-
Empowering Women in the Muslim World
›December 2, 2010 // By Wilson Center StaffOriginally featured in the Wilson Center’s Centerpoint, November 2010.
For decades, women in the Middle East have actively struggled for equal status before the laws of their respective countries. They have strived to attain equal participation in politics and society, and progressive justice throughout the region. While they have made progress in some parts of the region, many challenges remain. The Wilson Center’s Middle East Program recently held three meetings to discuss challenges as well as progress to empowering women across the Muslim world.
A Modern Narrative
The American Islamic Congress (AIC) recently published a report, “A Modern Narrative for Muslim Women in the Middle East: Forging a New Future,” that highlights past and present triumphs and difficulties – economic, legal, political, religious, and social –for women’s rights throughout the region. On September 30, the Middle East Program co-sponsored a meeting with the AIC to review the status of women in Saudi Arabia and Jordan, based on findings in the AIC’s report.
Fawziah Al-Hani, manager of the Gherass Center for Social Education in Saudi Arabia, expressed frustration about the progress women have made in her native Saudi Arabia. She said women there are perceived as second-class citizens by the country’s legal, economic, political, religious, and social institutions. Women’s issues are rarely discussed in Saudi political and social spheres, and women are not represented in government or the business sector. She said if women are allowed to be active outside the home, they are mostly restricted to educational and health activities.
While she is frustrated about these restrictive Saudi policies toward women, Al-Hani said she maintains hope, as changes take place within the society and government through new initiatives and movements.
Rana Husseini, a human rights activist, author, and journalist, detailed the changes to the status of women in Jordan over the past 20 years. Husseini, whose human rights activities over the past two decades in Jordan have focused on honor crimes and other women’s issues, said Jordan has made substantial progress on women’s rights as a result of intense media and civil society activism. While there is room for improvement, she said women are now participating in government and significant reforms have been made to the judicial system.
Though the effectiveness of quotas for women in government may be debated, Husseini noted that quotas facilitate women’s participation in elections and government service. In fact, she said, there are some 50 women judges in Jordan. She noted that honor killings, except in extreme cases, are becoming rarer, and harsher sentences are being imposed for honor crimes.
With constant pressure on the government and society, reforms will continue, said Husseini, who is optimistic about the future for women rights in Jordan and in the Middle East as a whole.
Demographic Realities
Why do many Middle Eastern women not enjoy the same economic opportunities as women of other regions? Can they be empowered to participate at a greater level? Nadereh Chamlou, a senior adviser at the World Bank, attributed the gender inequality to restrictive social norms. She said the region’s women must be empowered to participate in a more significant way if their countries are to effectively exploit, instead of squander, the current economic “window of opportunity.”
At a September 13 discussion, Chamlou said the good demographic news is that there are high numbers of working-age people and thus the potential for rapid economic growth. However, Middle Eastern countries have the highest dependency rates in the world, a fact that Chamlou attributed to the low economic participation of Middle Eastern women relative to female citizens’ participation in other parts of the world. This reality means the Middle East’s demographic composition will not be exploited to its full potential.
Increasing economic opportunities for women will require changing social norms, said Chamlou. She cited a study conducted by the World Bank in three Middle Eastern capitals – Amman, Jordan; Cairo, Egypt; and Sana’a, Yemen – that revealed the biggest reason for the poor representation of women in the workforce is the negative male attitude regarding women working outside the home. Notably, social norms and such negative male attitudes proved to restrict women’s participation far more than the need to attend to child-rearing duties. Despite the successful efforts of most Middle Eastern states to improve education opportunities, conservative social norms still pose a barrier to female empowerment.
Some simple changes could have a substantial impact. Chamlou recommended focusing on educated, middle-class women, undertaking more efforts to bring married women into the workforce, and emphasizing changing attitudes – particularly among conservative younger men – toward women working outside the home.
Lessons from Tunisia
In Tunisia, the progress of women’s empowerment can serve as a model for the region, noted women’s rights advocate Nabiha Gueddana, president and director-general of the National Agency for Family and Population in Tunisia.
