Showing posts from category water.
-
The World’s Toilet Crisis
›Forty percent of the world’s population – 2.6 billion people – do not have access to toilets, and some in the international aid community are finally dispensing with the euphemisms and calling this sanitation crisis what it is: “shit.”
In “The World’s Toilet Crisis” (trailer above), Adam Yamaguchi sets off in an episode of Current TV’s Vanguard program to tell the story of “the deadliest killer in the world…something no one wants to talk about.” All around the developing world, thanks in part to rapid population growth and poor development and environmental standards, “people are literally eating their own shit,” he said.
His journey takes him to India, where more people own cell phones, than toilets. The 55 percent of Indians who practice open defecation have contributed to another grim statistic: an estimated 840,000 children under the age of five die in India each year from diarrheal diseases.
India’s water quality is especially affected by lack of sanitation. In the documentary, Yamaguchi visits the Yamuna River, which is Delhi’s primary source of drinking water, and has become a “giant toilet” literally bubbling with methane gas. This phenomenon is not unique to India. Approximately 80 percent of sewage in developing countries goes untreated, polluting local water resources.
But it is women who feel the effects of lack of access to clean water and toilets most keenly. In 72 percent of households around the world, women are the primary water collectors, often travelling long distances for drinkable water. They face shame and harassment when going to the bathroom, causing them to suppress their need until dark, causing negative health effects. Waiting until nightfall also means that when women openly defecate, they often face molestation, violence, and rape. Teenage girls also often drop out of school once they begin to menstruate because toilets are not private, unsafe, or are simply nonexistent.
Reflecting on his motivations for making the documentary, Yamaguchi said that in order to expose this “global public health crisis,” he needed to be as graphic, shocking, and disgusting as possible.If you’re not grossed out by, or incensed by the fact that there is shit everywhere, you’re not really moved to act or change your ways. And that’s ultimately what’s happened in many places in the world. It’s a normal fact of life. You see it everywhere, and you think nothing of it. There are causes out there that are deep sexy causes or marketable causes. Shit or toilets – not the most marketable thing in the world.
“The World’s Toilet Crisis” forms part of a broader trend among sanitation advocates to use crude language to address a problem the international health and development community has traditionally shied away from talking about directly.
Tales of shit: Community-Led Total Sanitation in Africa, published shortly before World Toilet Day by the International Institute for Environment and Development, takes an equally direct approach to sanitation.
Community-Led Total Sanitation (CLTS) is an approach begun with great success by Dr. Kamal Kar in Bangladesh that relies on “triggering” to change community behavior. The report, which is prefaced by a three-page “International Glossary of Shit” listing the words for shit in other languages, emphasizes the need to “explicitly [talk] about and [make] visible the shit that is normally hidden beneath taboos and polite language.” By almost literally thrusting people’s shit right under their noses, communities learn what they have been ignoring: that they are “eating each others’ shit.”
Traditional sanitation programs often fail because “a high proportion of latrines constructed with subsidies are never used as toilets, but as storage space, animal shelters, or prayer rooms – the buildings are too high quality to be wasted on toilets!” says the report. CLTS, on the other hand, focuses on changing behavior at the community, rather than the individual level to create sustainable change that responds and adapts to a community’s distinct culture and needs.
“The World’s Toilet Crisis” shows the promise CLTS has of meeting the needs of the billions without toilets. In East Java, Yamaguchi joins a community leader to collect a “specimen” from a well-traveled river bank near the town, which he proceeds to show to a group of women in the town who are, predictably, revolted. The community then takes collective action to become “open-defecation free” and invest in toilets.
“The World’s Toilet Crisis” is not easy to watch, nor was it easy to film – seven minutes in, Yamaguchi vomits on the banks of the polluted Yamuna River. Disgust, however, is central to raising awareness and affecting change on both the community and global levels. As Yamaguchi explains, “You’re going to get grossed out by seeing this piece, and that’s part of the point.”
Sources: Community-Led Total Sanitation, Current TV, Earth Times, IIED, Water.org, World Toilet Organization, WHO, United Nations University.
