Showing posts from category security.
-
More on Tunisia’s Age Structure, its Measurement, and the Knowledge Derived
›February 4, 2011 // By Richard CincottaThis post is a response to the questions and comments that my fellow demographers Elizabeth Leahy Madsen, Jack Goldstone, and Jennifer Dabbs Sciubba put to my recent assessment of Tunisia’s chances for democracy. I’ve divided my response to address the principal questions. (Note: Throughout, “young adults” refers to 15-24 year olds, and “working age population” refers to those between 15-64 years old.)
1. Tunisia’s age structure is still quite young – aren’t the effects associated with youth bulge still at work?
Tunisia’s age structure (median age, 29 years) is in the early stages of transiting between the instability that typically prevails in countries with youthful age structures (median age <25), and the stability that is typical of mature structures (median age between 35 to 45). I classify Tunisia’s age structure as intermediate (between 25 to 35). The Jasmine Revolution has featured a mix of both types of sociopolitical behavior: some violence and property damage, perpetuated by both the state and demonstrators; evidence of a mature, professionally-led institution (the Tunisian army); and demonstrations that are peaceful and in which women and older people participate.
By any legitimate youth bulge measure, Tunisia’s age-structure is similar to that of South Korea, Taiwan, and Thailand’s during the mid-1990s. In 2010, Tunisia’s proportion of young adults in the working age population was almost precisely the same as South Korea’s in 1993. South Korea’s median age in 1993 was 28.5, compared to Tunisia’s 29 today.
Consistent with these numerical similarities, Tunisia’s political behavior is not much different than the sociopolitical events observed in South Korea, Taiwan, or Thailand in the early 1990s when these countries experienced an age structure of similar maturity. As these countries matured, political violence and destructive protests occurred less frequently but dissidence lingered in more peaceful, isolated incidents. For example, South Korea experienced several deadly anti-U.S. demonstrations in 1988-89 and only a few minor incidents in the early 1990s. By 1993, the public was demonstrating against extremism, and public protest had turned peaceful and symbolic.
Even today, public protest in Thailand (median age, 33 years) is commonplace. Thai political rights are constrained, and accordingly the country has been dropped in Freedom House’s annual assessment of political freedoms from “free” to “partly free.” However, unlike the student and worker riots that occurred sporadically throughout the 1970s and 80s, Thai demonstrations are typically non-confrontational political rallies attended by T-shirt-clad grandparents and families who bus into town for the event.
2. Why use the population’s median age rather than the youth bulge measures that political demographers (including me) have previously employed with considerable success?
I’m experimenting, and so far, I’ve found that median age replicates prior published results concerning civil conflict and stable liberal democracy. Median age’s ability to span the entire length of the demographic life-cycle of the state is its primary advantage. Youth bulge indicators do not; neither do indicators focused on working-age adults, nor those measuring seniors. In addition, median age integrates many factors that change in parallel with the age-structural transition, including income, education, women’s participation in society, secularization, and technological progress. Still, median age doesn’t track the youth bulge measures perfectly, so why use it?
Currently, foreign affairs policymakers see few linkages between a country’s (1) risk of civil and political violence; (2) its propensity to accumulate savings and human capital; (3) its chances of attaining stable liberal democracy; (4) the challenges that arise to adequately funding pensions and senior healthcare; and (5) rapid ethnic change in low fertility societies. Political demographers understand that these effects on the state are indeed related and that the rising and ebbing probabilities associated with these effects occur sequentially. Understanding this sequence is key to understanding the world’s international relations future. Median age allows political demographers to view that sequence.
As Jennifer Sciubba points out, the disadvantage of median age is its apparent lack of resonance with theories that have historically informed political demography, including theories of cohort crowding, dependent support, and life-cycle savings. I don’t believe that political and economic demographers should (or will) abandon these indicators, which help them observe the inner workings of age-structural phenomena. Nonetheless, I find it useful to make analysts aware of the advantageous and disadvantageous pressures that age structure exerts across the entire demographic life cycle of the state.
