Showing posts from category water.
-
Climate-Conflict Thresholds and Water as a Casualty of Conflict
›While numerous studies have examined the perils faced by businesses operating in conflict-affected or high-risk locations, Water as a Casualty of Conflict: Threats to Business and Society in High-Risk Areas, written by Kristina Donnelly, Mai-Lan Ha, Heather Cooley, and Jason Morrison, is the first such report to focus specifically on water. The report – a collaborative effort between the UN Global Compact and the Pacific Institute – aims to provide a framework for understanding the conflict-water-business nexus by first tracing the ways in which conflict and high-risk areas can adversely impact local and regional water systems and then illustrating the challenges such impacts can pose to businesses in conflict-affected or high-risk areas. Water as a Casualty of Conflict was published online this week and was introduced at a Rio+20 Corporate Sustainability Forum panel session.
In an article titled “Climate Change and Violent Conflict,” appearing in the May 18th edition of Science, authors Jürgen Scheffran, Michael Brzoska, Jasmin Kominek, Michael Link, and Janpeter Schilling attempt to sort out some of the controversy surrounding the intersection of climate change and violent conflict. They urge greater interdisciplinary research to identify and provide solutions for possible “tipping points” where the impacts of climate change may prove too great for human adaptive capacity. Such research has been scarce due to difficulties in collecting sufficient data. Moreover, the authors note that many of the extant studies on climate change and conflict are flawed because of how they define violent conflict. The commonly-used Uppsala Conflict Data Program and Peace Research Institute Oslo (UCDP-PRIO) Armed Conflict dataset, for instance, excludes by definition many riots, protests, incidences of livestock theft, and other violent or potentially violent behaviors. This is problematic because, as the authors point out, “in recent decades, climate variability may have been more associated with low-level violence and internal civil war – which fall below the UCDP-PRIO definition cutoff – than with armed conflict or war between countries.” -
African Nations Pioneer Natural Resource Accounting With ‘Gaborone Declaration’
›June 20, 2012 // By Graham NorwoodIn a move with potentially substantial ramifications for future sustainable development, 10 African nations have agreed to begin assigning monetary value to the benefits provided by non-commodity natural resources, including ecosystems such as forests, grasslands, and coral reefs.
Botswana, Gabon, Ghana, Kenya, Liberia, Mozambique, Namibia, Rwanda, South Africa, and Tanzania each affirmed their support for the “Gaborone Declaration” during last month’s Summit for Sustainability in Africa, co-hosted by Conservation International and the government of Botswana. The goal, according to Botswanan President Ian Khama, is to include these new valuations in national accounting, providing policymakers a clear perspective on the costs and benefits associated with the development or conservation of their natural resources for the first time.
Coming just prior to the Rio+20 conference, the signatories said they hoped assigning calculable costs to resource usage would encourage more sustainable development by bringing hitherto “invisible” costs and externalities into the open and onto the balance sheet.
Though the challenges of properly assessing the values of various ecosystem services are understandably many, the potential benefits of natural capital accounting are substantial.
According to SciDev.Net, the World Bank’s Vice President for Sustainable Development Rachel Kyte spoke in support of the declaration at the summit. She pointed out, for example, the advantage of knowing that a hectare of mangrove trees in a certain region of Thailand has been calculated to provide approximately $16,000 of flood protection when considering whether to clear-cut and sell the raw wood (worth about $850), convert the region into a shrimp farm ($9,000), or preserve it.
Such accounting may be particularly beneficial to the Gaborone signatories and other African nations, given growing concern among experts about foreign investment in land, natural resources, and even water on the continent.
But the declaration – and the very idea of natural capital accounting – is not without controversy.
Some argue that commodifying such resources will actually encourage their destruction rather than protect them by ascribing monetary values to previously free and shared resources, thus advantaging richer stakeholders and nations at the expense of poorer ones. As Hannah Griffiths of the UK-based World Development Movement recently wrote in The Guardian, “the result [of natural resource accounting] would be the further privatisation of essential elements of our planet to which we all share rights and have responsibilities.”
Along these lines, Nigerian environmental activist and chair of Friends of the Earth International, Nnimmo Bassey, has voiced his strenuous opposition to the plan made at the summit. “This declaration is blind to the fact that the bait of revenue from natural capital is simply a cover for continued rape of African natural resources,” he said in SciDev.
However, the signatories of the Gaborone Declaration dismissed these concerns and pointed to the value of natural resource accounting for sustainable development.
“Africa is where sustained and sustainable economic growth and stewardship of natural wealth become one and the same thing,” said Kyte at the summit. “By endorsing natural capital accounting as a tool for delivering on more inclusive green growth, Africa is showing the way for the rest of the world.”
