Showing posts from category oceans.
-
African Nations Pioneer Natural Resource Accounting With ‘Gaborone Declaration’
›June 20, 2012 // By Graham NorwoodIn a move with potentially substantial ramifications for future sustainable development, 10 African nations have agreed to begin assigning monetary value to the benefits provided by non-commodity natural resources, including ecosystems such as forests, grasslands, and coral reefs.
Botswana, Gabon, Ghana, Kenya, Liberia, Mozambique, Namibia, Rwanda, South Africa, and Tanzania each affirmed their support for the “Gaborone Declaration” during last month’s Summit for Sustainability in Africa, co-hosted by Conservation International and the government of Botswana. The goal, according to Botswanan President Ian Khama, is to include these new valuations in national accounting, providing policymakers a clear perspective on the costs and benefits associated with the development or conservation of their natural resources for the first time.
Coming just prior to the Rio+20 conference, the signatories said they hoped assigning calculable costs to resource usage would encourage more sustainable development by bringing hitherto “invisible” costs and externalities into the open and onto the balance sheet.
Though the challenges of properly assessing the values of various ecosystem services are understandably many, the potential benefits of natural capital accounting are substantial.
According to SciDev.Net, the World Bank’s Vice President for Sustainable Development Rachel Kyte spoke in support of the declaration at the summit. She pointed out, for example, the advantage of knowing that a hectare of mangrove trees in a certain region of Thailand has been calculated to provide approximately $16,000 of flood protection when considering whether to clear-cut and sell the raw wood (worth about $850), convert the region into a shrimp farm ($9,000), or preserve it.
Such accounting may be particularly beneficial to the Gaborone signatories and other African nations, given growing concern among experts about foreign investment in land, natural resources, and even water on the continent.
But the declaration – and the very idea of natural capital accounting – is not without controversy.
Some argue that commodifying such resources will actually encourage their destruction rather than protect them by ascribing monetary values to previously free and shared resources, thus advantaging richer stakeholders and nations at the expense of poorer ones. As Hannah Griffiths of the UK-based World Development Movement recently wrote in The Guardian, “the result [of natural resource accounting] would be the further privatisation of essential elements of our planet to which we all share rights and have responsibilities.”
Along these lines, Nigerian environmental activist and chair of Friends of the Earth International, Nnimmo Bassey, has voiced his strenuous opposition to the plan made at the summit. “This declaration is blind to the fact that the bait of revenue from natural capital is simply a cover for continued rape of African natural resources,” he said in SciDev.
However, the signatories of the Gaborone Declaration dismissed these concerns and pointed to the value of natural resource accounting for sustainable development.
“Africa is where sustained and sustainable economic growth and stewardship of natural wealth become one and the same thing,” said Kyte at the summit. “By endorsing natural capital accounting as a tool for delivering on more inclusive green growth, Africa is showing the way for the rest of the world.”
Conservation International CEO and Chairman Peter Seligmann agreed, calling the declaration “a very big deal, a very big moment, and a big step forward.” He connected it to the imminent Rio+20 conference as well, saying the pledge is “truly a beacon on the hill for the rest of societies” and that “it will be held up on top of that hill in Rio de Janeiro.”
Indeed, the World Bank has listed natural capital accounting as one of six key issues for Rio+20, and in a report last month titled Inclusive Green Growth: The Pathway to Sustainable Development, noted that “it is vital that economic values for environmental assets be comparable to other economic values.”
The World Bank has already made significant progress in promoting the practice through its Wealth Accounting and the Valuation of Ecosystem Services (WAVES) global partnership, encouraging at least 24 countries to use some form of natural resource accounting to date. WAVES aims to sign up 50 more nations and 50 private corporations beginning at Rio+20, as a part of its “50:50 Campaign.”
WAVES and the Gaborone Declaration show that natural capital accounting is gaining momentum as a means to incentivize more sustainable development. The international news media is beginning to take notice as well. The results of the Rio+20 conference will be a good opportunity to gauge just how far the idea has come and what the extent of its future application might be.
Sources: Conservation International, The Guardian, SciDev.Net, World Bank.
Photo Credit: “Saving the Sacred Rock,” courtesy of flickr user isurusen (Isuru Senevi); video: The World Bank. -
Imelda Abano on Environmental Reporting in the Philippines
›“What we are trying to do is to explore more strategies on how to improve environmental reporting in the Philippines – and on how to reach the government and communities as well,” said Imelda Abano, president of the Philippine Network of Environmental Journalists, Inc. (PNEJ) and senior correspondent at Business Mirror, in an interview with ECSP.