Video Credit: “The World’s Toilet Crisis – Vanguard Trailer,” courtesy of Current TV’s Vanguard. -
Bringing Cambodia Back from the Brink: An Audio Interview with Suwanna Gauntlett
›December 10, 2010 // By Hannah MarquseeThree decades after the Khmer Rouge regime wiped out an estimated 1.7 million people – one fifth of Cambodia’s total population – the environment and Cambodian people are still feeling the effects.
The Pol Pot regime’s policy of agrarian collectivization dramatically reorganized land ownership and relocated millions from urban to rural areas. The ensuing decades of Vietnamese occupation and civil war further changed Cambodia’s workforce, dislocating millions.
The “Khmer Rouge regime increased the destruction of natural resources exponentially,” Suwanna Gauntlett, founder and CEO of Wildlife Alliance, told ECSP in this interview. Today, 78 percent of Cambodia’s 14.5 million people live in rural areas, according to the World Bank, nearly all of whom work as subsistence farmers. These rural households account for almost 90 percent of Cambodia’s poor and 36 percent of the total population in 1997.
“These Forests Were Silent”
When Wildlife Alliance arrived in Cambodia in 2000, “these forests were silent,” Gauntlett said. “You couldn’t hear any birds, you couldn’t hear any wildlife and you could hardly see any signs of wildlife because of the destruction.”
In one village, Chi Phat, Gauntlett noted how years of slash-and-burn agriculture had left a “circle of death” around the village as farmers gradually encroached further into the forest.
Cambodians have compensated by turning from traditional subsistence farming to illegal logging, wildlife trafficking, slash-and-burn agriculture, mining, and other unsustainable development (with significant Chinese investment). This has contributed to food and water insecurity, rapid deforestation, habitat loss, and species extinctions. In 1990, 73 percent of Cambodia’s land was covered by forest. By 2007, that number had dropped to 57 percent. Cambodia’s 146 threatened plant and animal species have also felt the effects of this loss. The Indochinese tiger, native to Cambodia, is now thought to have less than 30 individuals remaining in the entire country.
Integrated Solutions
Focusing on the Cardamom mountain range – Cambodia’s largest remaining intact forest – Wildife Alliance established several community-based agriculture and ecotourism programs to help villagers escape the “vicious circle” of poverty and environmental destruction. Ten years later, “there’s been tremendous progress in the geographic areas of our projects,” said Gauntlett.
In another village, Sovanna Baitong, Wildlife Alliance’s community agriculture program has raised the incomes of some residents to over $200 a month when the national poverty level is $200 a year, Gauntlett said. Today this village has a school, a clinic that provides health care and family planning, and a micro-credit fund. This is all managed by the community leaders, 30 percent of whom are women.
Ten years ago, “it was a mess,” Gauntlett said. “It’s amazing to see the difference.”
However, in parts of the country where Wildlife Alliance does not operate, deforestation continues at an alarming pace, often fueled by Chinese and other foreign investment. In some parts of the country, “deforestation has led to very severe water shortages,” including villages where people have to walk up to 20 kilometers for water because “there is no more underground water,” said Gauntlett. This has troubling implications for Cambodian security, particularly with aggressive hydrological development of the Upper Mekong continuing in China and Laos.
“I’m afraid that’s what’s going to happen throughout Cambodia – that this water shortage will lead to food shortage [which] will lead to civil unrest,” Gauntlett said.
Sources: BBC, Cambodian Genocide Program, The Washington Post, Wildlife Alliance, World Bank, WWF, UNEP.
Photo Credit: “Farmer at Sovanna Baitong” and “Suwanna Gauntlett” Courtesy of Wildlife Alliance. -
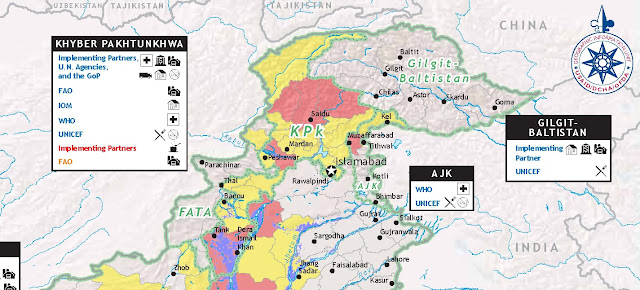
International Responses to Pakistan’s Water Crisis
›December 6, 2010 // By Michael KugelmanExcerpt from the executive summary of the NOREF Policy Brief, via the Norwegian Peacebuilding Centre:
Pakistan faces a multidimensional water crisis that claims hundreds of thousands of lives every year. The root causes of the crisis are twofold:- Circumstantial, which are linked to poor water-resource management policies (including water-wasting flood irrigation);
- Structural, tied to factors deeply ingrained in politics and society such as the obsession with India, inequitable rural land-ownership and endemic water misgovernance (for example, exploitation of the rotational irrigation system to the detriment of the poor).
