Showing posts from category *Blog Columns.
-
Water Security, Nonproliferation, and Aid Shocks in the Middle East
›In a report sponsored by the Stanley Foundation and the Stimson Center, authors Brian Finlay, Johan Bergenas, and Veronica Tessler discuss the implications of what a growing population and dwindling water supply will have on the people and governments of the Middle East. In the report, titled “Beyond Boundaries in the Middle East: Leveraging Nonproliferation Assistance to Address Security/Development Needs with Resolution 1540,” the authors point out that while the Middle East has six percent of the world’s population, it has only 0.7 percent of the world’s fresh water resources. This supply is expected to be halved in the coming decades due to “rapid population growth and increased standards of living in urban areas.” To make up for this shortfall, governments are turning to nuclear-powered desalination technology, which poses risks to the nonproliferation movement and the safety and stability of the region. (Editor’s note: for more on water as a strategic resource in the Middle East, see CSIS’ latest report.)
A recent study by Richard Nielsen, Michael Findley, Zachary Davis, Tara Candland, and Daniel Nielson from Bringham Young University examines the relationship of severe decreases in foreign aid to inciting violence among rebels in recipient countries. The study, “Foreign Aid Shocks as a Cause of Violent Armed Conflict”, examines aid shocks in 139 countries from 1981-2005. The authors find that when a donor country cuts off or suddenly limits aid due to economic or political reasons, this volatility upsets the status quo and gives strength to rebel groups who play upon the government’s inability to deliver adequate resources to the population. Instead of a sudden or sharp withdrawal in aid, Nielsen et al conclude that “if donors decide to remove aid, they should do so gradually over time because sudden large decreases in aid could be deadly.” -
Mapping the “Republic of NGOs” in Haiti
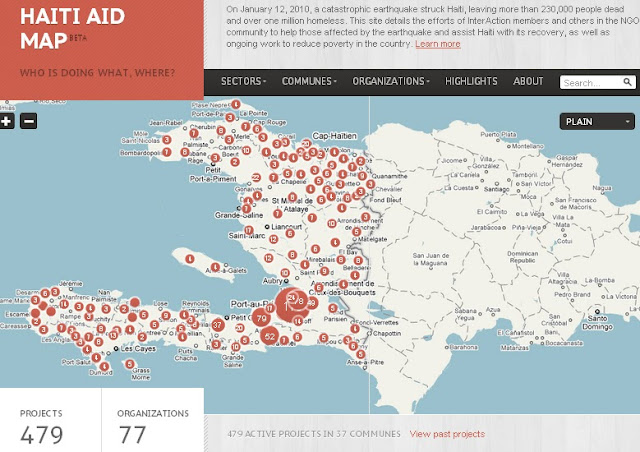
›One year after the devastating earthquake that hit Haiti, InterAction has teamed up with the U.S. Chamber of Commerce’s Business Civic Leadership Center and FedEx to launch the Haiti Aid Map, an interactive visual mapping platform of individual aid projects being conducted in Haiti. The goals of the map are to increase aid transparency, facilitate partnerships, and help NGOs and others better coordinate and allocate resources to aid relief and reconstruction efforts.
With an estimated 10,000 NGOs operating on the ground – the second largest per capita in the world – Haiti has been referred to as “a republic of NGOs.” The Haiti Aid Map is an effort to help the humanitarian community – which has been criticized for lack of accountability, poor transparency, and corruption – better coordinate its response.
The map features 479 projects being operated all over the country by 77 local and international NGOs, most of which are InterAction members. Projects can be browsed by location, sector, or organization and include information on project donors, budgets, timelines, and the number of people reached by the project.
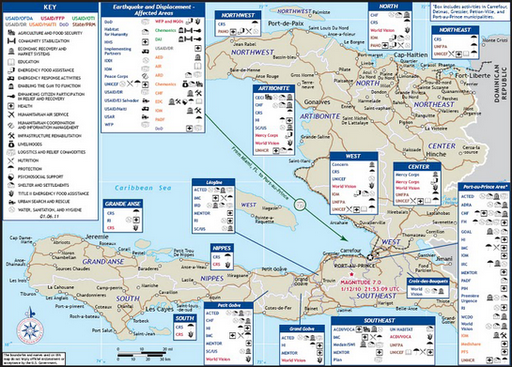
While InterAction’s map covers their donors’ response, it leaves out the thousands of government and other NGO projects being conducted in Haiti. USAID recently released a map of U.S. government projects in Haiti (see right) by sector and location.
“The goal is not to rebuild Haiti but to build a different Haiti,” said Sam Worthington, President and CEO of InterAction, speaking exactly one year after the earthquake struck at the map’s formal launch this month. “The relief effort will still be here a year from now.” The goal of the map will be to help coordinate activities as reconstruction continues in the future.
