-
The Ramsar Convention: A New Window for Environmental Diplomacy?
›In seeking ways to connect conservation with peacemaking, the Institute for Environmental Diplomacy and Security (IEDS) has released a study that examines an expanded role for the international wetlands treaty, the Ramsar Convention.
The Ramsar Convention: A New Window for Environmental Diplomacy? describes the wetlands convention, its place within the international environmental treaty world, and its potential to enhance environmental security during this dynamic time of increasingly insecure water supplies and climate change. With more than 40 years of work, the treaty has been quietly and effectively conserving wetlands and increasing recognition of the need to build international cooperation around them. The treaty has also helped define wetlands within greater biogeographic regions and led to formal identification of transboundary wetlands.
In the article, we set out to combine information from the convention’s 234 listed wetlands (13 of which have formal transboundary plans) with the Global Peace Index, which ranks countries using 23 indicators, such as number of conflicts, conflict deaths, military expenditures, and relations with neighboring countries. The result is a prioritized list of countries most in need of tools of conflict resolution.
Working within the framework of the convention builds capacity between high-conflict-risk nations and has potential to develop otherwise-difficult-to-establish trust because the process is transparent and all stakeholder voices are heard. This can be important even when the existing conflict has nothing to do with international wetlands.
The convention is active in many countries with ongoing conflicts, such as Afghanistan, the Democratic Republic of the Congo, Iran, Iraq, and Sudan, and efforts there may help inform the ongoing debate as to the efficacy of conservation as a tool for peacemaking.
As environmental conditions continue to evolve rapidly, the need for institutions that can work in the transboundary environment will increase. The established international infrastructure of the convention has the potential to be a greater force in peacemaking. Further research may help focus on the strengths and weaknesses of the current system and reveal ways for more effective peacemaking efforts.
Suggestions for ways to enhance the convention’s role in environmental diplomacy include working more closely with researchers and practitioners directly involved in the environmental peacemaking field, increased focus on developing capacity for increased flexibility to react to dynamic conditions, and more active promotion of formal transboundary agreements.
Pamela Griffin is an independent scholar at IEDS where she focuses on the diplomatic potential of transboundary wetlands. -
Taking a Livelihoods Approach to Understanding Environmental Security
›February 17, 2012 // By Kate DiamondSince the concept of “environmental security” first gained traction in the early 1990s, research on the issue has been overwhelmingly focused on how environmental change impacts state security. That has been to the detriment of policymakers trying to preempt instability and conflict, according to the University of Toronto’s Tom Deligiannis in his article, “The Evolution of Environment-Conflict Research: Toward a Livelihood Framework,” published in February’s Global Environmental Politics.
-
‘Dialogue TV’ With Sharon Burke, Neil Morisetti, and Geoff Dabelko: Climate, Energy, and the Military
›We are entering “an emerging security environment” where “what constitutes a ‘threat’ and what constitutes a ‘challenge’” requires a broader understanding of security than has often been the norm, according to Sharon Burke, Assistant Secretary of Defense for Operational Energy Plans and Programs. Burke was joined by the UK’s Climate and Energy Security Envoy Rear Admiral Neil Morisetti and ECSP’s Geoff Dabelko on a new installment of Dialogue TV. They debated what climate change and energy security mean for the world’s militaries.
-
Assigning Value to Biodiversity, and the 2011 Human Development Report
›New research in the journal BioScience reports the aggregate economic benefits of conserving high priority biodiversity areas outweigh the opportunity costs of alternative land uses by a multiple of three (where priority is assigned according to a global index of the mapped distributions of 4,388 threatened terrestrial species). The authors of “Global Biodiversity Conservation and the Alleviation of Poverty,” led by Will Turner, estimate the value of highly diverse habitats to the global poor in terms of direct benefits and potential external payments for ecosystem services. They find these environmental flows in excess of $1 per person, per day, for 331 million of the world’s poorest individuals and conclude by arguing that, “although trade-offs remain…results show win-win synergies…and suggest biodiversity conservation as a fundamental component of sustainable economic development.” (For further discussion of development around biodiversity hotspots, see Population Action International’s work on population growth.)
The 2011 UNDP Human Development Report, Sustainability and Equity: A Better Future for All, builds from the understanding that a “failure to reduce…grave environmental risks and deepening social inequalities threatens to slow decades of sustained progress by the world’s poor majority.” A resilient thread in the report highlights the importance of working to ensure women’s equality and reproductive rights for sustainability, claiming that “meeting unmet need for family planning by 2050 would lower the world’s carbon emissions an estimated 17 percent below what they are today.” The report closes with a wide range of policy suggestions that work towards the goal of equating sustainability and equity, including a supportive discussion of a currency transaction tax as a novel and feasible method of providing climate financing.
