-
The Yasuní-ITT Initiative Is a Practical Climate Solution That Must Be Embraced at Durban
›
As the world turns to Durban, South Africa, for this year’s UN climate summit, new findings are turning up the heat on the urgency to address climate change. The reality though is that we no longer have the luxury of resting our hopes solely on an internationally binding climate agreement; we must begin to look more closely at supporting immediate and tangible solutions. By complementing a global top-down effort of continued international negotiations with bottom-up approaches, we increase our chances at mitigating the most damaging effects of climate change. One of the most innovative models of such a bottom-up approach is the Yasuní-ITT Initiative being undertaken by the Government of Ecuador and supported by the UN Development Programme’s Multi-Partner Trust Fund Office (MPTF Office).
-
George Washington University’s PISA Helps Share Rural Vietnamese Climate Adaptation Strategies
›“Climate change is not a topic of debate in Vietnam, it’s a real challenge to future prosperity and security,” says George Washington University’s Partnerships for International Strategies in Asia (PISA) program in this video about their climate adaptation and mitigation work in Nam Dinh province. “[Vietnam’s] population density (265 people/square kilometer), its long coastline (3,444 km), its two major rivers (the Red and Mekong) – all help make it one of the 10 countries considered most vulnerable to climate change,” the narrator says.
-
Lessons From Peru to Nepal
Glacial Lake Outburst Floods: “The Threat From Above”
›
“We have never experienced so many potentially dangerous lakes in such a short period of time,” said Alton Byers of The Mountain Institute (TMI) during a roundtable discussion on glacial melt, glacial lakes, and downstream consequences at the Wilson Center on October 26. “There have always been glacial lake outburst floods,” said Byers. What has changed is how quickly these lakes now grow. “Suddenly, you wake up in the morning, and now there are hundreds and hundreds of these lakes above you – the threat from above,” he said.
-
Watch: Geoff Dabelko on Climate Adaptation and Peacebuilding at SXSW
›November 16, 2011 // By Wilson Center StaffThe problems of climate adaptation, poverty alleviation, and peacebuilding are common to many parts of the world. Yet the efforts to address them are often pursued separately or with little coordination. Capturing the co-benefits of building institutional capacity critical to all three areas is an idea that will likely receive little attention at next year’s Rio+20 Earth Summit in Brazil, says ECSP Director Geoff Dabelko.
-
Robert Olson for the Science and Technology Innovation Program
Geoengineering for Decision Makers
›Download Geoengineering for Decision Makers, by Robert Olson, from the Wilson Center. Excerpted below is the executive summary.
Geoengineering involves intentional, large-scale interventions in the Earth’s atmosphere, oceans, soils or living systems to influence the planet’s climate. Geoengineering is not a new idea. Speculation about it dates at least to 1908, when Swedish scientist Svente Arrhenius suggested that the carbon dioxide released from burning fossil fuels might help prevent the next ice age. Until recently, proposals for using geoengineering to counteract global warming have been viewed with extreme skepticism, but as projections concerning the impact of climate change have become more dire, a growing number of scientists have begun to argue that geoengineering deserves a second look.
