Yearly archive for 2011.
Show all posts
-
Reducing Urban Poverty: A New Generation of Ideas
›Download Reducing Urban Poverty: A New Generation of Ideas from the Wilson Center.
In 2008 the global population reached a remarkable turning point; for the first time in history, more than half of the world’s people were living in cities. Moving forward into the 21st century, the world faces an unprecedented urban expansion with projections for the global urban population to reach nearly five billion by the year 2030. Virtually all of this growth will occur in the developing world where cities gain an average of five million residents every month, overwhelming ecosystems and placing tremendous pressure on the capacity of local governments to provide necessary infrastructure and services. Failure to incorporate urban priorities into the global development agenda carries serious implications for human security, global security, and environmental sustainability.
Recognizing a need to develop and strengthen urban-focused practitioner and policymaking ties with academia, and disseminate evidence-based development programming, the Wilson Center’s Comparative Urban Studies Project, USAID’s Urban Programs Team, the International Housing Coalition, the World Bank, and Cities Alliance teamed up to co-sponsor an academic paper competition for graduate students studying urban issues. The first competition took place in the months leading up to the 5th World Urban Forum, held in Rio de Janeiro in March 2010.
This publication, Reducing Urban Poverty: A New Generation of Ideas, marks the second annual academic paper competition. “Reducing urban poverty” was chosen as the theme with each author focusing on one of three topics: land markets and security of tenure; health; and, livelihoods. A panel of urban experts representing the sponsoring institutions reviewed 70 submitted abstracts, from which 16 were invited to write full length papers. Of these, six were selected for this publication. We congratulate the graduate students who participated in this competition for their contribution to our understanding of the complex relationship between urbanization and poverty.
These papers highlight the new research and innovative thinking of the next generation of urban planners, practitioners, and policymakers. It is our hope that by infusing the dialogue on these issues between the academic and policy worlds with fresh perspectives, we will foster new and innovative strategies to reduce global urban poverty.
Sources: UNFPA, UN-HABITAT. -
In Colombia, Rural Communities Face Uphill Battle for Land Rights
›November 14, 2011 // By Kayly Ober“The only risk is wanting to stay,” beams a Colombian tourism ad, eager to forget decades of brutal internal conflict; however, the risk of violence remains for many rural communities, particularly as the traditional fight over drugs turns to other high-value goods: natural resource rights.
La Toma: Small Town, Big Threats
In the vacuum left by Colombia’s war on drugs, re-armed paramilitary groups remain a threat to many rural civilians. Organized groups hold footholds, particularly in the northeast and west, where they’ve traditionally hidden and exploited weak governance. Over the past five years, their presence has increased while their aims have changed.
A recent PBS documentary, The War We Are Living (watch below), profiles the struggles of two Afro-Colombian women, Francia Marquez and Clemencia Carabali, in the tiny town of La Toma confronting the paramilitary group Las Aguilas Negras, La Nueva Generacion. The Afro-Colombian communities the women represent – long persecuted for their mixed heritage – are traditional artisanal miners, but the Aguilas Negras claim that these communities impede economic growth by refusing to deal with multinationals interested in mining gold on a more industrial scale in their town.
For over seven years, the Aguilas Negras have sent frequent death threats and have indiscriminately killed residents, throwing their bodies over the main bridge in town. At the height of tensions in 2010, they murdered eight gold miners to incite fear. Community leaders know that violence and intimidation by the paramilitary group is part of their plan to scare and displace residents, but they refuse to give in: “The community of La Toma will have to be dragged out dead. Otherwise we’re not going to leave,” admits community leader Francia Marquez to PBS.
La Toma’s predicament is further complicated by corruption and general disinterest from Bogota. Laws that explicitly require the consent of Afro-Colombian communities to mine their land have not always been followed. In 2010, the Department of the Interior and the Institute of Geology and Minerals awarded a contract, without consultation, to Hector Sarria to extract gold around La Toma and ordered 1,300 families to leave their ancestral lands. Tension exploded between the local government and residents.
The community – spurred in part by Marquez and Carabali – geared into action; residents called community meetings, marched on the town, and set up road blocks. As a result, the eviction order was suspended multiple times, and in December 2010, La Toma officially won their case with Colombia’s Constitutional Court. Hector Sarria’s mining license as well as up to 30 other illegal mining permits were suspended permanently. But, as disillusioned residents are quick to point out, the decision could change at any time.
“Wayuu Gold”
Much like the people of La Toma, the indigenous Wayuu people who make their home in northeast Colombia have also found themselves the target of paramilitary wrath. Wayuu ancestral land is rich in coal and salt, and their main port, Bahia Portete, is ideally situated for drug trafficking, making them an enticing target. In 2004, armed men ravaged the village for nearly 12 hours, killing 12, accounting for 30 disappearances, and displacing thousands. Even now, seven years later, those brave enough to lobby for peace face threats.
Now, other natural resource pressures have emerged. In 2011, growing towns nearby started siphoning water from Wayuu lands, and climate change is expected to exacerbate the situation. A 2007 IPCC report wrote that “under severe dry conditions, inappropriate agricultural practices (deforestation, soil erosion, and excessive use of agrochemicals) will deteriorate surface and groundwater quantity and quality,” particularly in the Magdalena river basin where the Wayuu live. Glacial melt will also stress water supplies in other parts of Colombia. The threat is very real for indigenous peoples like the Wayuu, who call water “Wayuu gold.”
“Without water, we have no future,” says Griselda Polanco, a Wayuu woman, in a video produced by UN Women.
The basic right to water has always been a contentious issue for indigenous peoples in Latin America – perhaps most famously in Cochabomba, Bolivia – and Colombia is no different: most recently 10,000 protestors took to the streets in Bogota to lobby for the right to water.
Post-Conflict Land Tenure Tensions
Perhaps the Wayuu and people of La Toma’s best hope is in a new Victims’ Law, ratified in June 2011, but in the short term, tensions look set to increase as Colombia works to implement it. The law will offer financial compensation to victims or surviving close relatives. It also aims to restore the rights of millions of people forced off their land, including many Afro-Colombian and indigenous peoples.
But “some armed groups – which still occupy much of the stolen land – have already tried to undermine the process,” reports the BBC. “There are fears that they will respond violently to attempts by the rightful owners or the state to repossess the land.”
Rhodri Williams of TerraNullius, a blog that focuses on housing, land, and property rights in conflict, disaster, and displacement contexts, wrote in an email to New Security Beat that there are many hurdles in the way of the law being successful, including ecological changes that have already occurred:Perhaps the biggest obstacle is the fact that many usurped indigenous and Afro-Colombian territories have been fundamentally transformed through mono-culture cultivation. Previously mixed ecosystems are now palm oil deserts and no one seems to have a sense of how restitution could meaningfully proceed under these circumstances. Compensation or alternative land are the most readily feasible options, but this flies in the face of the particular bond that indigenous peoples typically have with their own homeland. Such bonds are not only economic, in the sense that indigenous livelihoods may be adapted to the particular ecosystem they inhabit, but also spiritual, with land forming a significant element of collective identity. Colombia has recognized these links in their constitution, which sets out special protections for indigenous and Afro-Colombian groups, but has failed to apply these rules in practice. For many groups, it may now be too late.
As National Geographic explorer Wade Davis said at the Wilson Center in April, climate change can represent as much a psychological and spiritual problem for indigenous people as a technical problem. Unfortunately, as land-use issues such as those faced by Afro-Columbian communities, the Wayuu, and many other indigenous groups around the world demonstrate, there is a legal dimension to be overcome as well.
Sources: BBC News, Colombia Reports, International Displacement Monitoring Centre, PBS, Pulitzer Center on Crisis Reporting, UN Women. The War We Are Living, part of the PBS series Women, War, and Peace, was instrumental to the framing of this piece.
Image and Video Credit: “Countryside Near Manizales, Colombia,” courtesy of flickr user philipbouchard; The War We Are Living video, courtesy of PBS. -
Jotham Musinguzi on Investing in Family Planning for Development in Uganda
› “What we are seeing is not adequate, but we think we are seeing very good positive movement, and we want to build on that,” said Jotham Musinguzi, director of the African regional office for Partners in Population and Development (PPD) in Kampala, Uganda. Musinguzi is a public health physician by training who previously advised the government of Uganda on population and reproductive health issues. “We think that [the government] is now on a firm foundation to continue investing properly in family planning,” he said.
“What we are seeing is not adequate, but we think we are seeing very good positive movement, and we want to build on that,” said Jotham Musinguzi, director of the African regional office for Partners in Population and Development (PPD) in Kampala, Uganda. Musinguzi is a public health physician by training who previously advised the government of Uganda on population and reproductive health issues. “We think that [the government] is now on a firm foundation to continue investing properly in family planning,” he said.
Family Planning for Development
Uganda’s high population growth rate (the country has a total fertility rate of 6.4 children per woman, according to the UN) presents a number of challenges, said Musinguzi, exerting pressure on education and health systems, as well as on basic infrastructure, particularly for housing and transportation. Additionally, high levels of poverty and unemployment can become a source of instability.
Policymakers in Uganda are beginning to recognize the urgency of the issue, however, particularly in regards to young people, said Musinguzi. “They don’t have access to jobs, they don’t have the skills, and therefore the challenges of poverty eradication become even more important.”
Nonetheless, the country’s contraceptive prevalence rate is low, at 24 percent, with 41 percent of married women expressing an unmet need for family planning services, according to the 2006 Demographic and Health Survey (DHS) for Uganda. Low levels of investment and lack of government involvement remain the primary obstacles, according to Musinguzi, in addition to socio-cultural and religious barriers.
Uganda historically depended primarily on donor finance, rather than government funding, to support family planning and reproductive health services, Musinguzi said. However, over the past two years, the Ugandan government has increased investment due to concerted efforts by PPD, as well as USAID, the UN Population Fund, and civil society groups. “Our point was that if the government does not fund family planning, then they are going to find that achievement of the Millennium Development Goals…is going to be very challenging,” he said.
“I think the low investment in family planning in Uganda is a thing of the past, and we are now looking forward to really better investment in this field,” Musinguzi said. “I am sure we are going to witness quite a big change [in the 2011 DHS] in terms of access as a result of the proper social investment that the government is trying to do now.”
South-South Collaboration
“I have a keen and strong interest in South-South collaboration in the field of reproductive health, family planning, population, and development,” Musinguzi said. Countries in the South have experience linking programming on population and development, and may face similar challenges, he said. For instance, Bangladesh and Vietnam had successful family planning programs that helped blunt rapid population growth rates.
“Countries, like Uganda, and others which haven’t gotten there yet, could learn from these other countries,” said Musinguzi, by sharing best practices and lesson learned, and replicating applicable solutions.
PPD also has a regional project reaching out to policymakers to increase commitment and accountability for family planning and reproductive health services. For instance, parliamentarians may not realize that they can play a significant role, but they have a unique function in providing government and budget oversight, Musinguzi said. Furthermore, they can create legal and administrative frameworks that prioritize family planning programs.
“We continue to make the case for more investment in family planning and reproductive health, but also making sure we hold leaders accountable, to show more commitment, and make sure they improve on the welfare of the people that they represent,” Musinguzi concluded.
The “Pop Audio” series is also available as podcasts on iTunes.
Sources: MEASURE DHS, UN Population Division. -
Food Security, the Climate-Security Link, and Community-Based Adaptation
›In “The Causality Analysis of Climate Change and Large-Scale Human Crisis,” published in last month’s Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, authors David Zhang et al. write that changes in food supply are key indicators for the likelihood of climate change-induced conflict. Adding to the debate on the links between climate and conflict, the authors write that their purpose was to discover the specific causal mechanisms behind the relationship by analyzing various climate- and crisis-related variables across several periods of peace and conflict in pre-industrial Europe. They found that “climate-induced agricultural decline,” as opposed to resource scarcity caused by rapid population growth, was the clearest indicator of impending crises. “Malthusian theory emphasizes increasing demand for food as the cause,” write the authors, “whereas we found the cause to be shrinking food supply” – a distinction with “important implications for industrial and postindustrial societies.”
In “Using Small-Scale Adaptation Actions to Address the Food Crisis in the Horn of Africa: Going beyond Food Aid and Cash Transfers,” published in Sustainability, authors Richard Munang and Johnson Nkem advocate for community-based adaptation programs to increase resilience to food crises in the Horn of Africa. “Given that hunger and poverty are concentrated in rural areas,” the authors write, “targeting local food systems represents the single biggest opportunity to increase food production, boost food security, and reduce vulnerability.” The authors present a joint UNEP-UNDP adaptation initiative undertaken in Uganda as a framework for potential adaptation interventions in the Horn. They conclude that the initiative’s approach – pairing locally-focused sustainable farming techniques with a national-level emphasis on adaptation programs, and upscaling lessons learned from one level to the other – “will increase local buffering capacity against droughts, make communities more independent from direct aid, etc., build resilience and improve livelihoods overall.” -
Healthy People, Healthy Ecosystems: Results From a Public-Private Partnership
›“A lot of people probably don’t think that an organization with a name like ‘World Wildlife Fund’ would have a program on population, health, and the environment,” said WWF’s Tom Dillon at the Wilson Center, but actually it is very natural. “Most of the people we work with are in rural areas, and they depend on their natural resources for their own livelihoods and for their own well-being. Of course, if you are in that situation, in order to be a steward of the environment, you’ve got to have the basics. You have got to have your own health.”
Dillon was joined by staff from WWF, as well as Scott Radloff, director of USAID’s Office of Population and Reproductive Health, and Conrad Person, director of corporate contributions at Johnson & Johnson, to talk about the results of a three-year partnership between USAID, WWF, and Johnson & Johnson. The joint effort, a formal Global Development Alliance, provided health and family planning services, clean water, and sanitation to communities in three of WWF’s priority conservation landscapes: The Salonga National Park in the Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC), the Lamu Archipelago in Kenya, and the Terai Arch Landscape in Nepal.
By creating an innovative public-private partnership that linked health objectives, particularly related to family planning and maternal and child health, to environmental and conservation activities, “this alliance was ahead of its time,” said Radloff.
Human Health Linked to Environmental Health
The project had four objectives, said Terri Lukas, WWF’s population, health, and environment (PHE) program manager: improve family health; reduce barriers to family planning and reproductive health services; improve community management of natural resources and habitat conservation; and document and promote successful approaches.
“Human health cannot be separated from environmental health anywhere,” Lukas said, “but most especially when we are working with very poor people who live very close to nature.”
Projects Provide Integrated Services
The Salonga National Park in the DRC is home to many endangered species, including the bonobo, one of the four great apes. Local communities are very isolated, and lack access to safe drinking water and sustainable livelihoods, as well as basic health and family planning services, according to Lukas. The PHE project was able to train 135 voluntary community health workers in family planning and maternal and child health care, including 55 women. One year after the training, health workers were distributing contraception to more than 300 new users per month, Lukas said.
The alliance has also integrated health and family planning services into conservation programs in Kenya’s Kiunga Marine National Reserve, in part, “to demonstrate to the people that we care about them as well as the environment, and also to show them the synergies that exist between the health issue and the environment issue,” said WWF Program Coordinator Bahati Mburah. The region has been suffering through a year-and-a-half-long drought, and has one of the highest population growth rates in east Africa, placing considerable pressure on natural resources.
“We talk to [the fisher folk] about health and family planning, and how they are related to the management of fisheries,” said Mburah. With improved transportation and mobile outreach services provided by the project, 97 percent of women are now able to access family planning services within two hours of their home, she said.
The third site is in the Terai region along the southern border of Nepal. In this lowland region, the alliance is attempting to safeguard and restore forest areas in order to allow wildlife to move and breed more freely, while at the same time improving the health and economic prospects of the people. By linking these goals, support for conservation efforts increased from 59 percent to 94 percent of households, with 85 percent attributing positive attitude changes to increased access to health services and safe drinking water, according to Bhaskar Bhattarai, project coordinator for WWF-Nepal.
Documenting and Promoting Successful Approaches
Cara Honzak, WWF’s senior technical advisor on population, health, and environment, said the global objective of the alliance was to document and promote successful PHE approaches. Comprehensive baseline and endline surveys provided critical evidence that integrated PHE programming increases family planning use in remote areas, improves conservation buy-in within communities, and leads to increased participation of women in community leadership and decision-making.
“We have played a key role in producing some of the evidence that has been used throughout Washington [D.C.], especially to provide information to government bodies that are making decisions about bringing more money into family planning, health, and particularly in the environmental sector,” said Honzak.
“After two decades in the field, and working in this area, I wasn’t expecting many surprises. I couldn’t have been more wrong,” Lukas said. “These three years have changed almost everything about the way I now view health development…I have long called myself a conservationist, but now I say to my international health colleagues: we are all conservationists, and if we aren’t, we should be.”
