-
Resource Revolution: Supplying a Growing World in the Face of Scarcity and Volatility
›August 24, 2012 // By Kate DiamondOver the next two decades, as many as three billion people will join the middle class, even as billions more live without electricity, modern cooking fuel, and safe and reliable access to food and water. Resources are becoming more scarce and more difficult to extract, and combined with environmental factors ranging from climate change to soil erosion, those changes will make meeting middle class demand all the more difficult while leaving the world’s poorest more vulnerable to price shocks and resource shortages. In a recent report, the McKinsey Global Institute concludes that nothing less than a “step change” in how resources are managed will be required if individuals, businesses, and governments are to overcome these trends and pave the way for a more sustainable and equitable future.
-
Michael Kugelman, Sustainable Security
The Global Land Rush: Catalyst for Resource-Driven Conflict?
›July 31, 2012 // By Wilson Center StaffThe original version of this article, by Michael Kugelman, appeared on SustainableSecurity.org.
On May 11, the UN approved new international rules to govern how land is acquired abroad. These Voluntary Guidelines (VGs), the outcome of several years of protracted negotiations, are a response to growing global concern that nations and private investors are seizing large swaths of overseas agricultural land owned or used by small farmers and local communities for food, medicinal, or livelihood purposes. FAO head Jose Graziano da Silva describes the VGs as “a starting point that will help improve the often dire situation of the hungry and poor.”
It’s hard to quibble with the intent of the guidelines. They call for, among other things, protecting the land rights of local communities; promoting gender equality in land title acquisition; and offering legal assistance during land disputes.
Unfortunately, however, any utility deriving from the VGs will be strictly normative. As their name states explicitly, they are purely optional. A toothless set of non-obligatory rules will prove no match for a strategy that is striking both for its scale and for the tremendous power of its executioners.
Oxfam estimates that nearly 230 million hectares of land (an area equivalent to the size of Western Europe) have been sold or leased since 2001 (with most of these transactions occurring since 2008). According to GRAIN, a global land rights NGO, more than two million hectares were subjected to transactions during the first four months of 2012 alone. One of the largest proposed deals – an attempt by South Korea’s Daewoo corporation to acquire 1.3 million hectares of farmland in Madagascar – failed back in 2009. Still, even larger investments are being planned today, including a Brazilian effort to acquire a whopping six million hectares of land in Mozambique to produce corn and soy (Mozambique offered a concession last year).
Continue reading on SustainableSecurity.org.
Sources: BBC, Food and Agriculture Organization, GRAIN, MercoPress, Oxfam, Reuters.
Photo Credit: “Garde armé,” courtesy of flickr user Planète à vendre. -
In Mongolia, Climate Change and Mining Boom Threaten National Identity
›July 23, 2012 // By Kate Diamond
Mongolia, a vast, sparsely populated country almost as large as Western Europe, is at once strikingly poor and strikingly rich. Its GDP per capita falls just below that of war-torn Iraq, and Ulan Bator has some of the worst air pollution ever recorded in a capital city. At the same time, Mongolia sits atop some of the world’s largest mineral reserves, worth trillions of dollars, and its economy, already one of the world’s fastest growing, could expand by a factor of six by the end of the decade as those reserves are developed.
-
Fiona Harvey, The Guardian
Re|Source 2012 Conference: Global Fight for Natural Resources “Has Only Just Begun”
›July 18, 2012 // By Wilson Center StaffThe original version of this article, by Fiona Harvey, appeared in The Guardian.
The global battle for natural resources – from food and water to energy and precious metals – is only beginning, and will intensify to proportions that could mean enormous upheavals for every country, leading academics and business figures told a conference in Oxford on Thursday.
Sir David King, former chief scientific adviser to the UK government, who convened the two-day Re|Source 2012 conference, told The Guardian: “We are nowhere near realizing the full impact of this yet. We have seen the first indications – rising food prices, pressure on water supplies, a land grab by some countries for mining rights and fertile agricultural land, and rising prices for energy and for key resources [such as] metals. But we need to do far more to deal with these problems before they become even more acute, and we are not doing enough yet.”
Countries that are not prepared for this rapid change will soon – perhaps irrevocably – lose out, with serious damage to their economies and way of life, the conference was told.