Below are 10 of the major concerns about geoengineering that policymakers need to be aware of and give due consideration. These concerns apply mainly to solar radiation management (SRM), the form of geoengineering that attempts to cool the climate by reflecting a small amount of solar radiation back into space. SRM involves significantly higher risks than the other form of geoengineering, carbon dioxide removal (CDR) which involves removing carbon dioxide from the atmosphere and storing it in the ocean, plants, soil, or geological formations.- Unintended Negative Consequences: We may know too little about the Earth’s geophysical and ecological systems to be confident we can engineer the climate on a planetary scale without making an already bad situation even worse;
- Potential Ineffectiveness: Some proposed CDR methods are so weak that they would produce useful results only if sustained on a millennial timescale;
- Risk of Undermining Emissions-Mitigation Efforts: If politicians come to believe that geoengineering can provide a low-cost “tech fix” for climate change, it could provide a perfect excuse for backing off from efforts to shift away from fossil fuels;
- Risk of Sudden Catastrophic Warming: If geoengineering is used as a substitute for emissions reduction, allowing high concentrations of CO2 to build up in the atmosphere, it would create a situation where if the geoengineering ever faltered because of wars, economic depressions, terrorism or any other reasons during the millennium ahead, a catastrophic warming would occur too quickly for human society and vast numbers of plant and animal species to adapt;
- Equity Issues: Geoengineering efforts might succeed in countering the warming trend on a global scale, but at the same time cause droughts and famines in some regions;
- Difficulty of Reaching Agreement: It could be harder to reach global agreements on doing geoengineering than it is to reach agreements on reducing carbon emissions;
- Potential for Weaponization: Geoengineering research could lead to major advances in knowledge relevant for developing weather control as a military tool;
- Reduced Efficiency of Solar Energy: For every one percent reduction in solar radiation caused by the use of SRM geoengineering, the average output of concentrator solar systems that rely on direct sunlight will drop by four to five percent;
- Danger of Corporate Interests Overriding the Public Interest: Dangers include a lack of transparency in SRM technology development and the possibility that the drive for corporate profits could lead to inappropriate geoengineering deployments;
- Danger of Research Driving Inappropriate Deployment: Research programs have often created a community of researchers that functions as an interest group promoting the development of the technology that they are investigating.
Several of the best climate studies suggest that stabilizing the amount of carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gases below the level that risks dangerous climate change will require a social mobilization and technological transformation at a speed and scale that has few if any peacetime precedents. If correct, and the needed mobilization does not occur in the years immediately ahead, then decision makers later in the century could find themselves in a situation where geoengineering is the only recourse to truly dangerous climate change. The most fundamental argument for R&D; on geoengineering is that those decision makers should not be put in a position of either letting dangerous climate change occur or deploying poorly evaluated, untested technologies at scale. At the very least, we need to learn what approaches to avoid even if desperate.
Continue reading by downloading the full report from the Wilson Center.
Robert Olson is a Senior Fellow at the Institute for Alternative Futures. -
Food Security, the Climate-Security Link, and Community-Based Adaptation
›In “The Causality Analysis of Climate Change and Large-Scale Human Crisis,” published in last month’s Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, authors David Zhang et al. write that changes in food supply are key indicators for the likelihood of climate change-induced conflict. Adding to the debate on the links between climate and conflict, the authors write that their purpose was to discover the specific causal mechanisms behind the relationship by analyzing various climate- and crisis-related variables across several periods of peace and conflict in pre-industrial Europe. They found that “climate-induced agricultural decline,” as opposed to resource scarcity caused by rapid population growth, was the clearest indicator of impending crises. “Malthusian theory emphasizes increasing demand for food as the cause,” write the authors, “whereas we found the cause to be shrinking food supply” – a distinction with “important implications for industrial and postindustrial societies.”
In “Using Small-Scale Adaptation Actions to Address the Food Crisis in the Horn of Africa: Going beyond Food Aid and Cash Transfers,” published in Sustainability, authors Richard Munang and Johnson Nkem advocate for community-based adaptation programs to increase resilience to food crises in the Horn of Africa. “Given that hunger and poverty are concentrated in rural areas,” the authors write, “targeting local food systems represents the single biggest opportunity to increase food production, boost food security, and reduce vulnerability.” The authors present a joint UNEP-UNDP adaptation initiative undertaken in Uganda as a framework for potential adaptation interventions in the Horn. They conclude that the initiative’s approach – pairing locally-focused sustainable farming techniques with a national-level emphasis on adaptation programs, and upscaling lessons learned from one level to the other – “will increase local buffering capacity against droughts, make communities more independent from direct aid, etc., build resilience and improve livelihoods overall.” -
Twin Challenges: Population and Climate Change in 2050
›

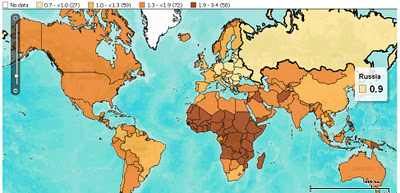
 With global population reaching 7 billion, a lot of attention has been paid to the question of how to sustainably support so many people, much less the 9 billion expected by 2050, or the 10 billion possible by 2100. Add in the environmental variability projected from climate change and the outlook for supporting bigger and bigger populations gets even more problematic. Two new maps – one by the Population Reference Bureau (PRB), the other by McGill University PhD candidate Jason Samson – show how the world might change over the next 40 years in the face of these twin challenges.