3. Can the deposed regime’s multi-faceted problems be captured by the age-structural transition?
No, age-structure cannot account for leadership – clumsy or deft, corrupt or honest. The method is limited to predictions that draw on sociopolitical behaviors that are associated with age structures, or by knowledge gained from deviations from these predictions. Nonetheless, I question the value of many of the after-the-fact observations of the Ben Ali Regime. Tunisia’s fallen regime was indeed oppressive, corrupt, and nepotistic – but so are most authoritarian regimes in Asia and Africa. Lack of job creation and preferential access to employment are valid grievances across much of the developing world, but the lack of informal sector statistics renders country comparisons difficult.
Some analysts have hypothesized that global warming has been a contributor (also applied to Egypt), others point to economic globalization and pressures on Tunisia’s middle class. Whether these assertions are wrong or right, it is difficult for me to see how such post hoc observations add to analysts’ knowledge of regime change or democratization or help them explain why other countries with similar problems have not undergone similar sociopolitical dynamics. In contrast, hypotheses based on quantitative relationships between age structural indicators and sociopolitical behaviors generate testable and repeatable predictions that can be checked and held accountable after an event.
What I find most surprising about the age-structural approach to predicting liberal democracy is how often states ascend to liberal democracy as they approach, or pass, the 0.50 probability mark. If either “triggers” of regime change or key institutions were very important, this observation would be unlikely.
A Concluding Note on Political Demography
If political demographers are serious about advancing policymakers’ ability to understand the present and future of global politics and security, political demography will have to become a scientific discipline – a field of study in which assertions are consistently tied to data and tested whenever possible. In many cases, though not all, we’re lucky – demographers provide us with timely estimates and projections at the national level. Nonetheless, for our field to succeed, political demographers must take full advantage of these data, encourage sub-national data to be collected and published, and make a clean break from the tradition of conjecture that currently pervades international relations.
Richard Cincotta is a consulting political demographer for the Wilson Center’s Environmental Change and Security Project and demographer-in-residence at the Stimson Center.
Sources: CIA World Factbook, Freedom House, Jadaliyya.
Image Credit: Adapted from “Viva the Tunisian Revolution,” courtesy of flickr user freestylee (Michael Thompson). -
Book Preview: ‘The Future Faces of War: Population and National Security’
›February 3, 2011 // By Christina DaggettThe word “population” doesn’t come up too often in national security debates, yet, a shift may be coming, as global population reaches the seven billion mark this year, youth-led unrest rocks the Middle East, and questions of aging enter the lexicon of policymakers from Japan and South Korea to Europe and the United States. What does a population of nine billion (the UN medium-variant projection for 2050) mean for global security? How will shrinking populations in Europe affect Western military alliances and operations? Is demography destiny?
The latter question has plagued demographers, policymakers, and academics for centuries, resulting in heated debate and dire warnings. Jennifer Dabbs Sciubba continues this debate in her new book, The Future Faces of War: Population and National Security, but with a decidedly more measured and optimistic tone (full disclosure: Sciubba was one of my professors). The book is targeted at policymakers but is accessible to anyone with an interest in the field of demography and national security. She will launch her book at an event hosted by the Wilson Center on March 14.
Turning Challenge Into Opportunity
The main themes of The Future Faces of War are challenge and opportunity. Yes, national security will be tested by a series of evolving demographic trends in the decades ahead, but with proper insight and preparation, states can turn these challenges into opportunities for growth and betterment. Sciubba writes, “How a state deals with its demographic situation – or any other situation for that matter – is more important than the trends themselves” (p.125).
Part of turning these population challenges into opportunity is understanding long-term trends – a daunting task given the range and number of trends to consider. Drawing on her own experiences in the defense community, Sciubba writes how policymakers were “receptive” to the idea of population influencing national security, but that the “overwhelming number of ways demography seemed to matter” made them hesitant to act (p.3). With the publication of this book, which clearly and concisely outlines the basics of each population trend with demonstrative examples, hopefully that hesitation will be turned into action.
Youth and Conflict
The first population trend Sciubba highlights is perhaps the one of most immediate concern to national security policymakers given recent world events. In the chapter “Youth and Youthful Age Structures,” Sciubba discusses the security implications of those countries (in particular those in Africa, the Middle East, and Central Asia) with a majority of their population under the age of 29. She writes, “Most important for national security, countries with youthful age structures are generally the least developed and least democratic in the world, and tend to have the highest risk of civil conflict” (p. 18). In fact, between 1970 and 1999 countries with very young and youthful age structures were two to four times more likely to experience civil conflict than countries with more mature age structures.