Conservation International CEO and Chairman Peter Seligmann agreed, calling the declaration “a very big deal, a very big moment, and a big step forward.” He connected it to the imminent Rio+20 conference as well, saying the pledge is “truly a beacon on the hill for the rest of societies” and that “it will be held up on top of that hill in Rio de Janeiro.”
Indeed, the World Bank has listed natural capital accounting as one of six key issues for Rio+20, and in a report last month titled Inclusive Green Growth: The Pathway to Sustainable Development, noted that “it is vital that economic values for environmental assets be comparable to other economic values.”
The World Bank has already made significant progress in promoting the practice through its Wealth Accounting and the Valuation of Ecosystem Services (WAVES) global partnership, encouraging at least 24 countries to use some form of natural resource accounting to date. WAVES aims to sign up 50 more nations and 50 private corporations beginning at Rio+20, as a part of its “50:50 Campaign.”
WAVES and the Gaborone Declaration show that natural capital accounting is gaining momentum as a means to incentivize more sustainable development. The international news media is beginning to take notice as well. The results of the Rio+20 conference will be a good opportunity to gauge just how far the idea has come and what the extent of its future application might be.
Sources: Conservation International, The Guardian, SciDev.Net, World Bank.
Photo Credit: “Saving the Sacred Rock,” courtesy of flickr user isurusen (Isuru Senevi); video: The World Bank. -
Gidon Bromberg at TEDx on Peacebuilding Through Water in the Middle East
›“Cooperation over water is not a privilege, it’s a necessity,” said Gidon Bromberg, co-director of Friends of the Earth Middle East, in a TEDx talk at Yale. He sees the shortage of water in Jordan, Israel, and Palestine as an opportunity to bring these contentious communities together – even more so during this period of upheaval in the region.
Water woes have long contributed to regional tensions, said Bromberg. Water rights between Israel and Palestine were supposed to be settled during the Oslo accords in 1993, but negotiations were unsuccessful and water discussions were consequently left unfinished. The lack of formal negotiations caused each side to seize whatever resources they could Although Jordan was not part of the negotiations, it does share water resources with Israel and the West Bank and thus has been impacted by the lack of formal allocation processes. Both Jordan and Israel have diverted flow of the Jordan River into dams and irrigation projects. As a result, the Jordan River has lost 98 percent of its historic flow and the Dead Sea has lost one-third of its surface area.
Today, Israel has restricted Palestinian water use such that Palestinians have access to water only once a week in winter and once every three weeks in the summer, leading them to store water in containers on their roofs, Bromberg said. Though mismanagement is as much to blame as conflict, he notes, Palestinians chafe under the limitations.
Yet Friends of the Earth Middle East has used this difficult situation to educate the public, propose reforms, and build trust between Palestinian, Jordanian, and Israeli communities. Bromberg highlighted “fear of a small but vocal minority on both sides” as a key factor in preventing dialogue between the communities, but insists that water can bring people together. Neighboring communities have to work together, he said, “not because they’re best friends,” but to improve their own water situations.
Friends of the Earth provides that opportunity with their Good Water Neighbors project and hopes the trust built between communities extends beyond water issues as well. Since communities have strong motives to solve these problems, they work together more effectively than high-level politicians who may not be as apt to collaborate.
A positive update on the state of the Jordan River given in an interview with ECSP in October suggests that Bromberg may be on to something.
Sources: Amnesty International, Friends of the Earth.
Video Credit: TEDx. -
Nancy Lindborg, The Huffington Post
For Yemen’s Future, Global Humanitarian Response Is Vital
›June 12, 2012 // By Wilson Center StaffThe original version of this article, by Nancy Lindborg, appeared on The Huffington Post.
This weekend in Sana’a, I had dinner with a group of young men and women activists who are on the forefront of Yemen’s historic struggle for a better future. They turned out for change with great courage last year, and at dinner, with great eloquence they outlined for me the many challenges facing Yemen during this critical transition period: conflict in the north and south, weak government institutions, cultural barriers to greater women’s participation, an upended economy, and one of the world’s highest birthrates. And, as one man noted, it is difficult to engage the 70 percent of Yemeni people who live in rural areas in dialogue about the future when they are struggling just to find the basics of life: food, health, water.
His comment makes plain the rising, complex humanitarian crisis facing Yemen. At a time of historic political transition, nearly half of Yemen’s population is without enough to eat, and nearly one million children under the age of five are malnourished, putting them at greater risk of illness and disease. One in 10 Yemeni children do not live to the age of five. One in 10. This is a staggering and often untold part of the Yemen story: a story of chronic nationwide poverty that has deepened into crisis under the strain of continuing conflict and instability.