However, international responses must be measured. They should actively target the circumstantial causes but, at the same time, recognize that their ability to take on the structural ones is limited. While the international community can help mitigate the effects of the underlying structural drivers, Pakistan itself must take the ultimate steps to eliminate them.
Circumstantial causes can be addressed through international aid provision and international exchanges. Aid provision must be generous enough to meet Pakistan’s prodigious needs but modest enough to respect the country’s limited absorptive capacities. It should emphasize the restoration of infrastructure and distribution systems, be more responsive to the needs of Sindh and Baluchistan provinces, and be channeled through both government agencies and civil society.
Despite the challenges the international community faces in addressing the structural causes, opportunities do abound. These include embarking on back-channel diplomacy to bring Pakistan and India closer together and cooperative projects with Pakistanis to make water distribution more equitable. To be effective, international responses must target all affected parties and be sensitive to ground realities. They should also be mindful of indigenous success stories and the factors that bring about that success.
The full report, “International Responses to Pakistan’s Water Crisis: Opportunities and Challenges,” is available through the Norwegian Peacebuilding Centre.
Michael Kugelman is program associate with the Asia Program at the Woodrow Wilson International Center for Scholars.
Image Credit: Adapted from “USG Humanitarian Assistance to Pakistan for Floods in FY 2010 and FY 2011 (as of 30 Nov 2010),” courtesy of USAID and ReliefWeb. -
Joydeep Gupta, ChinaDialogue
Nervous Neighbors: China-India Water Relations
›December 3, 2010 // By Wilson Center StaffExcerpted from the original article, “Nervous Neighbors,” on ChinaDialogue.net:
Only five rivers in the world carry more water than the Yarlung Zangbo, or Brahmaputra, as it is known when it reaches India. Only one carries more silt. Rising at a height of 5,300 meters in the Kailash range of the Middle Himalayas – an area holy to both Hindus and Buddhists – the river flows east through Tibet for 1,625 kilometers before taking a horseshoe bend, changing its name and flowing as the Brahmaputra into north-eastern India.
There, for 918 kilometers, it is both a lifeline, due to the water it carries, and a scourge, because of the floods it causes almost every year. It then takes a southward turn and flows into Bangladesh for 363 kilometers before it merges with the Ganges, together forming South Asia’s largest river, the Meghna, and flowing into the Bay of Bengal. This huge river, with its 25 large tributaries in Tibet and 105 in India, drains much of the eastern Himalayas.
As the world’s youngest mountain range, the Himalayas are particularly unstable – and so is the river. It has changed its course significantly at least once in the last 200 years, following a major earthquake. Smaller changes in course are common, wiping out farms and homes on one bank while depositing fertile silt on the other. Now humans are changing the course of this river: Chinese engineers have started to build the Zangmu hydroelectric power station in Lhoka prefecture, 325 kilometers from Lhasa, Tibet’s capital. The development has led to serious expressions of concern, particularly in India but also in China.
Continue reading on ChinaDialogue.net.
Joydeep Gupta is the project director (South Asia) of ChinaDialogue’s Third Pole Project.
Map Credit: Google Maps. -
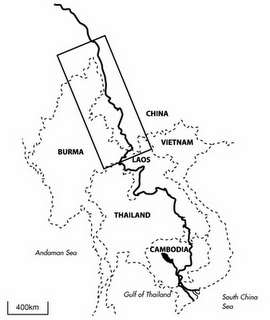
Managing the Mekong: Conflict or Compromise?