With an overwhelmingly coastal population of around 95 million, the 7,150 island archipelago of the Philippines is seen as highly vulnerable to environmental and climate-related threats. One of Albano’s major aims as president of the PNEJ is therefore to “empower local journalists to report more on environmental issues like biodiversity, climate change, disaster, and other environmental challenges in the Philippines,” she said.
Compelling reporting, she said, comes from “try[ing] to understand what the government is trying to say or what researchers or other organizations are trying to say,” and then relating that information back to the people “in the layman’s terms.”
Environmental issues require a lot of context, she said. One of the most important related issues in the Philippines is population growth.
“When you talk about environment issues, it really resonates or links to population issues,” Abano said. Current UN projections estimate that by 2050, the population could balloon to nearly 155 million. “This really affects our jobs, women, culture, and of course the population around the coastal areas.” -
Philippines’ Bohol Island Demonstrates Benefits of Integrated Conservation and Health Development
›
In March 2012, I participated in a study tour to the island of Bohol, near the unique Danajon double barrier reef ecosystem – the only one of its kind in the Philippines and one of only three in the Indian and Pacific Oceans. Nowhere is the connection between population dynamics and biodiversity more evident than in the Philippines, one of the most densely-populated countries on the planet, with more than 300 people per square kilometer. Nearly every major species of fish in the region shows signs of overfishing, according to the World Bank.
-
Andrew Freedman, Climate Central
Senate Hearing Focuses on Threat of Sea Level Rise
›April 21, 2012 // By Wilson Center StaffThe original version of this article, by Andrew Freedman, appeared on Climate Central.
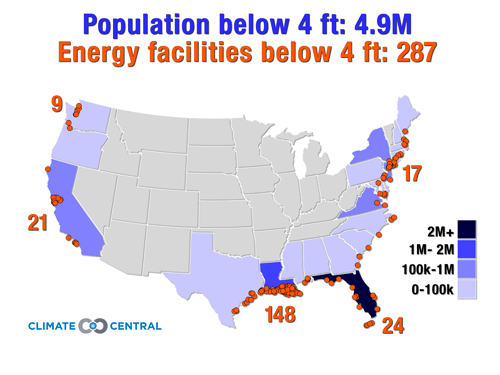
Sea level rise poses an increasingly grave threat to coastal energy facilities and communities during the course of the next several decades, with some impacts already evident, according to testimony delivered Thursday before a rare Senate hearing on climate science.
The hearing, held by the Senate Energy and Natural Resources Committee, focused on the challenges posed by sea level rise, which is one of the most visible manifestations of a warming planet.
“Sea level rise takes the current level of vulnerability and multiplies it,” said Committee Chairman Jeff Bingaman (D-N.M.). “When sea levels rise, the storm surge associated with extreme storms gets even worse, and even an average storm can have above-average consequences.”
Although Chairman Bingaman said he hoped the hearing would help restart “a national conversation” on climate change, the hearing instead may have served to highlight the continuing partisan divide on global climate change. While there were five Democrats in attendance, just one Republican – ranking member Lisa Murkowski (R-AK) – participated in the hearing, a fact not lost on Minnesota Democrat Al Franken, who called climate change the proverbial “elephant in the room.”
Continue reading on Climate Central.
Sources: U.S. Senate Energy and Natural Resources Committee.
Image Credit: Climate Central. -
The U.S. Military, Climate Change, and Maritime Boundaries
›The Defense Science Board, which advices the U.S. military on scientific and technical matters, writes in a recent task force report that the most immediate and destabilizing effects of climate change will impact U.S. security indirectly, through American reliance on already-vulnerable states that are “vital” sources of fuel and minerals or key partners in combatting terrorism. The report singles out three specific themes as particularly important to responding to near-term climate-driven threats and adapting to climate change’s long-term impacts: providing “better and more credible information [about climate change] to decision makers,” improving water management, and building better local adaptation capacity, particularly in African nations. Ultimately, the report concludes that the most effective, most efficient way the United States can respond to climate change is not militarily but “through anticipatory and preventative actions using primarily indigenous resources.”
In “Maritime Boundary Disputes in East Asia: Lessons for the Arctic,” published in International Studies Perspectives, James Manicom writes that as climate change makes access and exploration easier, there are lessons to be learned from East Asian states’ handling of maritime disputes for Arctic nations. Manicom finds that simply because a state may be party to the UN Convention on the Law of the Sea (UNCLOS), disputes over boundaries and “over the methods used to settle disputes” persist. Domestic identity politics also can and do affect the extent to which a state attempts to exert influence over disputed areas – a noteworthy conclusion given growing rhetoric in Arctic states over the national importance of disputed territories. Finally, Manicom points out that, while “high expectations of resource wealth” may fuel disputes and “political tension,” those expectations do not inevitably doom competing states to conflict over resources. -
‘Marketplace’ and ‘NewsHour’ Highlight Population, Health, and Environment Program in the Philippines
›The Danajon reef is the only double barrier reef in the Philippines, “one of the richest marine biodiversity hot spots in the world,” and it’s being devastated as the country’s exploding population depends on its waters for their food and livelihoods, reported Sam Eaton in a recent two-part series on population, health, and environment issues in the Philippines broadcast last month for American Public Media’s Marketplace and the PBS NewsHour.
