-
‘Wilson Center on the Hill:’ Haiti’s Long Road Ahead
›March 25, 2010 // By Wilson Center StaffNearly two months after the devastating 7.0 magnitude earthquake in Port-au Prince, Haiti, the country still needs assistance to provide basic healthcare and shelter, in addition to rebuilding Haiti’s economy, government, and institutions. As the international community and NGOs make the transition from emergency disaster relief to long-term reconstruction and capacity-building efforts, donor coordination and long-term commitment are crucial. Recently, on Capitol Hill, a panel of experts organized by Wilson Center on the Hill and the Wilson Center’s Latin American Program discussed Haiti’s continuing problems and challenges.
Patience Necessary
Johanna Mendelson Forman, a senior associate for the Americas Program at the Center for Strategic and International Studies, stressed that progress in Haiti will take time—perhaps five years to rebuild and 10 years to see positive economic growth. This timeline is often frustrating for donors—including Congress and U.S. citizens—who want to see immediate results, she noted. Nevertheless, Mendelson Forman discounted the myth that “because Haiti is a weak state it is not a sovereign state,” and emphasized that developing and strengthening the Haitian government remains necessary.
She observed that the post-earthquake efforts in Haiti have been different from previous United Nations interventions, particularly in terms of the Latin American community’s involvement. Brazil, for example, is leading relief operations. Other Latin American countries—including Haiti’s neighbor, the Dominican Republic—have committed to promoting a stable and secure Haiti. Here Mendelson Forman noted a new partnership initiated by the Dominican and Haitian governments. “[Dominican officials] understand that they are doomed if Haiti is doomed,” she said. “As members of the international community, it is our job to foster that reconciliation.”
Costs Are Rising
Andrew Philip Powell, a regional economic advisor in the Caribbean Country Department at the Inter-American Development Bank (IDB), said that while the IDB initially estimated damage from the earthquake at about $8 billion, the complete destruction of the government and commerce centered in Port-au-Prince could push that number much higher. The IDB and partner organizations are currently conducting a Post-Disaster Needs Assessment that will ultimately identify the official damages and ballpark the cost of reconstruction.
Powell stated that Haiti is “not starting from a blank slate,” citing a development strategy agreed upon in April 2009 by the Haitian government and international donors. In keeping with the strategy, he emphasized the need for effective coordination between donors and the Haitian government. At the same time, he said it is vital to encourage population dispersion by shifting government agencies and private-sector jobs to other parts of the country. Haiti needs roads and communication networks outside of the capital area, as well as export processing zones in outlying regions, to increase the economic opportunities outside of Port-au-Prince, he said.
However, with the large amounts of aid flowing into the country, Powell warned donors and Haitian officials to remain on the lookout for “Dutch disease”—a decline in the manufacturing sector following a sharp increase in natural resource prices, foreign assistance, or foreign direct investment. Its occurrence could increase Haiti’s dependency on aid in the future.
Challenges for Healthcare
Sheri Fink, a public policy scholar at the Woodrow Wilson Center and senior fellow at the Harvard Humanitarian Initiative, offered her perspective on Haiti’s continuing health crisis based on two trips to the country in the earthquake’s aftermath. There are signs of hope, including some normalcy and commerce returning to the camps, she noted, but problems in the health sector as a whole are increasing. As field hospitals put in place after the earthquake close, “there is a fear among Haitians that attention is starting to turn elsewhere,” she said.
According to Fink, “the work is far from done” in Haiti, a sentiment she said is shared by many departing health workers. The hospitals left standing are not prepared to deal with the influx of patients arriving at their doors following the closure of field hospitals, and government health workers are currently working without pay.
Fink also pointed out the risk of long-term earthquake-related health problems, including injuries suffered during aftershocks or from falling debris, inflamed chronic diseases, horrible conditions and lack of basic health services in camps, and the “looming nightmare” of infectious disease epidemics.
Fink called for more international involvement to avert a widening of the health crisis. “We’ve made a big commitment and to follow-up on the investment, to make it mean something; let’s not be satisfied with just bringing things back to where they were,” she said.
By Sarah Huston and David Klaus of Wilson Center on the Hill at the Woodrow Wilson International Center for Scholars.