›December 1, 2010 // By Russell SticklorAt nearly 5,000 kilometers long, the Mekong River is one of Asia’s most strategically important transboundary waterways. In addition to providing water for populations in the highlands of southern China, the Mekong helps support some 60 million people downstream in Southeast Asia, where the river is a key component of agricultural production and economic development.
In recent years, however, the Mekong has emerged as a flashpoint for controversy, pitting China against a coalition of downstream nations that includes Thailand, Laos, Cambodia, and Vietnam. The countries of the Lower Mekong argue that Beijing’s construction of multiple dams on the Upper Mekong is robbing them of critical water resources, by decreasing both the quality and quantity of water that makes it through Chinese floodgates and spillways. China, however, mindful of soaring energy demand at home, has continued its campaign to harness the hydroelectric potential of the Upper Mekong and its tributaries – but at what cost to the environment and Beijing’s relationships with Southeast Asia?
China’s Hand on the Faucet
China’s total energy demand just recently passed the United States and is expected to continue to increase in the near-term – by 75 percent over the next 25 years, according to the International Energy Agency.
As a result, Beijing has been looking to bolster its energy security by reaching out to develop energy resources in Africa, Latin America, and the Middle East, as well as along the Mekong and in the East and South China Seas.
In that context, China’s aggressive hydroelectric development of the Upper Mekong — known in China as the Láncang Jiang (shown in the boxed area of the map at right) — makes perfect sense. The river’s sizeable elevation drops make it a rich source of energy; already, 15 large-scale dams have either been completed or are under construction on the Upper Mekong in Tibet and Yunnan.
Those dams also provide China with enormous geopolitical leverage over downstream nations. With little more than the flick of a switch, the Chinese government could substantially curtail the volume of flow entering the Lower Mekong basin. Doing so would of course be tantamount to an act of war, since depleted flow volumes in the Lower Mekong would hinder crop irrigation, jeopardize food security, and endanger the health of the region’s economically critical freshwater fisheries, which are among the world’s most productive. Chinese floodgates and spillways essentially give Beijing de facto control over Southeast Asia’s water security.
The View Downstream
To date, China has never threatened to deliberately reduce the flow of the Mekong to its downstream neighbors. Nevertheless, the perception of threat in Southeast Asian capitals remains high.
Already, a number of the region’s governments — represented formally through the Mekong River Commission, a 15-year-old organization that China still has not joined as a full-fledged member — have complained that completed or in-progress Chinese dams are resulting in less water entering their countries, a phenomenon that becomes particularly pronounced during periods of drought, as observed this summer. Further, there is also the issue of water quality. Since Chinese dams trap silt being flushed out of the Himalayas, that nutrient-rich material cannot be carried downstream, where it historically has helped create fertile soils in the floodplains of the Lower Mekong basin.
Quality and quantity concerns aside, there are also structural issues concerning how Beijing goes about its business on the Upper Mekong. Since it is only a “Dialogue Partner” to members of the Mekong River Commission, China is not required to seek approval from downstream nations on hydroelectric development of the river’s Chinese stretch, even though that development has both direct and indirect implications for water security in the Lower Mekong basin. China has even shown a penchant for deliberate secrecy as it develops its stretch of the river, choosing to share a minimal amount of hydrological data with downstream neighbors and typically refraining from even announcing new dam projects.
“The Security Implications Could Hardly Be Greater”
Given its geographic position, Cambodia is particularly vulnerable to China’s stewardship decisions. With one of the poorest populations in Southeast Asia and also one of the highest fertility rates, at 3.3 births per woman, the potential for water scarcity issues is real. By mid-century, its population is projected to jump from its current 15 million to nearly 24 million.
“The government of Cambodia will be entirely at the mercy of Beijing,” said Wilson Center Scholar and Southeast Asian security expert Marvin Ott. “For Cambodia, the question becomes how they can curry China’s favor so as to avoid coercive use of the Mekong — or find some way of exerting counter-pressure on Beijing.”
Overall, population for mainland Southeast Asia is projected to rise from its current 232 million to 292 million by 2050. This growth will require increased agricultural output across the region and thus increased reliance on the waters of the Lower Mekong. The Lower Mekong nations’ shared dependency on the river and China’s continued unilateralism in the Upper Mekong could have serious repercussions for the region, said Ott:The security implications could hardly be greater for the downstream states. With the dams, China will have literal control over the river system that is the lifeblood of Laos, Cambodia, and Vietnam. The power this gives China is equivalent to an invasion and occupation of a country by the Chinese army.