Unfortunately, in communities used to living on the edge, serious malnutrition is often not even recognized in children until they are so acutely ill that they need hospitalization.
Continue reading on The Huffington Post.
Nancy Lindborg is the assistant administrator of the Bureau for Democracy, Conflict, and Humanitarian Assistance at the U.S. Agency for International Development.
Sources: U.S. Department of State.
Photo Credit: Informal settlements near the Haddjah governorate, courtesy of E.U. Humanitarian Aid and Civil Protection. -
Bringing Environment and Climate to the 2012 Population Association of America Annual Meeting
›June 5, 2012 // By Sandeep BathalaOver 2,100 participants attended the 2012 Population Association of America (PAA) annual meeting in San Francisco this May. PAA was established in 1930 to research issues related to human population. This year, for the first time, the meeting featured a notable contingent of demographers, sociologists, and public health professionals working on environmental connections.
I followed as many of the environment-population discussions on newly published or prospective research papers as possible (about 20 in total). I found four papers particularly noteworthy for the connections made to women, family planning, and climate change adaptation.
Samuel Codjoe of the University of Ghana spoke about adaptation to climate extremes in the Afram Plains during one of the population, health, and environment (PHE) panels organized by Population Action International. Although developed nations are historically the major contributors of greenhouse gases due to comparatively high levels of consumptions, developing countries are the most vulnerable to the consequences of climate change – in part because of continued population growth. As a result, adaptation strategies in countries like Ghana are particularly important; and given women’s often-outsized role in water and natural resource issues, a focus on gender-specific adaptation even more so.
Codjoe presented an analysis of preferred adaptation strategies to flood and drought, broken down by gender and three common occupations – farming, fishing, and charcoal production). He said he hopes his assessment – part of a collaborative research effort with Lucy K.A. Adzoyi-Atidoh of Lincoln University – will aid in the selection and implementation of successful adaptation options for communities and households in the future.
“Understanding differences in the priorities that women place on adaptation may prove to be important in the effectiveness of climate change adaptation – and the sustainability of communities,” he said.
David López-Carr of the University of California, Santa Barbara, speaking on behalf of a group of researchers with World Wildlife Fund, teased out the gender dynamic further when he presented on ways to help the conservation sector determine next steps for existing PHE projects. Practitioners from seven of the eight PHE projects currently implemented by conservation organizations (defined by having been involved for at least three years in bringing family planning to local communities) recently said the links to women’s empowerment were among the most important aspects of successful projects.
López-Carr therefore emphasized the need for additional research on how PHE projects can support and empower women, both economically and socially. He also noted, like Codjoe, the potential impact women often have on the management of their community’s natural resources, saying this was another area where research on the empowering effect of PHE programs can provide further backing for integrated programs.
Karen Hardee of Futures Group spoke about how the experiences of integrated PHE projects, despite most not being designed to respond to climate change specifically, have lessons to offer climate change efforts. Her work was done in partnership with the Population Reference Bureau, Population Action International, and U.S. Agency for International Development. She concluded that community-based adaptation approaches should consider population dynamics in vulnerability assessments. Meeting unmet need for family planning, she said, can assist communities adapting to climate change by building resilience. And as result, “PHE approaches should be able to qualify for funding under community-based adaptation programs.”
Shah Md. Atiqul Haq of the City University of Hong Kong presented research he conducted in Bangladesh that found that women tended to feel that a large family size was not advantageous during floods. This, he said, was indicative of their increased understanding of vulnerability and an endorsement of providing knowledge and access to family planning services as part of climate change adaptation strategies.
The inclusion of more environment, and particularly PHE, related presentations at this year’s conference was good to see – perhaps a sign that demography is becoming a more complex and comprehensive field, with a focus more on population structure and its interactions with other issues, rather than a singular fascination with growth.
In particular, panelists showed that the nexus between demography, gender equity, and climate change continues to grow in importance, both in the research and practitioner communities.
Photo Credit: Tribal women and children in Kerala state, India, courtesy of flickr user Eileen Delhi. -
Environment, Natural Resource Guidelines for Peacekeepers Moves UN Closer to ‘Greening the Blue Helmets’
›May 30, 2012 // By Stuart KentUN peacekeepers not only operate in conflicts where land and natural resources are a component of the fighting but their own bases and operations can also impact the local environment. As well as documenting practical steps to minimize the footprint of field missions, a new report from the United Nations Environment Program (UNEP) reviews the relationship between natural resources and conflict and what it means for peacekeeping.