The risks of very young and youthful populations are well documented (Sciubba cites the examples of Somali piracy, religious extremism, and child soldiers in Africa), but what has not been as widely discussed are the opportunities. Youthful states have a large pool of potential recruits for their armies, plenty of workers to drive economic development, and even an opportunity to grow democratically through social protest. Sciubba writes, “Youth can also be a force for positive political change as they demand representation and inclusion in the political process… social protest is not always a bad thing, even if it does threaten a country’s stability, because it may lead to more representative governance or other benefits” (p. 23). (For more on youth and the transition to democracy, see “Half a Chance: Youth Bulges and Transition to Democracy,” by Richard Cincotta, and his recent blog post about the Jasmine Revolution in Tunisia).
Graying of the Great Powers
At the other end of the demographic transition is population aging. Sciubba points out that the countries with the highest proportions of people aged 60 and older are also “some of the world’s most powerful and economically or politically strategic states” (p. 42). Europe, Japan, and the United States are all getting older (though the United States to a slightly lesser extent), and Sciubba states that the “graying” of these countries has the potential to greatly limit military preparedness, size, and funding. She points out that the number of recruits available will be much smaller and more money will have to be spent on pensions and health care for the growing number of elderly persons.
To counteract these challenges, Sciubba recommends that aging states seek out alliances with each other and countries with younger populations. She writes, “As part of strong alliances, states have strength in numbers, even if they are individually weakened by aging” (p. 47). Another alternative would be to improve military technology and efficiency to compensate for the drop in personnel.
Migration and Security: A “Unique” Relationship
Migration, the third pillar of demographic change after fertility and mortality, has what Sciubba calls a “unique relationship to national security” (p.83). Migration “is the only population driver that can change the composition of a state or a community within months, weeks, or even days” (p. 83). Mass migrations (such as those caused by a natural disaster or violent conflict) are the best examples of this trend. Some of the security challenges Sciubba highlights about migration are refugee militarization, competition for resources, and identity struggles among the native and migrant populations.
However, Sciubba also argues that both migrants and receiving countries can benefit. Origin states release pressure on their crowded labor markets and earn income from remittances, while receiving countries increase their labor market and mitigate population decline (a key component of U.S. growth).
Much of this has been studied before, but two new developments in migration trends that Sciubba calls to our attention are what she calls the “feminization of migration” (the increasing number of women who are likely to move for economic reasons) and migration as a result of climate change. Both are intriguing new areas of inquiry that deserve further study, but only get a passing mention in the book.
Making Her Case
The basic trends outlined above are only a small sampling of the wealth of information to be found in The Future Faces of War. Other noteworthy topics include a discussion on transitional age structures, urbanization, gender imbalances, HIV/AIDS, differential growth among ethnic groups, and many more. The topics are varied and wide-ranging and yet, Sciubba manages to connect them and makes her case convincingly for their inclusion in the broader national security dialogue. Sciubba has briefly written about many of these topics before, but this is the first time she (or anyone else, for that matter) has brought them together in one comprehensive book with such a focus on national security.
Christina Daggett is an intern with ECSP and a former student of Jennifer Dabbs Sciubba’s at Rhodes College.
Sources: Population Action International.