For its part, the PRC maintains that water woes in the Lower Mekong are not its doing. In response to the chorus of Southeast Asian claims that China diverts or stores more than its fair share of water, Beijing’s typical refrain has been that blame for low water levels downstream lies not with Chinese water resource management but with heightened precipitation variability associated with climate change. Chinese water officials also contend that the Lower Mekong countries’ complaints are misdirected because water from the Chinese-controlled sections of the Upper Mekong basin accounts for less than 20 percent of the Mekong’s total flow volume by the time the river reaches its natural outlet in the South China Sea.
There are some indications, however, that China may be experimenting with a more open approach to engaging downstream nations. Earlier this year, China overturned precedent by offering top Southeast Asian government officials a tour of what had once been a top-secret hydro project, the mammoth Xiaowan dam. Some critics insisted Beijing’s fear of growing U.S. influence in the Lower Mekong helped motivate the rare show of transparency, while others said it was a means to curry favor with Southeast Asian nations so that they would support China’s controversial resource-development strategies in the South China Sea. Yet regardless of motive, Beijing’s move away from secrecy – if sustained – could do a great deal to smooth over regional tensions.
Dammed If You Do, Damned If You Don’t
Beyond some limited transparency, Beijing also hopes to mitigate concerns about development of the Upper Mekong by offering funding or logistical support for similar large-scale hydroelectric facilities on the Lower Mekong. The move has been largely welcomed by the Mekong River Commission countries, which envision dams of their own generating much-needed energy input for national grids, accelerating continued economic modernization, and enhancing flood control. As of 2009, there were 12 dam projects for stretches of the Mekong south of the Chinese border and many more planned for key tributaries.
The danger in such deal-making is that the environmental costs will be lost in the shuffle. A series of major dams would fundamentally alter the Mekong’s hydrology, which could lead to the degradation of sensitive riverine ecosystems, the disruption of upstream migratory routes for fish that serve as local dietary staples, and the decline of fresh water fisheries that form the backbone of many local economies.
Given the long-term effects on the food, environmental, and economic security of the Lower Mekong heartland, Beijing’s attempt to ease water tensions with a new round of dam construction may end up doing far more harm than good. Unfortunately, with both China and the Mekong River Commission countries currently viewing the dam proposals as something of a win-win, planning and construction are likely to move forward over the coming years.
Sources: Financial Times, Foreign Policy, International Institute for Strategic Studies, Los Angeles Times, Mekong River Commission, National Geographic, New Asia Republic, Phnom Penh Post, Population Reference Bureau, Stimson Center.
Photo Credits: “Xiaowan Dam Site (Yunnan Province, China, 2005),” (Top) courtesy of flickr user International Rivers; Map (Middle) courtesy of International Rivers; “Thailand – Isaan, Mekong River,” (Bottom) courtesy of flickr user vtveen. -
Developing a Blueprint for Addressing Glacier Melt in the Region
Changing Glaciers and Hydrology in Asia
›“Glacier melt is part of larger hydrologic and climate systems, so effective programs will be cross-sectoral and yield co-benefits,” said Elizabeth L. Malone, senior research scientist at the Joint Global Change Research Institute and Pacific Northwest National Laboratory, speaking at the Wilson Center on November 16. “Looking more closely at glacier melt, we come to understand that upstream actions and choices have a potentially huge effect on downstream communities,” added Kristina Yarrow, health advisor at the U.S. Agency for International Development’s Asia and Middle East Bureaus.
Malone and Yarrow were joined by Mary Melnyk, senior advisor for natural resource management at USAID’s Asia and Middle East Bureaus, to discuss the agency’s new report, “Changing Glaciers and Hydrology in Asia: Addressing Vulnerabilities to Glacier Melt Impacts,” prepared by Malone in collaboration with CDM International and TRG. “This report is a move towards mainstreaming climate change across the development portfolio to ensure enduring success of our investments,” Melnyk said.