Speaking at a September 8 meeting, Gueddana said the Arab world can learn much from her native Tunisia regarding the positive effects of empowering women. Gueddana, also a candidate for undersecretary-general of UN Women at the United Nations, described how Tunisian women have been empowered politically, economically, and socially, and how this empowerment has benefited Tunisian society.
Tunisia has undergone substantial changes since achieving independence from France in 1956. Tunisian women had second-class status in the years prior, a time Gueddana described as one that relegated them to a life of constant child-rearing, illiteracy, and economic dependence.
Yet Tunisia has become a beacon for other Muslim societies: the country’s labor code allows full female participation in the economy and education is open equally to boys and girls. Family planning programs and important strides in health have considerably lowered the birth rate and lengthened the life expectancy of the average woman. Gueddana also noted that Tunisia’s economic growth is now five times greater than the growth rate of its population.
Measures to empower women in Tunisia have benefited not only women but Tunisian society as a whole, with significant shifts in men’s attitudes regarding women’s rights and roles in society. Gueddana indicated that her efforts extend beyond Tunisia, as she strives to help empower women throughout the world. She said such efforts will persist so long as women anywhere find themselves disadvantaged, dependent, and living as second-class citizens.
Women’s empowerment in society rests increasingly not in the political but in the economic and business domains (Editor’s note: one could add that women’s empowerment has the potential to considerably impact the environmental domain as well). While women have made considerable progress in the political arena, economic power is still male-dominated throughout the region.
Gueddana said the discussion of women’s rights should take place within the broader context of human rights. Violence against women, particularly sexual violence, is a widespread phenomenon across all societies and, unfortunately, often considered taboo for discussion. She said all citizens benefit when all have equal rights and can use them to expand their opportunities and achievements to enhance their societies.
Dana Steinberg is the editor of the Wilson Center’s Centerpoint.
Photo courtesy of Centerpoint. -
Top 10 Posts for November 2010
›Matthew Erdman’s report on PHE programing in Madagascar, Jennifer Sciubba’s response to the “aging” media blitz, a series on Nigeria’s cloudy future, and John Bongaart’s Pop Audio topped the list last month:
1. The Beat on the Ground: Toliara, Madagascar
Matthew Erdman Reports on Blue Ventures’ Integrated PHE Initiative
2. On the Beat: Where Have all the Malthusians Gone?
3. Nigeria’s Future Clouded by Oil, Climate Change, and Scarcity: Part One, The Delta
4. Pop Audio: John Bongaarts on the Impacts of Demographic Change in the Developing World
5. India’s Maoists: South Asia’s “Other” Insurgency
6. Guest Contributor Kavita Ramdas: What’s Good for Women Is Good for the Planet
7. Restrepo: Inside Afghanistan’s Korengal Valley
8. DRC’s Conflict Minerals: Can U.S. Law Impact the Violence?
9. Nigeria’s Future Clouded by Oil, Climate Change, and Scarcity: Part Two, The Sahel
10. The Ultimate Weapon Is No Weapon: Human Security and the New Rules of War and Peace -
Managing the Mekong: Conflict or Compromise?
›December 1, 2010 // By Russell SticklorAt nearly 5,000 kilometers long, the Mekong River is one of Asia’s most strategically important transboundary waterways. In addition to providing water for populations in the highlands of southern China, the Mekong helps support some 60 million people downstream in Southeast Asia, where the river is a key component of agricultural production and economic development.
In recent years, however, the Mekong has emerged as a flashpoint for controversy, pitting China against a coalition of downstream nations that includes Thailand, Laos, Cambodia, and Vietnam. The countries of the Lower Mekong argue that Beijing’s construction of multiple dams on the Upper Mekong is robbing them of critical water resources, by decreasing both the quality and quantity of water that makes it through Chinese floodgates and spillways. China, however, mindful of soaring energy demand at home, has continued its campaign to harness the hydroelectric potential of the Upper Mekong and its tributaries – but at what cost to the environment and Beijing’s relationships with Southeast Asia?
China’s Hand on the Faucet
China’s total energy demand just recently passed the United States and is expected to continue to increase in the near-term – by 75 percent over the next 25 years, according to the International Energy Agency.
