-
Health, Demographics, and the Environment in Southeast Asia
›“Health and Health-Care Systems in Southeast Asia: Diversity and Transitions,” launches a series in The Lancet on health in Southeast Asia. While social, political, and economic development have paved the way for substantial health improvements in some countries, demographic transitions are taking place at among the fastest rates in the world, including reductions in fertility, population aging, and rural-to-urban migration. An epidemiological shift is occurring as well, from infectious to chronic diseases. Rapid urbanization and population movement can not only affect the emergence and spread of new infectious diseases directly, but can also exacerbate environmental changes that indirectly contribute to the burden of waterborne and vector-borne diseases. The series, available early online, addresses these concerns in more detail. Moving forward, the authors advocate for “enhanced regional cooperation in the health sector to share knowledge and rationalize health systems operations, leading to further public health gains for the region’s diverse populations.”
In “A Stormy Future for Population Health in Southeast Asia,” author Colin D. Butler responds to the series, stressing that the health of the future generation is dependent on actions today. Environmental change will likely bring sea-level rise that threatens urban centers and food bowls, causing regional food scarcity, exacerbating diseases like dengue fever, increasing the number of extreme weather events, and contributing to resource scarcity throughout the region. With increasing need for sustainable development in the region, Butler concludes that “stronger human factors will be essential to counter the increased physical stresses that seem to be the inevitable destiny of Southeast Asia, largely as a result of the actions of people who have never seen its shores.” -
Demographic Trends and Policy Implications in Northeast Asia
›Japan, the People’s Republic of China, Taiwan, and Korea are all aging societies. On February 26, the Wilson Center’s Asia Program hosted an event to consider issues related to demographic change in Northeast Asia. What will be the effect of aging on economic output in these countries? Can welfare states established for much younger populations in developed economies survive the stress of demographic change, or will governments in Northeast Asia need to radically rethink the provision of care to the elderly? Can immigration reform alleviate many of the problems associated with more elderly populations in Northeast Asia? And will current demographic shifts foster more benign or more belligerent interstate relations in the region?
At the event, Harvard University School of Public Health research associate Jocelyn Finlay noted that demographic trends are often overlooked in explaining economic growth in Japan, South Korea, and Taiwan between 1960 and 2000. Demographers estimate that decreases in infant mortality and adult fertility levels, which resulted in an increase of workers relative to dependents, accounted for up to a third of economic growth in these countries during this period. As the age cohort born after 1945 enters into retirement, however, the increase in dependents relative to new workers will be a contributing factor to sluggish growth. Finlay mentioned that pro-natalism and pro-immigration policies, and policies that encourage women and the elderly to participate in the workplace, could help to mitigate the effects of an aging society on economic growth but noted that such policies were all difficult to implement.
These difficulties were examined in further detail by Ito Peng, professor of sociology at the University of Toronto. Peng noted that East Asian democracies have traditionally maintained very lean welfare states, relying instead on private institutions such as extended families to carry much of the burden of, for example, care for the elderly. However, public provision of care for the aged is increasing in these countries, where the nuclear family has become the norm. Governments must actively pursue strategies to increase the number of workers and therefore income tax revenues to pay for the resulting increases in public spending.
However, policies intended to expand the tax base often have unintended consequences. For example, encouraging people to have larger families often has the effect of forcing mothers to stay at home to care for their children, depriving the labor force of a productive worker in the short term. To address this problem, Japan and South Korea have increased the level of public childcare provision. However Peng believes that there needs to be greater integration between the private and public spheres to make Northeast Asian workplaces, still a sphere of male dominance, friendlier to working mothers. Companies that insist on significant overtime duties could, for example, find ways to let working parents maintain a work-life balance that allows them to personally care for their children. Northeast Asian countries can also institute pro-immigration policies to bring more young workers from abroad. However, sustained immigration policies are also difficult in nations, like Japan and South Korea, without a history of accepting newcomers.
