-
New USGS Report and Maps Highlight Afghanistan’s Mineral Potential, But Obstacles Remain
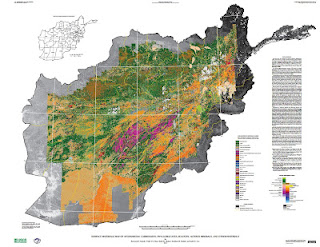
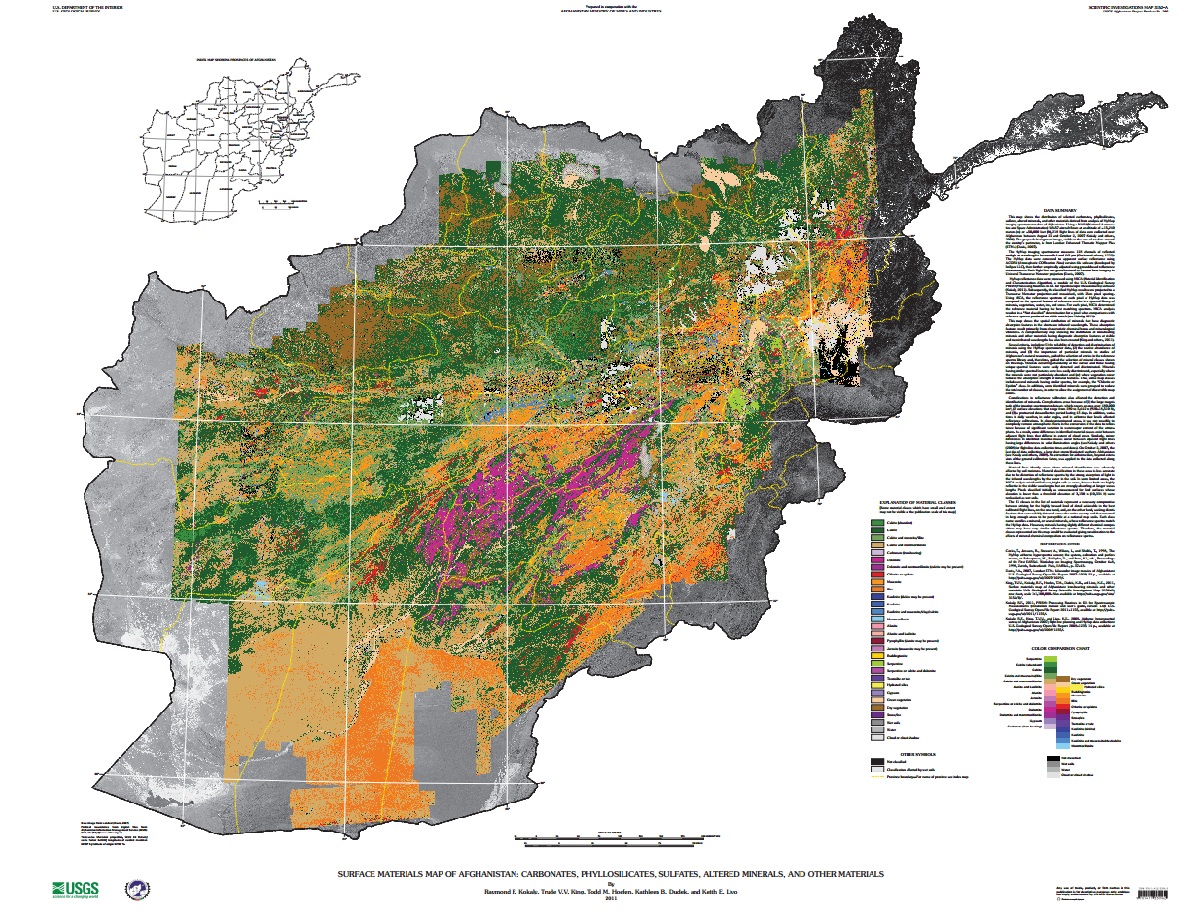
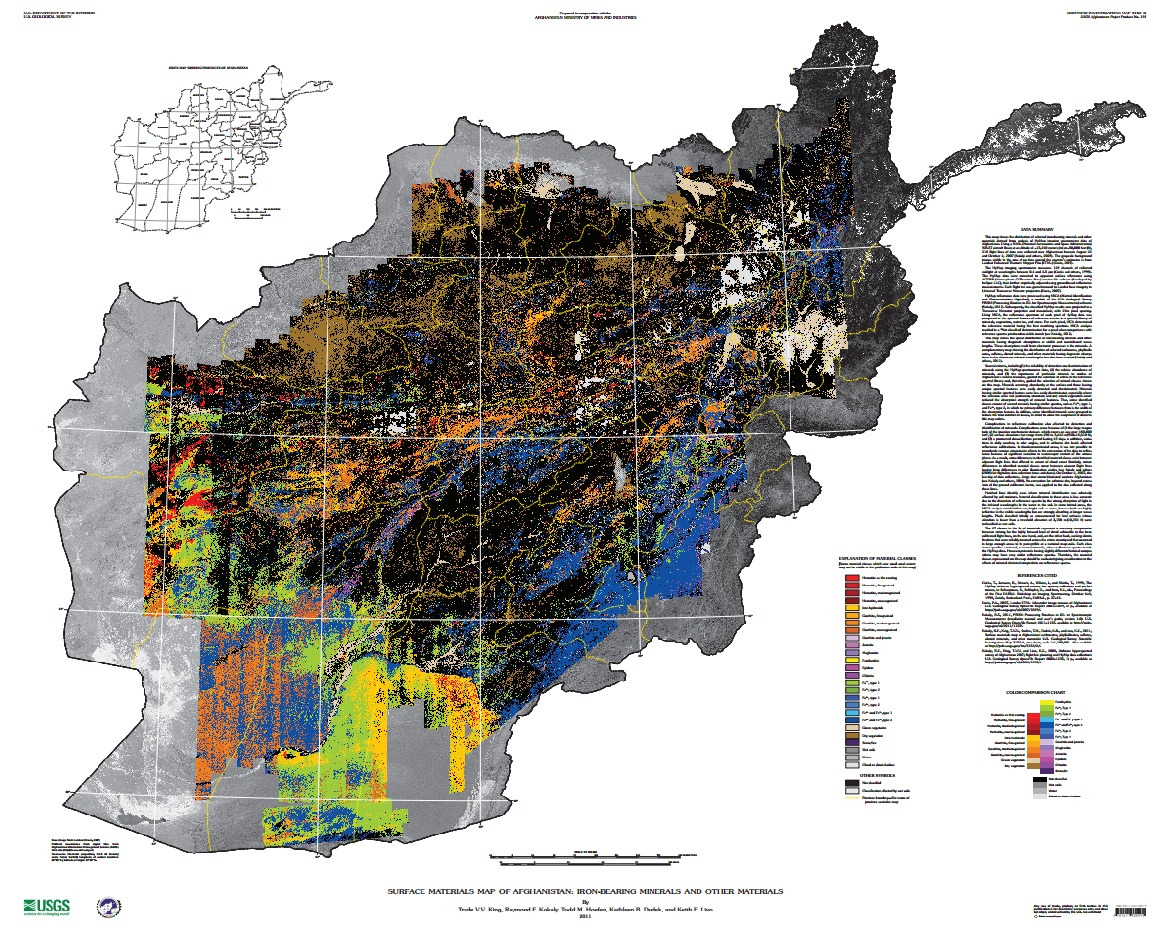
›Two maps released to the public for the first time this month illustrate the vast wealth of mineral deposits in the war-torn nation of Afghanistan. The maps, created through a joint effort from the U.S. Geological Survey and Department of Defense Task Force for Business and Stability Operations, are the first of their kind to provide large-scale coverage of a country using a technology called hyperspectral imaging, which measures the reflectance of material on the Earth’s surface simultaneously across a continuous band of wavelengths broken up into 10 to 20 nanometer intervals. More than 800 million individual pixels of data were collected during a period of 43 days in 2007 by a NASA aircraft. Each data point was then “compared to reference spectrum entries in a spectral library of minerals, vegetation, water, ice, and snow in order to characterize surface materials across the Afghan landscape.”


Two maps released to the public for the first time this month illustrate the vast wealth of mineral deposits in the war-torn nation of Afghanistan. The maps, created through a joint effort from the U.S. Geological Survey and Department of Defense Task Force for Business and Stability Operations, are the first of their kind to provide large-scale coverage of a country using a technology called hyperspectral imaging, which measures the reflectance of material on the Earth’s surface simultaneously across a continuous band of wavelengths broken up into 10 to 20 nanometer intervals. More than 800 million individual pixels of data were collected during a period of 43 days in 2007 by a NASA aircraft. Each data point was then “compared to reference spectrum entries in a spectral library of minerals, vegetation, water, ice, and snow in order to characterize surface materials across the Afghan landscape.”
Accompanying the release of the maps is a USGS study, completed in September of 2011, that largely confirms earlier reports from the DOD and USGS on the size of Afghanistan’s untapped mineral resources. The first reports received widespread media coverage last year, and updated estimates indicate that upwards of $900 billion worth of mineral reserves are present in a number of different forms including copper, iron, gold, and, most notably, more than one million metric tons of rare earth elements.
Scientists involved with the project believe that there may be even more reserves awaiting discovery. “I fully expect that our estimates are conservative,” said Robert Tucker from the USGS in an interview with Scientific American. “With more time, and with more people doing proper exploration, it could become a major, major discovery.”