Photo Credits: “Children at IDP Camp Playful During UNAMID Patrol,” courtesy of flickr user United Nations Photo. Book cover image provided by, and used with the permission of, Jennifer Dabbs Sciubba and ABC-CLIO. -
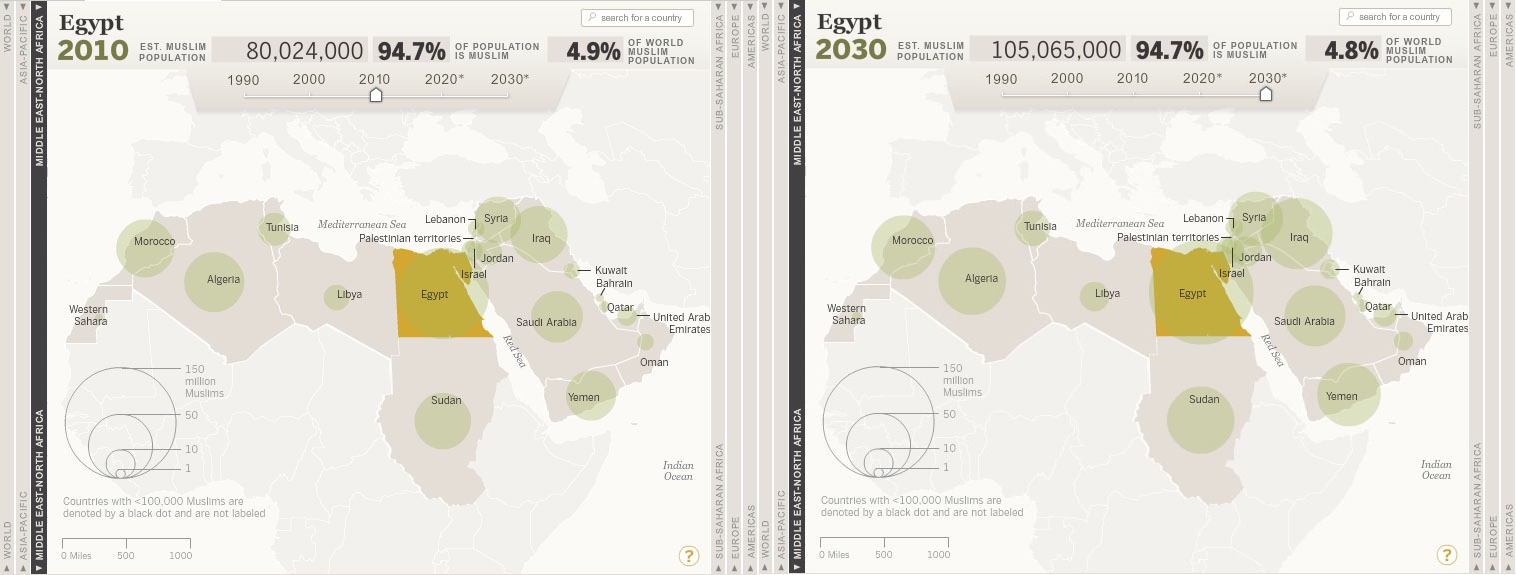
Mapping Muslim Population Growth
›Recent unrest in Tunisia, Egypt, Yemen, and elsewhere across the Middle East has led to a resurgence of interest in the region’s demography, just in time, it turns out, for the Pew Forum on Religion and Public Life’s 2011 refresh of its report on Muslim population growth, which this year includes a new interactive feature, “The Global Muslim Population.”
According to the report, current security hot-spots such as Afghanistan, Iraq, Yemen, Syria, Somalia, and Nigeria will continue to grow considerably faster than the mean.
On the flip side, the report also found that the median age in the Middle East-North Africa region is rising – a generally agreed upon good indicator for the prospects of more liberal, democratic regimes – and though global Muslim population will continue to grow faster than the world’s non-Muslim population, this growth will be slower than in decades past.
The accompanying interactive feature allows users to select a region (the Americas, Europe, Middle East/North Africa, Sub-Saharan Africa, or Asia-Pacific), a specific country, and a decade (1990-2030) in their search. In the example above, Egypt will add 25 million Muslims to its population over the next two decades, representing a 30 percent increase. Comparatively, from 1990 to 2010, Egypt’s Muslim population increased by 48.5 percent.
The user is able to see the estimated Muslim population of the country, the percent of the total population that is Muslim, and the country’s percent share of the world’s total Muslim population (as seen in the example above of Egypt in 2010 and 2030). In addition, these variables can be sorted in tables.
It’s important to note though, write the authors of the report, that projections are not predictions:This report makes demographic projections. Projections are not the same as predictions. Rather, they are estimates built on current population data and assumptions about demographic trends; they are what will happen if the current data are accurate and the trends play out as expected. But many things – immigration laws, economic conditions, natural disasters, armed conflicts, scientific discoveries, social movements and political upheavals, to name just a few – can shift demographic trends in unforeseen ways, which is why this report adheres to a modest time frame, looking just 20 years down the road.
Image Credit: Pew Research Center’s Forum on Religion and Public Life.