For Richard Cincotta, demographer-in-residence at the Stimson Center and consultant for the Wilson Center’s Environmental Change and Security Program, demographic change will be a major factor in determining the way states in Northeast Asia approach security. To illustrate the relationship between demography and security, Cincotta noted that Japan’s militarist period in the 1930s and 1940s occurred when its population was younger, more ambitious, and more energetic. With older societies, countries in Northeast Asia will be able to recruit fewer males for the military, meaning their foreign policies may shift more towards caution.
The exception, however, is China, where the number of potential male recruits far outnumbers those of its neighbors. This means that Japan, South Korea, and Taiwan will come under more pressure to intensify the use of human capital by promoting more professionalized and better equipped militaries. They will also have incentives to resolve any differences with their key ally, the United States, as well as among each other. Cincotta suggested that we may be seeing the start of a new type of Cold War, where Pacific Northeast Asian states cooperate to check a potential Chinese regional hegemon.
Bryce Wakefield is a program associate with the Asia Program at the Woodrow Wilson Center.
Photo Credit: “Mouth wide open,” courtesy of flickr user Azzazello. -
A Dialogue on Managing the Planet
›“Collectively, the impact of humanity on the way the planet works is enormous and headed in disturbing directions,” said George Mason University professor Thomas Lovejoy in January at the first in a monthly series, “Managing the Planet,” led jointly by George Mason University and the Woodrow Wilson Center. The series will focus on how to take “environmental management to the scale of the entire planet,” as climate change, increasing energy consumption, and population growth place increasing stress on natural resources. We need to “chart a better course for the human future,” said Lovejoy.
Joining Lovejoy at the kickoff meeting were Dennis Dimick, executive environment editor at National Geographic, and Professor Molly Jahn of the University of Wisconsin-Madison. [Video Below]
Signs From Earth
“The entire human enterprise is based on the assumption of a stable climate,” said Lovejoy. The “most dramatic part of the story” in recent decades has been the melting of ice in the Arctic and in the mountain ranges of tropical zones. At current rates, tropical glaciers will completely disappear within the next 15 years. Though scientists predicted it would last until at least 2015, Bolivia’s Chacaltaya glacier – once renowned as the world’s highest elevation ski area – was reduced to a “few lumps of ice” in 2009, according to the BBC.
Glacial melt has raised water temperatures, altered species migrations, and threatened water supplies, coastal ecosystems, and the communities that depend on them, said Lovejoy. Higher ocean temperatures also cause the “fundamental partnership” between coral reefs and algae to break down, and “the Technicolor world essentially goes black and white,” he said.
Ocean acidification, fresh water shortages, melting glaciers, pollution, forest fires, and a “vast whipsaw” of temperature and weather extremes are just some of the effects human consumption has had on the planet, said Dimick. “It’s a sign from the Earth. It is telling us, ‘not all is well.’”
Finding Balance
As the world’s population nears seven billion this year, “we have one planet, yet we live like we live on four,” said Dimick. National Geographic’s new series “Population 7 Billion” seeks to answer the questions, he said, of “how do we find balance? How do we find ways to lower the intensity of our demands on an Earth that is telling us it is strained?”
Finding solutions to these challenges will require us to “look forward and confront the future,” said Dimick. “We need to rethink our whole global energy system,” he said, and “rethink our basic premise about what we need, as opposed to what we want.”
The global emissions limit of 450 parts per million (ppm) of carbon – the level needed to achieve the two-degree warming limit agreed upon at Cancun and Copenhagen – “is probably too high,” said Lovejoy. Most scientists agree that 350 ppm is a safer level; however, the world is already at “390 and climbing,” he noted, and global temperatures are projected to rise two degrees Celsius by 2035. If we want global warming to stop at two degrees, carbon emissions will need to stop growing by 2016, he said.
Figuring Out “Plan B”
“We have a problem that is presenting itself in a whole host of ways, with urgency that cannot be denied or dismissed,” said Jahn. “The way we do agriculture is a very significant contributor” to that problem, she said. Today, in the United States, “we waste 40 percent of the food we grow,” she said.
