Showing posts from category *Main.
-
Jay Ulfelder, Dart-Throwing Chimp
Public-Health Campaigns as Outsized Threats to Authoritarian Rule
›August 17, 2011 // By Wilson Center StaffThe original version of this article, by Jay Ulfelder, appeared on his blog, Dart-Throwing Chimp.
Are certain forms of popular activism more likely to hasten the fall of dictatorships than others? This question occurred to me after reading a recent Washington Post story describing how one Russian woman, Darya Makarova, has turned her own frustration with the poor health care given to her (now dead) young son into a wider campaign that’s has caught Moscow’s eye:Thousands have turned out for her rallies, written letters, signed petitions or joined in Internet forums. Since Maxim’s death in November, she has raised money to reopen a children’s clinic, with an emergency room, in her community. She has shamed the city into buying three new ambulances, with proper equipment. She has launched a nonprofit organization, Health Care for Children, that has national ambitions. Politicians have sought her out. Pavel Astakhov, who holds the newly created title of children’s ombudsman, came from Moscow to see her – and then appointed her his unpaid deputy, giving her more access and clout. Even officials from the sprawling and notoriously indifferent Health Ministry started to pay attention.
I can see why government officials would be nervous about this still-modest and outwardly apolitical campaign. Popular activism around matters of public health and safety seems like it should pose a special challenge to authoritarian regimes, like Russia’s, that stake their right to rule on paternalistic claims about their ability to deliver both social welfare and social protection.
Movements organized around failures of public health and safety are threatening to these regimes because they call out the paternalistic state for failing at its own game. Whatever the form of government involved, one of the modern state’s fundamental roles is to protect its citizens from public health threats. Even when they serve this function poorly, most autocrats claim to be trying, and these campaigns reveal that they are not succeeding.
Continue reading on Dart-Throwing Chimp.
Photo credit: “Your Health rests with…,” courtesy of flickr user okeos. -
Russell Sticklor, World Politics Review
The Hungry Planet: Global Food Scarcity in the 21st Century
›August 16, 2011 // By Wilson Center StaffThe original version of this article, by Russell Sticklor, appeared on World Politics Review.
At the dawn of the 20th century, the world population was inching toward a modest two billion. In the 111 years since, notwithstanding the impact of war, genocide, disease, and famine, the global population has soared, reaching three billion around 1960 and now quickly approaching the neighborhood of seven billion. By 2050, the planet will likely be home to two billion more.
We may not be witnessing the detonation of the “population bomb” that Paul Ehrlich warned of in his seminal 1968 book, but such rapid demographic change is clearly pushing the international community into uncharted territory. With a limited amount of arable land and a finite supply of fresh water for irrigation, figuring out how to feed a planet adding upward of 70 million people each year looms as one of the 21st century’s most pressing challenges.
The push to ensure global food security transcends the desire to avoid repeating the famines that devastated the Soviet Union, China, North Korea, Ethiopia, and so many other corners of the world during the past century. Instead, aid and development organizations today rightly view food insecurity problems as deeply intertwined with issues of economic development, public health, and political stability, particularly in the developing world. To maintain order in the international community and prevent the emergence of new failed states in the decades ahead, it will be critical to find innovative means of feeding the rapidly growing populations of sub-Saharan Africa, the Middle East, and South and East Asia.
Continue reading on World Politics Review.
Note: World Politics Review has graciously white-listed all entrances from NSB for this article, so as long as you use the above link, you should be able to read the full article for free.
Russell Sticklor is a consultant for the Environmental Change and Security Program.
Photo Credit: “Crowded market street,” courtesy of flickr user – yt –. -
Laurie Mazur, RH Reality Check
Why Women’s Rights Are Key to Thriving in the Age of the “Black Swan”
›August 16, 2011 // By Wilson Center StaffThe original version of this article, by Laurie Mazur, appeared on the RH Reality Check blog.
Welcome to the age of the “black swan.”
The tornado that nearly leveled the city of Joplin, Missouri in May was a black swan; so was the 9.0 magnitude earthquake and tsunami that rocked Japan in March; and the “hundred-year floods” that now take place every couple of years in the American Midwest.
A black swan is a low-probability, high-impact event that tears at the very fabric of civilization. And they are becoming more common: Weather-related disasters spiked in 2010, killing nearly 300,000 people and costing $130 billion.