While there’s been talk about “greening” UN peacekeeping for years, the details about the economic, environmental, and mission benefits contained in Greening the Blue Helmets: Environment, Natural Resources and UN Peacekeeping Operations suggest that this talk is getting closer to reality.
As of December 2011, the UN’s Department of Peacekeeping Operations was responsible for 121,591 personnel, 17,000 vehicles, and 257 aircraft across 16 different operations worldwide. These forces account for more than half of the entire UN system’s carbon emissions and can significantly strain the resources of fragile host communities, according to the report.
Building on the 2009 Environmental Policy for UN Field Missions, the UNEP report provides a dozen best practice examples from ongoing missions.
Field cases serve as evidence of how increasing water and energy efficiency, safely discarding solid and hazardous wastes, protecting cultural and historical sites, and ensuring a limited footprint after the closing down of camps, can save environmental and financial resources. These measures, the report claims, also reduce the risk of tension with host communities, such as occurred in Haiti when an outbreak of Cholera was traced to unsanitary water management practices at a UN camp.
Technologies recommended include better waste management systems, improved water systems, energy efficient buildings, and green energy capacities. However, some improvements can be made by simply encouraging behavioral changes; the UN mission in Timor-Leste reduced energy consumption by 15 percent over 12 months using a “CarLog” system to encourage fuel efficiency. With a 2009 global fuel bill of $638 million, even a 15 percent margin relates to a significant figure (much like the logic behind similar efficiency efforts within the U.S. military).
However, uncertain mission lengths are a major barrier to the adoption of more efficient technologies. Despite UN operations lasting an average of seven years and evidence indicating that capital investments could be recovered within one to five years in some cases, year-to-year mandates complicate long-term planning.
Natural Resource Nexus
Conceptually, the nexus of natural resources, conflict, and peacebuilding must be a central concern of peacekeeping operations, asserts the report.
In Africa alone, 13 operations have been conducted in response to conflicts associated with natural resources, at a cost of around $32 billion. Exploitation of natural resources such as diamonds, timber, and oil has financed and fueled conflicts in Sierra Leone, the Democratic Republic of the Congo, and Liberia. Communal tensions over access to scarce land and water resources are also considered an exacerbating influence on conflict dynamics in much of Sudan and now South Sudan, according to the report.
Addressing this nexus can also provide opportunities to reduce and redress conflict. In Darfur, firewood collection is a dangerous task for women and girls. By making “firewood patrols” a regular feature of the UN forces’ protection, the prevalence of sexual violence has been limited.
The UN Assistance Mission in Afghanistan is cited in the report for its efforts to hire ex-combatant and vulnerable populations to aid in the reforestation of extensively degraded pistachio woodlands from 2003 to 2009.
“Natural resources can provide opportunities for emergency employment and…sustainable livelihoods for former combatants,” write the authors.
Countries recovering from episodes of violence tend to have a low capacity to effectively and equitably manage a natural resource base that itself may have been degraded by conflict. Recent attention, however, is being paid to the peacebuilding potential of managing shared resources.
According to the report, “while only 54 percent of peace agreements reached between 1989 and 2004 contained provisions on natural resources, all of the major agreements concluded between 2005 and 2010 included such provisions.” This includes the renovation of land tenure systems, management of valuable extractive industries, and reallocation of resource rents.
Preventing Predatory Extraction
As peace begins to take hold, “access to land may be a key determining factor affecting the successful reintegration of a former combatant into a community.”
According to interview data from Northern Uganda, 93 percent of male LRA ex-combatants were unable to access land after demobilization. Often due to the death of an elder relative, sale of land by a family member, or land grabs by other members of the community.
While shared resources can build trust between communities, spoiler groups that use aggressive means to secure resource rents in the aftermath of conflict can endanger a fragile peace. The report identifies a role here for peacekeeping forces – and in particular for their civilian contingent – to identify these potential risks and opportunities for action.
In particular, the report recommends a higher level of clarity about the relationship between peacekeeping forces and so called “expert panels” – groups of civilian specialists called upon by the Security Council to provide advice on an official basis about natural resources in the aftermath of conflict.
The UN mission in the Democratic Republic of Congo, for instance, was given a direct mandate in 2008 to work with the DRC expert panel and to “use its monitoring and inspection capacities to curtail the provision of support to illegal armed groups derived from illicit trade in natural resources.”
UNEP Program Officer Matti Lehtonen, in an email interview, called the panels a “tremendous asset that is not yet used up to its full potential.” However, he noted, “expert panels and peacekeeping missions are different tools with different objectives so there is also a need to maintain a degree of independence.”