The map is the first part of a larger mapping platform, called the NGO Aid Map, which will include not only the Haiti aid map but also projects working on food security in other developing countries. The food security map is due to be launched in March 2011.
Sources: Clinton Foundation, InterAction, NPR, ReliefWeb, USIP.
Image Credit: Adapted from Haiti Aid Map. -
Elizabeth Malone on Climate Change and Glacial Melt in High Asia
› “There’s nothing more iconic, I think, about the climate change issue than glaciers,” says Elizabeth Malone, senior research scientist at the Joint Global Change Research Institute and Pacific Northwest National Laboratory. Malone served as the technical lead on “Changing Glaciers and Hydrology in Asia: Addressing Vulnerability to Glacier Melt Impacts,” a USAID report released in late 2010 that explores the linkages between climate change, demographic change, and glacier melt in the Himalayas and other nearby mountain systems.
“There’s nothing more iconic, I think, about the climate change issue than glaciers,” says Elizabeth Malone, senior research scientist at the Joint Global Change Research Institute and Pacific Northwest National Laboratory. Malone served as the technical lead on “Changing Glaciers and Hydrology in Asia: Addressing Vulnerability to Glacier Melt Impacts,” a USAID report released in late 2010 that explores the linkages between climate change, demographic change, and glacier melt in the Himalayas and other nearby mountain systems.
Describing glaciers as “transboundary in the largest sense,” Malone points out that meltwater from High Asian glaciers feeds many of the region’s largest rivers, including the Indus, Ganges, Tsangpo-Brahmaputra, and Mekong. While glacial melt does not necessarily constitute a large percentage of those rivers’ downstream flow volume, concern persists that continued rapid glacial melt induced by climate change could eventually impact water availability and food security in densely populated areas of South and East Asia.
Rapid demographic change has potentially factored into accelerated glacial melt, even though the connection may not be a direct one, Malone adds.
Atmospheric pollution generated by growing populations contributes to global warming, while black carbon emissions from cooking and home heating can eventually settle on glacial ice fields, accelerating melt rates. Given such cause-and-effect relationships, Malone says that rapid population growth and the continued retreat of High Asian glaciers are “two problems that seem distant,” yet “are indeed very related.”
The “Pop Audio” series is also available as podcasts on iTunes. -
Watch: Amy Webb Girard on Integrated Development Strategies for Improved Women’s Nutrition
›“When women become pregnant…their nutrient needs shoot through the roof,” said Amy Webb Girard of Emory University’s School of Public Health in this interview with ECSP and the Global Health Initiative. Girard explains that under-nutrition is a major problem for women – especially pregnant women – in resource-poor settings.
“For example, iron requirements almost double during the course of pregnancy, but iron is one of those nutrients that are really difficult to get,” Girard explained. Meat is not readily available in many developing countries and the iron in non-meat foods is not absorbed as completely. As a result, “women by and large are unable to meet those nutrient needs,” she said.
Fortunately, there is “an arsenal of nutritional interventions available,” noted Girard, including micro-nutrient supplements, behavior change strategies, and integrated facility- and community-based delivery methods.
“Additionally I think it’s very important that we also look at food production. This is a key, key thing,” said Girard. “Women who are able to produce their own foods [and] households that can produce their own foods have greater food security.”
“A lot of these agricultural strategies serve double purposes,” Girard said. “They not only increase the available food and the quality of that food, they improve women’s livelihoods, they give them a source of income, they give them – as some studies have shown – greater ability to negotiate within their own households for how money should be spent [and] whether they should access care or not. So they actually empower women in ways beyond nutrition.” -
National Geographic’s Population Seven Billion
›The short feature above and accompanying cover article in the January 2011 issue launch National Geographic’s seven-part year-long series examining global population. The world is set to hit seven billion this year, according to current UN projections, and may reach nine billion by 2045.
The authors point out that today, 13 percent of people don’t have access to clean water globally and 38 percent lack adequate sanitation. Nearly one billion people have inadequate nutrition. Natural resources are strained. Is reducing population growth the key to addressing these problems?
Not according to Robert Kuznig, author of National Geographic’s lead article, who writes that “fixating on population numbers is not the best way to confront the future…the problem that needs solving is poverty and lack of infrastructure, not overpopulation.”
“The most aggressive population control program imaginable will not save Bangladesh from sea-level rise, Rwanda from another genocide, or all of us from our enormous environmental problems,” writes Kuznig. Speaking on NPR’s Talk of the Nation last week, he reiterated this message, saying global problems “have to be tackled whether we’re eight billion people on Earth, or seven, or nine, and the scale for them is large in any case.”
Instead, the challenge is simultaneously addressing poverty, health, and education while reducing our environmental impact, says Kuznig.