“Plan A…was about maximizing productivity at all costs,” said Jahn. “It looks like we may need another plan.” But figuring out “Plan B” will require steps by both policy and science communities. “We still have enormous gaps in our understanding towards even the basic science platform upon which these very important decisions about ways forward lie,” she said.
Managing the planet must begin with managing data so that we can “transition between data, information, and knowledge, and march this information out to…those making decisions that matter,” said Jahn. The information management structure that developed in the medical sciences and led to the creation of the National Library of Medicine is a useful model for managing the planet, she argued. “Personalized medicine” for the planet would allow people to use data to make better decisions about who should be doing what and where.
Using and expanding the knowledge base is a crucial step towards bringing together the science and policy communities on an international scale in search of solutions to managing the planet. “If we work together, we can change the world,” said Dimick.
Sources: 350 Science, BBC, Earth System Research Laboratory, United Nations Environment Program, United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change.
Photo Credit: “Sun Over Earth (NASA, International Space Station, 07/21/03),” courtesy of flickr user NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center. -
Food Price Shocks and Instability Highlight Weaknesses in Governance and Markets
›
Unrest across the Middle East has been front-page news for weeks, with commentators searching for explanations to account for the shifting political winds. Many, such as Thomas Friedman and Kevin Hall, have drawn connections between food prices and instability. But, as they point out, high food prices do not deterministically lead to unrest. Instead, rising prices highlight the degree to which governments and governance processes provide and ensure sustainable livelihoods for their people. What these and other commentators point to is that recognizing the role of government in providing food and security is vital: high food prices, they argue, don’t directly cause unrest, but high food prices in poorly managed countries creates a dangerous environment in which unrest may be more likely.
-
The International Framework for Climate-Induced Displacement
›In an article sponsored by the East-West Center, author Maxine Burkett discusses the challenges climate-induced migration presents to the people of the Pacific Islands. In the brief, titled “In Search of Refuge: Pacific Islands, Climate-Induced Migration, and the Legal Frontier,” Burkett states that millions of people in the Pacific Islands will be forced to leave their homes because of “increased intensity and frequency of storms and floods, sea-level rise, and desertification.” These low-lying islands could face a loss of agriculture and freshwater resources, or even be wiped out altogether, an outcome for which there is no international legal precedent.
In “Swimming Against the Tide: Why a Climate Displacement Treaty is Not the Answer,” published in the International Journal of Refugee Law, Jane McAdam takes a different position on the plight of so-called “climate refugees.” McAdam argues that focusing on an international treaty for these migrants distracts from efforts to establish responses for adaptation, internal migration, and migration over time. The article, writes the author, “does not deny the real impacts that climate change is already having on communities,” but rather questions the utility and political consequences of “pinning ‘solutions’ to climate change-related displacement on a multilateral instrument.” -
More on Tunisia’s Age Structure, its Measurement, and the Knowledge Derived
›February 4, 2011 // By Richard CincottaThis post is a response to the questions and comments that my fellow demographers Elizabeth Leahy Madsen, Jack Goldstone, and Jennifer Dabbs Sciubba put to my recent assessment of Tunisia’s chances for democracy. I’ve divided my response to address the principal questions. (Note: Throughout, “young adults” refers to 15-24 year olds, and “working age population” refers to those between 15-64 years old.)
1. Tunisia’s age structure is still quite young – aren’t the effects associated with youth bulge still at work?
Tunisia’s age structure (median age, 29 years) is in the early stages of transiting between the instability that typically prevails in countries with youthful age structures (median age <25), and the stability that is typical of mature structures (median age between 35 to 45). I classify Tunisia’s age structure as intermediate (between 25 to 35). The Jasmine Revolution has featured a mix of both types of sociopolitical behavior: some violence and property damage, perpetuated by both the state and demonstrators; evidence of a mature, professionally-led institution (the Tunisian army); and demonstrations that are peaceful and in which women and older people participate.