These pieces address contradictions between environmentally sustainable behavior and the development imperative. Though both acknowledge that the traditional development model of high intensity economic growth has imperiled the environment upon which the livelihoods of many hundreds of millions depend, they suggest practical ways forward. The Human Development Report in particular adopts some of the strongest language yet, claiming that, “the message is clear: our development model is bumping up against concrete limits.” This honest attempt to work through, rather than around, the tension between development and sustainability is perhaps an indication that we are at last beginning to take seriously the concept of sustainable development. -
Afghanistan and Pakistan: Demographic Siblings? [Part Two]
›February 15, 2012 // By Elizabeth Leahy MadsenLate last year, Afghanistan’s first-ever nationally representative survey of demographic and health issues was published, providing estimates of indicators that had previously been modeled or inferred from smaller samples. My first post on the survey focused on the methodology and results, which found that Afghanistan is not as much of a demographic outlier as many observers had assumed. But perhaps the most surprising finding is how the results compare to those of Afghanistan’s neighbor, Pakistan.
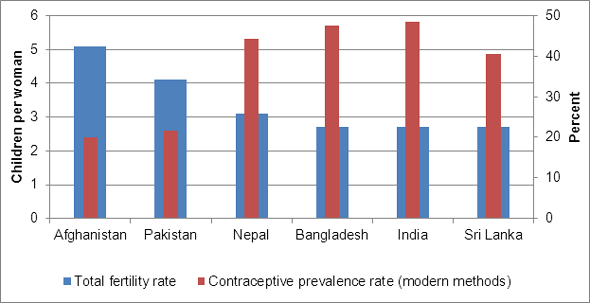
The political future of each country depends largely on the other and, with Afghanistan making progress on reproductive health issues that remain stalled in Pakistan, their demographic trajectories are heading toward closer synchronization as well. In one key measure – use of contraception among married women – Afghanistan is almost identical to Pakistan. The modern contraceptive prevalence rate is 19.9 percent, slightly lower than the rate of 21.7 percent in Pakistan.
While Pakistan faces its own serious political instability, it is widely regarded as more developed than its neighbor. Afghanistan is included in the UN’s grouping of least developed countries, and Pakistan is not. Pakistan’s GDP per capita is almost twice as high. On the surface, this should suggest lower fertility. There is a general negative relationship between economic development and fertility, though demographers are quick to point out its complexities, and David Shapiro and colleagues have found that countries with larger increases in GDP actually experience slower fertility declines.
Pakistan’s fertility rate of 4.1 children per woman is in fact 20 percent lower than Afghanistan’s, but the similarities in contraceptive use, which is one of the direct determinants of fertility, suggest that this gap could be shrinking. If Afghanistan’s median age at marriage (18 compared to 20 in Pakistan) was higher and more women were educated (76 percent of women have never been to school compared to 65 percent in Pakistan), the two fertility rates might be closer.
Pakistan’s Entrenched Challenge
Why are these indicators closer than might be expected? Relative to the other countries in South Asia, Pakistan has had considerably less success in promoting family planning use. Bangladesh has a per capita income about half that of India and one-quarter that of Sri Lanka, yet the three countries’ fertility rates are identical. Nepal has the lowest income in the region – even slightly below Afghanistan – yet more than 40 percent of married women use modern contraception and fertility is three children per woman. And then there is Pakistan. Despite a per capita income 90 percent that of India, only 22 percent of married women use modern contraception and fertility remains persistently high at over four children per woman.
The weaknesses of Pakistan’s family planning program have been well-documented. Government commitment has been lacking and cultural expectations and gender inequities are a powerful force to promote large family size. The country’s most recent DHS report cited disengagement with the program among local agencies, low levels of outreach into communities, and weak health sector support as likely causes for the stagnation of contraceptive use. In summer 2011, the Pakistani government abolished the federal Ministry of Health and empowered provincial governments with all responsibilities for health services. This transfer of authority could pay dividends by increasing local ownership of health care, but some in and outside Pakistan have raised concerns about the loss of regulatory oversight and information sharing entailed in total decentralization.
Compared to the Afghanistan survey, the most recent Pakistan Demographic and Health Survey provides more detail on women’s motivations and preferences regarding fertility and family planning. Overall, 55 percent of married women in Pakistan have a “demand” for family planning; that is, they wish to avoid pregnancy or report that their most recent pregnancy or birth was mistimed or unwanted. More than half of these women are using family planning, while the remaining 25 percent of married women have an “unmet need.”