Amartya Sen, a Nobel prize-winning economist, said that the free market would not necessarily provide the best solution to sharing out the world’s resources. Governments would need to step in, he said, to ensure that people had access to the basics of life, and that the interests of businesses and the financial markets did not win out over more fundamental human needs.
Continue reading on The Guardian.
Photo Credit: “Aerial view of the Jonah natural gas field, upper Green River valley, Wyoming, 2001,” courtesy of flickr user SkyTruth and Peter Aengst/The Wilderness Society. -
IFPRI Launches First ‘Global Food Policy Report’
›June 27, 2012 // By Carolyn Lamere“The Global Food Policy Report is the first publication that represents the major, major food policy developments in the past year and the outlook for 2012,” said Director of the International Food Policy Research Institute (IFPRI) Shenggen Fan in a video to promote the launch of the institute’s most comprehensive policy publication yet. The report is focused on regional developments, new research, debates, and legislation regarding food security both within individual states and at the international level.
A Guidebook for Policy
The 2008 global food crisis launched food security back onto the global agenda. A rapid rise in food prices contributed to instability around the world, and policymakers began to realize that access to food is an important security issue (high food prices have been linked to riots, for example).
“For 2012, food prices will remain very high and volatile, and some of the long-term trends like climate change, population growth, and demographic shifts towards more urbanized and higher income [populations] will continue to put pressure on global food security,” predicted Fan.
But the report notes that much of the fluctuation in global food prices is due to a lack of knowledge, not necessarily scarcity. The authors point to issues of preparedness and regulation as exacerbating factors and suggest that more detailed information, like that provided in the report, can help provide better solutions to policymakers.
Fan said that, by design, the report is “nontechnical, so the nontechnical person such as politicians, policymakers, practitioners, or anybody else who is interested in food security can use it as a comprehensive handbook.”
Making Connections Between Disciplines
The report draws on the expertise of dozens of authors who discuss topics ranging from biofuels to climate change. Rajul Pandya-Lorch, head of IFPRI’s 2020 Vision Initiative, spoke about the utility of collaboration among different disciplines in an interview with IFPRI: “I think for me 2011 was the time when we began to realize that we cannot think of agriculture simply for agriculture; we need to think of agriculture as a way in which we can impact on other development outcomes, especially nutrition and health,” she said.
Kathy Spahn, president and CEO of Helen Keller International, a speaker at the launch event, agreed. “The development community is beginning to realize that achieving food security is about more than just growing more food. It is also about growing more nutritious foods and making sure these foods are available and accessible to the families in need,” she wrote for Helen Keller International.
Fan emphasized that although agriculture has become more prominently featured in discussions of development, it is important to continue to link it to other outcomes. “We must find new ways to exploit the links between agriculture and other sectors, including health, nutrition, water, and energy,” he wrote in the overview of the report.
Past Developments and Future Outlook
Several key developments are highlighted that shaped food security in 2011. Food prices were particularly volatile – rising for the first half of the year then dropping – which caused a renewed global emphasis on food from policymakers.
New players ranging from emerging economies to the private sector “are increasingly reshaping the structure and nature of the global food landscape,” write the authors. The G-20 is “claiming a growing role” to help manage economic issues, and states like China, Brazil, and India are becoming more vocal regarding global food policy. Partnerships between governments and private companies have also become more common.
These and other developments described in the report will have an impact into 2012 and beyond. The report points out that “food emergencies” caused by natural disasters like the 2011 drought in the Horn of Africa will likely occur in 2012 as well, but also emphasizes that these cannot overshadow more long-term drivers of food insecurity, like land degradation.
The report describes four “high-priority areas of action” for this year. First, the G-20 should try to reduce price volatility (although some have argued volatility is less a problem than consistently high prices). Second, policymakers should work to improve agricultural production specifically through strategies like soil nutrient management which provide high yields but are more sustainable than high use of fertilizers. States should also ensure that the infrastructure necessary to make these strategies successful is in place. The next target is based on the Rio+20 conference, namely that participants should “integrate economic, social, and environmental sustainability efforts” to improve outcomes like nutrition and health. There were in fact several seminars on cross-discipline partnerships at the conference, and the importance of integration was mentioned in the outcome text that emerged.
Finally, the report calls for further collaboration across disciplines, in emulation of the internal IFPRI effort for the report which included a wide variety of expertise. The authors emphasized that though progress has been made, the challenge of achieving global food security will remain a concern for the near future, and cooperation across communities will be critical.