By any legitimate youth bulge measure, Tunisia’s age-structure is similar to that of South Korea, Taiwan, and Thailand’s during the mid-1990s. In 2010, Tunisia’s proportion of young adults in the working age population was almost precisely the same as South Korea’s in 1993. South Korea’s median age in 1993 was 28.5, compared to Tunisia’s 29 today.
Consistent with these numerical similarities, Tunisia’s political behavior is not much different than the sociopolitical events observed in South Korea, Taiwan, or Thailand in the early 1990s when these countries experienced an age structure of similar maturity. As these countries matured, political violence and destructive protests occurred less frequently but dissidence lingered in more peaceful, isolated incidents. For example, South Korea experienced several deadly anti-U.S. demonstrations in 1988-89 and only a few minor incidents in the early 1990s. By 1993, the public was demonstrating against extremism, and public protest had turned peaceful and symbolic.
Even today, public protest in Thailand (median age, 33 years) is commonplace. Thai political rights are constrained, and accordingly the country has been dropped in Freedom House’s annual assessment of political freedoms from “free” to “partly free.” However, unlike the student and worker riots that occurred sporadically throughout the 1970s and 80s, Thai demonstrations are typically non-confrontational political rallies attended by T-shirt-clad grandparents and families who bus into town for the event.
2. Why use the population’s median age rather than the youth bulge measures that political demographers (including me) have previously employed with considerable success?
I’m experimenting, and so far, I’ve found that median age replicates prior published results concerning civil conflict and stable liberal democracy. Median age’s ability to span the entire length of the demographic life-cycle of the state is its primary advantage. Youth bulge indicators do not; neither do indicators focused on working-age adults, nor those measuring seniors. In addition, median age integrates many factors that change in parallel with the age-structural transition, including income, education, women’s participation in society, secularization, and technological progress. Still, median age doesn’t track the youth bulge measures perfectly, so why use it?
Currently, foreign affairs policymakers see few linkages between a country’s (1) risk of civil and political violence; (2) its propensity to accumulate savings and human capital; (3) its chances of attaining stable liberal democracy; (4) the challenges that arise to adequately funding pensions and senior healthcare; and (5) rapid ethnic change in low fertility societies. Political demographers understand that these effects on the state are indeed related and that the rising and ebbing probabilities associated with these effects occur sequentially. Understanding this sequence is key to understanding the world’s international relations future. Median age allows political demographers to view that sequence.
As Jennifer Sciubba points out, the disadvantage of median age is its apparent lack of resonance with theories that have historically informed political demography, including theories of cohort crowding, dependent support, and life-cycle savings. I don’t believe that political and economic demographers should (or will) abandon these indicators, which help them observe the inner workings of age-structural phenomena. Nonetheless, I find it useful to make analysts aware of the advantageous and disadvantageous pressures that age structure exerts across the entire demographic life cycle of the state.
3. Can the deposed regime’s multi-faceted problems be captured by the age-structural transition?
No, age-structure cannot account for leadership – clumsy or deft, corrupt or honest. The method is limited to predictions that draw on sociopolitical behaviors that are associated with age structures, or by knowledge gained from deviations from these predictions. Nonetheless, I question the value of many of the after-the-fact observations of the Ben Ali Regime. Tunisia’s fallen regime was indeed oppressive, corrupt, and nepotistic – but so are most authoritarian regimes in Asia and Africa. Lack of job creation and preferential access to employment are valid grievances across much of the developing world, but the lack of informal sector statistics renders country comparisons difficult.
Some analysts have hypothesized that global warming has been a contributor (also applied to Egypt), others point to economic globalization and pressures on Tunisia’s middle class. Whether these assertions are wrong or right, it is difficult for me to see how such post hoc observations add to analysts’ knowledge of regime change or democratization or help them explain why other countries with similar problems have not undergone similar sociopolitical dynamics. In contrast, hypotheses based on quantitative relationships between age structural indicators and sociopolitical behaviors generate testable and repeatable predictions that can be checked and held accountable after an event.