The report identifies a set of key recommendations for the UN moving forward:- Ensure that pre-deployment and in-mission training includes instruction on environment and natural resource management
- Aid and encourage disarmament, demobilization, and reintegration programs to look closely at emergency employment and sustainable livelihoods related to natural resources and the environment
- Support and encourage civil affairs personnel to seek ways to capitalize on peacebuilding opportunities around natural resources and the environment
- Systematically inform the Security Council of linkages between natural resources and conflict in states where the Council may be considering action
- Where natural resources have fueled or financed conflict, provide peacekeepers with a more systemic mandate to act on these issues
- Effectively implement best practices identified in the 2009 environmental policy
Photo Credit: UN peacekeepers in Côte d’Ivoire distribute water during a 2007 mission, courtesy of United Nations Photo. -
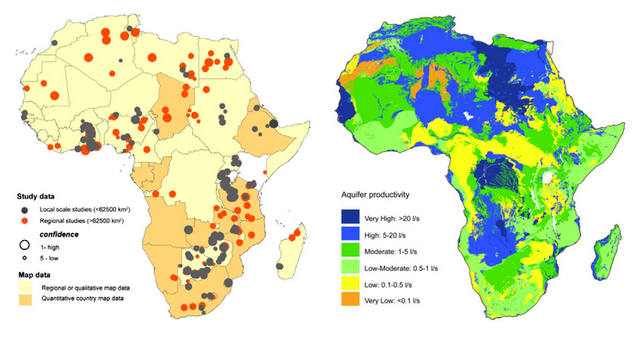
Full Extent of Africa’s Groundwater Resources Visualized for the First Time
›“In Africa, groundwater is the major source of drinking water and its use for irrigation is forecast to increase substantially to combat growing food insecurity,” yet, a lack of quantitative data has meant that “groundwater storage is consequently omitted from assessments of freshwater availability,” according Alan Macdonald, Helen Bonsor, and Brighid Dochartaigh of the British Geological Survey, and Richard Taylor of University College London, writing in Environmental Research Letters.
The authors hope to remedy this with new research presented in “Quantitative Maps of Groundwater Resources in Africa.” They used estimates compiled from geologic data and 283 aquifer summaries from 152 different publications to quantitatively visualize, for the first time, the full extent of Africa’s groundwater resources.
Tapping a Hidden Resource
The study estimates the scale of the continent’s groundwater resources at around 0.66 million km3. This volume, the authors explain, is “more than 100 times the annual renewable freshwater resources, and 20 times the freshwater stored in African lakes.”
Tapping into this massive resource is not always straightforward, however. The largest aquifers, and those most able to support high yielding bores, are concentrated in the arid regions of North Africa. The depth of these aquifers and their distance from major populations creates substantial economic challenges for extraction.
The geographic distribution of aquifers across sub-Saharan Africa is also quite variable, and local geology can determine not just the availability and accessibility of water but also its quality. For instance, geologic specificities can result in elevated levels of arsenic and other undesirable chemicals. Furthermore, “contamination…is common in urban areas from widespread and dispersed faecal effluent from on-site sanitation and leaking sewers.”
Tempering Expectations
Throughout Africa, “groundwater provides an important buffer to climate variability and change,” say the authors. But these buffers are not a singular solution to the threat of future water scarcity.
As the analysis shows, most aquifers, especially south of the Sahara, are unlikely to sustain boreholes of a higher capacity than that required by community-level hand pumps (one liter per second of flow at minimum). Yet, commercial irrigations schemes and urban towns typically demand boreholes greater than five liters per second, according to the study.
So, groundwater extraction may help communities and some small-scale farmers maintain access to water, particularly because many aquifers are found to possess the storage capacity required “to sustain abstraction through inter-annual variations in recharge,” however, “strategies for increasing irrigation or supplying water to rapidly urbanizing cities that are predicted on the widespread drilling of high yielding boreholes are likely to be unsuccessful.” Especially, the authors assert, where drilling precedes detailed local scale mapping of the available resources.
Sources: Environmental Research Letters.
Image Credit: Figures 1 and 3, courtesy of Environmental Research Letters. -
The Global Water Security Assessment and U.S. National Security Implications
›
“Water security is about much more than access to H2O,” said Jane Harman, director, president, and CEO of the Wilson Center at the May 9 meeting, “Global Water Security: The Intelligence Community Assessment.” The event – part of the Wilson Center’s National Conversation Series – brought together a number of experts to discuss a recently released intelligence community assessment of global water security. [Video Below]