Black swan events are proliferating for many reasons – notably climate change and the growing scale and interconnectedness of the human enterprise. World population doubled in the last half-century to just under seven billion people, so there are simply more people living in harm’s way, on geologic faults and along vulnerable coastlines. As the human enterprise has grown, we have reshaped natural systems to meet human needs, weakening resilience of ecosystems, and by extension our own. In effect, we have re-engineered the planet and ushered in a new era of radical instability.
At the same time, the world’s people are increasingly linked by systems of staggering complexity and size: think of electrical grids and financial markets. What were once local disasters now reverberate across the globe.
So what does this have to do with women’s rights, you may ask? A lot, as it turns out. The great challenge of the 21st century is to build societies that can cope with the flock of black swans that are headed our way. Advancing and securing women’s rights, especially reproductive rights, is central to meeting that challenge.
Continue reading on RH Reality Check.
Laurie Mazur is the editor of A Pivotal Moment: Population, Justice & the Environmental Challenge, which received a Global Media Award from the Population Institute in 2010.
Sources: Munich Re.
Photo Credut: “Cygnus atratus (Black Swan),” courtesy flickr user Arthur Chapman. -
International River Basins: Mapping Institutional Resilience to Climate Change
›Institutions that manage river basins must assess their ability to deal with variable water supplies now, said Professor Aaron Wolf of Oregon State University at the July 28 ECSP event, “International River Basins: Mapping Institutional Resilience to Change.” “A lot of the world currently can’t deal with the variability that they have today, and we see climate change as an exacerbation to an already bad situation.”
Wolf and his colleagues, Jim Duncan of the World Bank and Matt Zentner of the U.S. Department of Defense, discussed their efforts to map basins at risk for future tensions over water, as identified in their coauthored World Bank report, “Mapping the Resilience of International River Basins to Future Climate Change-Induced Water Variability.” [Video Below]
Floating Past the Rhetoric of “Water Wars”
Currently, there are 276 transnational water basins that cross the boundaries of two or more countries, said Wolf. “Forty percent of the world’s population lives within these waters, and interestingly, 80 percent of the world’s fresh water originates in basins that go through more than one country,” he said. Some of these boundaries are not particularly friendly – those along the Jordan and Indus Rivers, for example – but “to manage the water efficiently, we need to do it cooperatively,” he said.
Wolf and his colleagues found that most of the rhetoric about “water wars” was merely anecdotal, so they systematically documented how countries sharing river basins actually interact in their Basins at Risk project. The findings were surprising and counterintuitive: “Regularly we see that at any scale, two-thirds of the time we do anything over water, it is cooperative,” and actual violent conflict is extremely rare, said Wolf.
Additionally, the regions where they expected to see the most conflict – such as arid areas – were surprisingly the most cooperative. “Aridity leads to institutions to help manage aridity,” Wolf said. “You don’t need cooperation in a humid climate.”
“It’s not just about change in a basin, it’s about the relationship between change and the institutions that are developed to mitigate the impacts of change,” said Wolf. “The likelihood of conflict goes up when the rate of change in a basin exceeds the institutional capacity to absorb the change.”
Expanding the Database for Risk Assessment
Oregon State University’s Transboundary Freshwater Dispute Database (TFDD) tracks tabular and spatial information on more than 680 freshwater treaties along 276 transboundary river basins, said Jim Duncan. The team expanded the database to include recent findings on variability, as well as the impacts of climate change on the future variability of those basins. “We have a lot more information that we are able to work with now,” Duncan said.
Analyzing the institutional vulnerability of treaties along with hydrological hazards, they found the risk of tension concentrated in African basins: The Niger, Congo, and Lake Chad basins “popped out,” said Duncan. When predicting future challenges, they found that basins in other areas, such as Southeastern Asia and Central Europe, would also be at risk.
Duncan and his colleagues were able to identify very nuanced deficiencies in institutional resilience. “Over half of the treaties that have ever been signed deal with variability only in terms of flood control, and we’re only seeing about 15 percent that deal with dry season control,” said Duncan. “It’s not the actual variability, but the magnitude of departure from what they’re experiencing now that is going to be really critical.”
Beyond Scarcity
“Generally speaking, it’s not really the water so much that people are willing to fight over, but it’s the issues associated with water that cause people to have disagreements,” said Matt Zentner. Water issues are not high on the national security agendas of most governments; they only link water to national security when it actively affects other sectors of society, such as economic growth, food availability, and electric power, he said. Agricultural production – the world’s largest consumer of water – will be a major concern for governments in the future, he said, especially in developing countries economically dependent on farming.