What I find most surprising about the age-structural approach to predicting liberal democracy is how often states ascend to liberal democracy as they approach, or pass, the 0.50 probability mark. If either “triggers” of regime change or key institutions were very important, this observation would be unlikely.
A Concluding Note on Political Demography
If political demographers are serious about advancing policymakers’ ability to understand the present and future of global politics and security, political demography will have to become a scientific discipline – a field of study in which assertions are consistently tied to data and tested whenever possible. In many cases, though not all, we’re lucky – demographers provide us with timely estimates and projections at the national level. Nonetheless, for our field to succeed, political demographers must take full advantage of these data, encourage sub-national data to be collected and published, and make a clean break from the tradition of conjecture that currently pervades international relations.
Richard Cincotta is a consulting political demographer for the Wilson Center’s Environmental Change and Security Project and demographer-in-residence at the Stimson Center.
Sources: CIA World Factbook, Freedom House, Jadaliyya.
Image Credit: Adapted from “Viva the Tunisian Revolution,” courtesy of flickr user freestylee (Michael Thompson). -
Book Preview: ‘The Future Faces of War: Population and National Security’
›February 3, 2011 // By Christina DaggettThe word “population” doesn’t come up too often in national security debates, yet, a shift may be coming, as global population reaches the seven billion mark this year, youth-led unrest rocks the Middle East, and questions of aging enter the lexicon of policymakers from Japan and South Korea to Europe and the United States. What does a population of nine billion (the UN medium-variant projection for 2050) mean for global security? How will shrinking populations in Europe affect Western military alliances and operations? Is demography destiny?
The latter question has plagued demographers, policymakers, and academics for centuries, resulting in heated debate and dire warnings. Jennifer Dabbs Sciubba continues this debate in her new book, The Future Faces of War: Population and National Security, but with a decidedly more measured and optimistic tone (full disclosure: Sciubba was one of my professors). The book is targeted at policymakers but is accessible to anyone with an interest in the field of demography and national security. She will launch her book at an event hosted by the Wilson Center on March 14.
Turning Challenge Into Opportunity
The main themes of The Future Faces of War are challenge and opportunity. Yes, national security will be tested by a series of evolving demographic trends in the decades ahead, but with proper insight and preparation, states can turn these challenges into opportunities for growth and betterment. Sciubba writes, “How a state deals with its demographic situation – or any other situation for that matter – is more important than the trends themselves” (p.125).
Part of turning these population challenges into opportunity is understanding long-term trends – a daunting task given the range and number of trends to consider. Drawing on her own experiences in the defense community, Sciubba writes how policymakers were “receptive” to the idea of population influencing national security, but that the “overwhelming number of ways demography seemed to matter” made them hesitant to act (p.3). With the publication of this book, which clearly and concisely outlines the basics of each population trend with demonstrative examples, hopefully that hesitation will be turned into action.
Youth and Conflict
The first population trend Sciubba highlights is perhaps the one of most immediate concern to national security policymakers given recent world events. In the chapter “Youth and Youthful Age Structures,” Sciubba discusses the security implications of those countries (in particular those in Africa, the Middle East, and Central Asia) with a majority of their population under the age of 29. She writes, “Most important for national security, countries with youthful age structures are generally the least developed and least democratic in the world, and tend to have the highest risk of civil conflict” (p. 18). In fact, between 1970 and 1999 countries with very young and youthful age structures were two to four times more likely to experience civil conflict than countries with more mature age structures.
The risks of very young and youthful populations are well documented (Sciubba cites the examples of Somali piracy, religious extremism, and child soldiers in Africa), but what has not been as widely discussed are the opportunities. Youthful states have a large pool of potential recruits for their armies, plenty of workers to drive economic development, and even an opportunity to grow democratically through social protest. Sciubba writes, “Youth can also be a force for positive political change as they demand representation and inclusion in the political process… social protest is not always a bad thing, even if it does threaten a country’s stability, because it may lead to more representative governance or other benefits” (p. 23). (For more on youth and the transition to democracy, see “Half a Chance: Youth Bulges and Transition to Democracy,” by Richard Cincotta, and his recent blog post about the Jasmine Revolution in Tunisia).
