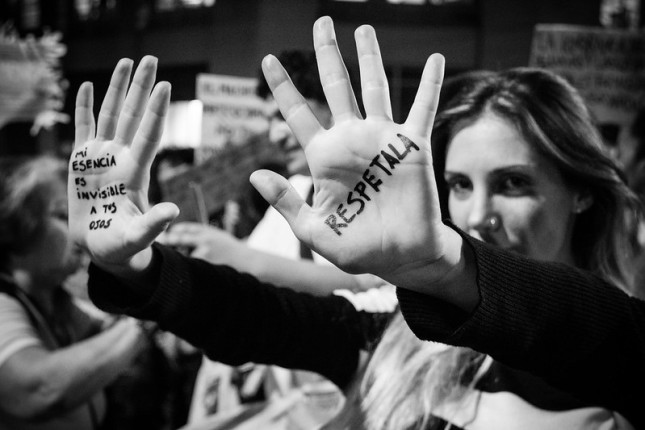-
Environmental Security Weekly Watch: December 8-12, 2025
›A window into what we’re reading at the Stimson Center’s Environmental Security Program
Race for Copper Damages Protected Region in Colombia (Mongabay)
As Colombia looks to meet the growing demand for strategic minerals, activists working in the department of Choco allege that the country’s only industrial copper mine is harming both the environment and a local community. The El Roble copper mine has operated since 1990 at the base of a valley crossed by the Atrato River, but its acquisition by Canadian multinational Atico Mining in 2013 has meant that daily production has doubled from 400 to 1,000 metric tons over the past 12 years. El Roble also lacks the environmental license required by Colombia’s Mining Code, and continues to operate under a less stringent 1987 environmental management plan, which activists say omits required environmental impact studies.
-
Mexico Is Growing Old. Can It Build a Care System in Time?
›
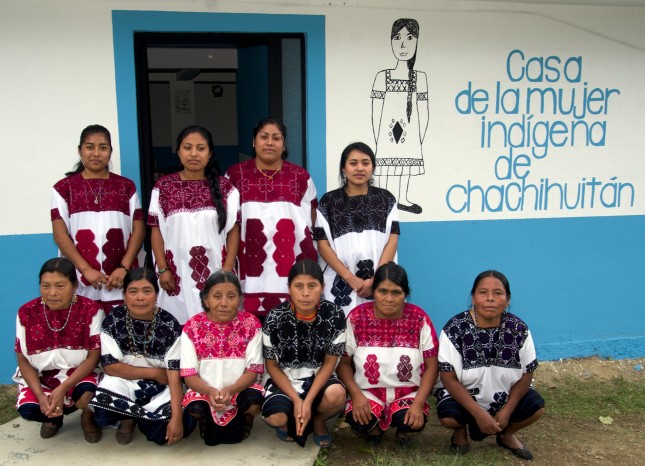
Elvia León, the youngest of seven children, wanted to leave Bomintzhá back in 1987. “I told my mother that I didn’t want to live in that kind of poverty, and she supported me.” Her father was less pleased with her plans to abandon their small community in Mexico’s Hidalgo state to study in the city of Querétaro. “The culture here is that women are meant to be at home, doing domestic chores.”
-
Gender Inequality in Mexico’s Fractured Public Health System
›Dot-Mom // From the Wilson Center // Guest Contributor // April 20, 2022 // By Samantha Kane Jiménez
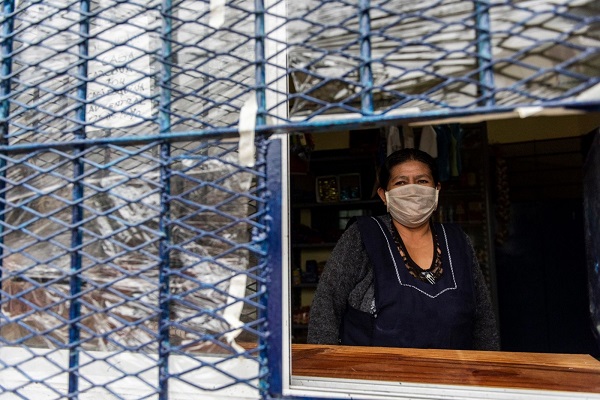
In recent years, Mexican women have experienced a significant downgrade in the quality and accessibility of public healthcare – and not due to the COVID-19 pandemic – said Irene Tello, Executive Director of Mexican impunity watchdog Impunidad Cero, at a recent event hosted by the Wilson Center’s Mexico Institute. The expert panel agreed that the greatest barriers for Mexican women seeking medical attention lie in the current government’s nearsighted health policies and mismanagement of the public health sector.