Photo: Courtesy Flickr user United Nations Development Programme -
The Feed for Fresh News on Population
›March 25, 2010 // By Wilson Center StaffUSAID’s Gloria Steele offers written testimony on the FY2011 Global Health and Child Survival (GH CS) budget request before the House Appropriations Subcommittee on State, Foreign Operations
Andrew Revkin gives a shout-out to family planning and notes the lack of population discussion at Copenhagen in his blog post, “From Wishful Thinking to Real-World Action on Climate“
Video of Secretary of State Hilary Clinton addressing the Commission on the Status of Women in which she discusses the Global Health Initiative, maternal mortality, family planning, and “gendercide“
Family planning-environmental connections headline PATH‘s March edition of Outlook
Youth bulges and social conflict are noted in Nicholas Kristoff’s recent article on child marriages in Yemen
Follow Geoff Dabelko on Twitter for more population, health, environment, and security updates -
Energy Is a “Constraint on Our Deployed Forces”: DOD DOEPP Nominee Sharon Burke
›March 24, 2010 // By Wilson Center Staff“I believe right now that energy is a vulnerability and constraint on our deployed forces,” said Department of Defense nominee and CNAS Vice President Sharon Burke yesterday morning at her confirmation hearing before the Senate’s Armed Services Committee. She described the tremendous cost—in lives, capital, and operational flexibility—of meeting the current fuel needs of troops in Afghanistan. Leading DOD’s efforts to account for the “full cost and full burden of energy,” she said, will be one of her priorities if she is confirmed.
“The committee and Congress have shown an acute interest in operational energy by creating this position,” said Burke, who would be the first person to serve as Director of Operational Energy Plans and Programs (DOEPP). “Sharon Burke has a deep understanding of the energy and climate change challenges facing the Department of Defense,” according to Geoff Dabelko, director of the Wilson Center’s Environmental Change and Security Program. “She would be able to hit the ground running if confirmed.”
Burke said that previous Congressional and presidential mandates have pushed DOD to improve the energy posture of its domestic facilities. She hopes to achieve similar successes in the operational arena. While she was reluctant to privilege any single solution, she suggested that more efficient weapon platforms and tactical vehicles, alternative fuels, and better business and acquisition processes could all be part of the mixture.
In response to a question from Senator Chambliss (R-GA) about climate change, Burke said, “I think the Quadrennial Defense Review (QDR) does a very good job laying out the proper role of the military forces.” The Wilson Center recently hosted a panel discussion on the QDR and the UK Defence Green Paper, at which the speakers repeatedly referred to the future DOEPP.
The nomination hearing largely avoided any tension concerning climate science and mitigation policies, focusing instead on military operations and ensuring the maximum effectiveness of U.S. forces. “My top priority would be mission-effectiveness,” Burke said. E&E; News reports Burke is expected to be confirmed.
Photo: Sharon Burke courtesy CNAS. -
Is the Melting Arctic a Security Challenge or Crisis? The View From Russia and Washington
›March 24, 2010 // By Geoffrey D. DabelkoIn his opening remarks at the Security Council of the Russian Federation’s meeting on climate change last week, Russian President Dmitry Medvedev framed climate change as a force for increased competition and “disputes between countries.” Unsurprisingly, he focused on the Arctic region and what he called the “inadmissible” and “unfair” threats to Russia’s access to the region’s resources:
We must not forget either that climate change can give rise not only to physical change, change in the nature around us, but can also see the emergence of disputes between countries over energy exploration and extraction, the use of marine transport routes, bioresources, and shortages of water and food resources. The countries bordering the Arctic region are already actively engaged in expanding their research, economic, and even military presence in the Arctic. Unfortunately, in this situation, we are seeing attempts to limit Russia’s access to exploring and developing Arctic energy deposits, which is inadmissible from a legal point of view and unfair in terms of our country’s geographical location and very history.
His reference to “shortages of water and food resources” fits squarely within the increasingly common view of climate change’s potential as a “conflict accelerant” (see, e.g., the U.S. Department of Defense’s 2010 Quadrennial Defense Review) or “threat multiplier” (as in CNA’s National Security and the Threat of Climate Change and statements from representatives of the UK and EU foreign offices).
But his Arctic comments sounded different than what I’ve been hearing in Washington. The Arctic rightfully gets a lot of attention for alarming rates of physical change, newly accessible resources, and potential new shipping routes. Yet remarks at a recent spate of Arctic climate and security discussions suggest officials in Washington view the geopolitical and trade issues more as “challenges” than “crises.”