As a result, Beijing has been looking to bolster its energy security by reaching out to develop energy resources in Africa, Latin America, and the Middle East, as well as along the Mekong and in the East and South China Seas.
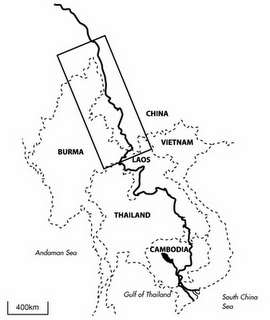
In that context, China’s aggressive hydroelectric development of the Upper Mekong — known in China as the Láncang Jiang (shown in the boxed area of the map at right) — makes perfect sense. The river’s sizeable elevation drops make it a rich source of energy; already, 15 large-scale dams have either been completed or are under construction on the Upper Mekong in Tibet and Yunnan.
Those dams also provide China with enormous geopolitical leverage over downstream nations. With little more than the flick of a switch, the Chinese government could substantially curtail the volume of flow entering the Lower Mekong basin. Doing so would of course be tantamount to an act of war, since depleted flow volumes in the Lower Mekong would hinder crop irrigation, jeopardize food security, and endanger the health of the region’s economically critical freshwater fisheries, which are among the world’s most productive. Chinese floodgates and spillways essentially give Beijing de facto control over Southeast Asia’s water security.
The View Downstream
To date, China has never threatened to deliberately reduce the flow of the Mekong to its downstream neighbors. Nevertheless, the perception of threat in Southeast Asian capitals remains high.
Already, a number of the region’s governments — represented formally through the Mekong River Commission, a 15-year-old organization that China still has not joined as a full-fledged member — have complained that completed or in-progress Chinese dams are resulting in less water entering their countries, a phenomenon that becomes particularly pronounced during periods of drought, as observed this summer. Further, there is also the issue of water quality. Since Chinese dams trap silt being flushed out of the Himalayas, that nutrient-rich material cannot be carried downstream, where it historically has helped create fertile soils in the floodplains of the Lower Mekong basin.
Quality and quantity concerns aside, there are also structural issues concerning how Beijing goes about its business on the Upper Mekong. Since it is only a “Dialogue Partner” to members of the Mekong River Commission, China is not required to seek approval from downstream nations on hydroelectric development of the river’s Chinese stretch, even though that development has both direct and indirect implications for water security in the Lower Mekong basin. China has even shown a penchant for deliberate secrecy as it develops its stretch of the river, choosing to share a minimal amount of hydrological data with downstream neighbors and typically refraining from even announcing new dam projects.
“The Security Implications Could Hardly Be Greater”
Given its geographic position, Cambodia is particularly vulnerable to China’s stewardship decisions. With one of the poorest populations in Southeast Asia and also one of the highest fertility rates, at 3.3 births per woman, the potential for water scarcity issues is real. By mid-century, its population is projected to jump from its current 15 million to nearly 24 million.
“The government of Cambodia will be entirely at the mercy of Beijing,” said Wilson Center Scholar and Southeast Asian security expert Marvin Ott. “For Cambodia, the question becomes how they can curry China’s favor so as to avoid coercive use of the Mekong — or find some way of exerting counter-pressure on Beijing.”
Overall, population for mainland Southeast Asia is projected to rise from its current 232 million to 292 million by 2050. This growth will require increased agricultural output across the region and thus increased reliance on the waters of the Lower Mekong. The Lower Mekong nations’ shared dependency on the river and China’s continued unilateralism in the Upper Mekong could have serious repercussions for the region, said Ott:The security implications could hardly be greater for the downstream states. With the dams, China will have literal control over the river system that is the lifeblood of Laos, Cambodia, and Vietnam. The power this gives China is equivalent to an invasion and occupation of a country by the Chinese army.
For its part, the PRC maintains that water woes in the Lower Mekong are not its doing. In response to the chorus of Southeast Asian claims that China diverts or stores more than its fair share of water, Beijing’s typical refrain has been that blame for low water levels downstream lies not with Chinese water resource management but with heightened precipitation variability associated with climate change. Chinese water officials also contend that the Lower Mekong countries’ complaints are misdirected because water from the Chinese-controlled sections of the Upper Mekong basin accounts for less than 20 percent of the Mekong’s total flow volume by the time the river reaches its natural outlet in the South China Sea.