Some experts think that current international treaties are not enough, said Zentner. Peter Gleick of the Pacific Institute has said that “the existing agreements and international principles for sharing water will not adequately handle the strain of future pressures, particularly those caused by climate change.”
How transboundary water treaties fare as the climate and consumption rates change is not as simple as measuring flow; the strength of governing institutions, the parties involved, and other variables all play major roles as well, said Zentner. “When you have flexibility built within [a treaty], it allows it to be a living, breathing, and important part of solving those [water] problems.”
Download the full event transcript here.
Sources: Oregon State University, Pacific Institute.
Photo Credit: “Confluence of the Zanskar and Indus,” courtesy of Flickr user Sanish Suresh. -
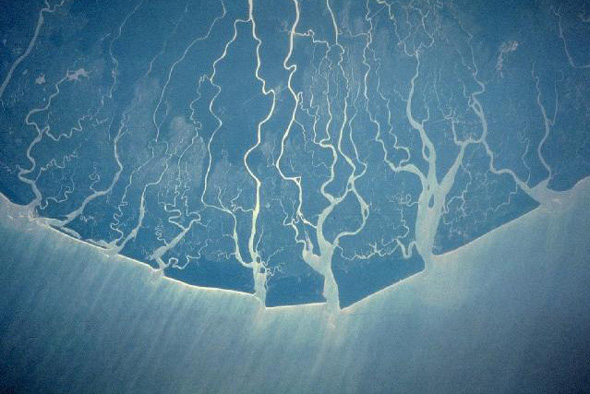
Deirdre LaPin, Niger Delta Working Group
Next Step, Clean Up the Niger Delta: The UNEP Ogoni Environmental Report
›August 12, 2011 // By Wilson Center StaffThe original version of this article, by Deirdre LaPin, appeared on the Niger Delta Working Group and AllAfrica.
The long-awaited report from the United National Environmental Program (UNEP) on oil damage in the Ogoni area was presented to President Goodluck Jonathan on August 4 in Abuja. This important study, the first of its kind in the Niger Delta, was conceived well before 2006 by the Federal Government as part of the Ogoni reconciliation and peace process led by Father Matthew Kukah (recently named Bishop of Sokoto). Intended as a major assessment of the impacts of oil production in the Ogoni region, UNEP in an early statement described the aim as to “clarify and de-mystify concerns expressed by local communities.” [Audio Below]
Shell Petroleum Development Company (SPDC) suspended active production in Ogoniland in late 1993 as a response to growing resistance to industry presence led by the martyred freedom fighter and writer Ken Saro-Wiwa. However, the company remained responsible during its withdrawal for monitoring and maintaining its installations, and especially the critical Trans-Niger pipeline serving Bonny Terminal. It also left behind a number of spill sites.
Deirdre LaPin on the History of Inequality in the Niger Delta [Excerpted Version] by ECSP WWC
Over the years the company had mixed success in negotiating with local communities access to spills sites or achieving their complete remediation. The impoverished local population also pursued informal oil production that centered on bunkering (oil pipeline tapping) and bush refining – increasing opportunities for further spills and pollution. In keeping with the “polluter pays” principle, the operator SPDC joint venture funded the U.S. $9.5 million UNEP study.
Last week the press had a field day with the freshly unveiled report.
Journalists whisked together highlights and added spice from the region’s contested history. Some articles cooked in the press kitchen missed key ingredients or simply got them mixed up. The best among them focused on the findings from the study’s careful scientific analysis, which led UNEP to the conclusion that “pollution has perhaps gone further and penetrated deeper than many may have previously supposed.”
This forceful opinion stated in the foreword by UNEP’s executive director Achim Steiner represents a long step beyond the study’s original technical terms of reference or the limited policy aims supporting reconciliation and “de-mystification.”
Now in 2011, UNEP’s thoughtful recommendations, while not assigning blame, point clearly to the need for a genuine shift in the priorities and practices of the oil industry and governmental regulatory agencies operating throughout the Niger Delta. The muscular sub-text rippling throughout the report makes clear that nothing less than ending pollution and full remediation of Ogoniland (and indeed the whole Niger Delta region) should be accepted as an end point.
Continue reading on the Niger Delta Working Group.