For example, last month at the Stimson Center, and just yesterday at the Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Lab, the U.S. Navy’s director of Task Force Climate Change and oceanographer, Rear Admiral David Titley, used “challenge” rather than “crisis” to depict the security situation in the far North. At numerous panels, officials and experts expressed confidence that the Arctic Council and related institutions are forums robust enough to manage current and future disputes.
Ironically, one of those key institutions is UNCLOS, the Law of the Sea treaty, which has been ratified by 157 countries, but not the United States. U.S. military and civilian officials alike see ratification as a key step for the United States to represent its interests in these critical multilateral settings. Nevertheless, we can anticipate some knee-jerk demagoguery about the treaty ceding U.S. sovereignty to the United Nations, so the Senate is unlikely to take up the issue until after the fall 2010 elections.
I want to thank friend and colleague Alexander Carius, co-director of Adelphi Research, for calling President Medvedev’s speech to my attention.
Photo: Russian President Dmitry Medvedev, courtesy Flick user World Economic Forum -
Tapping In: ‘Secretary Clinton on World Water Day’
›March 23, 2010 // By Julien Katchinoff “It’s not every day you find an issue where effective diplomacy and development will allow you to save millions of lives, feed the hungry, empower women, advance our national security interests, protect the environment, and demonstrate to billions of people that the United States cares. Water is that issue,” declared Secretary of State Hillary Clinton at a World Water Day event hosted by the National Geographic Society and Water Advocates.
“It’s not every day you find an issue where effective diplomacy and development will allow you to save millions of lives, feed the hungry, empower women, advance our national security interests, protect the environment, and demonstrate to billions of people that the United States cares. Water is that issue,” declared Secretary of State Hillary Clinton at a World Water Day event hosted by the National Geographic Society and Water Advocates.Alongside speeches by representatives from government and the non-profit sector, Secretary Clinton repeatedly emphasized America’s support for water issues. “As we face this challenge, one thing that will endure is the United States’ commitment to water issues,” she asserted. “We’re in this for the long haul.” Beyond simply highlighting the importance of the issue, Secretary Clinton also affirmed commitment to new programmatic, cross-cutting initiatives that will target water as a keystone for development and peace.
ECSP Director Geoff Dabelko, who attended the event, noted that Secretary Clinton’s speech ran counter to the much publicized notion that water scarcity is an unavoidable catalyst for conflict.
She came down squarely on the side of inclusion by identifying water as both a ‘human security’ and ‘national security’ issue. At the same time, she did not fall prey to the common pitfall of arm-waving about water wars. She flagged conflict and stability concerns, but also raised solutions through meeting needs associated with water and development. She went out of her way to emphasize water’s potential for peace and confidence-building, reflecting a commitment to capturing opportunities rather than merely identifying threats.
Secretary Clinton highlighted five crucial areas that comprise the United States’ whole-of-government approach to water issues:
1. Building capacity:
Through efforts with international partners, the United States hopes to strengthen the abilities of water-stressed nations to manage vital water resources. Agencies such as the Millennium Challenge Corporation and USAID are implementing initiatives that will enhance national ministries and encourage regional management cooperatives.2. Elevating diplomatic efforts:
A lack of coordination between the numerous UN agencies, governments, and multilateral funding organizations hinders global water progress. By bringing this work together, the United States can act as a leader, demonstrating a positive diplomatic precedent for fragile and water-stressed nations.3. Mobilizing financial support:
Relatively small grants have achieved large impacts. Work by the United States to strengthen capital markets in the water sector shows that it is possible to earn large returns on water investments. Successful examples range from educational and awareness-building programs, to desalinization and wastewater treatment plants.4. Harnessing the power of science and technology:
Although there is no silver technological bullet to solve the global water crisis, simple solutions, such as ceramic filters and chlorine disinfection systems, do help. Additionally, sharing government-accumulated technological knowledge can have significant impacts, as demonstrated in a recent NASA-USAID project establishing an Earth-observation monitoring and visualization system in the Himalayas.5. Broadening the scope of global partnerships:
By encouraging partnerships and elevating water in its global partnership initiatives with NGOs, non-profits, and the private sector—all of which are increasingly engaged in water issues—the Department of State hopes to maximize the effectiveness of its efforts.The holistic approach advocated by Secretary Clinton reflects a distinct evolution of American diplomacy within this area, which is strongly supported by the water community. “The policy directions outlined in the speech, the five streams, represent a victory for those in and outside of government who have argued for a broad, rather than narrow, view of water’s dimensions,” said Dabelko. “The diversified strategy focuses on long-term and sustainable interventions that respond to immediate needs in ways most likely to make a lasting difference.”