Over the course of the study, scientists from the USGS and Afghan Geological Survey combined the newly-created spectral data with existing maps to identify 24 areas of interest (AOIs) that warranted hands-on investigation.
The two hyperspectral maps illustrate different parts of the electromagnetic spectrum. Shortwave infrared wavelengths reveal carbonates, phyllosilicates, and sulfates, while visible and near-infrared wavelengths show iron-bearing minerals, which yield products ranging from copper to rare earth elements and uranium. Each map classifies 31 different types of materials by color.
Although the hyperspectral maps only show mineral deposits on the surface, geologists were able to estimate what lies beneath by combining new data with samples previously taken from trenches, drill holes, or underground workings at the AOIs by Soviet and Afghan scientists. According to the USGS, “A number of the AOIs were field checked by USGS and DOD geologists between 2009 and 2011, and the previous geologic interpretations and concepts were confirmed.”
Actual Extraction: Not Easy
Afghanistan has been “scouring the globe for investors to develop its mines in an attempt to lift one of the world’s poorest nations out of misery through investment,” according to The Wall Street Journal. Contracts have already been awarded to China and India to develop copper and iron mines, respectively, and another round of bidding is currently in progress for four unexploited sites that are being closely eyed by countries such as the United States, Australia, and Turkey.
But significant hurdles remain in the quest to turn Afghanistan’s buried minerals into a steady source of income for the government and the Afghan people. Security is still a major concern and United States will pull out a vast majority of its combat troops by 2014. The government has established a Mines Protection Unit to guard sites where ground has already been broken, and plans to increase the size of the unit as necessary to provide security for all mining projects nationwide. For now the Afghan Ministry of Mines is only taking bids for projects in the more secure northern part of the country, where deposits of copper and gold are located. As the nation develops and stabilizes, massive resources of rare earth elements located in the notoriously volatile Helmand Province will open for bids.
Security isn’t the only factor affecting the country’s mining prospects. “If you want to do mineral resource development, there are two things you need to pay attention to: water and energy resources. Where is the power going to come from? You can’t develop these large mineral deposits without energy,” said director of the USGS program in Afghanistan, Jack Medlin, in an interview with EARTH magazine.
There are also the traditional pitfalls of developing extractive industries, especially in poor and conflict-prone countries, including corruption, inequity, land disputes, and environmental degradation. And the fact that Afghanistan is landlocked, making supply lines in an out of the country difficult (as the United States has discovered).
Despite the many hurdles, there is plenty of optimism for an Afghan future brightened by mineral wealth. The new data shows that previous reports of substantial resources were not far off, and the Afghan economy, which for years has relied on opium as its biggest export, could certainly use the help. “The prognosis is extremely encouraging and could play a significant role in recovery from decades of war,” USAID advisor Wayne Pennington told EARTH.
For the full resolution versions of the hyperspectral imaging maps (~90MB each) see here and here.
Keenan Dillard is a cadet at the United States Military Academy at West Point and an intern with the Woodrow Wilson Center’s Environmental Change and Security Program.
Sources: Afghan Geological Survey, Afghan Ministry of Mines, Christian Science Monitor, U.S. Department of Defense, EARTH, The New York Times, Scientific American, U.S. Geological Survey, The Wall Street Journal, World Bank.
Image Credit: USGS.
-
Urbanization and the Global Climate Dilemma
›
Urbanization and climate change may be the two most important trends to shape global development in the decades ahead. On the one hand, urban cities have the potential to serve as engines of change, driving economic growth in some of the world’s least developed countries and pulling more people out of poverty than at any other time in history. On the other hand, climate change could undercut all of this by exacerbating resource scarcity and putting vulnerable communities at risk from sea level rise and more frequent and intense storms.
-
Linking Water, Sanitation, and Biodiversity Conservation in Sub-Saharan Africa
›July 25, 2012 // By Kate DiamondWater, poverty, and the environment are “intrinsically connected,” and the development programs targeting them should be as well, writes David Bonnardeaux in Linking Biodiversity Conservation and Water, Sanitation, and Hygiene: Experiences From sub-Saharan Africa, a new Africa Biodiversity Collaborative Group briefing. In a review of 43 programs across sub-Saharan Africa, including four in-depth case studies, Bonnardeaux finds that natural synergies between water, sanitation, and hygiene (WASH) programming and conservation work provide opportunities for greater effectiveness in addressing both.
Integrating WASH and Conservation: A Natural Match
“WASH interventions are generally reliant on natural resources and processes, whether indirectly or directly,” he writes, and “WASH services produce outputs that are potentially detrimental to the environment if not managed properly.” At the same time, poor ecosystem management can “threaten biodiversity and jeopardize the vital services that these ecosystems in turn provide to humanity, in the form of regulation of stream flow, erosion prevention, water filtration, aquifer recharge, carbon sequestration, wildlife habitat, outdoor recreation, and flood abatement.”