“You don’t have to impose prescriptive policies for population growth, but basically if you can help people develop a nice, comfortable lifestyle and give them the access to medical care and so on, they can do it themselves,” said Richard Harris, a science correspondent for NPR, speaking with Kuznig on Talk of the Nation.
Kuznig’s article highlights the Indian state of Kerala, where thanks to state investments in health and education, 90 percent of women in the state can read (the highest rate in India) and the fertility rate has dropped to 1.7 births per woman. One reason for this is that educated girls have children later and are more open to and aware of contraceptive options.
Whither Family Planning?
In a post on Kuznig’s piece, Andrew Revkin, of The New York Times’ Dot Earth blog, points to The New Security Beat’s recent interview with Joel E. Cohen about the crucial role of education in reducing the impact of population growth. Cohen asks: “Is it too many people or is it too few people? The truth is, both are real problems, and the fortunate thing is that we have enough information to do much better in addressing both of those problems than we are doing – we may not have silver bullets, but we’re not using the knowledge we have.”
Although the National Geographic article and video emphasize the connections between poverty reduction, health, education, and population growth, both give short shrift to family planning. It’s true that fertility is shrinking in many places, and global average fertility will likely reach replacement levels by 2030, but parts of the world – like essentially all of sub-Saharan Africa for example – still have very high rates of fertility (over five) and a high unmet demand for family planning. Globally, it is estimated that 215 million women in developing countries want to avoid pregnancy but are not using effective contraception.
Development should help reduce these levels in time, but without continued funding for reproductive health services and family planning supplies, the declining trends that Kurznig cites, which are based on some potentially problematic assumptions, are unlikely to continue.
As Kuznig told NPR, “you need birth-control methods to be available, and you need the people to have the mindset that allows them to want to use them.”
At ECSP’s “Dialogue on Managing the Planet” session yesterday at the Wilson Center, National Geographic Executive Editor Dennis Dimick urged the audience to “stay tuned – you can’t comprehensively address an issue as global and as huge as this in one article, and within this series later in the year we will talk about [family planning] very specifically.” Needless to say, I look forward to seeing it, as addressing the unmet need for family planning is a crucial part of any comprehensive effort to reduce population growth and improve environmental, social, and health outcomes.
Sources: Center for Global Development, Dot Earth, NPR, Population Reference Bureau, World Bank.
Video Credit: “7 Billion, National Geographic Magazine,” courtesy of National Geographic. -
Watch: Cynthia Brady on Natural Resources, Climate Change, and Conflict at USAID
›“While we know that natural resources alone are neither necessary nor sufficient to drive conflict, we do know that competition over resources and their revenues often helps to drive conflict and to sustain it over time,” said Cynthia Brady, a senior conflict advisor at USAID’s Office of Conflict Management and Mitigation. “We also know that climate change impacts are going to interact with those dynamics, so we need to better understand how, in order to really program effectively against it in the future.”
Brady spoke to an audience of peacebuilding professionals at the 2010 Alliance for Peacebuliding Conference in Annapolis, Maryland, this fall. She noted that the issue of climate security is a relatively new one and when talking about the risks of climate-related conflict, it’s important to avoid hyperbole.
“The science of analyzing both the risks of climate impacts and the risks of conflict is pretty uncertain – they’re both still evolving,” Brady said. “There’s a very limited evidence base of real-world analysis from which we draw about this intersection.”
“I think it’s really important that we avoid over-simplification and we really focus, as peacebuilding and conflict practitioners, on the reality that conflict is such a complex phenomenon, and that opens a lot of opportunities for various points of intervention,” said Brady. -
Greater Than the Sum of Its Parts: Quantifying the Integration of Population, Health, and Environment in Development
›It makes intrinsic sense that integrated approaches working across development sectors are a good thing – especially when it comes to the complex issues facing people in developing countries and the environment in which they live. After all, integration avoids overlap and redundancies, and adds value to results on the ground. Yet, quantifying the benefit of integration has been difficult and to date, little on this topic has been published in the peer-reviewed literature.
Not anymore. Our article, “Integrated management of coastal resources and human health yields added value: a comparative study in Palawan (Philippines),” recently published in the journal Environmental Conservation, breaks new ground. Rigorous time-series data and regression analysis document evidence of different disciplines working together to produce synergies not obtainable by any one of the disciplines alone.
The article presents quasi-experimental research recently conducted in the Philippines that tested the hypothesis that a specific model of integration – one in which family planning information, advocacy, and service delivery were integrated with coastal resources management – yields better results than single-sector models that provide only family planning or coastal resources management services.