Sources: Pew Forum on Religion and Public Life. -
The Age of Revolution? Demography Experts Comment on Tunisia’s Shot at Democracy
›January 28, 2011 // By Schuyler NullAs unrest continues across several Middle Eastern countries, analysts are scrambling to explain the “arc of revolution.” Richard Cincotta’s recent post on the “Jasmine Revolution” predicts a relatively high chance of Tunisia attaining liberal democracy, based on demographic factors and long-term trends, and it’s drawn some well-thought out and provocative feedback from fellow demographers Elizabeth Leahy Madsen, Jack Goldstone, and Jennifer Sciubba.
Elizabeth Leahy Madsen is a senior research associate at Population Action International and author of The Shape of Things to Come: Why Age Structure Matters to a Safer, More Equitable World:I have two questions. First, have you shifted to a new definition of age structures (intermediate, etc.) based on median population age? In the past, you and other demographic security researchers have measured age structure as the relative proportion of different age groups within the population, either the total population, total adult population, or working-age population. Why did you select median population age for this analysis? A quick review of the figures available on the UN Population Division’s website shows that the relative size of the 15-24 age group within Tunisia’s total population has been vacillating within the range of 19-21 percent since 1975. In 2005, that “youth bulge” was 21 percent, the highest since 1980, but there has been a rapid decline to 19 percent by 2010.
Jack A. Goldstone is the director of the Global Policy Center at George Mason University and author of a number of books on social movements, revolutions, and international politics:
As you say, no matter how age structure is measured, Tunisia is much further through the demographic transition than other countries in the Arab world. I would like to see this highlighted more in media coverage of the revolution, particularly in accounts of similar attempts to provoke uprisings that have taken place in Algeria, Egypt, and Yemen in recent weeks. From a demographic perspective, those attempts are less likely to achieve success (except possibly in Algeria, based on your map).
My second question is for further elaboration on the steps that lead from a dissipating youth bulge to a greater likelihood of attaining democracy (leaving aside the also-difficult question of sustainability). If I understand your description of the mechanisms at work, in an authoritarian regime with a youth bulge, the government is able to keep its hold on power because the presence of a youth bulge either creates volatility or the threat of volatility in the eyes of the commercial elites whose support is critical to the regime. Does this support exist even in situations where volatility is rare, in which case the large youthful population is manipulated or whitewashed by the regime as a threat to stability? Then, as the age structure matures and becomes less youthful, the regime can no longer invoke youth (directly or indirectly) as a danger, and therefore support for the regime from the elites erodes?
You don’t specifically mention economic conditions in Tunisia, apart from Ben Ali’s resource hoarding, but issues such as unemployment rates have been frequently highlighted in media accounts of the revolution. In addition to the unpredictable triggers such as the self-immolation in Tunisia’s case, do deeper-seated structural problems such as high unemployment and/or rampant corruption have to be extant to provoke revolution in an authoritarian context? Or is the dissolution of a youthful age structure combined with an unpredictable trigger sufficient?Richard’s insights into Tunisia’s prospects for democracy are terrific and I agree with him. However, in regard to the causes of the rebellion, I have to disagree with him in one respect – Tunisia in 2010 is very much a youth bulge country, at least as far as political theory would see it. As Henrik Urdal has shown, youth bulge should not be measured as the size of the youth cohort (15-24) against the entire population, but as the fraction of youth in the adult population (those aged 15 and older). The 0-14 group is politically not relevant, and should not be counted in assessing the impact of youth cohorts on the total population’s political mobilization potential.
Jennifer Sciubba is a Mellon Environmental Fellow at Rhodes College and the author of The Future Faces of War: Population and National Security:
For Tunisia, median age may in fact be misleading (as I didn’t realize until I looked at the age pyramids that Richard has posted). Because birth rates fell very rapidly after 1995, median age in 2010 is intermediate, but if you look only at the population aged 15 and up, you still see very large cohorts of youth compared to total adults.
Because Tunisia’s birth rate only started falling sharply after 1995, the large cohorts born in 1986-1995 – now age 15-24 – still make up a very large portion (33 percent) of all adults. While the next cohorts are much smaller, meaning this youth bulge will soon fade, it is still very much present, as Richard’s graphs show.
There is no automatic link between a certain age structure and political rebellion, but the combination of a large youth bulge and economic frustration among youth is a potent force for political instability. That combination is certainly one feature of Tunisia in 2010, although the extreme corruption of the Ben Ali regime and his family was a galling and critical factor in the widespread rejection of his regime.