In her concluding remarks, Secretary Clinton sounded a positive note, noting that for all of the press and attention devoted to the dangers of the global water crisis and the possible dark and violent future, dire predictions may be avoided through a smart, coordinated approach. “I’m convinced that if we empower communities and countries to meet their own challenges, expand our diplomatic efforts, make sound investments, foster innovation, and build effective partnerships, we can make real progress together, and seize this historic opportunity.”
Photo Credits: State Department Official Portrait; UNEP.
-
Maternal and Newborn Health as a Priority for Strengthening Health Systems
›Among the many initiatives that have recently been launched to strengthen health systems in the developing world, there is little consensus on execution. Traditional strategies for improving the health system, such as the vertical approach, which prioritizes communicable diseases, or the horizontal approach, which prioritizes non-communicable diseases, are limited in scope and fail to include a comprehensive gender lens.
To overcome the shortcomings of these two health financing approaches, the “diagonal” strategy combines them by “clearly defining priorities and utilizing these priorities to drive general improvements of the health system,” said Julio Frenk, dean of the Harvard University School of Public Health, at the Global Health Initiative’s third event in the “Advancing Policy Dialogue on Maternal Health” series.
Along with panelists Helen de Pinho of Columbia University, and Agnes Soucat of the World Bank, Frenk discussed how prioritizing key maternal health indicators can improve health systems and support the implementation of evidence-based interventions. Putting Women and Health First
Putting Women and Health First
Drawing on his experience as Mexico’s minister of health, Frenk said that clearly defining a set of priorities grounded in “women and health” drove the improvement of Mexico’s health system. “Picture three concentric circles. The core of these concentric circles is the prevention of maternal mortality and disability; the second circle [includes] other aspects of sexual and reproductive health in addition to pregnancy and delivery; the third circle includes other fundamental areas of women’s health and the intersection of women with the health system,” said Frenk.
Mexico used maternal mortality rates to measure quality of care and rectify weaknesses in the health system. “Every maternal death triggered an audit that could lead to a hospital losing its license to operate,” said Frenk. Additionally, these audits helped to identify gaps and prioritize investments in “equipment and supply of drugs…and networks [for] obstetric emergencies,” he added.
“This illustrates how you can take a specific set of priorities and drive them through,” argued Frenk. “Global health needs to get out of the traditional confines that have split the community between vertical and horizontal and adopt more integrated frameworks like the notion of women and health,” he said, which “will leave behind a better health system to deal with the next challenge.”
Measuring Maternal Health
The maternal health community agrees that to reduce maternal mortality rates, access to emergency obstetric care (EmOC) must be improved. “A simple assessment of an emergency obstetric care facility combines a number of aspects that are core to strong health systems,” said de Pinho. To reduce maternal mortality, a strong health system must be able to positively answer these key questions:
These questions monitor the availability, utilization, and quality of care, which signals whether “the health system is actually responding to the woman’s needs when they need it,” said de Pinho. These maternal health indicators “paint a picture for where next steps need to be taken,” she said.- Are there enough facilities providing EmOC and are they well distributed?
- Are women with obstetric complications using these facilities?
- Is the quality of the EmOC services adequate?
Rwanda’s Innovations in Health Financing
“When we talk to ministries of health we ask them what are the low-hanging fruits we can reach in the six years” until the deadline for meeting the Millennium Development Goals (MDGs), said Soucat. To implement methods with proven results, additional research data, monetary support, and political will are all necessary. Rwanda’s ministry of health used the health-related MDGs—particularly MDG 5 to reduce maternal deaths by 75 percent—to reform the health system and hold institutional and individual actors accountable.
Rwanda’s health system was reformed through five key pillars:
“The heart of the reform is to increase accountability to its citizens,” said Soucat. Rwanda’s results-based financing offered “incentives and salary supplements to workers who saw more patients and provided higher quality of care,” she said. Impact assessments demonstrate that all income groups in Rwanda benefited from this health care scheme; in three years family planning tripled and assisted deliveries increased by 13 percent –“something that has never been observed in Africa,” she said.- Fiscal decentralization increased community participation and allocated funds to district governments
- Performance contracts were established between the president and district mayors
- A performance-based financing system distributed money to health facilities based on results
- Community health insurance increased access and reduced out-of-pocket expenditures
- Autonomous health facilities were allowed to hire and fire personnel
Rwanda’s Ministry of Health conducted rigorous assessments to ensure quality services and demonstrate impact to the Ministry of Finance. “When talking about maternal health a strong dialogue between the Ministry of Health and Ministry of Finance is needed more than ever and centered around the production of results,” argued Soucat. Scaling up the results-based finance scheme in other African countries is possible, she said, but additional research is needed to better understand this scheme at the decentralized level. -
‘A Question of Quality: ’ World Water Day 2010
›March 22, 2010 // By Julien KatchinoffWorld Water Day 2010, dedicated to the issue of water quality, points to a challenge that is often omitted from the scarcity debate. Today, through a variety of global events, publications, and speeches, a large coalition of organizations, companies, and institutions will underline the importance of healthy ecosystems and water quality necessary for human well-being.