“The idea and the impact of the report is to make people aware of the problems that we are facing and the concerns…clearly the problem is not resolved and it’s something that we need to take very seriously,” said contributor Maximo Torero in an interview with IFPRI. “There’s a lot of work to be done to try to do this.”
Sources: Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation, CNN, Hellen Keller International, International Food Policy Research Institute, UN Conference on Sustainable Development.
Video Credit: IFPRI. -
African Nations Pioneer Natural Resource Accounting With ‘Gaborone Declaration’
›June 20, 2012 // By Graham NorwoodIn a move with potentially substantial ramifications for future sustainable development, 10 African nations have agreed to begin assigning monetary value to the benefits provided by non-commodity natural resources, including ecosystems such as forests, grasslands, and coral reefs.
Botswana, Gabon, Ghana, Kenya, Liberia, Mozambique, Namibia, Rwanda, South Africa, and Tanzania each affirmed their support for the “Gaborone Declaration” during last month’s Summit for Sustainability in Africa, co-hosted by Conservation International and the government of Botswana. The goal, according to Botswanan President Ian Khama, is to include these new valuations in national accounting, providing policymakers a clear perspective on the costs and benefits associated with the development or conservation of their natural resources for the first time.
Coming just prior to the Rio+20 conference, the signatories said they hoped assigning calculable costs to resource usage would encourage more sustainable development by bringing hitherto “invisible” costs and externalities into the open and onto the balance sheet.
Though the challenges of properly assessing the values of various ecosystem services are understandably many, the potential benefits of natural capital accounting are substantial.
According to SciDev.Net, the World Bank’s Vice President for Sustainable Development Rachel Kyte spoke in support of the declaration at the summit. She pointed out, for example, the advantage of knowing that a hectare of mangrove trees in a certain region of Thailand has been calculated to provide approximately $16,000 of flood protection when considering whether to clear-cut and sell the raw wood (worth about $850), convert the region into a shrimp farm ($9,000), or preserve it.
Such accounting may be particularly beneficial to the Gaborone signatories and other African nations, given growing concern among experts about foreign investment in land, natural resources, and even water on the continent.
But the declaration – and the very idea of natural capital accounting – is not without controversy.
Some argue that commodifying such resources will actually encourage their destruction rather than protect them by ascribing monetary values to previously free and shared resources, thus advantaging richer stakeholders and nations at the expense of poorer ones. As Hannah Griffiths of the UK-based World Development Movement recently wrote in The Guardian, “the result [of natural resource accounting] would be the further privatisation of essential elements of our planet to which we all share rights and have responsibilities.”
Along these lines, Nigerian environmental activist and chair of Friends of the Earth International, Nnimmo Bassey, has voiced his strenuous opposition to the plan made at the summit. “This declaration is blind to the fact that the bait of revenue from natural capital is simply a cover for continued rape of African natural resources,” he said in SciDev.
However, the signatories of the Gaborone Declaration dismissed these concerns and pointed to the value of natural resource accounting for sustainable development.
“Africa is where sustained and sustainable economic growth and stewardship of natural wealth become one and the same thing,” said Kyte at the summit. “By endorsing natural capital accounting as a tool for delivering on more inclusive green growth, Africa is showing the way for the rest of the world.”
Conservation International CEO and Chairman Peter Seligmann agreed, calling the declaration “a very big deal, a very big moment, and a big step forward.” He connected it to the imminent Rio+20 conference as well, saying the pledge is “truly a beacon on the hill for the rest of societies” and that “it will be held up on top of that hill in Rio de Janeiro.”
Indeed, the World Bank has listed natural capital accounting as one of six key issues for Rio+20, and in a report last month titled Inclusive Green Growth: The Pathway to Sustainable Development, noted that “it is vital that economic values for environmental assets be comparable to other economic values.”
The World Bank has already made significant progress in promoting the practice through its Wealth Accounting and the Valuation of Ecosystem Services (WAVES) global partnership, encouraging at least 24 countries to use some form of natural resource accounting to date. WAVES aims to sign up 50 more nations and 50 private corporations beginning at Rio+20, as a part of its “50:50 Campaign.”
WAVES and the Gaborone Declaration show that natural capital accounting is gaining momentum as a means to incentivize more sustainable development. The international news media is beginning to take notice as well. The results of the Rio+20 conference will be a good opportunity to gauge just how far the idea has come and what the extent of its future application might be.