That points to another bit of misleading data. Many (including me) assumed that because Tunisia’s recent economic growth was strong, at five percent per year, economic grievances could not be so widespread. But that is wrong, because we did not appreciate how much of that growth has been grabbed by Ben Ali’s family (which according to one account had ownership interests in half the businesses in the country) and cronies. Substantial growth from which many have been excluded – especially youth – is in fact a reason for widespread grievances, and that was another key factor behind the mass protests.Like Jack and Liz note, using median age helps us understand Tunisia’s progress along the demographic transition, but it doesn’t really help us understand the protests in Tunisia or in other countries across the “arc of revolution.” Median age obscures the individual experiences of young adults who are putting their lives at risk to speak out in protest or setting themselves on fire in desperation. As Jack points out, from a theoretical point of view, Tunisia is very much experiencing cohort crowding – whether we call it “youth bulge” or “early worker bulge” the outcome is the same. To say that Tunisia is not a youth bulge country misses the point.
Cincotta has promised a reply to the comments is forthcoming, which we can forgive him, frankly, given the length and complexity of these great responses.
Part of the reason we political demographers buy into the link between youth bulge and conflict is the idea of cohort crowding. As Richard Easterlin points out, a cohort’s economic and social prospects tend to have an inverse relationship to the cohort’s size relative to those around it, other things being constant. In Tunisia’s case, those between ages 25-35 are part of a larger cohort than those preceding ones so they are crowded out of the labor market and will tend to have lower relative income compared to preceding generations, which are smaller.
As I note in my book, one study of Tunisians looking for work reported that young adults felt crowded out of benefits in the family, school, and labor markets. In particular, according to a study by M. Bedoui and G. Ridha:“…family and marital problems were common. They became poorer, lost confidence, and became fatalistic and submissive. Over the long run the majority saw unemployment as a source of disequilibrium, humiliation, and even oppression.” (in Hilary Silver, “Social Exclusion: Comparative Analysis of Europe and Middle East Youth,” Middle East Youth Initiative Working Paper p. 30.)
That quotation seems eerily prescient in Tunisia’s case. Mohamed Bouazizi certainly seemed to succumb to fatalism, and the protests started as economic but quickly moved to political. Political, social, and economic marginalization are connected. While there is some diversity in age structure across the Middle East, the populations of those aged 15-24 in Egypt, Lebanon, Tunisia, Jordan, Algeria and Iran, which experienced youth protests in 2009, are all between 27 and 34 percent of all adults ages 15-59, with Lebanon and Tunisia at the lower end of the spectrum and Egypt and Jordan at the higher. As we can see from the population pyramid of each of these states, there is a clear population bulge at these ages.
We also have to think about the cohort effect. The cohort effect describes shared historical experiences of particular age groups. Across the “arc of revolution,” young adults are plugged into Facebook, Twitter, and other internet forums to share experiences of marginalization and revolution. This likely informs their choice of whether or not to speak out.
Sources: Huffington Post, Middle East Youth Initiative, The New York Times, Telegraph.
Photo Credit: “055,” courtesy of flickr user Nasser Nouri. -
Carl Haub, Behind the Numbers
Taiwan’s Birth Rate Lowest Recorded in History
›January 27, 2011 // By Wilson Center StaffExcerpted from the original article, by Carl Haub, on the Population Reference Bureau’s Behind the Numbers blog:
Taiwan’s government has just announced that the country’s total fertility rate (or TFR, the average number of children a woman would bear in her lifetime if the birth rate of a particular year were to remain unchanged) in 2010 was the lowest in its history at 0.91 children per woman. It’s the lowest rate any country has ever reported in history. The announcement itself is a bit of a projection since births have been officially reported only through November 2010. The country’s TFR had declined to 1.1 in 2005 and had remained there through 2009.
The rather spectacular drop in 2010 was due to an additional reason: 2010 is the Year of the Tiger on the Chinese calendar, beginning on February 14. The Tiger year is particularly inauspicious for births since Tigers, while seen as brave, are also seen as headstrong and possibly difficult to work with. It is quite common for employers to consider the zodiac of job applicants and Tigers may be avoided so that parents have some concrete reasons to avoid having a child in Tiger years. While there has been a lot of concern over the demographic situation for some time, Taiwan’s President Ma Ying-jeou has now called for measures to increase the birth rate to be raised to the “national security level.”