There are some indications, however, that China may be experimenting with a more open approach to engaging downstream nations. Earlier this year, China overturned precedent by offering top Southeast Asian government officials a tour of what had once been a top-secret hydro project, the mammoth Xiaowan dam. Some critics insisted Beijing’s fear of growing U.S. influence in the Lower Mekong helped motivate the rare show of transparency, while others said it was a means to curry favor with Southeast Asian nations so that they would support China’s controversial resource-development strategies in the South China Sea. Yet regardless of motive, Beijing’s move away from secrecy – if sustained – could do a great deal to smooth over regional tensions.
Dammed If You Do, Damned If You Don’t
Beyond some limited transparency, Beijing also hopes to mitigate concerns about development of the Upper Mekong by offering funding or logistical support for similar large-scale hydroelectric facilities on the Lower Mekong. The move has been largely welcomed by the Mekong River Commission countries, which envision dams of their own generating much-needed energy input for national grids, accelerating continued economic modernization, and enhancing flood control. As of 2009, there were 12 dam projects for stretches of the Mekong south of the Chinese border and many more planned for key tributaries.
The danger in such deal-making is that the environmental costs will be lost in the shuffle. A series of major dams would fundamentally alter the Mekong’s hydrology, which could lead to the degradation of sensitive riverine ecosystems, the disruption of upstream migratory routes for fish that serve as local dietary staples, and the decline of fresh water fisheries that form the backbone of many local economies.
Given the long-term effects on the food, environmental, and economic security of the Lower Mekong heartland, Beijing’s attempt to ease water tensions with a new round of dam construction may end up doing far more harm than good. Unfortunately, with both China and the Mekong River Commission countries currently viewing the dam proposals as something of a win-win, planning and construction are likely to move forward over the coming years.
Sources: Financial Times, Foreign Policy, International Institute for Strategic Studies, Los Angeles Times, Mekong River Commission, National Geographic, New Asia Republic, Phnom Penh Post, Population Reference Bureau, Stimson Center.
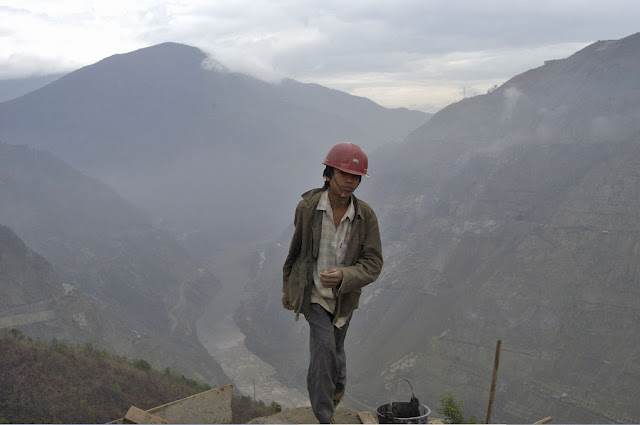
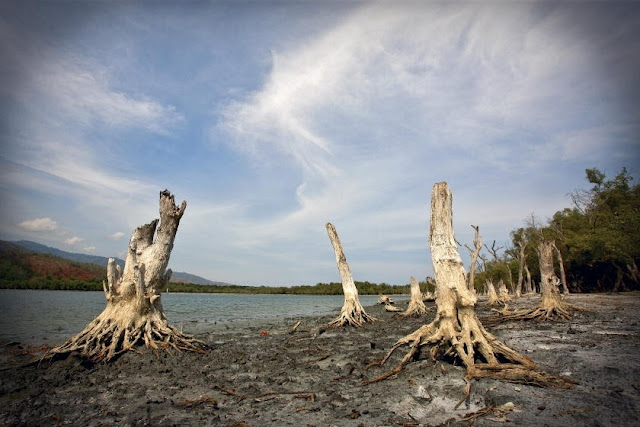
Photo Credits: “Xiaowan Dam Site (Yunnan Province, China, 2005),” (Top) courtesy of flickr user International Rivers; Map (Middle) courtesy of International Rivers; “Thailand – Isaan, Mekong River,” (Bottom) courtesy of flickr user vtveen. -
World AIDS Day 2010: Not Yet in a Position to Say “Mission Accomplished”
›December 1, 2010 // By Schuyler NullToday is World AIDS day. More than 33 million people are currently living with HIV around the world, according to the UN, and the vast majority of them (22 million) are located in sub-Saharan Africa.