With global population reaching 7 billion, a lot of attention has been paid to the question of how to sustainably support so many people, much less the 9 billion expected by 2050, or the 10 billion possible by 2100. Add in the environmental variability projected from climate change and the outlook for supporting bigger and bigger populations gets even more problematic. Two new maps – one by the Population Reference Bureau (PRB), the other by McGill University PhD candidate Jason Samson – show how the world might change over the next 40 years in the face of these twin challenges.
Nine Billion in 2050
PRB’s map, built using their DataFinder tool, shows the world in 2050 in terms individual country growth rates between now and then. Japan, Russia, and countries in Eastern Europe are set to grow more slowly than anywhere else, and some of that group will actually shrink by 10 to 20 percent of their current size. Western, Central, and Eastern Africa will be home to the highest increases. Niger’s 2050 population is expected to be 340 percent its 2011 size – the largest growth of any country.
The map is based on country-level data pulled from a number of sources: the UN Population Division’s latest “World Population Prospects,” the UN Statistics Division’s “Demographic Yearbook 2008,” the U.S. Census Bureau’s International Database, and PRB’s own estimates. It’s unclear what numbers come from which sources, though it is clear that PRB’s 2050 estimates span the UN’s range of medium, high, and constant-fertility variants. In spite of these variations, none of PRB’s estimates come anywhere near the UN Population Division’s low variant estimates.
PRB’s map, echoing its 2011 World Population Data Sheet, shows a world where sub-Saharan Africa will bear the brunt of population growth. The average country in Africa in 2050 is projected to be slightly more than twice its 2011 size; the average European country is expected to barely break even. Africa is home to more countries whose populations are estimated to least double (34) or triple (4) than any other continent. Europe, meanwhile, is home to more countries whose populations will stagnate (8), or even shrink (19), than anywhere else. Interestingly, the Caribbean is a close second in terms of countries whose populations are projected to stay the same (seven to Europe’s eight), and Asia is second to Europe in terms of countries whose populations are projected to shrink (Georgia, Japan, Armenia, South Korea, and Taiwan).
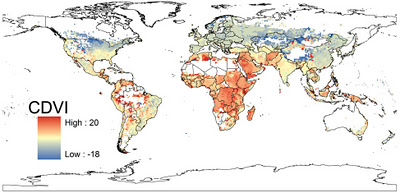
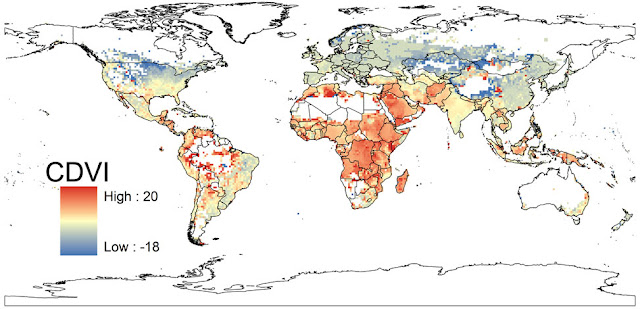
More People, More Climate Change, More Vulnerability
Samson’s map takes on the same time period but projects where people will be most vulnerable to the effects of climate change. Since his map takes into account population growth (measuring where people are most vulnerable, remember), unsurprisingly, Africa, the Middle East, Southeast Asia, and central South America are covered in bright red dots, indicating high vulnerability. Conversely, North America, Europe, and much of Central Asia are in shades of blue.