Continue reading on Behind the Numbers.
Sources: Asia Times, USA Today.
Photo Credit: Adapted from “070923 sleeping baby,” courtesy of flickr user Wowo and her families. -
Tunisia’s Shot at Democracy: What Demographics and Recent History Tell Us
›January 25, 2011 // By Richard Cincotta
While events in Tunisia, beginning mid-December and leading ultimately to President Ben Ali’s departure within a month, have rocked the Arab world, they leave an open question: Will Tunisia’s “Jasmine Revolution” ultimately lead to the Arab world’s first liberal democracy? [Video Below]
-
Water Security, Nonproliferation, and Aid Shocks in the Middle East
›In a report sponsored by the Stanley Foundation and the Stimson Center, authors Brian Finlay, Johan Bergenas, and Veronica Tessler discuss the implications of what a growing population and dwindling water supply will have on the people and governments of the Middle East. In the report, titled “Beyond Boundaries in the Middle East: Leveraging Nonproliferation Assistance to Address Security/Development Needs with Resolution 1540,” the authors point out that while the Middle East has six percent of the world’s population, it has only 0.7 percent of the world’s fresh water resources. This supply is expected to be halved in the coming decades due to “rapid population growth and increased standards of living in urban areas.” To make up for this shortfall, governments are turning to nuclear-powered desalination technology, which poses risks to the nonproliferation movement and the safety and stability of the region. (Editor’s note: for more on water as a strategic resource in the Middle East, see CSIS’ latest report.)
A recent study by Richard Nielsen, Michael Findley, Zachary Davis, Tara Candland, and Daniel Nielson from Bringham Young University examines the relationship of severe decreases in foreign aid to inciting violence among rebels in recipient countries. The study, “Foreign Aid Shocks as a Cause of Violent Armed Conflict”, examines aid shocks in 139 countries from 1981-2005. The authors find that when a donor country cuts off or suddenly limits aid due to economic or political reasons, this volatility upsets the status quo and gives strength to rebel groups who play upon the government’s inability to deliver adequate resources to the population. Instead of a sudden or sharp withdrawal in aid, Nielsen et al conclude that “if donors decide to remove aid, they should do so gradually over time because sudden large decreases in aid could be deadly.” -
How Population Growth Is Straining the World’s Most Vital Resource
Turning Up the Water Pressure [Part Two]
›January 19, 2011 // By Russell SticklorThis article by Russell Sticklor appeared originally in the Fall 2010 issue of the Izaak Walton League’s Outdoor America magazine. Read part one here.
As concerns over water resources have grown around the globe, so too have proposed solutions, which range from common sense to absurd. Towing icebergs into the Persian Gulf or floating giant bags of fresh water across oceans to water-scarce countries are among the non-starters. But more moderate versions of those ideas are already being put into practice. These solutions showcase the power of human ingenuity — and reveal just how desperate some nations have become to secure water.
For example, India is doing business with a company out of tiny Sitka, Alaska, laying the framework for a water-export deal that could see huge volumes of water shipped via supertankers from the water-rich state of Alaska to a depot south of Mumbai. Depending on the success of this arrangement, moving bulk water via ship could theoretically become as commonplace as transoceanic oil shipments are today.
There is far greater potential, however, in harnessing the water supply of the world’s oceans. Perhaps more than any other technological breakthrough, desalination offers the best chance to ease our population-driven water crunch, because it can bolster supply. Although current desalination technology is not perfect, Eric Hoke, an associate professor of environmental engineering at the University of California-Los Angeles, told me via email, it is already capable of converting practically any water source into water that is acceptable for use in households, agriculture, or industrial production. Distances between supply and demand would be relatively short, considering that 40 percent of the world’s population — some 2.7 billion people — live within 60 miles of a coastline.