“We have halted and begun to reverse the epidemic. Fewer people are becoming infected with HIV and fewer people are dying from AIDS,” said Executive Director Michel Sidibé in the 2010 edition of UNAIDS’ annual report.“However we are not yet in a position to say ‘mission accomplished.’ Growth in investment for the AIDS response has flattened for the first time in 2009. Demand is outstripping supply. Stigma, discrimination, and bad laws continue to place roadblocks for people living with HIV and people on the margins.”
Particularly in sub-Saharan Africa, “people on the margins” often means women and children. As a result, there has been more and more integration of HIV/AIDS programs with gender and maternal health. The environmental community has also worked closely with HIV/AIDS interventions in places where the destruction of natural resources makes certain populations more vulnerable than others and valuable conservation efforts are threatened.
As development efforts become more cross-sectoral, it’s important to keep in mind and maximize these connections between community, economic, and environmental health.
Check out The New Security Beat’s coverage of HIV/AIDS integration with other health and environment programs including coverage from the Global Health Initiative’s “Integrating HIV/AIDS and Maternal Health Services” event last year, a sit-down interview on the challenges facing HIV-positive adolescents with Harriet Birungi of the Population Council in Kenya, and an examination of how gender-based violence contributes to women’s vulnerability to HIV.
Sources: Population Reference Bureau, UN, World Wildlife Federation.
Map Credit: World AIDS Campaign. -
Developing a Blueprint for Addressing Glacier Melt in the Region
Changing Glaciers and Hydrology in Asia
›“Glacier melt is part of larger hydrologic and climate systems, so effective programs will be cross-sectoral and yield co-benefits,” said Elizabeth L. Malone, senior research scientist at the Joint Global Change Research Institute and Pacific Northwest National Laboratory, speaking at the Wilson Center on November 16. “Looking more closely at glacier melt, we come to understand that upstream actions and choices have a potentially huge effect on downstream communities,” added Kristina Yarrow, health advisor at the U.S. Agency for International Development’s Asia and Middle East Bureaus.
Malone and Yarrow were joined by Mary Melnyk, senior advisor for natural resource management at USAID’s Asia and Middle East Bureaus, to discuss the agency’s new report, “Changing Glaciers and Hydrology in Asia: Addressing Vulnerabilities to Glacier Melt Impacts,” prepared by Malone in collaboration with CDM International and TRG. “This report is a move towards mainstreaming climate change across the development portfolio to ensure enduring success of our investments,” Melnyk said.
Mainstreaming Climate Change
Providing information about the science, vulnerabilities, and current efforts to respond to environmental change and glacier melt in Asia, the new report also features a number of practical, cross-sectoral approaches to addressing glacial retreat in Asia that, if implemented well, could produce multiple benefits. The report highlights the complexity of the issues surrounding glacier melt in the region, and the critical need to prepare today for future environmental changes.
“Climate change in general, and glacier melt specifically, can potentially impact all sectors: economic growth, governance, and health,” Melnyk said. Because there is a lack of scientific knowledge on glacial retreat in Asia and limited financial and human resources to address these issues, it is critical to maximize results through programs that will provide environmental, health, and development co-benefits.
“The challenge is that, in practice, addressing issues of climate change and other environmental security issues still are not a part of the day-to-day business across sectors,” Melnyk said. This report is a first step in the right direction to raise awareness and action on these issues and “although there is uncertainty, we need to move forward – the time to act is now,” she concluded.