Samson built his index using four environmental predictors – annual mean temperature, mean temperature diurnal range, total annual precipitation, and precipitation seasonality – taken from WorldClim’s 2050 forecasts, and 2005 sub-national population data from Columbia’s Center for International Earth Science Information Network. In spite of the sub-national population data, Samson makes a point to justify his use of supranational climate data in order to best reflect “the scale at which climate conditions vary.” He writes that localized issues like urbanization and coastal flooding “are probably best investigated with targeted regional models rather than by attempting to modify global models to include all factors of potential regional importance.”
Samson’s research shows that, generally, people living in places that are already hot will be more vulnerable to climate change over time, while people in more temperate climates will feel a negligible impact. Though he projects the largest real temperature changes will happen in temperate climates like North America and Europe, the comparatively smaller changes in Africa, the Middle East, Southeast Asia, and central South America are expected to have a greater impact because those regions are already very hot, their natural resources are stressed, and they are expected to bear the brunt of population growth over the next few decades.
These findings reflect a disparity between those responsible for climate change and those bearing the brunt of it, which, although not surprising, “has important implications for climate adaptation and mitigation policies,” said Sampson, discussing the map in a McGill press release.
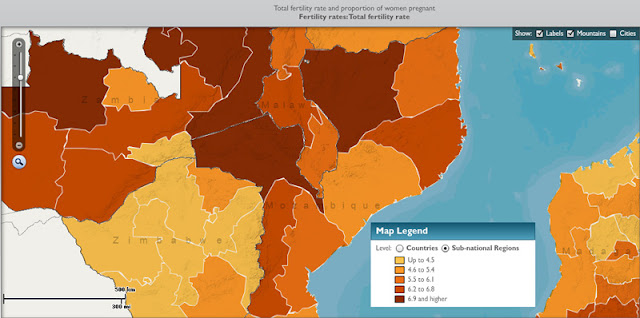
Sub-National Data “Present a Very Different Picture”
Though they offer a useful approximate glimpse at what the world might look at in 2050, both of these maps fall prey to over-aggregation. By looking at national rather than sub-national data, we miss how nuanced population growth rates can be within a country. Stimson Center Demographer-in-Residence Richard Cincotta wrote in a recent New Security Beat post that “national level comparisons of total fertility rates tend to communicate the false impression of a world with demographically homogeneous states.” Sub-national data, including differences between urban and rural areas and minority-majority fertility rates, “present a very different picture.”
And that difference matters. When it comes to looking at how population interacts with other issues, like the environment, poverty, and conflict, the importance of a sub-national approach becomes evident. In its 2011 data sheet, PRB writes that “poverty has emerged as a serious global issue, particularly because the most rapid population growth is occurring in the world’s poorest countries and, within many countries, in the poorest states and provinces.”
Edward Carr, an assistant geography professor at the University of South Carolina currently serving as a AAAS science fellow with USAID, argues that national-level data obscures our ability to understand food insecurity as well. The factors that drive insecurity “tend to be determined locally,” writes Carr in a post on his blog, and “you cannot aggregate [those factors] at the national level and get a meaningful understanding of food insecurity – and certainly not actionable information.”
The same is true when it comes to climate vulnerability. In a report from The Robert S. Strauss Center’s Climate Change and African Political Stability Program, authors Joshua Busby, Todd Smith, and Kaiba White write that “research announcing that ‘Africa is vulnerable to climate change,’ or even ‘Ethiopia is vulnerable,’ without explaining which parts of Ethiopia are particularly vulnerable and why, is of limited value to the international policy community.”
“It is of even less use to Africans themselves, in helping them prioritize scarce resources,” add Busby et al.
