-
Comparing Urban Governance and Citizen Rights in China and India
›Today, according to Xuefei Ren, 129 cities in China and 45 in India have populations of over a million people. Such large-scale urbanization has created major governance challenges. Speaking at a May 23 Asia Program event co-sponsored with the Kissinger Institute on China, United States Studies, and the Comparative Urban Studies Project, Ren, a Wilson Center Fellow, examined two case studies of urbanization-driven governance in China and India and their effect on citizen rights.
Her first case study involved housing demolitions and urban re-development in Shanghai and Mumbai. In Shanghai, nearly a million households were relocated between 1995 and 2008 to make way for hotels, airports, and luxury apartments. City regulations in 1991 and 2001 legalized forced demolitions, and no prior consent from residents was needed.
However, Ren noted that displaced residents “are not quite powerless.” She highlighted the case of a woman who sued the city government after being relocated and was eventually granted the compensation she had requested. In 2003, China’s central government ordered a freeze on large-scale demolitions. Several years later, it passed a “landmark” property rights law.
Meanwhile, in Mumbai, local officials in the early 2000s had their own re-development plans. The Indian city is rife with overcrowded, low-income housing; slums are populated by seven million citizens (40 percent of the city’s total population), and comprise up to 10 percent of Mumbai’s total land area.
In 2004, aware that most of the slums were located in desirable areas – near airports or in central business districts – city planners recognized a major development opportunity. Over the next two years, officials launched a demolition campaign that left 400,000 people homeless. According to Ren, certain categories of residents were theoretically entitled to compensation, but with “legal protections carrying little weight,” most of them received nothing.
Yet, as in Shanghai, Mumbai’s city dwellers successfully fought back. Housing activists staged acts of “direct agitation,” including a series of street protests and road blockages. Such tactics, said Ren, were “disruptive but effective.” The Mumbai courts sided against the activists in 2006, but India’s Supreme Court later issued a ruling in their favor.
Fighting Land Acquisitions: A Comparison
Ren’s second case study compared land acquisition efforts outside the slums.
Last year, residents in Wukan, a village along China’s southeast coast in the province of Guangdong, launched a protest movement against land seizures. They alleged that government officials had sold their land to developers and failed to provide residents with appropriate compensation. The protestors made two demands: the return of their land and the holding of local elections.
Notably, Ren said, protestors in Wukan affirmed their support for the Communist Party, and never framed their movement as an anti-government effort. In March 2012, local elections were in fact held, with two leaders of the protest movement voted into office (one as village chief, the other as his deputy).
Ren also discussed an attempt by India’s Tata Motors corporation to acquire land in Singur, a village about 100 miles from Calcutta in the state of West Bengal. The company wanted to use this land to construct a factory for the Nano, a small, cheap car marketed to India’s urban middle class. In 2005, the West Bengal government, which had been controlled by the Communist Party of India-Marxist (CPI-M) for nearly 30 years, actively wooed the firm. State authorities “went overboard” in offering Tata Motors subsidies and highly fertile land, said Ren. Small landowners were obliged to surrender their plots at low prices, and in 2006 the corporation formally took over the land (nearly 1,000 acres altogether), despite heavy opposition from peasants.
However, violent protests continued and after several months, Tata Motors was forced to pull out of West Bengal. Then, in a state election in May 2011, the Trinomool Congress Party, led by the populist leader Mamata Banerjee, swept the CPI-M from power. Banerjee had run her campaign on a promise to restore the land to Singur’s farmers.
Just weeks after the new government assumed power, West Bengal passed a law that would allow for about 400 acres from the Tata Motors project to be returned to farmers who had refused government compensation for their land.
Ren acknowledged that in both countries, citizenship rights are not enjoyed by all and tend to be unevenly distributed across social groups. Still, she concluded, Chinese and Indian cities “have become strategic sites for reassembling citizen rights.” By asserting their land and housing rights, city denizens “are becoming active citizens.”
Michael Kugelman is a program associate with the Wilson Center’s Asia Program. He can be reached at michael.kugelman@wilsoncenter.org and on Twitter @michaelkugelman.
Photo Credit: Mumbai pipes, courtesy of flickr user lenskap. -
Environment, Natural Resource Guidelines for Peacekeepers Moves UN Closer to ‘Greening the Blue Helmets’
›May 30, 2012 // By Stuart KentUN peacekeepers not only operate in conflicts where land and natural resources are a component of the fighting but their own bases and operations can also impact the local environment. As well as documenting practical steps to minimize the footprint of field missions, a new report from the United Nations Environment Program (UNEP) reviews the relationship between natural resources and conflict and what it means for peacekeeping.
