-
Al Jazeera Maps Water Flashpoints Around the World
›Historically, the concept of “water wars” – inter-state wars fought solely over water – has been fairly unsubstantiated. But continued population growth, accelerating development, and environmental changes are making water more scarce and in turn increasing the chances of related tensions and violence. To illustrate the growing role water plays in tensions around the world, Al Jazeera has put together a map linked to a series of stories they’ve done on water “flashpoints.”
-
Ecological Footprint Accounting: Measuring Environmental Supply and Demand
›September 12, 2012 // By Kate Diamond
Twenty-five years have passed since the Brundtland Commission first brought sustainable development to international prominence. Today, the United Nations appears on track to replace the soon-to-expire Millennium Development Goals with “Sustainable Development Goals,” marking the extent to which the international community has embraced the concept. And yet, in spite of its prominence, a specific and measureable definition of sustainability remains lacking.
-
Regulating the Resource Curse: U.S. Adopts International Transparency Rules for Oil Industry
›
It’s not often that a change in accounting rules could reduce the probability of war. But that’s exactly what happened at the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) last month.
-
Nile Basin at a Turning Point as Political Changes Roil Balance of Power and Competing Demands Proliferate
›September 4, 2012 // By Carolyn Lamere
In 1979, Egyptian President Anwar Sadat famously said that “the only matter that could take Egypt to war again is water.” Sadat’s message was clear: the Nile is a matter of national security for Egypt.
Indeed, Egypt relies on the Nile for 95 percent of its water. But it is not the only state with an interest in the world’s longest river. There are 11 states in the Nile River basin, which stretches from Africa’s Great Lakes region – Tanzania, Uganda, Kenya, Rwanda, Burundi, and the Democratic Republic of the Congo – to the Ethiopian and Eritrean highlands through South Sudan, Sudan, and Egypt to the Mediterranean Sea.
-
Geoff Dabelko on the Evolution of Integrated Development and PHE
›August 27, 2012 // By Schuyler Null“Population-health-environment [PHE] connections have really been a focus of ours here at the Wilson Center for the last 15 years,” said outgoing ECSP Director Geoff Dabelko in an interview at the Wilson Center. The goal of ECSP’s project – HELPS (health, environment, livelihoods, population, and security) – is “really trying to understand these issues together.”
-
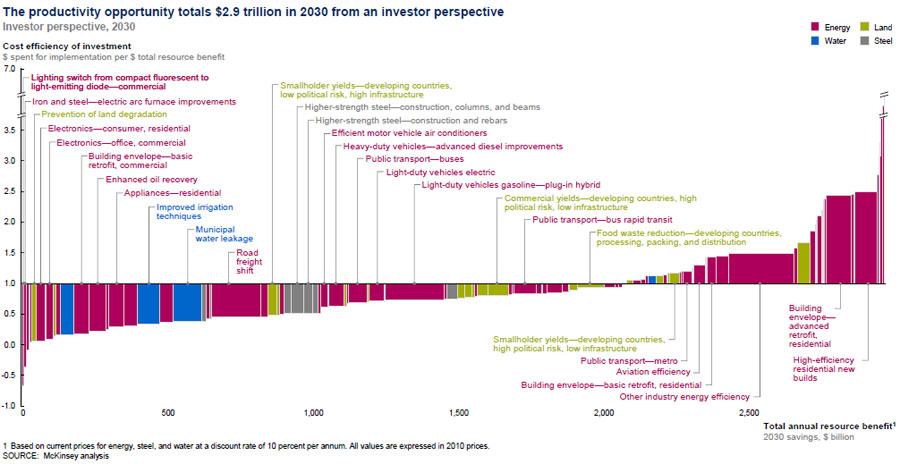
Resource Revolution: Supplying a Growing World in the Face of Scarcity and Volatility
›August 24, 2012 // By Kate DiamondOver the next two decades, as many as three billion people will join the middle class, even as billions more live without electricity, modern cooking fuel, and safe and reliable access to food and water. Resources are becoming more scarce and more difficult to extract, and combined with environmental factors ranging from climate change to soil erosion, those changes will make meeting middle class demand all the more difficult while leaving the world’s poorest more vulnerable to price shocks and resource shortages. In a recent report, the McKinsey Global Institute concludes that nothing less than a “step change” in how resources are managed will be required if individuals, businesses, and governments are to overcome these trends and pave the way for a more sustainable and equitable future.
-
Christina Larson, Yale Environment 360
Gauging the Impact of Warming On Asia’s Life-Giving Monsoons
›August 21, 2012 // By Wilson Center Staff
The original version of this article, by Christina Larson, appeared on Yale Environment 360.
Bouncing along bad roads in a jeep through central Mongolia, with bright blue skies and high clouds overhead, we drive for miles through a treeless landscape, passing only dry grasslands dotted with cattle and white yurts. But as we head north – myself, two U.S. scientists, and one Mongolian forestry expert – we begin to notice Siberian pine and larch growing on the northern slopes of rolling hills, but not the southern slopes, and at some elevations, but not others. In water-scarce Mongolia, as my travel companion Neil Pederson of Columbia University’s Lamont-Doherty Earth Observatory explained, the precarious growth of trees is limited by temperature and moisture availability; small variations – northern slopes are slightly cooler and wetter – can make all the difference.
-
Family Planning Saves Lives, Can Help Mitigate Effects of Climate Change
›Contraceptives prevented an estimated 272,040 maternal deaths in 2008, reducing worldwide maternal mortality by 44 percent, according to a recent paper by Saifuddin Ahmed, Qingfeng Li, Li Liu, and Amy O. Tsui, published in The Lancet. But the prevention of maternal deaths could have been even higher. The study, “Maternal Deaths Averted by Contraceptive Use: An Analysis of 172 Countries,” estimates that an additional 104,000 maternal deaths – many occurring in developing parts of Africa and South Asia – could have been averted simply by satisfying existing unmet need for contraception. In sub-Saharan Africa, for example, only 22 percent of women who are married or sexually active use contraception – a far cry from the 65 percent which the study suggests is the point at which maternal deaths avoided by contraceptive use begin to plateau. Not surprisingly, this has also yielded some of the highest regional fertility rates in the world.

Such high fertility rates are driving growing concerns about scarcity and capacity in the region, and how climate change might exacerbate already-difficult development hurdles. This nexus of issues was the subject of a recent policy brief by Population Action International and the African Institute for Development Policy, titled Population, Climate Change, and Sustainable Development in Africa. The brief points out that “a large share of Africa’s population lives in areas susceptible to climate variation and extreme weather events,” and that there is an inherent tension the continent faces as it seeks to balance high population growth with climate change-induced reductions in the availability of natural resources, like water and arable land. The authors urge policymakers, rather than focusing on environment, population, and health individually, to “connect population dynamics and climate change” to address their interlinked challenges together.
Showing posts from category natural resources.