Mainstreaming Climate Change
Providing information about the science, vulnerabilities, and current efforts to respond to environmental change and glacier melt in Asia, the new report also features a number of practical, cross-sectoral approaches to addressing glacial retreat in Asia that, if implemented well, could produce multiple benefits. The report highlights the complexity of the issues surrounding glacier melt in the region, and the critical need to prepare today for future environmental changes.
“Climate change in general, and glacier melt specifically, can potentially impact all sectors: economic growth, governance, and health,” Melnyk said. Because there is a lack of scientific knowledge on glacial retreat in Asia and limited financial and human resources to address these issues, it is critical to maximize results through programs that will provide environmental, health, and development co-benefits.
“The challenge is that, in practice, addressing issues of climate change and other environmental security issues still are not a part of the day-to-day business across sectors,” Melnyk said. This report is a first step in the right direction to raise awareness and action on these issues and “although there is uncertainty, we need to move forward – the time to act is now,” she concluded.
Multiple Sectors, Multiple Benefits
“Cross-sector collaboration and programs, when done correctly, can have a much greater impact than when doing a vertical program within a specific sector,” Yarrow said, stressing the importance of multidisciplinary approaches to address environment, health, and development issues. Understanding the health impacts of climate-related environmental change now can help prepare us to address these specific impacts in the future.
“On a global scale, there is indeed a relationship between population growth, environmental change, and development,” Yarrow said. In Asia, stress on water resources due to climate change and rapid population growth will likely exacerbate health problems caused by lack of clean water. Proactively expanding and improving programs that address the causes and effects of diarrheal disease and under-nutrition can help address these vulnerabilities and make communities more resilient.
“Finding innovative ways to improve access to and integrate family planning messages and services into climate adaptation programs will also yield some important co-benefits,” Yarrow said. Family planning can slow population growth, which could help reduce projected demand for water supplies, as well as potentially reduce the amount of water pollution.
Yarrow also added that “population growth affects glacier melt indirectly through the consumption of resources that exacerbate black carbon.” Black carbon, which is produced by cooking and heating with biomass fuels, contributes to regional climate change and severe health problems, including respiratory illness and pneumonia. Accompanied by efforts to promote alternative fuels, family planning could reduce black-carbon emissions, significantly improve health, and strengthen community resilience to climate change.
“Though challenging, integrating across sectors is absolutely essential – we’re not experts yet, but we’re definitely getting better,” Yarrow said. “Understanding and addressing the multiple issues like climate change, poor health, poverty, dependence on natural resources, and governance challenges that these communities are dealing with in a comprehensive and holistic fashion will improve results.”
Responding to Glacier Melt
“We simply do not have the kind of broad-scale knowledge that we would like to have,” Malone said. Current data on glacier melt is scarce and very few direct measurements of glacier volume exist, making calculations of glacier retreat difficult. Moving forward, it is critical to respond to this lack of information by improving regional scientific cooperation on glaciers, snowpack, and water resources in High Asia, and strengthening climate and water monitoring capacity.
“Even the smallest amounts of glacier-melt contribution correspond to the regions of the highest population, so any change in water supply has large implications,” Malone said. Glaciers may not be disappearing as fast as had been previously thought, but “climate change is happening in the Himalayas and is having an effect.”
“If systems – both human and ecological – are already stressed, they are less able to be resilient in the face of changes. But the good news is that we can take actions now that will be crucially important to how societies can respond in the future,” Malone said.
Implementing cross-sector projects can help to target places where environmental, economic, health, and even security issues overlap. Focusing on water resource management, ecosystems, and the needs of high-mountain communities, as well as mitigating climate change by reducing emissions of black carbon, can help reduce both direct and indirect vulnerabilities and improve resilience to future changes.
“The results of this report allow USAID and others to grasp the complexity of these issues, understand the critical gaps, and to respond to the changes in the glaciers to come,” Melnyk said. The next step is applying the knowledge gathered in the report to practitioners in the field and in policy discussions.
“A crucial role USAID can play is to link partners in the government and private sectors to build capacity and spark synergies among new initiatives to really integrate new initiatives with concerns about glacier melt,” Malone concluded.