-
U.S., Mexico Sign Rio Grande Water Agreement
›
U.S. and Mexican officials settled a water dispute that had been simmering for several months and led to protests by Mexican farmers concerned about water access.
-
The Resurgence of Indigenous Midwifery in Canada, New Zealand, and Mexico
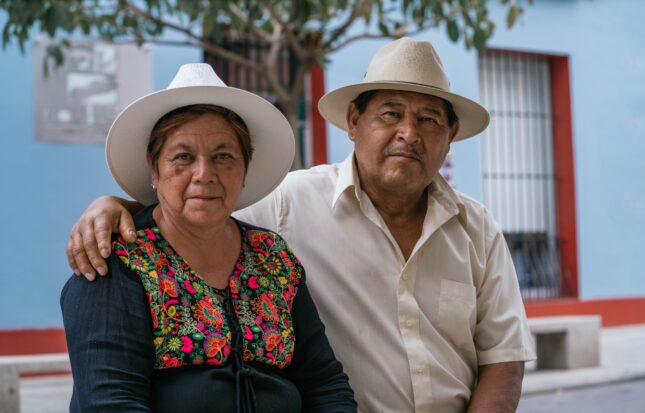
› Globally, Indigenous women experience worse maternal health outcomes than non-Indigenous women. In the United States, the risk of maternal death is twice as high for Native women than for white women, while in Australia the risk is four and a half times higher. This week’s Friday Podcast highlights remarks from a recent Wilson Center event with the United Nations Population Fund (UNFPA) and the International Confederation of Midwives about Indigenous midwifery.
Globally, Indigenous women experience worse maternal health outcomes than non-Indigenous women. In the United States, the risk of maternal death is twice as high for Native women than for white women, while in Australia the risk is four and a half times higher. This week’s Friday Podcast highlights remarks from a recent Wilson Center event with the United Nations Population Fund (UNFPA) and the International Confederation of Midwives about Indigenous midwifery. -
Knowledge Keepers: Why We Need Indigenous Midwives
›
“We need more Indigenous midwives,” said Claire Dion Fletcher, an Indigenous Potawatomi-Lenape Registered Midwife and co-chair of the National Aboriginal Council of Midwives (NACM), at a recent Wilson Center event with the United Nations Population Fund (UNFPA) and the International Confederation of Midwives about Indigenous midwifery. Globally, Indigenous women experience worse maternal health outcomes than non-Indigenous women. In the United States, risk of maternal death is twice as high for Native women than white women, while in Australia the risk is four and a half times higher.
-
Accessing Justice: Femicide and the Rule of Law in Latin America
›Dot-Mom // From the Wilson Center // July 17, 2020 // By Annelise Gilbert, Beatriz García Nice, Olivia Soledad & Anya Prusa
“The pandemic is just making visible a reality that has been going on for decades,” said Claudia Calvin, Founder of Mujeres Construyendo (Women Building) and a member of Nosotras Tenemos Otros Datos (We Have Other Data). She spoke at a recent Wilson Center event on femicide and the rule of law in Latin America. The panelists discussed the longstanding roots of this issue and new barriers to protecting women and preventing violence during the pandemic in the launch event for a project examining gender-based violence in Latin America, co-hosted by the Brazil Institute, Latin America Program, Mexico Institute, and Maternal Health Initiative. “Violence against women and femicides are not new,” Calvin said. But what is new is the fact that the media and civil society are bringing this topic to our attention, she said.
-
Pandemic of Violence: Protecting Women during COVID-19
›Covid-19 // Dot-Mom // From the Wilson Center // May 27, 2020 // By Anya Prusa, Beatriz García Nice & Olivia Soledad
COVID-19 is having a profound impact on Latin American women. Gender-based violence increased drastically after governments imposed lockdowns, leaving policymakers and law enforcement scrambling to prevent attacks. Latin America was already one of the most dangerous regions for women, with the highest rate of sexual violence and some of the highest femicide numbers in the world. The Economic Commission for Latin America and the Caribbean registered 3,529 femicides in 2018, or one woman killed every two hours due to her gender. For many women living through the coronavirus pandemic in Latin America, the greater health risk might be staying home.
Showing posts from category Mexico.






 Globally, Indigenous women experience worse maternal health outcomes than non-Indigenous women. In the United States, the risk of maternal death is
Globally, Indigenous women experience worse maternal health outcomes than non-Indigenous women. In the United States, the risk of maternal death is