A participating partner in this initiative, the National Geographic Society, has made its special issue on water, Water: Our Thirsty World, available for free online. After registration, readers may find the following stories interesting:
“Water is Life” – Barbara Kingsolver
“The Big Melt” – Brook Larmer
“Sacred Waters” – John Stanmeyer
“The Burden of Thirst” – Tina Rosenberg
“Silent Streams” – Douglas H. Chadwick
“California’s Pipe Dreams” – Joel K. Bourne, Jr.
“Parting the Waters” – Don Belt
“The Last Drop” – Elizabeth Royte
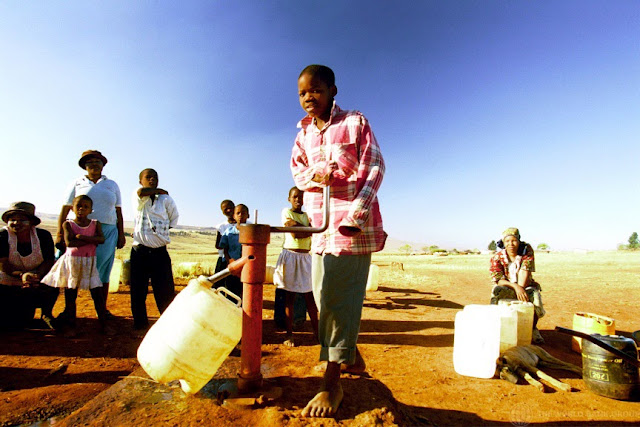
Photo Credits: “Rural water pump near Ulundi, South Africa” Photo: Flickr User Trevor Samson, World Bank Photo Collection -
Imagine There Are No Countries: Conservation Beyond Borders in the Balkans
›International peace parks have captured the imagination of visionaries like Nelson Mandela, who called them a “concept that can be embraced by all.” Such parks—also known as transboundary protected areas—span national boundaries, testifying to the peaceful collaborative relationship between neighboring countries and to the co-existence of humans and nature.
Peace parks seek to simultaneously promote regional peace and stability, conserve biodiversity, and stimulate job creation. How can they accomplish such ambitious goals?- Biodiversity: The political borders and physical barriers within the park are removed, allowing animals and humans to migrate freely. In addition, surveys of the area’s biodiversity don’t stop at sovereign borders, but are instead conducted on an ecosystem basis.
- Job creation: Developing eco-tourism—one of the fastest-growing industries in the world—provides people living near peace parks an incentivized alternative to exhausting the very resource base on which their survival depends.
- Peace and stability: To jointly manage natural resources successfully requires countries to collaborate through cross-boundary committees on conservation, safety and security, finance, human resources, legislation, and tourism.
 My organization, International Peace Park Expeditions, uses experiential peacebuilding, academic programs, and professional trainings in international peace parks to integrate theory with practice. We seek to develop leadership and collaboration among three distinct, but complementary, groups: students and professors, transboundary protected area professionals, and youth from the peace park countries.
My organization, International Peace Park Expeditions, uses experiential peacebuilding, academic programs, and professional trainings in international peace parks to integrate theory with practice. We seek to develop leadership and collaboration among three distinct, but complementary, groups: students and professors, transboundary protected area professionals, and youth from the peace park countries.