Unintended pregnancies and births play a major role in shaping Pakistan’s demographic trajectory. The DHS survey finds that 24 percent of births occur earlier than women would like or were not wanted at all. If unwanted births were prevented, Pakistan’s fertility rate would be 3.1 children per woman rather than 4.1. Yet 30 percent of married women are using no contraceptive method and do not intend to in the future. The most common reasons for not intending to use family planning are that fertility is “up to God” and that the woman or her husband is opposed to it.
Linked Destinies
Just as Afghanistan and Pakistan’s political circumstances have become more entwined, their demographic paths are more closely in parallel than we might have expected. For Afghanistan, given the myriad challenges in the socioeconomic, political, cultural, and geographic environments, this is good news; for Pakistan, where efforts to meet family planning needs have fallen short of capacity, it is not. While Afghanistan is doing better than expected, Pakistan should be doing better.
Regardless, both countries are at an important juncture. With very young age structures and the attendant pressures on employment and government stability, each government must reduce unmet need for family planning or face mounting difficulties to providing for their populations in the future. In addition to rolling out health services, turning the share of women without education from a majority into zero would be an excellent way to start.
Elizabeth Leahy Madsen is a consultant on political demography for the Wilson Center’s Environmental Change and Security Program and senior technical advisor at Futures Group.
Sources: Afghanistan Ministry of Public Health, Bongaarts (2008, 1978), Cincotta (2009), Embassy of Afghanistan, Haub (2009), International Monetary Fund, MEASURE DHS, Nishtar (2011), Population Action International, Savedoff (2011), Shapiro et al. (2011), UN-OHRLLS, UN Population Division, U.S. Census Bureau, The Washington Post.
Image Credit: Chart arranged by Elizabeth Leahy Madsen, data from MEASURE DHS. -
Afghanistan’s First Demographic and Health Survey Reveals Surprises [Part One]
›February 14, 2012 // By Elizabeth Leahy Madsen
Late last year, Afghanistan’s first-ever nationally representative survey of demographic and health issues was published, providing estimates of indicators that had previously been modeled or inferred from smaller samples. It shows that Afghan women have an average of five children each, lower than most experts had anticipated, and that their rate of modern contraceptive use is just slightly lower than that of women in neighboring Pakistan.
-
Michael D. Lemonick, Climate Central
Challenge of Making Climate Change News Sound Newsy
›The original version of this article, by Michael D. Lemonick, appeared on Climate Central.
Dog bites man: news or not? If you’re a journalist, you don’t even need to think about it. The phrase is our professional shorthand for an idea that hardly qualifies as news, that it’s not out of the ordinary. Man bites dog (goes the second half of the cliché), now that’s news!
It’s not an ironclad rule, though: if the dog bites the man after winning first place at the Westminster Dog Show, or if a marauding dog is biting its way through a terrified neighborhood, or if First Dog Bo bites Sasha or Malia – that’s news, too.
So when January 2012 was officially declared America’s fourth warmest January on record by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), was that news or not? Here at Climate Central, we thought it was. But then, we would. Do a Google News search, and you’ll find that a whopping eight news outlets agreed with us, and one of them was the Weather Channel, so it hardly counts. (Extra points to msnbc.com, which came up with a clever angle: It feels like it must be the warmest January ever, but surprise! It’s only fourth!) But for most media, it was kind of ho-hum, because, really, haven’t we heard it all before? It’s always the warmest this, or the second-warmest that.
For scientists who think about climate, though, that’s the point. Especially in the past decade – a time when climate skeptics argue, bizarrely, that global warming has stopped – these records or near-records are being set all the time, and extreme weather events, including droughts, heat waves, and torrential storms, have been more frequent and more severe.
Continue reading on Climate Central.
Sources: National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration.
Image Credit: “India – climate change canvas,” courtesy of Piotr Fajfer/Oxfam International. -
‘Marketplace’ and ‘NewsHour’ Highlight Population, Health, and Environment Program in the Philippines
›The Danajon reef is the only double barrier reef in the Philippines, “one of the richest marine biodiversity hot spots in the world,” and it’s being devastated as the country’s exploding population depends on its waters for their food and livelihoods, reported Sam Eaton in a recent two-part series on population, health, and environment issues in the Philippines broadcast last month for American Public Media’s Marketplace and the PBS NewsHour.
The report is part of joint project called Food for 9 Billion, with Homelands Productions, the Center for Investigative Reporting, APM, and PBS. Previous reports examined food security in East Africa and Egypt.