Multiple Sectors, Multiple Benefits
“Cross-sector collaboration and programs, when done correctly, can have a much greater impact than when doing a vertical program within a specific sector,” Yarrow said, stressing the importance of multidisciplinary approaches to address environment, health, and development issues. Understanding the health impacts of climate-related environmental change now can help prepare us to address these specific impacts in the future.
“On a global scale, there is indeed a relationship between population growth, environmental change, and development,” Yarrow said. In Asia, stress on water resources due to climate change and rapid population growth will likely exacerbate health problems caused by lack of clean water. Proactively expanding and improving programs that address the causes and effects of diarrheal disease and under-nutrition can help address these vulnerabilities and make communities more resilient.
“Finding innovative ways to improve access to and integrate family planning messages and services into climate adaptation programs will also yield some important co-benefits,” Yarrow said. Family planning can slow population growth, which could help reduce projected demand for water supplies, as well as potentially reduce the amount of water pollution.
Yarrow also added that “population growth affects glacier melt indirectly through the consumption of resources that exacerbate black carbon.” Black carbon, which is produced by cooking and heating with biomass fuels, contributes to regional climate change and severe health problems, including respiratory illness and pneumonia. Accompanied by efforts to promote alternative fuels, family planning could reduce black-carbon emissions, significantly improve health, and strengthen community resilience to climate change.
“Though challenging, integrating across sectors is absolutely essential – we’re not experts yet, but we’re definitely getting better,” Yarrow said. “Understanding and addressing the multiple issues like climate change, poor health, poverty, dependence on natural resources, and governance challenges that these communities are dealing with in a comprehensive and holistic fashion will improve results.”
Responding to Glacier Melt
“We simply do not have the kind of broad-scale knowledge that we would like to have,” Malone said. Current data on glacier melt is scarce and very few direct measurements of glacier volume exist, making calculations of glacier retreat difficult. Moving forward, it is critical to respond to this lack of information by improving regional scientific cooperation on glaciers, snowpack, and water resources in High Asia, and strengthening climate and water monitoring capacity.
“Even the smallest amounts of glacier-melt contribution correspond to the regions of the highest population, so any change in water supply has large implications,” Malone said. Glaciers may not be disappearing as fast as had been previously thought, but “climate change is happening in the Himalayas and is having an effect.”
“If systems – both human and ecological – are already stressed, they are less able to be resilient in the face of changes. But the good news is that we can take actions now that will be crucially important to how societies can respond in the future,” Malone said.
Implementing cross-sector projects can help to target places where environmental, economic, health, and even security issues overlap. Focusing on water resource management, ecosystems, and the needs of high-mountain communities, as well as mitigating climate change by reducing emissions of black carbon, can help reduce both direct and indirect vulnerabilities and improve resilience to future changes.
“The results of this report allow USAID and others to grasp the complexity of these issues, understand the critical gaps, and to respond to the changes in the glaciers to come,” Melnyk said. The next step is applying the knowledge gathered in the report to practitioners in the field and in policy discussions.
“A crucial role USAID can play is to link partners in the government and private sectors to build capacity and spark synergies among new initiatives to really integrate new initiatives with concerns about glacier melt,” Malone concluded.
Photo Credit: “Nepal Sagamartha Trek,” courtesy of flickr user mckaysavage. -
IGWG’s K4Health Gender and Health Toolkit Is a One-Stop Shop for Integration
›November 30, 2010 // By Ramona Godbole
Addressing and analyzing gender norms, roles, and relations is increasingly viewed as critical in the development of equitable, effective, and sustainable health care. However, there has been relatively little integration of gender into health policies, programs, and systems.
The Interagency Gender Working Group (IGWG) – founded in 1997 as a way to bring together NGOs and parts of USAID to share best practices – has partnered with K4Health to create a Gender and Health Toolkit specifically designed to bridge this gap.IGWG’s Gender and Health Toolkit provides access to hundreds of tools, databases, training modules, websites, and publications in one place. Broadly divided into sections including program design, implementation approaches, capacity building, monitoring and evaluation, health systems, best practices examples, and even country-specific case studies, the toolkit provides nearly everything needed to begin integrating gender into new or existing public health programs.