The report is part of joint project called Food for 9 Billion, with Homelands Productions, the Center for Investigative Reporting, APM, and PBS. Previous reports examined food security in East Africa and Egypt.
The Philippines “import more rice than any other country on the planet,” said Eaton. The “highest population growth rates in all of Southeast Asia” as well as dwindling natural resources – nearly 100 million people live in a land area the size of Arizona – have created a cycle of poverty. The first step to breaking that cycle, he said, is improving access to family planning.
Growing Families, Growing Poverty
The Canayong family, living on the edge of a garbage dump in a Manila slum, offers a vivid example of what poverty means in the Philippines. Clarissa Canayong has had 14 children – 4 died from measles and dengue fever, the remaining 10 spend their days alongside Clarissa, sifting through the dump for things they need and things they can sell. At the end of a good day, the family has earned around $7 to survive on. All in all, Clarissa’s “inability to provide enough food, and to pay for her children’s education, all but guarantees she and her family will remain poor,” said Eaton.
The archipelago adds about two million people every year, putting population on track to double in size sometime around 2080. “And that’s only if something is done to close the birth control gap,” said Eaton, as those projections build in an expectation that growth will slow.
“As cities all across the country expand, the displaced often end up migrating to urban slums,” he said. “Population growth among poor Filipinos is twice the national average,” meaning that once a family enters poverty, they end up in a cycle “that’s nearly impossible to break.”
The Difference Family Planning Can Make
If Clarissa had had access to family planning, she told Eaton, she would have wanted to have only two children. In Humayhumay, where residents have access to a community-based family planning distribution program started by PATH Foundation Philippines, Inc., families have that luxury of choice.
Working through local partners, the PATH Foundation identifies and trains community-based vendors to sell contraception – both pills and condoms, said Dr. Joan Castro, who began the program in Humayhumay. The idea is to make buying contraceptives “as easy as buying soft drinks or matches.”
Both Jason Bostero, a farmer and fisherman in Humayhuay, and his wife, Crisna, grew up in large families – so large, in Crisna’s case, that “sometimes, we would only eat once a day because we were so poor. We couldn’t go to school. I did not finish school because there were just so many of us,” she told Eaton.
Now that they have access to contraceptives, a smaller family size means their income is “just right” to feed everyone three times a day. For the community as a whole, smaller family sizes mean that the nearby fish stocks that provide the community with food and income have a chance to replenish themselves in the absence of overfishing.
“In just six years since the program was first established here,” reported Eaton, “family sizes have plummeted from as many as 12 children to a maximum of about 4 today.”
Exception to the Rule
Humayhumay is an exception to the rule in the Philippines. There is no state funding for birth control in the country, and over the past few years, major international donors like USAID and the United Nations have ended their family planning work in the country. More than a quarter of poor Filipinos have no access to any type of family planning service, and more than half of all pregnancies are unintended, said Eaton.
Family planning has long been a contentious issue in the country. Eaton spoke to Congressman Walden Bello, who has spent more than a decade trying to pass legislation to establish universal access to birth control and improve other family planning and reproductive services. The Catholic Church, said Bello, is a powerful (80 percent of Filipinos are Catholic) and consistent opponent. In October 2010, the Church went so far as to threaten President Benigno Aquino with excommunication after he voiced support for access to contraception.
Rather than limit population growth, the Church argues the country should increase food production. But land is limited, rice imports are already the highest in the world, and, “according to the World Bank, every major species of fish here shows signs of severe overfishing,” said Eaton.
Looking Forward and Abroad
Eaton pointed to the Philippines’ neighbors as examples to emulate: “A long history of government-supported family planning has…paved the way for Thailand to become one of the world’s biggest rice exporters” and helped to cut back poverty in the country, said Eaton.
Indonesia too, he pointed out, has largely avoided the population growth-resource depletion-poverty cycle, thanks in part to a state- and faith-backed family planning program. (As Elizabeth Leahy Madsen wrote in a recent New Security Beat post, the decision of Indonesia’s religious leaders to throw their support behind family planning in the 1960s was a key factor in success there.)
Considering the obstacles, the Philippines face an uphill battle before family planning services become similarly universal. But the political tides may already be turning: last April, the President said he would support the reproductive health legislation even if it meant excommunication.