While there’s been talk about “greening” UN peacekeeping for years, the details about the economic, environmental, and mission benefits contained in Greening the Blue Helmets: Environment, Natural Resources and UN Peacekeeping Operations suggest that this talk is getting closer to reality.
As of December 2011, the UN’s Department of Peacekeeping Operations was responsible for 121,591 personnel, 17,000 vehicles, and 257 aircraft across 16 different operations worldwide. These forces account for more than half of the entire UN system’s carbon emissions and can significantly strain the resources of fragile host communities, according to the report.
Building on the 2009 Environmental Policy for UN Field Missions, the UNEP report provides a dozen best practice examples from ongoing missions.
Field cases serve as evidence of how increasing water and energy efficiency, safely discarding solid and hazardous wastes, protecting cultural and historical sites, and ensuring a limited footprint after the closing down of camps, can save environmental and financial resources. These measures, the report claims, also reduce the risk of tension with host communities, such as occurred in Haiti when an outbreak of Cholera was traced to unsanitary water management practices at a UN camp.
Technologies recommended include better waste management systems, improved water systems, energy efficient buildings, and green energy capacities. However, some improvements can be made by simply encouraging behavioral changes; the UN mission in Timor-Leste reduced energy consumption by 15 percent over 12 months using a “CarLog” system to encourage fuel efficiency. With a 2009 global fuel bill of $638 million, even a 15 percent margin relates to a significant figure (much like the logic behind similar efficiency efforts within the U.S. military).
However, uncertain mission lengths are a major barrier to the adoption of more efficient technologies. Despite UN operations lasting an average of seven years and evidence indicating that capital investments could be recovered within one to five years in some cases, year-to-year mandates complicate long-term planning.
Natural Resource Nexus
Conceptually, the nexus of natural resources, conflict, and peacebuilding must be a central concern of peacekeeping operations, asserts the report.
In Africa alone, 13 operations have been conducted in response to conflicts associated with natural resources, at a cost of around $32 billion. Exploitation of natural resources such as diamonds, timber, and oil has financed and fueled conflicts in Sierra Leone, the Democratic Republic of the Congo, and Liberia. Communal tensions over access to scarce land and water resources are also considered an exacerbating influence on conflict dynamics in much of Sudan and now South Sudan, according to the report.
Addressing this nexus can also provide opportunities to reduce and redress conflict. In Darfur, firewood collection is a dangerous task for women and girls. By making “firewood patrols” a regular feature of the UN forces’ protection, the prevalence of sexual violence has been limited.
The UN Assistance Mission in Afghanistan is cited in the report for its efforts to hire ex-combatant and vulnerable populations to aid in the reforestation of extensively degraded pistachio woodlands from 2003 to 2009.
“Natural resources can provide opportunities for emergency employment and…sustainable livelihoods for former combatants,” write the authors.
Countries recovering from episodes of violence tend to have a low capacity to effectively and equitably manage a natural resource base that itself may have been degraded by conflict. Recent attention, however, is being paid to the peacebuilding potential of managing shared resources.
According to the report, “while only 54 percent of peace agreements reached between 1989 and 2004 contained provisions on natural resources, all of the major agreements concluded between 2005 and 2010 included such provisions.” This includes the renovation of land tenure systems, management of valuable extractive industries, and reallocation of resource rents.
Preventing Predatory Extraction
As peace begins to take hold, “access to land may be a key determining factor affecting the successful reintegration of a former combatant into a community.”
According to interview data from Northern Uganda, 93 percent of male LRA ex-combatants were unable to access land after demobilization. Often due to the death of an elder relative, sale of land by a family member, or land grabs by other members of the community.
While shared resources can build trust between communities, spoiler groups that use aggressive means to secure resource rents in the aftermath of conflict can endanger a fragile peace. The report identifies a role here for peacekeeping forces – and in particular for their civilian contingent – to identify these potential risks and opportunities for action.
In particular, the report recommends a higher level of clarity about the relationship between peacekeeping forces and so called “expert panels” – groups of civilian specialists called upon by the Security Council to provide advice on an official basis about natural resources in the aftermath of conflict.