The Lure of Desalination
Although desalination plants are already up and running from Florida to Australia, the jury is still out on the role desalination can play in mitigating the world’s fresh water crisis. Concerns persist over the environmental impact seawater-intake pipes have on marine life and delicate coastal ecosystems. Another question is cost: Desalination plants consume enormous amounts of electricity, which makes them prohibitively expensive in most parts of the world. Desalination technology may not be able to produce water in sufficient scale — or cheaply enough — to accommodate the growing need for agricultural water. “Desalination is more and more effective [in producing] large quantities of water,” notes Laval University Professor Frédéric Lasserre in an interview. “But the capital needed is huge, and the water cost, now about 75 cents per cubic meter, is far too expensive for agriculture.” Although desalination might be “a good solution for cities and industries that can afford such water,” Lasserre predicts it “will never be a solution for agricultural uses.”
Nevertheless, desalination’s promise of easing future water crunches in populous coastal regions gives the technology game-changing potential at the global level. “Desalination technology,” Columbia University’s Upmanu Lall told said in an email, “will improve to the point that [water scarcity] will not be an issue for coastal areas.”
A Glass Half Full
With world population projected to grow by at least 2 billion during the next 40 years, water will likely remain a chief source of global anxiety deep into the 21st century. Because water plays such a fundamental role in everyday life across every society on earth, its shared stewardship may become an absolute necessity.
Take India and Pakistan’s landmark Indus Waters Treaty of 1960, which is still in effect today. The agreement — signed by two countries that otherwise can’t stand each other — shows that when crafted appropriately and with enough patience, international water-sharing pacts can help defuse tensions over water access before those tensions escalate into violence. Similar collaboration on managing shared waters in other areas of the world — a process that can be a bit bumpy at times — has proven successful to date.
Meanwhile, more widespread distribution of reliable family planning tools and services across Latin America, sub-Saharan Africa, and Asia will also be needed if the international community hopes to meaningfully address water scarcity concerns. Better access to healthcare and family planning tools would empower women to take greater control over their reproductive health and potentially elevate living standards in crowded parts of the developing world. Smaller family sizes would help decelerate population growth over time, easing the burden on water and soil resources in many areas. The key is ensuring such efforts have adequate funding. The United States recently pledged $63 billion over the next six years through its Global Health Initiative to help partner countries improve health outcomes through strengthened health systems, with a particular focus on improving the health of women and children.
Putting a dent in the global population growth rate will be important, but it must be accompanied by a sustained push for conservation — nowhere more so than in agriculture. Investing in the repair of a leaky irrigation infrastructure could help save water that might otherwise literally slip through the cracks. Attention to maintaining healthy soil quality — by practicing regular crop rotation, for example — could also help boost the efficiency of irrigation water.
Setting a Fair Price
The most enduring changes to current water-use practices may have to come in the form of pricing. In most parts of the world, including parts of the United States, groundwater removal is conducted with virtually zero oversight, allowing farmers to withdraw water as if sitting atop a bottomless resource. But as groundwater tables approach exhaustion, the equation changes; as Ben Franklin famously pointed out, “when the well’s dry, we know the worth of water.”
The key, then, is to establish the worth of water before this comes to pass. Smart pricing could encourage conservation by making it less economical to grow water-intensive crops, particularly those ill-suited to a particular climate. “Some crops being grown should not be grown . . . once the true cost of water is factored in,” Nirvikar Singh, a University of California-Santa Cruz economics professor who focuses on water issues, told me via email. Pricing would also provide a revenue stream for modernizing irrigation infrastructures and maintaining sewage systems and water treatment centers, further bolstering water efficiency and quality both in the United States and around the globe.
To be sure, implementing a pricing scheme for water resources — which have been essentially free throughout history — will be unpopular in many parts of the world. It’s natural to expect some pushback from the public as water managers and governments take steps to address the 21st century water crunch. But given the resource’s undeniable and universal value on an ever-more crowded planet, few options exist aside from using the power of the purse to push for more efficient water use.
In the end, however, water pricing must be combined with greater public value on water conservation — we must not flush water down our drains before using it to its full potential. Whether that involves improving the water transportation infrastructure, recycling wastewater, taking shorter showers, or turning to less water-intensive plants and crops, steps big and small need to be taken to better conserve and more equitably divide the world’s water to irrigate our farms, grow our economies, and sustain future generations.
Sources: Columbia Water Center, National Geographic, Population Reference Bureau, White House.
Photo Credits: “Juhu Beach Crowded,” courtesy of flickr user la_imagen, and “Irrigation (China),” courtesy of flickr user spavaai.