at a panel during the Maternal Mental Health Technical Consultation hosted by the United States Agency for International Development’s (USAID) MOMENTUM Country and Global Leadership, in collaboration with WHO and the United Nations Population Fund.
-
Digital Water Diplomacy: Keeping Water Dialogues Afloat
›
In 2020, the world experienced the convergence of the global water and climate change crises, the COVID-19 pandemic, and economic recession. The compounded emergencies hit even well-prepared countries hard. For the more than 50 percent of the world’s population that relies on transboundary freshwater sources for their drinking water, the renewed urgency for access to water for sanitation raised additional challenges. Effectively responding to the crises demanded an elevated degree of communication and coordination between neighboring states precisely when coordination and collaboration processes encountered new barriers to effective transboundary engagement. As neighboring states instituted travel restrictions, water dialogues had to adapt through digital water diplomacy processes.
-
Creating a New Normal with a New Global Public Health System
›
“Ask a big enough question, and you need more than one discipline to answer it,” said modern dance legend Liz Lerman.
As the COVID-19 pandemic spread across the globe, the World Health Organization (WHO) warned that there would be no going back to normal. They knew a failure to make timely and accurate public health decisions for a pandemic would prove to be the “difference between life and death.” How correct they were.
-
A Conversation with Steven Gale on USAID’s New Foresight Unit
›
“I think most people will agree today that the development landscape is, well, it’s highly uncertain, it’s increasingly complex,” says Steven Gale, Lead of the Futures/Foresight Team at the U.S Agency for International Development (USAID), in this week’s Friday Podcast. “I think the future is even going to be more complex.”
-
A New Year Brings Enduring Challenges: Financing for Water and Sanitation Utilities During COVID-19
›
Eleven months have passed since COVID-19 was declared a global pandemic by the World Health Organization (WHO). As we rang in the new year, the world surpassed two million deaths due to COVID-19. While it is encouraging that 77 countries have distributed 168 million COVID-19 vaccine doses, only a small fraction of these are in low-income countries. Vaccinations may not be widely distributed in most of sub-Saharan Africa until 2022-2023. Furthermore, the new COVID-19 variant recently discovered in South Africa is estimated to be 50 percent more contagious, underscoring the need for a collaborative international response.
-
Leverage COVID-19 Data Collection Networks for Environmental Peacebuilding
›Environmental peacebuilding could benefit from COVID-era data innovation. A well-documented obstacle environmental peacebuilders face is a lack of shared, empirical datasets among parties engaged in, recovering from, or descending into conflict. Current innovations in data collection may soon help seal these gaps.
Countries throughout the world have expanded their data collection capabilities to track the spread of COVID-19. From text message contact tracing to drone surveillance, these innovations inform national responses and shape the global case counting webpages that many of us anxiously refresh every day. The information networks established during the pandemic may endure far into the future, informing new goals, projects, and policies.
-
Earth Intel: Enhancing Researcher-Practitioner Partnerships to Address Eco-Security Challenges
›
“One of the most important accomplishments of the MEDEA program was to convince the intelligence community that near-term climate change is important for national security,” said D. James Baker, former Administrator of the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) and member of the MEDEA Program, at a panel at the American Geophysical Union’s virtual 2020 Fall Meeting. Organized by ISciences LLC’s Tom Parris, CASE Consultants International’s Eileen Shea, and Columbia University’ Robert Chen, the panel focused on how to build an effective knowledge-to-action enterprise that helps policymakers and society respond to emerging eco-security challenges. (See below for links to short, pre-recorded videos panelists shared prior to the panel to inform the discussion.)
Showing posts from category data.