The UN mission in the Democratic Republic of Congo, for instance, was given a direct mandate in 2008 to work with the DRC expert panel and to “use its monitoring and inspection capacities to curtail the provision of support to illegal armed groups derived from illicit trade in natural resources.”
UNEP Program Officer Matti Lehtonen, in an email interview, called the panels a “tremendous asset that is not yet used up to its full potential.” However, he noted, “expert panels and peacekeeping missions are different tools with different objectives so there is also a need to maintain a degree of independence.”
The report identifies a set of key recommendations for the UN moving forward:- Ensure that pre-deployment and in-mission training includes instruction on environment and natural resource management
- Aid and encourage disarmament, demobilization, and reintegration programs to look closely at emergency employment and sustainable livelihoods related to natural resources and the environment
- Support and encourage civil affairs personnel to seek ways to capitalize on peacebuilding opportunities around natural resources and the environment
- Systematically inform the Security Council of linkages between natural resources and conflict in states where the Council may be considering action
- Where natural resources have fueled or financed conflict, provide peacekeepers with a more systemic mandate to act on these issues
- Effectively implement best practices identified in the 2009 environmental policy
Photo Credit: UN peacekeepers in Côte d’Ivoire distribute water during a 2007 mission, courtesy of United Nations Photo. -
Full Extent of Africa’s Groundwater Resources Visualized for the First Time
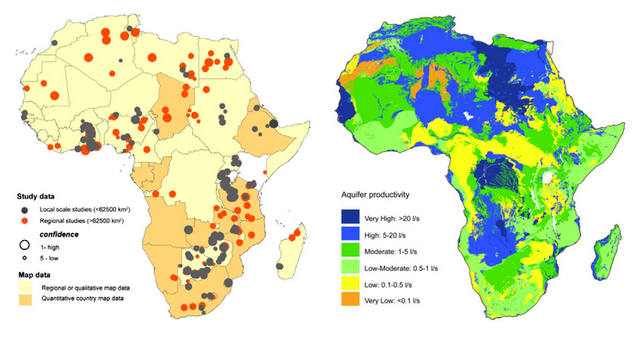
›“In Africa, groundwater is the major source of drinking water and its use for irrigation is forecast to increase substantially to combat growing food insecurity,” yet, a lack of quantitative data has meant that “groundwater storage is consequently omitted from assessments of freshwater availability,” according Alan Macdonald, Helen Bonsor, and Brighid Dochartaigh of the British Geological Survey, and Richard Taylor of University College London, writing in Environmental Research Letters.
The authors hope to remedy this with new research presented in “Quantitative Maps of Groundwater Resources in Africa.” They used estimates compiled from geologic data and 283 aquifer summaries from 152 different publications to quantitatively visualize, for the first time, the full extent of Africa’s groundwater resources.
Tapping a Hidden Resource
The study estimates the scale of the continent’s groundwater resources at around 0.66 million km3. This volume, the authors explain, is “more than 100 times the annual renewable freshwater resources, and 20 times the freshwater stored in African lakes.”
Tapping into this massive resource is not always straightforward, however. The largest aquifers, and those most able to support high yielding bores, are concentrated in the arid regions of North Africa. The depth of these aquifers and their distance from major populations creates substantial economic challenges for extraction.
The geographic distribution of aquifers across sub-Saharan Africa is also quite variable, and local geology can determine not just the availability and accessibility of water but also its quality. For instance, geologic specificities can result in elevated levels of arsenic and other undesirable chemicals. Furthermore, “contamination…is common in urban areas from widespread and dispersed faecal effluent from on-site sanitation and leaking sewers.”
Tempering Expectations
Throughout Africa, “groundwater provides an important buffer to climate variability and change,” say the authors. But these buffers are not a singular solution to the threat of future water scarcity.
As the analysis shows, most aquifers, especially south of the Sahara, are unlikely to sustain boreholes of a higher capacity than that required by community-level hand pumps (one liter per second of flow at minimum). Yet, commercial irrigations schemes and urban towns typically demand boreholes greater than five liters per second, according to the study.
So, groundwater extraction may help communities and some small-scale farmers maintain access to water, particularly because many aquifers are found to possess the storage capacity required “to sustain abstraction through inter-annual variations in recharge,” however, “strategies for increasing irrigation or supplying water to rapidly urbanizing cities that are predicted on the widespread drilling of high yielding boreholes are likely to be unsuccessful.” Especially, the authors assert, where drilling precedes detailed local scale mapping of the available resources.