For more on the Niger Delta, be sure to also read “Nigeria’s Future Clouded by Oil, Climate Change, and Scarcity,” which includes the full audio interview with Deidre LaPin (excerpted above) on the history of the Niger Delta.
Sources: UNEP.
Photo Credit: NASA Space Shuttle Overflight photo of the Niger Delta, courtesy of NASA. -
Benefits of Integrating Population, Health, and Environment
›“Mainstreaming Environment and Climate Change: Health,” a joint publication from the International Institute for Environment and Development and Irish Aid, is part of a series that aims to show the links between the environment, climate change, and key development sectors, while suggesting key solutions to move into national policies. This health-focused briefing asserts that “nearly one quarter of the global disease burden can be attributed to the environment.” While anyone is prone to the negative effects of climate change, the poor are especially vulnerable because they often live in some of the most precarious environmental conditions. Consequently, the briefing argues that “improving environmental health – raising its profile at national, state and local levels, and integrating environmental health issues into development plans and activities – is critical if we are to reduce poverty and meet the Millennium Development Goals.”
In An Assessment of the Benefits of Integrating Family Planning and Environmental Management Activities in the Visayas Region of the Philippines, a study from the University of Rhode Island’s Coastal Resources Center, authors Richard B. Pollnac and Kira Dacanay argue that benefits can be reaped from integrated population, health and environment (PHE) development, but only under certain conditions. Factors influencing the level of benefits include “levels of participation in integrated projects [both by individuals and communities], and how NGOs implement these projects.” Thus, it is important to “tailor strategies based on place-based context and personal characteristics of different participants,” write Pollnac and Dacanay. In the Philippines, the authors suggest that one of the actions future PHE initiatives should take is to “stimulate more project participation, with special efforts in larger, less dense communities and tailor strategies better to different targeted populations within the community.” -
Robert Engelman, Yale Environment 360
The World at 7 Billion: Can We Stop Growing Now?
›August 11, 2011 // By Wilson Center StaffThe original version of this article, by Robert Engelman, appeared on Yale Environment 360.
Demographers aren’t known for their sense of humor, but the ones who work for the United Nations recently announced that the world’s human population will hit seven billion on Halloween this year. Since censuses and other surveys can scarcely justify such a precise calculation, it’s tempting to imagine that the UN Population Division, the data shop that pinpointed the Day of 7 Billion, is hinting that we should all be afraid, be very afraid.
We have reason to be. The 21st century is not yet a dozen years old, and there are already one billion more people than in October 1999 – with the outlook for future energy and food supplies looking bleaker than it has for decades. It took humanity until the early 19th century to gain its first billion people; then another 1.5 billion followed over the next century and a half. In just the last 60 years the world’s population has gained yet another 4.5 billion. Never before have so many animals of one species anything like our size inhabited the planet.
And this species interacts with its surroundings far more intensely than any other ever has. Planet Earth has become Planet Humanity, as we co-opt its carbon, water, and nitrogen cycles so completely that no other force can compare. For the first time in life’s 3-billion-plus-year history, one form of life – ours – condemns to extinction significant proportions of the plants and animals that are our only known companions in the universe.
Did someone just remark that these impacts don’t stem from our population, but from our consumption? Probably, as this assertion emerges often from journals, books, and the blogosphere. It’s as though a geometry text were to propound the axiom that it is not length that determines the area of a rectangle, but width. Would we worry about our individual consumption of energy and natural resources if humanity still had the stable population of roughly 300 million people – less than today’s U.S. number – that the species maintained throughout the first millennium of the current era?
Continue reading on Yale Environment 360.
Robert Engelman is executive director of the Worldwatch Institute, an environmental research organization based in Washington, D.C.
Photo Credit: “Daybreak,” courtesy of flickr user Undertow851. Dawn breaks over California in the United States April 17, 2011 in this photo by NASA astronaut Ron Garan from the International Space Station. The lights of Los Angeles appear in the foreground while San Francisco appears in the back near the horizon. -
Conflict Minerals in the DRC: Still Fighting Over the Dodd-Frank Act, One Year Later
›August 11, 2011 // By Schuyler Null
One year after the Dodd-Frank Act passed Congress with a provision that was aimed at preventing the sourcing of “conflict minerals” by SEC-registered companies, backlash seems to be growing over the impact of the measure, particularly on artisanal miners in the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC).