-
Welcome Back, Family Planning
›January 8, 2010 // By Gib Clarke “When women and girls have the tools to stay healthy and the opportunity to contribute to their families’ well-being, they flourish and so do the people around them,” Secretary of State Hillary Clinton declared today in a speech renewing U.S. support for universal access to reproductive health services and supplies around the world. “Investing in the health of women, adolescents, and girls is not only the right thing to do; it is also the smart thing to do.”
“When women and girls have the tools to stay healthy and the opportunity to contribute to their families’ well-being, they flourish and so do the people around them,” Secretary of State Hillary Clinton declared today in a speech renewing U.S. support for universal access to reproductive health services and supplies around the world. “Investing in the health of women, adolescents, and girls is not only the right thing to do; it is also the smart thing to do.”
Introduced by Melanne Verveer, the first ever ambassador-at-large for global women’s issues, Clinton’s much anticipated statement marked the 15th anniversary of the International Conference on Population and Development (ICPD) and reconfirmed a U.S. commitment to meeting Millennium Development Goals 4 (reducing child mortality) and 5 (reducing maternal mortality and increasing the proportion of births attended by skilled health personnel). Reproductive health and development luminaries Nafis Sadik, UN Foundation President and former Senator Tim Wirth, and newly installed USAID Administrator Rajiv Shah were also in attendance.
Clinton began with a look back to the ICPD—which she called the “first ever global forum that recognized the connection between women’s health, the quality of women’s lives, and human progress on a broader scale”—and the progress since. Declaring that “we have made measurable progress since 1994 in improving the health and the lives of women and children, especially girls,” she cited a number of improvements, including higher child survival rates, use of modern contraceptives, and female education enrollment.
Switching from the past to the present, Clinton described how women and girls continue to bear the brunt of a variety of social ills: they have higher rates of poverty, illiteracy, and malnutrition, and are the most adversely affected by conflict, “from the Congo to Bosnia to Burma.”
After reciting the data on unsafe abortions, STDs and HIV/AIDS, fistulas, and female genital cutting, she declared that “these numbers are not only grim…they are intolerable.” She added, “We can not accept it morally, politically, socially, economically.”
But Clinton’s remarks were not solely focused on health and family planning issues. Echoing arguments made by Nicholas Kristof and others, Clinton described how women’s health and women’s rights directly and significantly impact most major problems in the world, including economics, natural resource conflicts, and national security.
These challenges will require sustained effort and funding, said Clinton, adding that the Obama Administration’s $63 billion Global Health Initiative would address the health challenges of HIV/AIDS and maternal and reproductive health in an integrated manner. All of the administration’s programs would seek to help countries strengthen their own health systems to meet their unique needs—both of their women and girls, but also their populations in general. In all of these efforts, she said including men and boys as “advocates and allies” remains important.
Praise for the speech has been swift—a letter of commendation from a number of foundations was sent to the secretary immediately afterwards.
Maternal and reproductive health have experienced elevated and perhaps unprecedented funding and attention in recent years, especially over the last few months. Secretary Clinton’s impassioned speech is almost certain to keep this momentum alive.
Photo: Courtesy SEIU International -
2010: Worldwide Year of the Census
›To kick-off the New Year, we’re highlighting CensusInfo 2010—an initiative to help countries distribute their census data in a format that is free, flexible, and customizable to meet diverse public needs. For us, it’s a new tool to access and visualize census data from around the globe.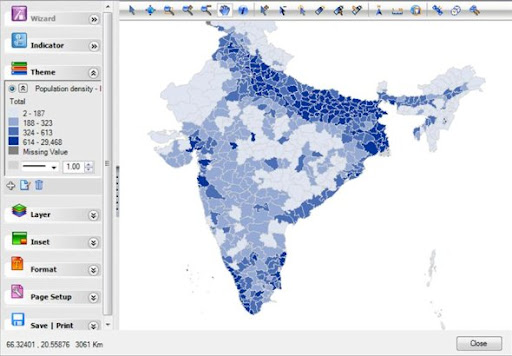
The CensusInfo software(the program must be downloaded and installed) allows users to create tables, graphs, and color-coded maps depicting indicators such as population density, fertility rate, and sex ratio. The data’s resolution—national, regional, district, or smaller—is up to the user, but limited by the information reported by each country’s census bureau. When older data is available, users can also view trends over time.
The heart of CensusInfo is data presentation. Robust options include: capacity to import new datasets, compatibility with Google Earth and NASA’s World Wind technologies, and the ability to download visualizations as images, “animated flipbooks,” and videos.
Aside from the relatively steep learning curve to master each of its functions, the software is principally limited by the small number of countries in its database: only 10 countries are included in the software’s pre-installed dataset. That number, however, could increase in the near future.
In what CensusInfo 2010 hopes will be a trend, the Palestinian Central Bureau of Statistics, as of August 2009, became the first National Office of Statistics to independently incorporate its data into CensusInfo. While a powerful piece of software, CensusInfo’s potential rests on whether others follow suit.
Photo Credit: CensusInfo’s output of population density in India. -
How Copenhagen Has Changed Geopolitics: The Real Take-Home Message Is Not What You Think
› A fascinating and potentially game-changing geopolitical pas-de-deux unfolded in Copenhagen. The international media and punditocracy christened the United States and China the new G2 in reference to the expected preeminent leadership roles the two hold among their respective developed and developing country contingents. What increasingly became clear, however, was that a different G2 was influencing the agenda: China and India.
A fascinating and potentially game-changing geopolitical pas-de-deux unfolded in Copenhagen. The international media and punditocracy christened the United States and China the new G2 in reference to the expected preeminent leadership roles the two hold among their respective developed and developing country contingents. What increasingly became clear, however, was that a different G2 was influencing the agenda: China and India.
India demonstrated that, while it wants an alliance with the United States and its Western allies, a subservient allegiance is not an option.
This was clear in the way India approached a key Copenhagen sticking point—verification. India had been down this road before with the U.S.-India nuclear deal, where Washington’s insistence on external verification was seen by some Indian strategists as undermining India’s sovereignty and security, and as a potential excuse to impose costly sanctions.
Indian concerns about verification created an opportunity for China which, despite the vastly different mix of emissions in both countries, was able to entice India into an alliance. India brought along its IBSA partners, South Africa and Brazil, and it was this expanded group, meeting in conclave, that President Obama gatecrashed in his search for solutions.
Two very important messages were delivered in Copenhagen. First, India told the West it could no longer be taken for granted—it had options. Second, China told India it would be open to a new relationship based on mutual interest.
Going in to Copenhagen, visions for the conference were more varied than many realized. The West primarily thought it was negotiating a trade deal (as evidenced by the drop in EU carbon trading prices after the talks failed to deliver a climate market deal). China, too, was negotiating a trade deal, but remained open to opportunities to gain larger strategic advantages. India, on the other hand, sought a stage to drive home its major geopolitical positions.
Coming out of Copenhagen, the conference’s narrative is clearer: This was geopolitics pure and simple.
India—home to the world’s most populous democracy, a thriving economy, and one of the world’s largest English-speaking populations—is a natural U.S. ally. Its recent experience with the United States on nuclear cooperation, however, has made it wary. Such paranoia gave Beijing an opportunity to entice Delhi into an alliance at Copenhagen. Despite China’s development of Pakistan as a nuclear client state, ongoing border disputes and skirmishes, and other conflicts between the two emerging powers, Beijing succeeded.
If the United States and its Western allies are to coax India (and by extension, a substantial portion of the developing world) into going along with an ambitious emissions reduction program, or indeed any other trade regime, they will need to desist from seeking to impose measures that Delhi regards as protectionist and self-serving.
For the West, moving the world’s most populous democracy to its side, and not China’s, is worth certain concessions. Not just for the sake of a climate deal, but also for larger strategic purposes. At Copenhagen, the West incorrectly lumped India with China, and this mistaken assement proved to be self-fulfilling.
Analysis of India has long suffered from “hyphenation.” First it was India-Pakistan, now India-China. At the beginning the India-China link was competitive, but Copenhagen has shown it has the potential to become cooperative. India should be assessed on its own terms. If geopolitics abhors a stand alone, however, then the time has come to rehyphenate democratic, economically strong, English-speaking India. It would be in the United States and its allies’ benefit to create a new cooperative link: India-U.S.
A longer version of this article was originally published by UPI-Asia.com.
Cleo Paskal is a fellow at Chatham House in London and author of Global Warring: How Environmental, Economic, and Political Crises Will Redraw the World Map (Palgrave). Scott Savitt, a former Beijing-based correspondent for United Press International, is the author of the forthcoming memoir Crashing the Party (Atlas). ©Copyright Cleo Paskal and Scott Savitt.
Photo: Prime Minister of India Manmohan Singh. Courtesy World Economic Forum. -
Making the Connections: An Integration Wish List for Research, Policy, and Practice
›January 3, 2010 // By Geoffrey D. DabelkoNew York Times columnist Nick Kristof is likely a well-known voice to New Security Beat readers. His ground-level development stories from around the world expose a range of neglected issues that usually struggle for mainstream media coverage: maternal health, microcredit, human trafficking, family planning, sanitation, micronutrients, and poverty, among others.
Kristof brought many of these threads together Half the Sky, a book he coauthored with his wife Sheryl WuDunn. I asked about the challenges of addressing these connected problems when I interviewed the couple and two frontline White Ribbon Alliance maternal health practitioners this fall at the Wilson Center.
Now Kristof is asking readers to suggest topics for him to cover in 2010. My suggestions to him are actually a wish list for the wider development community. In short, how can scholars, policymakers, practitioners, and communities better research and analyze these connected topics and then fashion integrated responses? I posted my comment on Kristof’s blog, On the Ground (and I ask your indulgence for the less than polished writing):I’d love for you [Kristof] to explore the challenge of integration from both problem and response perspectives. People in poverty lead integrated lives (just like we wealthier folks do), face connected challenges, and need integrated or multiple responses. Single-sector programs may deliver quicker, more obvious, and/or more countable impacts (or parallel advantages for single-discipline research endeavors). Yet time and time again we see such approaches only partially meeting needs or not meeting them sustainably. There is also a persist danger of undercutting others’ efforts and/or creating high opportunity costs.
These questions topped my wish list to Kristof last night while procrastinating on other writing. What would be on your wish list for Kristof, the development community, or even just New Security Beat? We at the Environmental Change and Security Program (ECSP) would love to hear from NSB readers so we can keep covering the questions that interest you.
So which integrated research, policy analysis, or field-based programs explicitly recognize that trends that appear to be on the periphery are hardly peripheral? At the same time, if programs try to be all things to all people, they can become bloated, unrealistic, and/or unsustainable.
For example, are the Millennium Villages examples of the former or the latter? How about the much smaller programs under the population-health-environment grouping? What went wrong with Campfire programs to cause so many to abandon the approach? Have the loosened restrictions on what constitutes an appropriate PEPFAR intervention addressed this integration problem, or will politics (exclusion of family planning in PEPFAR, for example) mean we cannot capture the full benefits of integration?
And the big Kahuna: how is the rhetoric and analytical argument around the 3Ds (defense, development, and diplomacy) made real and practicable in the field (as in the United States we anticipated early this year the results of the Quadrennial Defense Review (QDR), Quadrennial Diplomacy and Development Review (QDDR), and Presidential Study Directive on Global Development Policy (PSD))?
And finally, does our (read donors’) penchant for measuring impact and quantifying results force us to narrow interventions to the point of missing key connections in cause and effect of the problems we are trying to address? Is there a better mix of defining and measuring success that captures the challenges and benefits of integration? -
‘DotPop: ’ New Toolkit for Population, Health, and Environment
›December 29, 2009 // By Wilson Center StaffThe PHE Toolkit, launched by Building Actors and Leaders for Advancing Community Excellence in Development (BALANCED), is a new source of information and resources on Population, Health, and Environment (PHE).
The interactive online library of documents, videos, and other resources will provide “one-stop shopping” for the target audience of program managers working on health, family planning, development, and conservation programs—as well as policymakers, researchers, academics, and educators. All users can contribute resources and participate in discussions through the toolkit.
The Environmental Change and Security Program, along with several PHE partner organizations, helped build the framework and will contribute its PHE resources to the toolkit. ECSP is also a member of the PHE Gateway, which can be accessed through the toolkit.
The PHE toolkit is one of five public toolkits housed on the Knowledge for Health (K4Health) website, which is supported by USAID’s Bureau of Global Health. Together, the current and forthcoming toolkits will form an updated and vibrant community for information on health, including family planning, HIV/AIDS, and reproductive health.
The PHE toolkit is made possible through the collaboration of Johns Hopkins University Center for Communication Programs (JHU/CCP) and the BALANCED Project. BALANCED is spearheaded by the Coastal Resources Center (CRC) at the University of Rhode Island and its partners, PATH Foundation Philippines Inc. and Conservation International. -
Price of Coal Surges!
›December 23, 2009 // By Geoffrey D. DabelkoThe price of coal surged this morning as a new buyer entered the market. A high-volume rush order came in from the North Pole in the last few hours, accounting for the surge. Shaking his head, one dazed trader said the size of the order was equivalent to the yearly total of a medium-size country with no green energy sector.
When pressed to reveal the source of the demand, traders grudgingly admitted a white-bearded man clad in red had suddenly appeared, agitated and mumbling about those who simply couldn’t be good for goodness’ sake. He had come straight from the Bella Center and was scrolling through a long list of names on his Blackberry. “It just keeps getting longer and longer!” he cried. With a bottle of Carlsberg in hand, he made some final calculations and proclaimed he had a sudden need for coal ready for delivery in two day’s time.
Satisfied he’d have adequate supplies ready for pickup in every country from the North to the South, he made his way up to the roof of the trading house. Those close at hand overheard him say, “Good night to you all, but I won’t see you next year. I’ll have to come up with something else for these naughty types. They will probably just burn this stuff.”
“At least Mexico City will be warmer!”
Photo: Courtesy David Hawxhurst, Woodrow Wilson Center -
‘DotPop:’ Copenhagen’s Collapse: An Opportunity for Population?
›December 22, 2009 // By Gib ClarkeWhile the negotiators failed to reach a comprehensive agreement in Copenhagen, the population and reproductive health community might find a silver lining in the stormclouds that derailed COP-15.
Developing countries’ strong protests of their lack of culpability for the climate problem, on one hand, and the dramatic examples of their vulnerability on the other, have focused the world on the problems of poor people—and on potential solutions, including family planning.
The Case of the Missing “P”
The New York Times’ Andrew Revkin complained that population was the “The Missing ‘P’ Word in Climate Talks,” but PAI’s Kathleen Mogelgaard argues in New Security Beat that “there is encouraging evidence that voices of those advocating for increased attention to the role of population and reproductive health and rights in climate change responses are being heard” in Copenhagen, including new funding from the Danish government for family planning.
At a breakfast last week, luminaries including Gro Harlem Brundtland and IPCC Chairman Rajendra K. Pachauri discussed UNFPA’s latest report, Facing a Changing World: Women, Population and Climate in Copenhagen.
According to lead author Robert Engelman, the report is “helping many more people to see population and climate in a more hopeful light, linked as they are through the right of women to equal standing with men and access to reproductive health care for all.”
Women, Population, and Climate
“Climate change is ultimately about people,” declared Congresswoman Carolyn Maloney at the recent Washington, DC, launch of the report. Though the issues are complex and multi-faceted, Engelman said that the report’s message is “stark and optimistic”: that “women in charge of their own lives” can have positive impacts on change climate mitigation and adaptation.
“Women are more sustainable consumers,” said UNFPA’s José Manuel Guzmán at the launch, noting that in many cases women make buying decisions for their families, so empowering them with information and tools is a wise approach to combating climate change.
Inequitable Impacts
Women – especially poor women – contribute fewer greenhouse gas emissions than men, yet are more vulnerable to the impacts of climate change. Unfortunately, this fundamental inequality is difficult to quantify, since most data sources are not disaggregated by gender. The report recommends improving data quality to better informing policy decisions.
Tim Wirth, president of the UN Foundation and the Better World Fund, noted that women face a “double whammy”: they are already less likely to go to school and to have access to paying livelihoods, and more likely to have HIV. Climate change will only increase the inequity.
People Power
PAI’s Karen Hardee called on the population community to focus their efforts on the next phase of negotiations – adaptation. A recent PAI report found that while 37 of 41 National Adaptation Plans of Action say that population pressures exacerbate the effects of climate change, only six include slowing population growth or addressing reproductive health and family planning as a key priority.
“The focus has been on where and what the impacts of climate change will be,” said Guzman, but the conversation needs to shift to who will be affected, and an analysis of their vulnerabilities and their capacities to adapt.
For real progress to occur, said Engelman, “climate needs to be seen through a more human lens.” -
Eco-Tourism: Kenya’s Development Engine Under Threat
› Africa’s elephants and black rhinos—already at risk—are increasingly threatened as the price of black market ivory rises, global markets contract, and unemployment rates rise. To fight poaching of these tusked animals, Ian Craig, founder of the Lewa Conservancy in Kenya and the brains behind the Northern Rangelands Trust, takes a unique approach to conservation that involves both local community members and high-level government officials, as well as private and public sector investors.
Africa’s elephants and black rhinos—already at risk—are increasingly threatened as the price of black market ivory rises, global markets contract, and unemployment rates rise. To fight poaching of these tusked animals, Ian Craig, founder of the Lewa Conservancy in Kenya and the brains behind the Northern Rangelands Trust, takes a unique approach to conservation that involves both local community members and high-level government officials, as well as private and public sector investors.
In the 1970s the black rhino population was at about 20,000. Less than three decades later, it had fallen to 200. Today, the population is about 600, of which 79 live in the Lewa Conservancy. The vast regions of Kenya covered by the Northern Rangelands Trust and the Lewa Conservancy are difficult to govern, so the conservancies partner with local communities to ensure the security necessary to protect the animals from poachers. By investing in community institutions, the conservancies create long-term sustainability and self-sufficiency.
But why should local communities—often beset by poverty, disease, and hunger—care about saving elephants or rhinoceroses rather than killing them for their tusks or meat? Revenue from tourism can total hundreds of thousands of dollars, especially because of the high cost and exclusive nature of tourism facilities in the area. This money is then injected back into community programs to improve adult literacy, school nutrition, health care, micro-credit, water and irrigation systems, community livestock and agriculture, and forestry and aquaculture.
In some politically volatile areas, the conservancy serves not only as a platform for ecological security, but also as a mediator of disputes. Where livestock theft is rampant, multi-ethnic anti-poaching teams have been able to act as intermediaries. Community elders and other traditional leaders serving on the conservancies’ boards have bi-annual meetings to further intra- and inter-regional cooperation. Along with regular managerial and council meetings, the board meetings set standards for good practices, open dialogue for policymaking and cooperation, and act as a unique platform for communication between different ethnic and regional groups.
Community members understand they have a stake in protecting not only the animals, but in ensuring security and building trust within the country. With its unique combination of local-level engagement, the cooperation and support of the Kenyan Wildlife Service and the national government, and with the resources available to the conservancies as a group, the Lewa Wildlife Conservancy hopes to create a model of conservation that can be used across Africa and in other at-risk regions.
The future is shaky: ivory prices continue to rise, the migration of animals has facilitated poaching, and small arms are abundantly available. However, the new community-focused approach has helped to create positive attitudes that aren’t just about saving animals, but about developing the nation.
Justine Lindemann is program assistant with the Africa Program at the Woodrow Wilson International Center for Scholars.
Photo: Elephants in Lewa Conservancy area, courtesty Flickr user Mara 1
 A Publication of the Stimson Center.
A Publication of the Stimson Center.

 “When women and girls have the tools to stay healthy and the opportunity to contribute to their families’ well-being, they flourish and so do the people around them,” Secretary of State
“When women and girls have the tools to stay healthy and the opportunity to contribute to their families’ well-being, they flourish and so do the people around them,” Secretary of State  A fascinating and potentially game-changing geopolitical pas-de-deux unfolded in Copenhagen. The international media and punditocracy christened
A fascinating and potentially game-changing geopolitical pas-de-deux unfolded in Copenhagen. The international media and punditocracy christened 

 Africa’s elephants and black rhinos—already at risk—are increasingly threatened as the
Africa’s elephants and black rhinos—already at risk—are increasingly threatened as the 