Graying of the Great Powers
At the other end of the demographic transition is population aging. Sciubba points out that the countries with the highest proportions of people aged 60 and older are also “some of the world’s most powerful and economically or politically strategic states” (p. 42). Europe, Japan, and the United States are all getting older (though the United States to a slightly lesser extent), and Sciubba states that the “graying” of these countries has the potential to greatly limit military preparedness, size, and funding. She points out that the number of recruits available will be much smaller and more money will have to be spent on pensions and health care for the growing number of elderly persons.
To counteract these challenges, Sciubba recommends that aging states seek out alliances with each other and countries with younger populations. She writes, “As part of strong alliances, states have strength in numbers, even if they are individually weakened by aging” (p. 47). Another alternative would be to improve military technology and efficiency to compensate for the drop in personnel.
Migration and Security: A “Unique” Relationship
Migration, the third pillar of demographic change after fertility and mortality, has what Sciubba calls a “unique relationship to national security” (p.83). Migration “is the only population driver that can change the composition of a state or a community within months, weeks, or even days” (p. 83). Mass migrations (such as those caused by a natural disaster or violent conflict) are the best examples of this trend. Some of the security challenges Sciubba highlights about migration are refugee militarization, competition for resources, and identity struggles among the native and migrant populations.
However, Sciubba also argues that both migrants and receiving countries can benefit. Origin states release pressure on their crowded labor markets and earn income from remittances, while receiving countries increase their labor market and mitigate population decline (a key component of U.S. growth).
Much of this has been studied before, but two new developments in migration trends that Sciubba calls to our attention are what she calls the “feminization of migration” (the increasing number of women who are likely to move for economic reasons) and migration as a result of climate change. Both are intriguing new areas of inquiry that deserve further study, but only get a passing mention in the book.
Making Her Case
The basic trends outlined above are only a small sampling of the wealth of information to be found in The Future Faces of War. Other noteworthy topics include a discussion on transitional age structures, urbanization, gender imbalances, HIV/AIDS, differential growth among ethnic groups, and many more. The topics are varied and wide-ranging and yet, Sciubba manages to connect them and makes her case convincingly for their inclusion in the broader national security dialogue. Sciubba has briefly written about many of these topics before, but this is the first time she (or anyone else, for that matter) has brought them together in one comprehensive book with such a focus on national security.