Event Resources- Bhaskar Bhattarai presentation
- Cara Honzak presentation
- Terri Lukas presentation
- Bahati Mburah presentation
- Photo gallery
- Video
-
Emily Puckart, MHTF blog
Maternal Health in Kenya: New Research Unnecessary, Time to Address Existing Gaps
›The original version of this article, by Emily Puckart, appeared on the Maternal Health Task Force blog.
During the recent Wilson Center/African Population and Health Research Center meeting in Nairobi on improving health systems through a maternal health framework, participants focused on knowledge gaps in the Kenyan health system that can negatively affect maternal healthcare. This focus on gaps sparked discussion around research needed (or not needed) in the maternal health field, supply gaps, and gaps between addressing technical, medical issues of maternal health (like preeclampsia or postpartum hemorrhage), and larger society-wide gaps like gender equity. The gaps highlighted by participants at the Nairobi dialogue included:- Gaps in knowledge: During the dialogue, members of the Kenyan maternal health community discussed the possibility of strengthening community health workers as an information delivery platform. Participants wondered about the possibility of using community health workers to distribute information both downward to the end user (patients), and then again to gather information from end users and distribute it upwards through the system to reflect the opinions of the direct users of the healthcare system.
- Supply gaps: Participants argued that while there is a large body of information in terms of maternal health supplies at the national level in Kenya, there is not as much data on supplies at the actual health facility level, where it is much needed and would be very helpful to successfully treat patients.
- Gaps in healthcare delivery: There is a strong need to address inequality in the distribution of health services as there are unequal services in rural and urban areas. Within those broad areas there may be further inequalities, as even in urban areas, slum areas or neighborhoods on the edges of cities may have less access to quality healthcare than populations that live in wealthier areas of the city or closer to the city center. Further there are broader questions of gender and access to care. Where women are not able to control household finances, they may be unable to access and pay for lifesaving care. Participants framed the question in a rights framework, “Do we value the lives of women less than men?”
- Health workforce gaps: There is a mismatch between the supply of health workers and the absorption of those trained health workers in Kenya. Many of them are not incentivized professionally or financially to stay in the system where they are trained. These health workers may leave for other countries or prefer to stay in urban areas depriving rural areas of a surplus of trained health workers.
- Gaps between words and actions: Several of the small working groups pointed to accountability as a serious issue, as there are gaps between the words of politicians on health issues and actual actions. The gap between the government promised funding for health and the actual lower amount of spending was consistently highlighted during the Nairobi dialogue as a serious gap in holding governments accountable for their promises.
The lively conversation provoked by a broad discussion of gaps in the Kenyan health system provided fertile ground to develop action points on maternal healthcare that participants then presented on the second day of the meeting to several Kenyan members of parliament. Ideally, this will be the first discussion of many as maternal health advocates, field workers, and researchers coalesce around ways to address the gaps in maternal healthcare in Nairobi and elsewhere.
Emily Puckart is a senior program assistant at the Maternal Health Task Force (MHTF).
Photo Credit: Jonathan Odhong, African Population and Health Research Center. -
Twin Challenges: Population and Climate Change in 2050
›

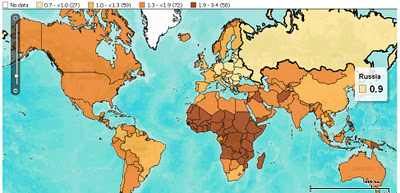
 With global population reaching 7 billion, a lot of attention has been paid to the question of how to sustainably support so many people, much less the 9 billion expected by 2050, or the 10 billion possible by 2100. Add in the environmental variability projected from climate change and the outlook for supporting bigger and bigger populations gets even more problematic. Two new maps – one by the Population Reference Bureau (PRB), the other by McGill University PhD candidate Jason Samson – show how the world might change over the next 40 years in the face of these twin challenges.
With global population reaching 7 billion, a lot of attention has been paid to the question of how to sustainably support so many people, much less the 9 billion expected by 2050, or the 10 billion possible by 2100. Add in the environmental variability projected from climate change and the outlook for supporting bigger and bigger populations gets even more problematic. Two new maps – one by the Population Reference Bureau (PRB), the other by McGill University PhD candidate Jason Samson – show how the world might change over the next 40 years in the face of these twin challenges.