Given the connections between the two, WASH and conservation efforts would benefit from programmatic integration, according to Bonnardeaux. To bring the two closer together, he recommends three tools for policymakers and development programmers: integrated river basin management and basin planning; payments for watershed services (also known as payments for environmental services); and population, health, and environment (PHE) programming.
A Whole-of-Basin Perspective
“The causal link between WASH and ecosystem health and integrity is most accentuated when
dealing with freshwater ecosystems,” writes Bonnardeaux.
In Tanzania’s Pangani River Basin, one of his in-depth case studies, a growing reliance on hydropower, urbanization, and increased agricultural demand is altering a valuable ecosystem marked by endemism and iconic landscapes, including Mount Kilimanjaro.
In response, the government and international organizations are partnering through the Pangani River Basin Management Project to developing a greater understanding of the basin’s hydrology and ecosystem, how local populations interact with that ecosystem, and how potential development scenarios could impact the basin in the future. That knowledge, paired with an intensive training program for local water officials, is enabling stronger integrated resource management, which in turn could lay the groundwork for integrating WASH and conservation interventions, writes Bonnardeaux.
Economic incentives – in this case, payments for watershed services – offer another valuable tool for building support for conservation efforts, especially when upstream communities bear a disproportionate burden of safeguarding watersheds.
In South Africa, another case study country, “increased economic development and urbanization have taken its toll on” the country’s wetlands, while unemployment and poverty have remained a persistent problem in slum areas, writes Bonnardeaux. Through the government-run Working for Wetlands program, both the environmental and socioeconomic problems of development are being targeted for improvement. The program hires “the most marginalized from society” to clear wetlands of invasive plants in order to improve its natural filtration capabilities and, in turn, improves the quality of water feeding the burgeoning urban areas.
Although Working for Wetlands, now 17 years old, has been “hugely successful,” Bonnardeaux warns that such economic incentive programs are, more often than not, extremely difficult to carry out effectively. “While there is great potential for this incentive-based conservation approach,” Bonnardeaux notes, “the reality is there are many barriers to its effective implementation.”
Building Long-Term Support for Conservation With Near-Term PHE Successes
Building support for conservation can be a difficult task. The impacts of conservation programming are “often undervalued,” Bonnardeaux writes, in part because results tend to become apparent only over the longer term. By pairing conservation efforts with nearer-term programming, like PHE efforts targeting immediate health needs, development workers can foster the kind of local support that is essential for pursuing long term goals.
The Jane Goodall Institute’s Lake Tanganyika Catchment Reforestation and Education Project (TACARE), in northwest Tanzania, offers a case in point. Established in 1994, TACARE began as a conservation program meant to protect the areas around Gombe National Park, where Goodall first began her chimpanzee research in the 1960s. Local communities, however, were more interested in better health, “with an emphasis on clear water and reduction in water-borne diseases like cholera,” writes Bonnardeaux.
By adopting local health and poverty priorities, he writes, TACARE was able to establish trust and goodwill with the communities it served, which in turn enabled it to pursue longer-term conservation goals aimed at protecting the region’s natural biodiversity.
Bonnardeaux’s work shows that regardless of how policymakers choose to combine WASH and conservation goals, well-implemented integration can yield immense benefits for practitioners, funders, and local communities.
“Linking various sectors such as WASH, forestry, agriculture, population, and community development,” he writes, “can result in cost and effort sharing which in turn can increase the effectiveness of the project including improved conservation and improved livelihoods and health.”
Sources: Bonnardeaux 2012.
Photo Credit: “Intaka Island towards Table Mountain,” courtesy of flickr user Ian Junor. -
Tobias Feakin on the Debate in Europe About Climate Change and the Military
›“We established [the Climate Change Security Program] as a methodology of exposing the defense community in the U.K. and Europe to some of the more nuanced security debates that are going on around climate change, environmental change, and resource shortages,” said Tobias Feakin, senior research fellow at the Royal United Services Institute for Defense and Security Studies (RUSI) in an interview with ECSP.
What they found when they first approached the U.K. defense establishment in 2006, was surprising. “They opened [that] door wide open and said, ‘actually, you know what, we’ve been looking at this, we’ve been concerned about this for a long time, and we’ve already started including it in our long-term planning and strategic thinking.’”
“One of the reasons that the defense community has been looking at this issue is that they have a longer-term vision, if you like, than other departments,” Feakin said. “They have to think about procurement decisions which are going to be stretching out…up to 30 years into the future, so there are bigger demands on them to be thinking about these kinds of strategic issues.”
