-
Climate Change’s Health Impacts, and the Rights-Based Argument for Family Planning
› UNFPA’s recently released State of World Population 2012 brings family planning to the center of the development debate. “There is indisputable evidence that when family planning is integrated into broader economic and social development initiatives, it can have a positive multiplier effect on human development and the well-being of entire nations,” the authors write. The report employs a rights-based approach to make the case for universal access to family planning – a goal which we are far from as 222 million women from the developing world currently have an unmet need for modern contraceptives. Meeting this need and improving quality of reproductive healthcare elsewhere would cost an additional $4.1 billion a year, but save approximately $5.7 billion in maternal and newborn health services. Other recommendations include increasing financial support and political commitment to ensure that family planning is of high quality, reducing the number of unintended pregnancies and abortions, including emergency contraception in family planning services, and engaging boys and men.
UNFPA’s recently released State of World Population 2012 brings family planning to the center of the development debate. “There is indisputable evidence that when family planning is integrated into broader economic and social development initiatives, it can have a positive multiplier effect on human development and the well-being of entire nations,” the authors write. The report employs a rights-based approach to make the case for universal access to family planning – a goal which we are far from as 222 million women from the developing world currently have an unmet need for modern contraceptives. Meeting this need and improving quality of reproductive healthcare elsewhere would cost an additional $4.1 billion a year, but save approximately $5.7 billion in maternal and newborn health services. Other recommendations include increasing financial support and political commitment to ensure that family planning is of high quality, reducing the number of unintended pregnancies and abortions, including emergency contraception in family planning services, and engaging boys and men. -
Linking the Environment and Women’s Health at the World Conservation Congress
›November 30, 2012 // By Payal Chandiramani
People don’t often think of gender issues when they think of the environment, but in fact sustainable development in many of the world’s most bio-diverse regions has a lot to do with women’s health and well-being.
At this year’s World Conservation Congress, where the theme was improving the inherent resilience of nature, ECSP’s Sandeep Bathala presented alongside Blue Ventures’ Gildas Andriamalala about the connections between women’s health and the environment – specifically on the potential of population, health, and environment (PHE) approaches as an effective sustainable development strategy.
-
Considering “Soft Geoengineering”
›Even as the climate debate has been paralyzed by politics, the concept of geoengineering has been in the news lately, most notably in October when Russ George dumped 120 tons of iron particles into the Pacific Ocean in a scheme to try and score carbon credits. Earlier this month, the Wilson Center’s Science and Technology Innovation Program hosted an event taking a look at “soft geoengineering” – techniques that might have low or minimal environmental side effects but still address or reverse climate change.
-
‘The Global Farms Race’: Comprehensive Study of Large-Scale Land Acquisitions Launches at Wilson Center
›Last month, Oxfam made an extraordinary request. It asked the World Bank to freeze its investments in agricultural land.
At a time when urbanization and growing service industries are bringing great neglect to agricultural sectors across much of the developing world, why would Oxfam want the World Bank to suspend its generous levels of agricultural funding?
-
‘The New York Times’ Highlights Converging Development Trends in Brazil’s Amazon
›
The Amazon is home to some of the world’s most expansive rainforest – and, increasingly, some of Brazil’s fastest growing cities. Urbanization and deforestation are upending the traditional image of the Amazon, turning one of the world’s most biodiverse regions into an economic and demographic explosion, according to an in-depth article by Simon Romero in The New York Times.
-
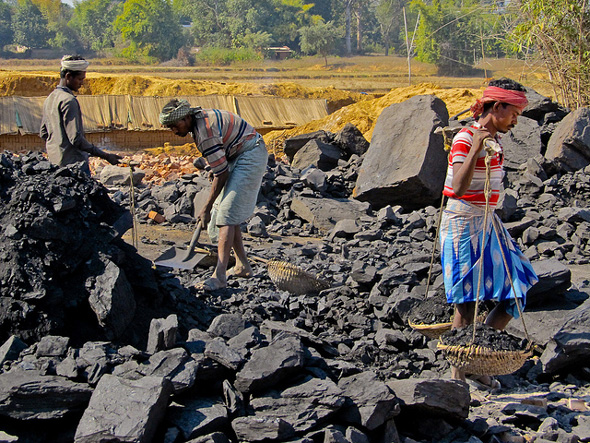
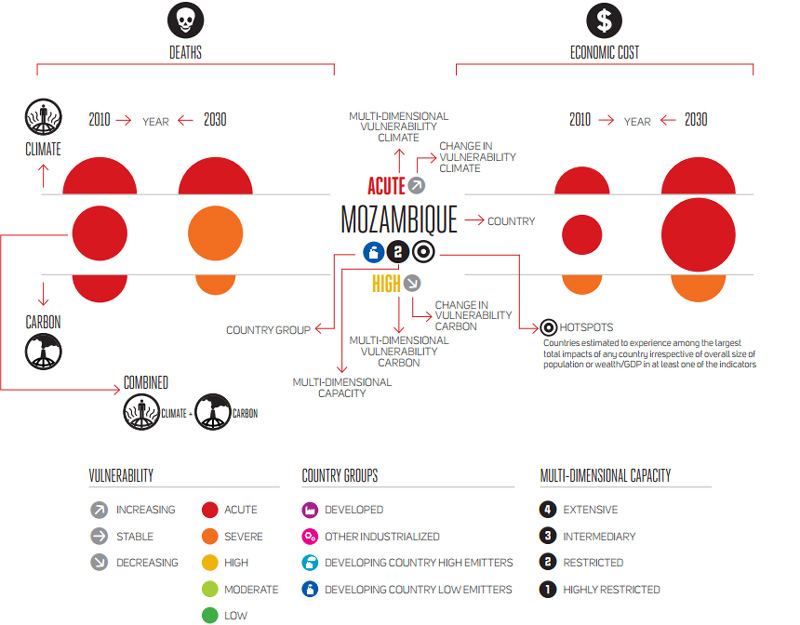
Does Climate Change Kill Five Million People A Year? DARA’s 2012 Climate Vulnerability Monitor
›Five million people die each year due to climate- or carbon-related causes, and total mortality by 2030 could total 100 million people, according to new report from DARA, a nonprofit organization that works to improve aid to those affected by conflict and climate change and quantify the global cost of climate change and carbon use. But the report has drawn some fire for being too alarmist.
-
Feminized Development in Latin America: Understanding the Confluence of Gender Equity and Cultural Tensions
›
Poverty in Latin America has become increasingly “feminized,” said John Coonrod, executive vice president of The Hunger Project, at the Wilson Center on October 22. As a result, many governments and NGOs are starting to focus on the needs of women, especially indigenous women. [Video Below]
-
India’s Environmental Security Challenge: Water, Coal, Natural Gas, and Climate Change Fuel Friction
›November 23, 2012 // By Michael Kugelman
The original version of this article appeared in NATO Review.
Few regions are more environmentally insecure than South Asia.
The region faces rising sea levels and regularly experiences coastal flooding – of particular concern in a region with heavily populated and arable-land-rich coastal areas. Additionally, it is highly vulnerable to glacial melt. The Western Himalayas, which provide water supplies to much of South Asia, have experienced some of the most rapid melt in the world.
 A Publication of the Stimson Center.
A Publication of the Stimson Center.