Nine Billion in 2050
PRB’s map, built using their DataFinder tool, shows the world in 2050 in terms individual country growth rates between now and then. Japan, Russia, and countries in Eastern Europe are set to grow more slowly than anywhere else, and some of that group will actually shrink by 10 to 20 percent of their current size. Western, Central, and Eastern Africa will be home to the highest increases. Niger’s 2050 population is expected to be 340 percent its 2011 size – the largest growth of any country.
The map is based on country-level data pulled from a number of sources: the UN Population Division’s latest “World Population Prospects,” the UN Statistics Division’s “Demographic Yearbook 2008,” the U.S. Census Bureau’s International Database, and PRB’s own estimates. It’s unclear what numbers come from which sources, though it is clear that PRB’s 2050 estimates span the UN’s range of medium, high, and constant-fertility variants. In spite of these variations, none of PRB’s estimates come anywhere near the UN Population Division’s low variant estimates.
PRB’s map, echoing its 2011 World Population Data Sheet, shows a world where sub-Saharan Africa will bear the brunt of population growth. The average country in Africa in 2050 is projected to be slightly more than twice its 2011 size; the average European country is expected to barely break even. Africa is home to more countries whose populations are estimated to least double (34) or triple (4) than any other continent. Europe, meanwhile, is home to more countries whose populations will stagnate (8), or even shrink (19), than anywhere else. Interestingly, the Caribbean is a close second in terms of countries whose populations are projected to stay the same (seven to Europe’s eight), and Asia is second to Europe in terms of countries whose populations are projected to shrink (Georgia, Japan, Armenia, South Korea, and Taiwan).
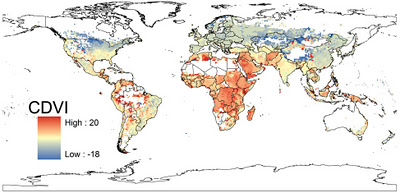
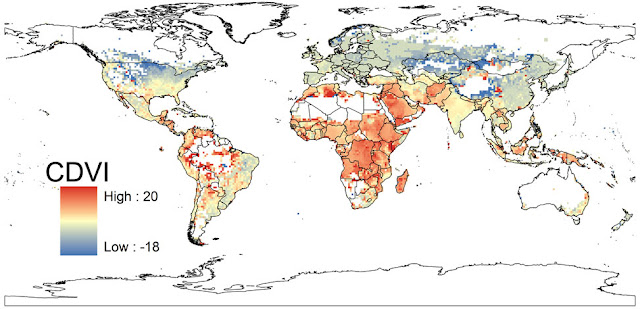
More People, More Climate Change, More Vulnerability
Samson’s map takes on the same time period but projects where people will be most vulnerable to the effects of climate change. Since his map takes into account population growth (measuring where people are most vulnerable, remember), unsurprisingly, Africa, the Middle East, Southeast Asia, and central South America are covered in bright red dots, indicating high vulnerability. Conversely, North America, Europe, and much of Central Asia are in shades of blue.
Samson built his index using four environmental predictors – annual mean temperature, mean temperature diurnal range, total annual precipitation, and precipitation seasonality – taken from WorldClim’s 2050 forecasts, and 2005 sub-national population data from Columbia’s Center for International Earth Science Information Network. In spite of the sub-national population data, Samson makes a point to justify his use of supranational climate data in order to best reflect “the scale at which climate conditions vary.” He writes that localized issues like urbanization and coastal flooding “are probably best investigated with targeted regional models rather than by attempting to modify global models to include all factors of potential regional importance.”
Samson’s research shows that, generally, people living in places that are already hot will be more vulnerable to climate change over time, while people in more temperate climates will feel a negligible impact. Though he projects the largest real temperature changes will happen in temperate climates like North America and Europe, the comparatively smaller changes in Africa, the Middle East, Southeast Asia, and central South America are expected to have a greater impact because those regions are already very hot, their natural resources are stressed, and they are expected to bear the brunt of population growth over the next few decades.
These findings reflect a disparity between those responsible for climate change and those bearing the brunt of it, which, although not surprising, “has important implications for climate adaptation and mitigation policies,” said Sampson, discussing the map in a McGill press release.