Feakin co-authored International Dimensions of Climate Change, a 2011 report for the British government which highlights the security threats and challenges, both internal and external, that the U.K. will face as result of climate change.
While the defense community acknowledged the need to include climate change in their planning processes, members of the policymaking community expressed concern that they did not, “have enough detailed understanding of what this [climate change] is going to mean in a security paradigm,” said Feakin. To meet that need, RUSI has been conducting regional and country-based studies in order to determine how things might play out.
Dialogue on the issue has transcended Great Britain and is now taking place among member states of the European Union, although Feakin notes that, “there’s perhaps more hesitancy in terms of framing the debate in the security paradigm and perhaps a slight perception that it might be leading us down the wrong path when mitigation efforts should be at the top of the order of play.”
Despite these ongoing debates, Feakin believes that the security aspect of climate change helps to “make a comprehensive case that we have a situation that does have to be dealt with and there are going to be multiple players in that.” Efforts to address climate change will be civilian-led, but the defense community will play an important supporting role in the future, he said.
“It’s something we have to plan for and we will be part of the response.” -
Open Data Initiatives at USAID Reflect Move Towards Collaboration, Enabling Efforts
›Over the past year and a half, USAID has been busy reinventing itself. The announcement of its USAID FORWARD initiative and the release (jointly, with the State Department) of the first Quadrennial Diplomacy and Development Review in late 2010 signaled significant changes for the organization, including several reforms designed to modernize operations and improve transparency. Part of that effort is making data collection and dissemination more open.
Thus far, the results have been encouraging.
September of last year saw the launch of an awareness campaign focused on the Horn of Africa, co-sponsored by the Ad Council and called, somewhat confusingly, USAID FWD (famine, war, drought). As part of the program, USAID published a collection of regional maps, aggregating the organization’s substantial data pool and showing everything from food and water security to the movement of refugees and IDPs (internally displaced persons).
Using data from its own FEWS.NET site, USAID created the maps with open-source tools, allowing other organizations and concerned individuals to leverage the data for additional aid and outreach activities. Many, including the ONE Campaign and InterAction, were quick to incorporate the maps and underlying data into their own activities.
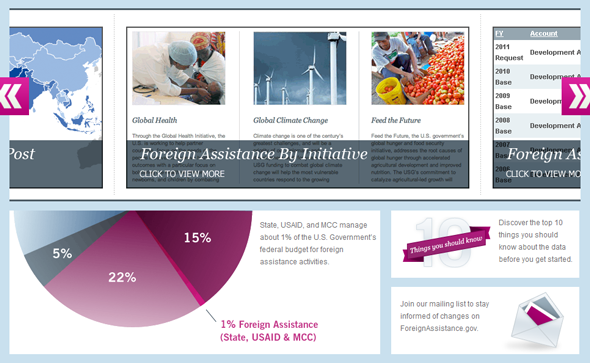
In order to promote greater data access and transparency, USAID also collaborated with the Department of State to create the Foreign Assistance Dashboard, a website that provides sortable aid budget allocation data to the general public. Launched in late 2010 with frequent updates since, the site allows users to see easily how aid is apportioned by region, sector, initiative, or other categories.
For instance, visitors can see that USAID more than quadrupled its humanitarian assistance to Pakistan in 2010 as a result of that country’s devastating flooding. Aid then fell back to near 2009 levels the following year.
Recently, USAID has also taken its open data efforts to the Web. Faced with 117,000 records of development loans provided by its own Development Credit Authority and lacking proper geographic coding, the organization undertook a pioneering experiment in crowdsourcing this June. Civilian volunteers from the online technical communities GISCorps and the Standby Task Force pitched in to help code the data, as did unaffiliated citizens attracted by social media campaigns.
The end results were outstanding: the volunteers finished the job in just 16 hours, although USAID had initially expected the operation to take 60.
Representatives from USAID recently published an illuminating case study about the crowdsourcing experiment and launched it at the Wilson Center. “By leveraging partnerships, volunteers, other federal agencies, and the private sector, the entire project was completed at no cost,” the report noted, adding that USAID hoped to have “blaze[d] a trail to help make crowdsourcing a more accessible approach for others.” One of the case study authors, Shadrock Roberts, noted that “we need to be working as hard to release relevant data we already have as we are to create it.”
USAID’s recent experiments with transparency and greater civilian participation appear to be part of a larger organizational shift toward greater openness and collaboration. Administrator Rajiv Shah seemed to confirm this in a March interview with Foreign Policy, when he spoke at length about the benefits of partnering with the private sector as well as other NGOs.