Sources: Environmental Research Letters.
Image Credit: Figures 1 and 3, courtesy of Environmental Research Letters. -
Digging for Crumbs: Michael Klare on the Global Scramble for the World’s Last Resources
›May 25, 2012 // By Stuart KentYale Environment 360 has a good interview up with Hampshire College Professor Michael Klare about the thinking behind his recent book, The Race for What’s Left: The Global Scramble for the World’s Last Resources. According to Klare, increased scarcity and a surging global appetite for natural resources have led us into an unprecedented period of exploitation where maintaining a supply of crucial resources means exploiting ever more remote, fragile, and dangerous regions of the globe (Afghanistan and the Arctic, for example).
Touching on everything from Canada’s tar sands and “fracking” in the United States, to rare earth minerals and agricultural land grabs, Klare explains the security implications of this newest resource “scramble” and his hopes for future solutions.
We’ve excerpted the first question and answer of the interview, by Diane Toomey, below, but the complete discussion is worth a read.Yale Environment 360: You make the point that when it comes to the age-old competition for raw materials, we’re in an unprecedented age. How so?
Continue reading on Yale Environment 360.
Michael Klare: I do believe that’s the case. Humans have been struggling to gain control of vital resources since the beginning of time, but I think we’re in a new era because we’re running out of places to go. Humans have constantly moved to new areas, to new continents, when they’ve run out of things in their home territory. But there aren’t any more new continents to go to. We’re going now to the last places left on earth that haven’t been exploited: the Arctic, the deep oceans, the inner jungles in Africa, Afghanistan. There are very few places left that haven’t been fully tapped, so this is humanity’s last chance to exploit the earth, and after this there’s nowhere else to go.
Photo Credit: Drilling in Siberia, courtesy of flickr user MOBmole. -
Imelda Abano on Environmental Reporting in the Philippines
›“What we are trying to do is to explore more strategies on how to improve environmental reporting in the Philippines – and on how to reach the government and communities as well,” said Imelda Abano, president of the Philippine Network of Environmental Journalists, Inc. (PNEJ) and senior correspondent at Business Mirror, in an interview with ECSP.
With an overwhelmingly coastal population of around 95 million, the 7,150 island archipelago of the Philippines is seen as highly vulnerable to environmental and climate-related threats. One of Albano’s major aims as president of the PNEJ is therefore to “empower local journalists to report more on environmental issues like biodiversity, climate change, disaster, and other environmental challenges in the Philippines,” she said.
Compelling reporting, she said, comes from “try[ing] to understand what the government is trying to say or what researchers or other organizations are trying to say,” and then relating that information back to the people “in the layman’s terms.”
Environmental issues require a lot of context, she said. One of the most important related issues in the Philippines is population growth.
“When you talk about environment issues, it really resonates or links to population issues,” Abano said. Current UN projections estimate that by 2050, the population could balloon to nearly 155 million. “This really affects our jobs, women, culture, and of course the population around the coastal areas.” -
Poor Land Tenure: A Key Component to Why Nations Fail
›The murder of five land rights campaigners during the last two months – one in Colombia, three in Brazil, and one in Cambodia – have not captured many headlines, but they are a reminder of the central role land tenure plays not just in rural economic development but also in sparking broadly distributed economic gains throughout a society.
-
Philippines’ Bohol Island Demonstrates Benefits of Integrated Conservation and Health Development
›
In March 2012, I participated in a study tour to the island of Bohol, near the unique Danajon double barrier reef ecosystem – the only one of its kind in the Philippines and one of only three in the Indian and Pacific Oceans. Nowhere is the connection between population dynamics and biodiversity more evident than in the Philippines, one of the most densely-populated countries on the planet, with more than 300 people per square kilometer. Nearly every major species of fish in the region shows signs of overfishing, according to the World Bank.
-
Valerie Hudson and Chad Emmett: Women’s Well-Being Is the Best Predictor of State Stability
›May 22, 2012 // By Kate Diamond“The best predictor of a state’s stability and security is the level of violence against women in society,” said Texas A&M University’s Valerie Hudson in this interview with ECSP. That link is “based on rigorous empirical analysis,” she said. “There’s something to it. It’s not just political correctness.”
 A Publication of the Stimson Center.
A Publication of the Stimson Center.