Photo Credit: “Nepal Sagamartha Trek,” courtesy of flickr user mckaysavage. -
Robert Walker on Family Planning Promotion and Global Population Growth
› “Expanding voluntary family planning access and ensuring that all women have access to reproductive health services is, to me at least, a no brainer,” said the Population Institute’s Robert Walker in this interview with ECSP. “I think it’s a win for women, for their health, for their welfare, the welfare of their families, for their communities, for the environment, and for the planet at large.”
“Expanding voluntary family planning access and ensuring that all women have access to reproductive health services is, to me at least, a no brainer,” said the Population Institute’s Robert Walker in this interview with ECSP. “I think it’s a win for women, for their health, for their welfare, the welfare of their families, for their communities, for the environment, and for the planet at large.”
While China and India dominate much of the global headlines about population growth, other parts of South Asia – namely Afghanistan and Pakistan – and sub-Saharan Africa receive comparatively little attention. For Walker, a renewed global effort to boost the quality and quantity of reproductive healthcare tools and services in these areas of the developing world is essential.
“This is very, very doable. We face a lot of really incredible challenges in the world today, particularly with respect to food, energy, water, and poverty. But if we can increase what we spend on international family planning assistance by three or four billion dollars a year, we can literally change the world,” Walker said. “And I think we desperately need to.”
The “Pop Audio” series is also available as podcasts on iTunes. -
Nigeria’s Future Clouded by Oil, Climate Change, and Scarcity [Part Two, The Sahel]
›November 19, 2010 // By Schuyler NullIf southern Nigeria’s demographic and environmental problems have helped fuel today’s conflicts, it’s the north’s issues that may feed the conflicts of tomorrow.
Nigeria’s lack of development and poor governance is not exclusive to the delta region, only more well-known because its oil reserves. The north of the country, which is predominately Muslim and accounts for more than half of Nigeria’s population, faces many of the same problems of environmental degradation, lack of jobs, and inadequate infrastructure. Northern Nigeria is also growing much faster than the south, with a total fertility rate of 6.6 children per woman, compared to 4.6 in the southern states. The median age of first-time mothers in northern Nigeria is only 18 years old.Nigeria holds nearly a fifth of the entire population of sub-Saharan Africa. By 2050, it’s expected to pass Indonesia, Brazil, and Bangladesh and take its place among the top five most populous countries in the world, according to UN estimates. But a litany of outstanding and new development, security, and environmental issues – both in the long-troubled Niger delta in the south and the newly inflamed north – present a real threat to one West Africa’s most critical countries.
If southern Nigeria’s demographic and environmental problems have helped fuel today’s conflicts, it’s the north’s issues that may feed the conflicts of tomorrow.
Nigeria’s lack of development and poor governance is not exclusive to the delta region, only more well-known because its oil reserves. The north of the country, which is predominately Muslim and accounts for more than half of Nigeria’s population, faces many of the same problems of environmental degradation, lack of jobs, and inadequate infrastructure. Northern Nigeria is also growing much faster than the south, with a total fertility rate of 6.6 children per woman, compared to 4.6 in the southern states. The median age of first-time mothers in northern Nigeria is only 18 years old.
Climate, Culture, and Discontent in the North
Last summer, in an offensive that stretched across four northern states, a hardline Islamist group called Boko Haram emerged suddenly to challenge the government, attacking police stations, barracks, and churches in escalating violence that claimed more than 700 lives, according to The Guardian. The government responded with a brutal crackdown, but recent targeted killings and a prison break seem to indicate the group is back.
Perhaps most distressingly, Boko Haram appears to have won some local support. Said one local cloth trader to The New York Times in an interview this October, “It’s the government’s fault. Our representatives and our government, they are not sincere. What one person acquires is enough to care for a massive amount of people.”
As in the south, mismanagement of natural resources has also played a role in creating a dangerous atmosphere of distrust in the government. After gold was discovered this spring in northwestern Nigeria, many under- and unemployed flocked to the region to try their luck, but they also unwittingly contaminated local water with high levels of lead. Although the state health officials say they have now identified more than 180 villages thought to be affected, the epidemic was only discovered after a French NGO stumbled upon it while testing for meningitis in June. More than 400 infant deaths have been connected to the mining, according to Reuters.