Practitioners can also post questions and comments about the toolkit through an integrated discussion board. The toolkit even has a database to share gender-related photos.
While designed primarily for gender and health specialists and practitioners, the scope of the toolkit extends beyond typical public health issues like maternal health, family planning, HIV/AIDS, and reproductive health. The toolkit links to resources and training modules covering a wide range of cross-cutting topics including gender-based violence; nutrition and food security; integrated population, health and environment; and conflict/post-conflict humanitarian assistance.
The accumulated wealth of knowledge presented in the IGWG Gender and Health Toolkit is an impressively comprehensive resource, and it should be bookmarked by environment, health, and gender specialists and interested policymakers alike.
Image Credit: K4Health. -
Climate-Proofing Development: An Interview With Karen Hardee
›November 29, 2010 // By Hannah Marqusee
While expectations are deflated for broad international consensus at the UN Climate Change Convention in Cancun, the need to “climate-proof” development efforts has been gaining ground in recent years as a necessary preventative measure to help developing countries adapt to the adverse effects of climate change.
-
PRB’s Jay Gribble at Kenya’s National Leaders Conference on Population and Development
›November 29, 2010 // By Wilson Center StaffJay Gribble, vice president of International Programs at the Population Reference Bureau (PRB), recently attended the Kenya National Leaders Conference on Population and Development, November 15-17, at the Kenyatta International Conference Center in Nairobi. During the conference, he produced a series of posts for PRB’s Behind the Numbers on some of his impressions. Gribble focuses on Kenya’s resurgent interest in integrating population issues into the development agenda, the country’s ongoing HIV/AIDS epidemic, and the importance of family planning.
Below are the introductory excerpts from his posts; to read the full posts, please visit Behind the Numbers.
“Anticipating Change in Kenya”
Sitting in the hall where Kenya’s National Leaders Conference will be starting in a few minutes, I can’t help but feel that there is an opportunity to refocus national attention to development…to the goal that I have heard repeatedly of becoming a Middle Income country. And to achieve this goal, they must first recognize that population is an underpinning development issue that cannot be ignored.
In the 1980s and 1990s, Kenya was a leader in reproductive health and maternal health, really setting a pace for the continent. But during the 2000s, Kenya turned its attention to other pressing issues – namely HIV/AIDS – and began to give less attention to population issues. Though HIV continues to be a plague, it is now time to return to the importance of slowing population growth, for until this fundamental issues is addressed, there will be less opportunity for education, jobs, and better health. At the same time, as a predominantly rural country with agriculture representing a major part of the economy, smaller families will be critical to maintaining farms that are large enough to feed families and the country.
Continue on PRB.
“As the Rich Get Richer, the Poor Get Children”
The Kenya National Leaders Conference has begun, representing the first time since 1989 that Kenya’s national population policy has been discussed in a large, open forum. With a new national constitution, Kenya is poised to redress many of the social and economic inequalities that have stood in the way of its development. In fact, the current population policy expires in December, 2010, and one of the purposes of this conference is to gather the input from leaders throughout the country on how a new policy should be framed. I find it impressive that such a large conference is convened to ensure that a new policy reflects the needs of the nation. The conference is also a forum for reaching leaders with important information about the need to address population growth through family planning if Kenya is to achieve its Vision 2030 development plan.
Continue on PRB.
“In Kenya, Prioritizing Population…and Family Planning”
As Kenya’s National Leaders Conference on Population and Development winds down today, it offers leaders an opportunity not only to think and talk about how population growth is an issue that underlies the country’s development, but to act on it too. Whether thinking about business, agriculture, or the environment, it is impossible to be strategic about Kenya’s future without also considering how rapid population growth will affect it.
In talking with Kenyans who grew up in the 1970s and 1980s – back when family planning and population growth were a priority – they remember the messages that were at the tips of people’s tongues – smaller families live better. Before the HIV/AIDS epidemic, family planning and slowing population growth was a priority and a source of national pride because it put Kenya on track for prosperity and development.
Continue on PRB.
Photo Credit: Adapted from “King Kenyatta?” courtesy of flickr user rogiro.
 A Publication of the Stimson Center.
A Publication of the Stimson Center.