The recently reported demise, or at least great diminishing, of President Obama’s Global Health Initiative (GHI), which closed its doors amid a heated turf battle between USAID, the State Department, and PEPFAR, lends credence to this theory as well. The official GHI blog stated last week that it would “shift focus from leadership within the U.S. Government to global leadership by the U.S. Government.” This appears to indicate greater future emphasis on collaboration, with an eye toward enabling non-USAID actors to play a greater role in the development process.
It remains to be seen how USAID’s role and strategy will change over the next few years. However, results from the organization’s initial attempts at open data and open government policies have been positive in many respects, and there is reason to hope they will continue to push the boundaries in these areas.
Sources: Center for Global Development, Foreign Assistance Dashboard, Foreign Policy, Global Health Initiative, USAID.
Image Credit: Foreign Assistance Dashboard. -
In Mongolia, Climate Change and Mining Boom Threaten National Identity
›July 23, 2012 // By Kate Diamond
Mongolia, a vast, sparsely populated country almost as large as Western Europe, is at once strikingly poor and strikingly rich. Its GDP per capita falls just below that of war-torn Iraq, and Ulan Bator has some of the worst air pollution ever recorded in a capital city. At the same time, Mongolia sits atop some of the world’s largest mineral reserves, worth trillions of dollars, and its economy, already one of the world’s fastest growing, could expand by a factor of six by the end of the decade as those reserves are developed.
-
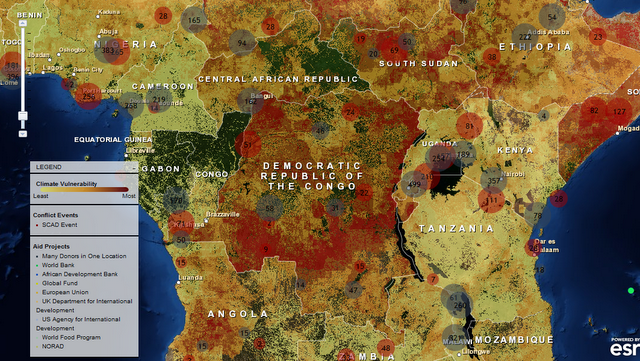
Visualizing Complex Vulnerability in Africa: The CCAPS Climate-Conflict Mapping Tool
›“Every crisis is complex, and the Sahel is no exception,” wrote USAID Assistant Administrator Nancy Lindborg in a recent Huffington Post article that called for “smarter programming and a coordivenated response” to chronic crises. “A regional drought has been overlaid with instability stemming from the coup in Mali and conflict in the northern part of that country where armed militant groups have forced the suspension of critical relief operations” and led to refugee movement into neighboring countries simultaneously challenged by drought and crop infestation. Understanding the complexity of this type of crisis, let alone visualizing the multiple factors that come into play, is a growing challenge for policymakers and analysts.
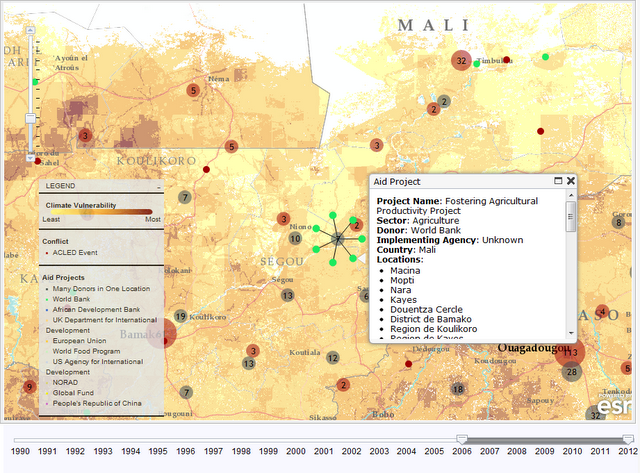
Enter version 2.0 of a mapping tool created by the Climate Change and African Political Stability Program (CCAPS) housed in the Robert S. Strauss Center for International Security and Law, based at the University of Texas, Austin.
In collaboration with the College of William and Mary, Trinity College, and the University of North Texas, and with funding by the U.S. Department of Defense’s Minerva Initiative, CCAPS originally launched the mapping tool in March of this year. The map is powered by mapping and data tools from Esri and allows users to view any combination of datasets on international development projects, national governance indicators, incidences of conflict, and climate vulnerability data.
With an intuitive interface and compelling visuals, the mapping tool is a valuable resource for policy analysts and researchers to assess the complex interactions that take place among these environmental, political, and social factors. Advanced filters allow the user to identify a subset of conflicts and aid projects and there are nine base map styles from which to choose. The mapping tool is anything but static. The team is constantly working to refine and enhance it through the inclusion of additional indicators and improvement of the interface. The updated version now includes CCAP’s new Social Conflict in Africa Database, which tracks a broad range of social and political unrest, and their partners’ real-time conflict dataset, the Armed Conflict Location and Event Dataset (ACLED), which tracks real-time conflict data. Impressively, the ACLED data will be updated weekly.