The Philippines “import more rice than any other country on the planet,” said Eaton. The “highest population growth rates in all of Southeast Asia” as well as dwindling natural resources – nearly 100 million people live in a land area the size of Arizona – have created a cycle of poverty. The first step to breaking that cycle, he said, is improving access to family planning.
Growing Families, Growing Poverty
The Canayong family, living on the edge of a garbage dump in a Manila slum, offers a vivid example of what poverty means in the Philippines. Clarissa Canayong has had 14 children – 4 died from measles and dengue fever, the remaining 10 spend their days alongside Clarissa, sifting through the dump for things they need and things they can sell. At the end of a good day, the family has earned around $7 to survive on. All in all, Clarissa’s “inability to provide enough food, and to pay for her children’s education, all but guarantees she and her family will remain poor,” said Eaton.
The archipelago adds about two million people every year, putting population on track to double in size sometime around 2080. “And that’s only if something is done to close the birth control gap,” said Eaton, as those projections build in an expectation that growth will slow.
“As cities all across the country expand, the displaced often end up migrating to urban slums,” he said. “Population growth among poor Filipinos is twice the national average,” meaning that once a family enters poverty, they end up in a cycle “that’s nearly impossible to break.”
The Difference Family Planning Can Make
If Clarissa had had access to family planning, she told Eaton, she would have wanted to have only two children. In Humayhumay, where residents have access to a community-based family planning distribution program started by PATH Foundation Philippines, Inc., families have that luxury of choice.
Working through local partners, the PATH Foundation identifies and trains community-based vendors to sell contraception – both pills and condoms, said Dr. Joan Castro, who began the program in Humayhumay. The idea is to make buying contraceptives “as easy as buying soft drinks or matches.”
Both Jason Bostero, a farmer and fisherman in Humayhuay, and his wife, Crisna, grew up in large families – so large, in Crisna’s case, that “sometimes, we would only eat once a day because we were so poor. We couldn’t go to school. I did not finish school because there were just so many of us,” she told Eaton.
Now that they have access to contraceptives, a smaller family size means their income is “just right” to feed everyone three times a day. For the community as a whole, smaller family sizes mean that the nearby fish stocks that provide the community with food and income have a chance to replenish themselves in the absence of overfishing.
“In just six years since the program was first established here,” reported Eaton, “family sizes have plummeted from as many as 12 children to a maximum of about 4 today.”
Exception to the Rule
Humayhumay is an exception to the rule in the Philippines. There is no state funding for birth control in the country, and over the past few years, major international donors like USAID and the United Nations have ended their family planning work in the country. More than a quarter of poor Filipinos have no access to any type of family planning service, and more than half of all pregnancies are unintended, said Eaton.
Family planning has long been a contentious issue in the country. Eaton spoke to Congressman Walden Bello, who has spent more than a decade trying to pass legislation to establish universal access to birth control and improve other family planning and reproductive services. The Catholic Church, said Bello, is a powerful (80 percent of Filipinos are Catholic) and consistent opponent. In October 2010, the Church went so far as to threaten President Benigno Aquino with excommunication after he voiced support for access to contraception.
Rather than limit population growth, the Church argues the country should increase food production. But land is limited, rice imports are already the highest in the world, and, “according to the World Bank, every major species of fish here shows signs of severe overfishing,” said Eaton.
Looking Forward and Abroad
Eaton pointed to the Philippines’ neighbors as examples to emulate: “A long history of government-supported family planning has…paved the way for Thailand to become one of the world’s biggest rice exporters” and helped to cut back poverty in the country, said Eaton.
Indonesia too, he pointed out, has largely avoided the population growth-resource depletion-poverty cycle, thanks in part to a state- and faith-backed family planning program. (As Elizabeth Leahy Madsen wrote in a recent New Security Beat post, the decision of Indonesia’s religious leaders to throw their support behind family planning in the 1960s was a key factor in success there.)
Considering the obstacles, the Philippines face an uphill battle before family planning services become similarly universal. But the political tides may already be turning: last April, the President said he would support the reproductive health legislation even if it meant excommunication.
Meanwhile, PATH Foundation’s Castro is hopeful that Humayhumay’s success story will lay the seeds for widespread public support for family planning. “The vision of the project is in this community you see more children educated who are able to become leaders and speak out for themselves in the future and be able to become stewards of their own sexuality and the future environment,” said Castro. “This is the legacy.”
Sources: BBC, Bloomberg News, Catholic News Agency, The Guardian, Population Reference Bureau, TIME Magazine, US Agency for International Development, U.S. Catholic.
Showing posts from category *Main.