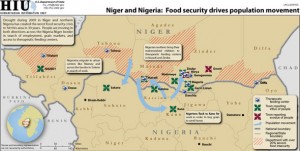
Contributing to natural resource-related misery in the north are climatic changes. Declining rainfall in the West African Sahel over the last century has pushed rain belts successively south, driving pastoralists into areas often already occupied. According to Anthony Nyong’s work, presented in ECSP Report 12, these changes have elevated competition over natural resources to the single most common cause of conflict in northern Nigeria in recent years. In addition to the long-term trend of declining rainfall, an acute drought in 2009 and another this year in neighboring Niger and Chad have created the worst food security crisis in 30 years. The droughts have also driven a great deal of cross-border migration into Nigeria, which itself saw lower than usual rainfall in the north, especially the northeast, around the ever-disappearing Lake Chad (see map above for resulting migration patterns).
In addition to the long-term trend of declining rainfall, an acute drought in 2009 and another this year in neighboring Niger and Chad have created the worst food security crisis in 30 years. The droughts have also driven a great deal of cross-border migration into Nigeria, which itself saw lower than usual rainfall in the north, especially the northeast, around the ever-disappearing Lake Chad (see map above for resulting migration patterns).
What rain did fall in the border areas fell suddenly and torrentially, causing rampant flooding that affected two million people. The floods not only caused physical damage but also came just before harvest season, destroying many crops and further reducing food security. Made more vulnerable by the number of displaced people and flooding, the area was then hit with its worst cholera outbreak in years, which has killed 1,500 people so far and spread south.
Cholera is not the only preventable disease to flourish in northern Nigeria in recent years. In 2003, cleric-driven fear of a U.S. plot to reduce fertility in Muslim women caused the widespread boycott of a UN-led polio vaccination drive. The fast-spreading disease then emerged in six of Nigeria’s neighbors where the disease had previously been eradicated. The northern states today remain the only consistently polio-endemic area in Africa, according to the Global Polio Eradication Initiative.
“A Stable Nigeria Is a Stable Africa”
Nigeria’s size and its wealth of natural resources make it a strategically important country for the future of the region. “A stable Nigeria is a stable Africa,” said Wilson Center scholar and former NEITI officer Uche Igwe in an interview. “Nigeria is 150 million people and the minute Nigeria becomes unstable, the West Africa sub-region will be engulfed.”
While there have been some strides in recent years in reducing corruption and addressing infrastructure needs (for example, NEITI’s work to promote revenue transparency), the development, health, environmental security, and human security situations remain dire in many parts of the country. With one of the fastest growing populations in the world and severe environmental problems in both the north and the south, scarcity will almost certainly be a challenge that Nigeria will have to face in the coming years. How the government responds to these challenges moving forward is therefore critical.
In 2008, in response to high oil prices, British Prime Minister Gordon Brown announced his intentions to send military aid to help combat Niger Delta militants. The statement was met with dismay from humanitarian organizations and caused the collapse of a ceasefire (which was then resumed for a time and now seems to be falling apart again). Brown was forced to backtrack into simply offering training support to Nigerian security forces.
In terms of U.S. assistance, USAID requested $560 million for Nigeria in FY 2010 – 75 percent of which is allocated towards HIV/AIDS – and the U.S. military has engaged in joint exercises with Nigerian forces. But so far, little has been done to integrate U.S. aid in a cohesive manner. Given the breadth of these issues, such integration is crucial.
“We need partners, like the United States and Europe, who have a stake in stability – in Nigeria, the Niger Delta, the Gulf of Guinea, and the world,” Igwe said. It remains to be seen what the Nigerian reaction would be to an offer of aid from the West that addresses not only the country’s security issues but also its myriad other problems, in a substantial and integrated fashion.
Part one on Nigeria’s future – The Delta – addresses oil, insurgency, and the environment in the south.
Sources: AFP, AFRICOM, AP, BBC, Global Polio Eradication Initiative, The Guardian, Independent, The New York Times, ReliefWeb, Reuters, SaharaReporters, USAID.
Photo Credit: “The Ranch,” courtesy of flickr user Gareth-Davies, and “Niger and Nigeria: Food security drives population movement,” courtesy of the U.S. State Department.