The mapping tool is anything but static. The team is constantly working to refine and enhance it through the inclusion of additional indicators and improvement of the interface. The updated version now includes CCAP’s new Social Conflict in Africa Database, which tracks a broad range of social and political unrest, and their partners’ real-time conflict dataset, the Armed Conflict Location and Event Dataset (ACLED), which tracks real-time conflict data. Impressively, the ACLED data will be updated weekly.
I asked CCAPS program manager Ashley Moran to clarify how the governance indicators work in the model. She explained:The national governance indicators are included in one of four baskets that make up the climate vulnerability model…and represent four potential sources of vulnerability: physical exposure to climate-related hazards, population density, household and community resilience, and governance and political violence. They used the term “basket” since most include several indicators that reflect the full dimensions of that source of vulnerability. The fourth basket includes five national governance indicators and one indicator of political violence.
Moran also shared plans to add more detailed national governance data to the map:We are developing a mapping tool specifically for the climate vulnerability model, which will allow users to see the component parts of the model. It will allow users to re-weight the baskets (e.g. if a user thought governance should have more weight within the model since the government response to climate hazards is key), and it will also allow users to examine an area’s vulnerability to just one or two baskets of the user’s particular interest (instead of all four baskets combined as the tool does now). When we launch this, a user will essentially be able to see the vulnerability model disaggregated into its component parts, so they’ll be able to map just the governance data in the model, if they want.
In the coming months, the CCAPS team will add more detailed historical and projected data on climate vulnerability, data on disaster response capacity, as well as international aid projects coded for climate relevance.
Each of these datasets on their own are a wealth of vital information, but understanding how they intersect and the potential impact of their interactions is crucial to improving our understanding of them individually and collectively and creating responses that are timely and long-lasting.
If you’re in the San Diego area next week, check out Ashley Moran’s presentation of the mapping tool at the Esri International User Conference and the Worldwide Human Geography Data Working Group.
Sources: The Climate Change and African Political Stability Program, The Huffington Post.
Image Credit: CCAPS -
Urban Resilience: What Is It and How Can We Promote It?
›A new study on the intersection of violence and economic development in cities breaks new ground by examining how communities respond to and cope with extant violence, rather than focusing on the root causes of violence in a given area. Authors Diane Davis, Harvard professor of urbanism and development, and John Tirman, executive director of MIT’s Center for International Studies, spoke at length about the origins, methodology, and findings of the report, Urban Resilience in Situations of Chronic Conflict, at the Wilson Center on July 12. The report was supported by USAID’s Office of Conflict Management and Mitigation.
“We made the decision that we weren’t going to produce yet another research project or study on the root causes of violence, because there is a lot of incredibly good work on that [already],” said Davis. “We wanted to take a totally different angle…to try to think about taking a more pragmatic approach that builds on how everyday people, who live with violence, respond.”
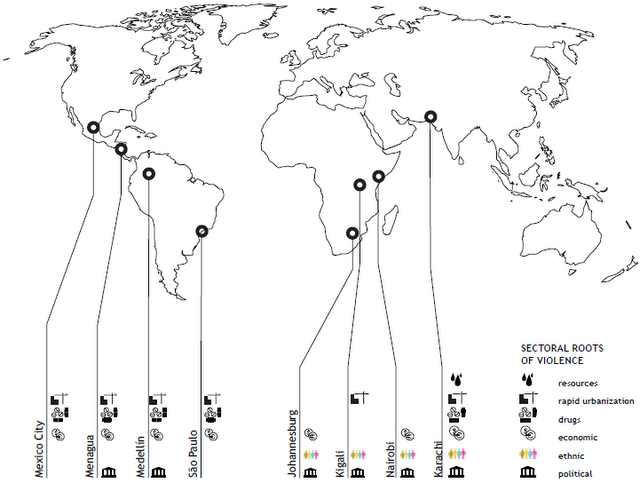
To do this, Davis and Tirman focused their research on seven cities around the world with histories of chronic violence, creating a case study for each and then comparing results. (An eighth city, Karachi, was jettisoned because it was deemed too unsafe for research.) The comparative process allowed Davis and Tirman to develop a basic theoretical framework for how different factors increase or decrease a community’s resilience to violence.
Defining Resilience
The term “resilience” lies at the heart of the new study. “The idea of ‘bouncing back,’ or returning to normalcy, is [generally] the measurement standard for looking at resilience,” Davis said.
However, she was quick to point out the problems with such a simplistic definition. “[In] cities of the developing world…things are in flux. So it’s really hard to know what a ‘bouncing back’ is if things are constantly changing.” “Also,” she added, “in many of the environments we were looking at, violence is a consequence of the way things were under normal conditions. So you don’t necessarily want to bounce back to those conditions that were producing the violence in the first place.”