Christina Daggett is an intern with ECSP and a former student of Jennifer Dabbs Sciubba’s at Rhodes College.
Sources: Population Action International.
Photo Credits: “Children at IDP Camp Playful During UNAMID Patrol,” courtesy of flickr user United Nations Photo. Book cover image provided by, and used with the permission of, Jennifer Dabbs Sciubba and ABC-CLIO. -
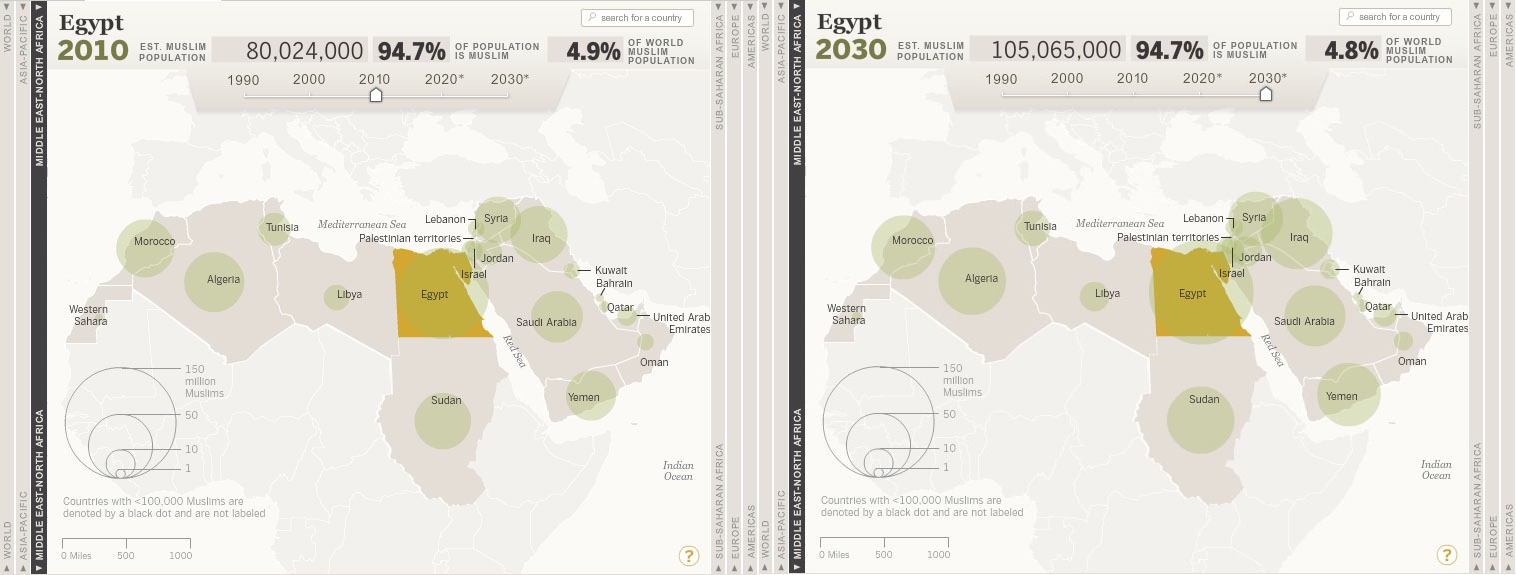
Mapping Muslim Population Growth
›Recent unrest in Tunisia, Egypt, Yemen, and elsewhere across the Middle East has led to a resurgence of interest in the region’s demography, just in time, it turns out, for the Pew Forum on Religion and Public Life’s 2011 refresh of its report on Muslim population growth, which this year includes a new interactive feature, “The Global Muslim Population.”
According to the report, current security hot-spots such as Afghanistan, Iraq, Yemen, Syria, Somalia, and Nigeria will continue to grow considerably faster than the mean.
On the flip side, the report also found that the median age in the Middle East-North Africa region is rising – a generally agreed upon good indicator for the prospects of more liberal, democratic regimes – and though global Muslim population will continue to grow faster than the world’s non-Muslim population, this growth will be slower than in decades past.
The accompanying interactive feature allows users to select a region (the Americas, Europe, Middle East/North Africa, Sub-Saharan Africa, or Asia-Pacific), a specific country, and a decade (1990-2030) in their search. In the example above, Egypt will add 25 million Muslims to its population over the next two decades, representing a 30 percent increase. Comparatively, from 1990 to 2010, Egypt’s Muslim population increased by 48.5 percent.
The user is able to see the estimated Muslim population of the country, the percent of the total population that is Muslim, and the country’s percent share of the world’s total Muslim population (as seen in the example above of Egypt in 2010 and 2030). In addition, these variables can be sorted in tables.
It’s important to note though, write the authors of the report, that projections are not predictions:This report makes demographic projections. Projections are not the same as predictions. Rather, they are estimates built on current population data and assumptions about demographic trends; they are what will happen if the current data are accurate and the trends play out as expected. But many things – immigration laws, economic conditions, natural disasters, armed conflicts, scientific discoveries, social movements and political upheavals, to name just a few – can shift demographic trends in unforeseen ways, which is why this report adheres to a modest time frame, looking just 20 years down the road.
Image Credit: Pew Research Center’s Forum on Religion and Public Life.
Sources: Pew Forum on Religion and Public Life.
Showing posts from category population.