Understanding the joint problems of climate change and population growth on a global level helps frame the challenges facing the world as it moves toward 8, 9, and possibly 10 billion. But knowing the ins and outs of how these issues interact on a local level will be a necessary step before policymakers and others can hope to craft meaningful responses that minimize our vulnerability to these challenges over the coming decades.
Sources: Center for International Earth Science Information Network at Columbia University, Climate Change and African Political Stability Program at the Robert S. Strauss Center, McGill University, Population Reference Bureau, UN Population Division, UN Statistics Division, U.S. Census Bureau, University of South Carolina, WorldClim.
Image Credit: “2050 Population As a Multiple of 2011,” courtesy of PRB; CDVI map used with permission, courtesy of McGill University; Sub-national total fertility rates in Southern Africa, courtesy of MEASURE DHS, arranged by Schuyler Null. -
New Report Launched: ‘The World’s Water’, Volume Seven
›“The water problem is real and it is bad,” said MacArthur “Genius” Fellow and founder of the Pacific Institute Peter Gleick at the October 18 launch of the seventh volume the institute’s biennial report on freshwater resources. “It’s not bad everywhere, and it’s not bad in the same way from place to place, but we are not doing what we need to do to address all of the different challenges around water.”
“The World’s Biggest Problem”
Worldwide, more than a billion people lack access to safe drinking water, while two and a half billion lack access to adequate sanitation services. “This is the world’s biggest water problem,” said Gleick, “the failure to meet basic human needs for water – it’s inexcusable.”
Gleick predicts that the world will fail to meet the Millennium Development Goals for water and sanitation by 2015, and noted that measures of illness for water-related diseases are rising, rather than falling.The World’s Water series provides an integrated way of thinking about water by exploring major concepts, important data trends, and case studies that point to policies and strategies for sustainable use of water. Volume seven includes chapters on climate change and transboundary waters, corporate water management, water quality challenges, Australia’s drought, and Chinese and U.S. water policy. The new volume also includes a set of side briefs on the Great Lakes water agreement, the energy required to produce bottled water, and water in the movies, as well as 19 new and updated data tables. An updated water conflict chronology looks at conflicts over access to water, attacks on water, and water used as a weapon during conflict.Peter Gleick on climate change and the water cycle.
Despite the added data, Gleick said that vast gaps remain in our knowledge and understanding about water. We lack accurate information on how much water the world has, where it is, how much humans use, and how much ecosystems need, he said. “So right off the bat, we are at a disadvantage.”
Focus on Efficiency, Infrastructure to Better Manage Water
One of the major concepts that has connected various volumes of The World’s Water is the concept of a “soft path for water” – a strategy for moving towards a more sustainable future for water through several key focus points: improved efficiency, decentralized infrastructure, and broadly rethinking water usage and supply.
Other cross-cutting themes include climate and water, peak water, environmental security, and the human right to water (formally recognized in a 2010 UN General Assembly resolution). “I would argue that all of these combined offer to some degree a different way of thinking about water, an integrated way of thinking about water,” Gleick said.
The China Issue
The role of China has been one of the most significant changes over the course of the series, said Gleick. The growth in the Chinese economy has led to a massive growth in demand for water (see the Wilson Center/Circle of Blue project, Choke Point: China), as well as massive contamination problems. The newest volume addresses these issues as well as China’s dam policies – internally, with neighboring countries, and around the world.
Gleick pointed out that China is one of the only nations (maybe the only) that still has a massive dam construction policy, and their installed capacity is already much larger than the United States, Brazil, or Canada. In addition, Chinese companies and financial interests are involved in at least 220 major dam projects in 50 countries around world. These projects have become increasingly controversial, for both environmental and political reasons, he said.
“My lens is typically a water lens,” Gleick said, but “none of us can think about the problems we really care about, unless we think about a more integrated approach.” Gleick emphasized the need for new thinking about sustainable, scalable, and socially responsible solutions. “We have to do more than we are doing, in every aspect of water,” he concluded.
Event Resources
Photo Credit: “Water,” courtesy of flickr user cheesy42.
Showing posts from category climate change.