“Also,” she added, “in many of the environments we were looking at, violence is a consequence of the way things were under normal conditions. So you don’t necessarily want to bounce back to those conditions that were producing the violence in the first place.”
Davis and Tirman sidestepped these problems by letting their research define successful resilience, rather than trying to fit their results to a prefabricated definition of the word. In doing so, they were able to identify several important commonalities in the cities and communities that displayed the most positive resilience to violence.
“Our findings suggest that resilience appears at the interface of civilian and state action,” Davis writes in the report. She underscored the significance of civilians as facilitators in both developing and implementing better security policies: “People who live in violence know more than academics or policymakers about what they can and can’t do to deal with the problem of violence,” she said.
Focus on Community
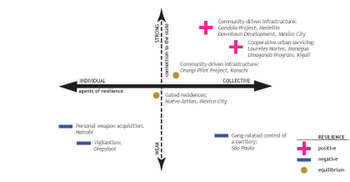
Davis and Tirman pointed out that the most successfully resilient cities they studied – Mexico City, Managua, and especially Medellín – seemed to have a number of civilian/state relationships defined “from below,” rather than the more problematic “top down” approach. This means that civilians and communities were participating on their own terms, collaborating with city planners and with law enforcement agencies to get their needs met rather than simply being what Davis called “yes men” to higher authorities.
Physical space – what Davis referred to as “the weight of the spatial” – also played a very significant role in Urban Resilience. She and Tirman made the conscious decision to incorporate physical planning and design into their research, eschewing the more typical sectoral approach to violence and security.
This methodological break from the existing literature was particularly useful in demonstrating that violence-plagued communities are often themselves the most important agents of resilience. “Citizens have to be able to make real decisions on their own,” Davis stressed in the Q&A; session that followed her and Tirman’s presentation. “[They] have to feel that ownership, that autonomy of the decisions in their neighborhood, even if they’re bad [decisions], because that’s what ties them to each other.”
“We think the starting point for generating resilience is really supporting and enabling communities to make dense horizontal relationships with others in their neighborhood, across sectors, that allow them to push back against perpetrators of violence.”
In other words, while the state can play a significant role in helping communities to mitigate violence, successful resilience ultimately requires the commitment and participation of the communities in question.
“The state might have a security program, it might have a planning program, but every decision has to be made with an understanding of what’s good for that particular neighborhood,” Davis said.
Places People Want to Protect
Davis was very succinct in offering recommendations based on the study. For policymakers and urban planners, she said resilience is formed by “a combination of good governance, security reform, and…inclusive urban planning.” Citing examples from Mexico City, Medellín, and elsewhere, Davis pointed to planning policies like mixed land use, greater pedestrian accessibility, and more parks and public spaces as ways that authorities could engender the kind of community pride so crucial to the development of positive urban resilience.
“[Focus on] generating vibrant public areas where people feel invested in protecting [them] and making them better,” she advised.
While many scholars have tended to look either at the state or local communities in isolation when considering violence and resilience, Davis argued that reducing violence was “a shared objective.” She thus stressed the importance of “co-production of security,” reiterating the overall notion that state and community actors need to work side-by-side in a form of what Davis and Tirman called “cooperative autonomy.”
In addition to Urban Resilience in Situations of Chronic Violence, Davis also authored the supplementary Toolkit for Urban Resilience in Situations of Chronic Violence. Both documents can be found on the MIT’s website. Davis and Tirman hope to add the seven individual case studies to the site soon.
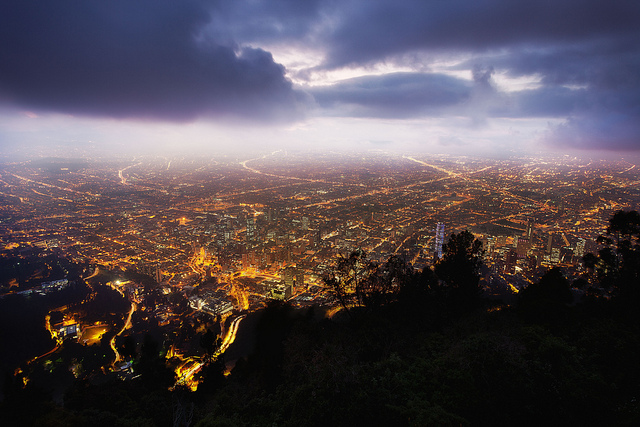
Event Resources:Photo Credit: “Bogota at night,” courtesy of flickr user WanderingtheWorld (Christopher Schoenbohm); charts courtesy of Davis and Tirman.
 A Publication of the Stimson Center.
A Publication of the Stimson Center.