Meanwhile, PATH Foundation’s Castro is hopeful that Humayhumay’s success story will lay the seeds for widespread public support for family planning. “The vision of the project is in this community you see more children educated who are able to become leaders and speak out for themselves in the future and be able to become stewards of their own sexuality and the future environment,” said Castro. “This is the legacy.”
Sources: BBC, Bloomberg News, Catholic News Agency, The Guardian, Population Reference Bureau, TIME Magazine, US Agency for International Development, U.S. Catholic. -
Watch: Dr. Vik Mohan on Integrating Family Planning and Conservation in Madagascar
›The integration of population, health, and environment programming “enables us to create synergies that mean we are more effective at achieving both health and conservation goals,” said Dr. Vik Mohan, director of sexual and reproductive health programming for Blue Ventures, in an interview with ECSP at the 2011 International Conference on Family Planning.
After Blue Ventures established their first clinic in 2007 in the village of Andavadoaka, on Madagascar’s southwest coast, “we felt immense pressure to scale up our intervention,” said Mohan. “We started with one clinic in one village, and now we have a multi-site service covering all 40 villages that we partner with for our community-based conservation work,” he said.
According to data compiled by Blue Ventures, the average total fertility rate in the region is 6.7 children per woman. The London-based eco-tourism-turned health and environment NGO offers a variety of family planning services to meet local demand, including mobile outreach clinics and community-based distribution of contraceptives. They also partner with Marie Stopes International to offer long-acting and permanent methods of contraception for those that want it.
“This Model Can Be Taken to Scale”
By integrating conservation and reproductive health messaging and service delivery, “we are getting greater buy-in from the community because they all see the added value of the breadth of things that we offer them,” Mohan said. “Men who came to hear about fisheries management get to hear about family planning technologies, practically for the first time in their lives.”
The fishermen are able to see the links between food security and population growth through their own experience, he added. “We believe very passionately this model can be taken to scale,” Mohan said. “This is something that could be easily replicated in other regions. Definitely in other coastal regions, but almost certainly in other remote areas – perhaps areas of high biodiversity where there are existing projects, perhaps conservation projects – but where there is an unmet need for healthcare and family planning in particular.”
“My advice to other organizations, whether you are doing healthcare or whether you are doing conservation, is just think holistically,” said Mohan. “If you are a conservation organization that recognizes that there is an unmet healthcare need for the communities that you work with, then…don’t be afraid to ask those questions, and don’t be afraid to build capacity to meet the need, if you find one. Or, don’t be afraid to partner with health NGOs to enable that need to be met.”
For more on Blue Ventures’ integrated efforts, see also ECSP FOCUS Issue 23, “To Live With the Sea: Reproductive Health Care and Marine Conservation in Madagascar,” co-authored by Vik Mohan. -
Eddie Walsh, The Diplomat
Indonesia’s Military and Climate Change
›July 22, 2011 // By Wilson Center StaffThe original version of this article, by Eddie Walsh, appeared on The Diplomat’s ASEAN Beat blog.
With more than 17,000 islands and 80,000 kilometers of coastline, Indonesia is extremely vulnerable to climate change. Analysts believe that rising temperatures will almost certainly have a negative impact on human security in Indonesia, which in turn will increase the probability of domestic instability and introduce new regional security concerns. With this in mind, it’s important that Indonesia’s armed forces take a range of measures to prioritize environmental security, including procuring new equipment, strengthening bilateral and multilateral relations, and undertaking training for new roles and missions.
Indonesians are expected to experience warmer temperatures, increased precipitation (in the northern islands), decreased precipitation (in the southern islands), and changes in the seasonality of precipitation and the timing of monsoons. These phenomena could increase the risk of either droughts or flooding, depending on the location, and could also reduce biodiversity, lead to more frequent forest fires and other natural disasters, and increase diseases such as malaria and dengue, as well incidences of diarrhea.
The political, economic, and social impact of this will be significant for an archipelago-based country with decentralized governance, poor infrastructure, and a history of separatist and radical conflict. According to a World Bank report, the greatest concern for Indonesia will be decreased food security, with some estimates projecting variance in crop yields of between -22 percent and +28 percent by the end of the century. Rising sea levels also threaten key Indonesian cities, including Jakarta and Surabaya, which could stimulate ‘disruptive internal migration’ and result in serious economic losses. Unsurprisingly, the poor likely will be disproportionately impacted by all of this.
Continue reading on The Diplomat.
Sources: World Bank.
Photo Credit: “Post tsunami wreckage Banda Aceh, Sumatra, Indonesia,” courtesy of flickr user simminch.