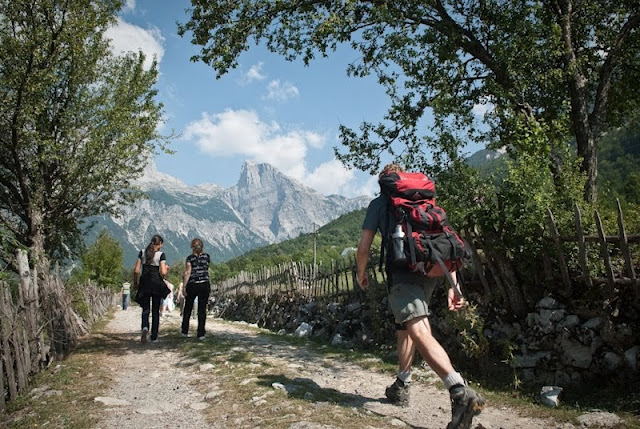
Our Summer 2010 programs focus on the proposed peace park in the Western Balkans’ Prokletije/Bjeshket e Namuna mountains, between Albania and the newly independent countries of Montenegro (2006) and Kosovo (2008), which were formerly part of Yugoslavia. The Balkans Peace Park Project, a UK charity and their local network of partner organizations and individuals, first conceptualized the Balkans Peace Park, an area of approximately 4000 square km, in 2001.
This summer, participants in our professional training symposium will collaboratively develop a more precise and dynamic map. Students and young leaders in our other two programs will learn about peace parks while trekking together across the borders into all three countries.
Experiential Peacebuilding (July 19-25, 2010)
Experiential Peacebuilding programs combine outdoor experiential education and practical skills training in peacebuilding to foster the development of a community of young leaders capable of catalyzing positive peaceful changes in their communities. This summer’s program is being developed in conjunction with our local partner organizations (ERA and Marimangut in Kosovo; Outdoor Albania and High Albania in Albania; and PSD Prokletija in Montenegro). The primary goals of these programs are to unite youth from conflict-affected communities to develop relationships across borders; transform negative attitudes and stereotypes; and create a core group of young leaders with the skills, tools, and motivation to generate and direct changes in their communities.
Academic Expedition (June 7-26 and August 2-21, 2010)This three-week, three-credit course, “Conservation Beyond Borders,” will combine traditional academic teaching with proven experiential learning methodologies to create a unique, dynamic expedition that will provide students with a strong understanding of the theory and practice of international peace parks. Course readings and lectures will provide the academic base, and guest lectures from subject-matter experts working in the field will create the bridge; both will address sustainable forestry management, biodiversity surveys, eco-tourism plans, development and infrastructure planning, environmental conservation, water resource management, peacebuilding initiatives, and cross-border projects. First-hand experience trekking through the proposed Balkans Peace Park, crossing the borders of Albania, Kosovo, and Montenegro, and living among the local people will bring theory to life.
Professional Training Symposium (July 8-9, 2010)
This year’s Professional Field Training Symposium, “Critical Transboundary Environmental Linkages,” will bring together experts, policymakers, and stakeholders from the Prokletije/Bjeshket e Namuna region to discuss cross-border ecotourism, biodiversity mapping, and sustainable forestry management. The symposium seeks to build trust through cross-border collaboration, and to improve environmental management in the peace park region. Participants will create a Google Earth map to house shared environmental data and visit two project sites in the proposed peace park. Todd Walters is the founder and executive director of International Peace Park Expeditions. He holds a master’s degree in International Peace and Conflict Resolution from American University’s School of International Service, and is a National Outdoor Leadership School (NOLS) certified wilderness guide. While at AU, he worked as an intern for the Environmental Change and Security Program.
Todd Walters is the founder and executive director of International Peace Park Expeditions. He holds a master’s degree in International Peace and Conflict Resolution from American University’s School of International Service, and is a National Outdoor Leadership School (NOLS) certified wilderness guide. While at AU, he worked as an intern for the Environmental Change and Security Program.
Photos courtesy IPPE/Cory Wilson.
 A Publication of the Stimson Center.
A Publication of the Stimson Center.




 “It’s not every day you find an issue where effective diplomacy and development will allow you to save millions of lives, feed the hungry, empower women, advance our national security interests, protect the environment, and demonstrate to billions of people that the United States cares. Water is that issue,” declared Secretary of State Hillary Clinton at a
“It’s not every day you find an issue where effective diplomacy and development will allow you to save millions of lives, feed the hungry, empower women, advance our national security interests, protect the environment, and demonstrate to billions of people that the United States cares. Water is that issue,” declared Secretary of State Hillary Clinton at a 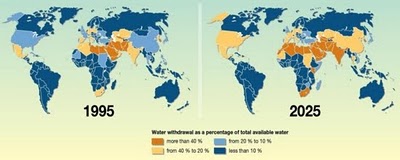
 Putting Women and Health First
Putting Women and Health First