Sub-National Data “Present a Very Different Picture”
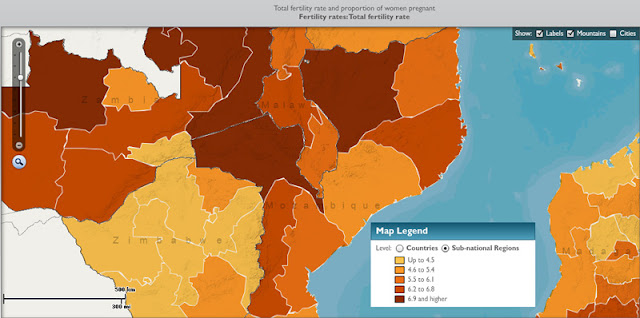
Though they offer a useful approximate glimpse at what the world might look at in 2050, both of these maps fall prey to over-aggregation. By looking at national rather than sub-national data, we miss how nuanced population growth rates can be within a country. Stimson Center Demographer-in-Residence Richard Cincotta wrote in a recent New Security Beat post that “national level comparisons of total fertility rates tend to communicate the false impression of a world with demographically homogeneous states.” Sub-national data, including differences between urban and rural areas and minority-majority fertility rates, “present a very different picture.”
And that difference matters. When it comes to looking at how population interacts with other issues, like the environment, poverty, and conflict, the importance of a sub-national approach becomes evident. In its 2011 data sheet, PRB writes that “poverty has emerged as a serious global issue, particularly because the most rapid population growth is occurring in the world’s poorest countries and, within many countries, in the poorest states and provinces.”
Edward Carr, an assistant geography professor at the University of South Carolina currently serving as a AAAS science fellow with USAID, argues that national-level data obscures our ability to understand food insecurity as well. The factors that drive insecurity “tend to be determined locally,” writes Carr in a post on his blog, and “you cannot aggregate [those factors] at the national level and get a meaningful understanding of food insecurity – and certainly not actionable information.”
The same is true when it comes to climate vulnerability. In a report from The Robert S. Strauss Center’s Climate Change and African Political Stability Program, authors Joshua Busby, Todd Smith, and Kaiba White write that “research announcing that ‘Africa is vulnerable to climate change,’ or even ‘Ethiopia is vulnerable,’ without explaining which parts of Ethiopia are particularly vulnerable and why, is of limited value to the international policy community.”
“It is of even less use to Africans themselves, in helping them prioritize scarce resources,” add Busby et al.
Understanding the joint problems of climate change and population growth on a global level helps frame the challenges facing the world as it moves toward 8, 9, and possibly 10 billion. But knowing the ins and outs of how these issues interact on a local level will be a necessary step before policymakers and others can hope to craft meaningful responses that minimize our vulnerability to these challenges over the coming decades.
Sources: Center for International Earth Science Information Network at Columbia University, Climate Change and African Political Stability Program at the Robert S. Strauss Center, McGill University, Population Reference Bureau, UN Population Division, UN Statistics Division, U.S. Census Bureau, University of South Carolina, WorldClim.
Image Credit: “2050 Population As a Multiple of 2011,” courtesy of PRB; CDVI map used with permission, courtesy of McGill University; Sub-national total fertility rates in Southern Africa, courtesy of MEASURE DHS, arranged by Schuyler Null. -
Rwanda: Dramatic Uptake in Contraceptive Use Spurs Unprecedented Fertility Decline
›November 8, 2011 // By Elizabeth Leahy Madsen
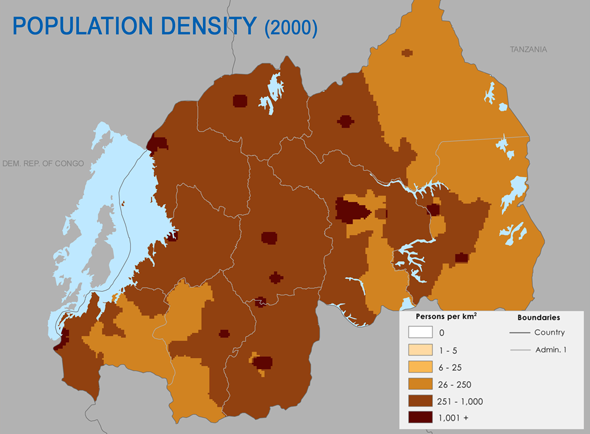
With over 400 people per square kilometer, the highest rate on the African mainland, population density is perhaps the most widely-discussed factor of Rwanda’s demography. Some scholars, notably Jared Diamond, have argued that it played a primary role in sparking the 1994 genocide through competition for land (although others present a more complex theory based in policies and governance).