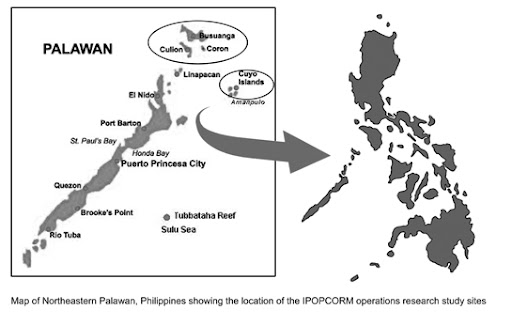
The study collected data from three island municipalities in the Palawan region of the Philippines, where the residents are dependent on coastal resources for their livelihoods. The integrated model was implemented in one municipality, while the single-sector models (one coastal resource management program and one reproductive health management program) were conducted in two separate municipalities.
The results of the study provide strong evidence that the integrated model outperformed the single-sector models in terms of improvements in coral reef and mangrove health; individual family planning and reproductive health practices; and community-level indicators of food security and vulnerability to poverty. Young adults – especially young men – at the integrated site were more likely to use family planning and delay early sex than at the sites where only family planning and reproductive health interventions were provided.
Coral reef health – as measured by a composite condition index – and mangrove health increased significantly at the integrated site, compared to the site where only coastal resource management interventions were provided. Data from the integrated site also showed a significant decline in the number of full-time fishers, as well as fewer people who knew someone that used cyanide or dynamite to fish – both factors that amplify a community’s vulnerability to food insecurity. Finally, the proportion of young people with income below the poverty threshold decreased by a significant margin in areas where the integrated population and coastal resources management (IPOPCORM) model was applied.
Let’s hope this research is just the beginning of a more thoughtful and effective approach to meeting multiple development goals in a lasting mannerEducational activities at the integrated site focused on illuminating the intrinsic relationship between fast-growing coastal communities in the Philippines and the diminishing health of the coral reefs and fisheries that they depend on for food and livelihoods. Community change agents, often fishermen and their families, talked to their neighbors and fellow fishers about the importance of planning and spacing families and establishing and respecting marine reserves to protect the supplies of food from the sea. They referred those interested in family planning to community-based social marketers of contraceptives or the nearest health center for other services.
These same community members also participated in activities to sustainably manage their coastal resources: working with local government officials to establish marine reserves, replant mangroves, serve as community fish wardens to patrol those reserves, test out alternative livelihoods such as seaweed farming, and start small businesses to diversify their income and reduce fishing pressure.
Development professionals should pay close attention to the conclusions of this study. In environmentally significant areas where human population growth is high, it will be difficult to sustain conservation gains without parallel efforts to address demographic factors and inequities in the distribution of health and family planning services. Integrating responses to population, health, and environment (PHE) issues provides an opportunity to address multiple stresses on communities and their environments and, as this study demonstrates, adds value in such a way that significantly improves community resilience and other outcomes.
This research allows those of us who believe strongly in integrating population, health, and environment programming to point to quantitative proof that the approach works. We now need to expand PHE programming to reach more people in other parts of the world where communities face a similar nexus of challenges. New initiatives have started taking the lessons from this research, applying them to new contexts in Africa and Asia, and scaling them up to reach many more in the Philippines.
Let’s hope this research is just the beginning of a more thoughtful and effective approach to meeting multiple development goals in a lasting manner in the places that need it most.Leona D’Agnes is the technical director of IPOPCORM, Joan Castro is the executive vice president of PATH Foundation Philippines Inc, and Heather D’Agnes is the Population, Health, Environment Technical Advisor in the U.S. Agency for International Development’s (USAID) Office of Population and Reproductive Health.
Sources: BALANCED, Link TV, PATH Foundation Philippines Inc., World Wildlife Foundation.
Image Credit: Philippines village (adapted) and municipalities map courtesy of PATH Foundation Philippines Inc. -
Women and Climate Change
›A new Worldwatch Institute report, “Population, Climate Change, and Women’s Lives,” by Robert Engelman, discusses the relationship between women’s equality and climate change. Slowing population growth will reduce greenhouse gas emissions and help societies adapt to climate change, says Engelman. What’s more, this can only be done through an investment in women’s rights and education. Population change comes primarily through reducing unintended pregnancies by offering men and women access to family planning services, improving education for all (especially girls and women), and promoting full gender equality. “Population change should be viewed as one element of the historic effort to bring women into equal standing with men,” writes Engelman.
A recent report by Scott Moreland, Ellen Smith, and Suneeta Sharma of the Futures Group analyzes just what the impact of meeting the unmet need for family planning would be on global population growth. Looking at 99 developing countries and the United States, the report, titled World Population Prospects and Unmet Need for Family Planning, found that by gradually meeting the global demand for family planning, population would be reduced to 6.3 billion people by 2050, below current world population and well below the UN medium fertility variant prediction, which is derived from past trends but does not take into account meeting unmet need for family planning. Meeting this need would only cost $3.7 billion more per year than the UN medium fertility variant scenario and less than the low scenario. $1.4 billion of this would cover the unmet demand in the United States.