Sources: Conservation International, The Guardian, SciDev.Net, World Bank.
Photo Credit: “Saving the Sacred Rock,” courtesy of flickr user isurusen (Isuru Senevi); video: The World Bank. -
Comparing Urban Governance and Citizen Rights in China and India
›Today, according to Xuefei Ren, 129 cities in China and 45 in India have populations of over a million people. Such large-scale urbanization has created major governance challenges. Speaking at a May 23 Asia Program event co-sponsored with the Kissinger Institute on China, United States Studies, and the Comparative Urban Studies Project, Ren, a Wilson Center Fellow, examined two case studies of urbanization-driven governance in China and India and their effect on citizen rights.
Her first case study involved housing demolitions and urban re-development in Shanghai and Mumbai. In Shanghai, nearly a million households were relocated between 1995 and 2008 to make way for hotels, airports, and luxury apartments. City regulations in 1991 and 2001 legalized forced demolitions, and no prior consent from residents was needed.
However, Ren noted that displaced residents “are not quite powerless.” She highlighted the case of a woman who sued the city government after being relocated and was eventually granted the compensation she had requested. In 2003, China’s central government ordered a freeze on large-scale demolitions. Several years later, it passed a “landmark” property rights law.
Meanwhile, in Mumbai, local officials in the early 2000s had their own re-development plans. The Indian city is rife with overcrowded, low-income housing; slums are populated by seven million citizens (40 percent of the city’s total population), and comprise up to 10 percent of Mumbai’s total land area.
In 2004, aware that most of the slums were located in desirable areas – near airports or in central business districts – city planners recognized a major development opportunity. Over the next two years, officials launched a demolition campaign that left 400,000 people homeless. According to Ren, certain categories of residents were theoretically entitled to compensation, but with “legal protections carrying little weight,” most of them received nothing.
Yet, as in Shanghai, Mumbai’s city dwellers successfully fought back. Housing activists staged acts of “direct agitation,” including a series of street protests and road blockages. Such tactics, said Ren, were “disruptive but effective.” The Mumbai courts sided against the activists in 2006, but India’s Supreme Court later issued a ruling in their favor.
Fighting Land Acquisitions: A Comparison
Ren’s second case study compared land acquisition efforts outside the slums.
Last year, residents in Wukan, a village along China’s southeast coast in the province of Guangdong, launched a protest movement against land seizures. They alleged that government officials had sold their land to developers and failed to provide residents with appropriate compensation. The protestors made two demands: the return of their land and the holding of local elections.
Notably, Ren said, protestors in Wukan affirmed their support for the Communist Party, and never framed their movement as an anti-government effort. In March 2012, local elections were in fact held, with two leaders of the protest movement voted into office (one as village chief, the other as his deputy).
Ren also discussed an attempt by India’s Tata Motors corporation to acquire land in Singur, a village about 100 miles from Calcutta in the state of West Bengal. The company wanted to use this land to construct a factory for the Nano, a small, cheap car marketed to India’s urban middle class. In 2005, the West Bengal government, which had been controlled by the Communist Party of India-Marxist (CPI-M) for nearly 30 years, actively wooed the firm. State authorities “went overboard” in offering Tata Motors subsidies and highly fertile land, said Ren. Small landowners were obliged to surrender their plots at low prices, and in 2006 the corporation formally took over the land (nearly 1,000 acres altogether), despite heavy opposition from peasants.
However, violent protests continued and after several months, Tata Motors was forced to pull out of West Bengal. Then, in a state election in May 2011, the Trinomool Congress Party, led by the populist leader Mamata Banerjee, swept the CPI-M from power. Banerjee had run her campaign on a promise to restore the land to Singur’s farmers.
Just weeks after the new government assumed power, West Bengal passed a law that would allow for about 400 acres from the Tata Motors project to be returned to farmers who had refused government compensation for their land.
Ren acknowledged that in both countries, citizenship rights are not enjoyed by all and tend to be unevenly distributed across social groups. Still, she concluded, Chinese and Indian cities “have become strategic sites for reassembling citizen rights.” By asserting their land and housing rights, city denizens “are becoming active citizens.”
Michael Kugelman is a program associate with the Wilson Center’s Asia Program. He can be reached at michael.kugelman@wilsoncenter.org and on Twitter @michaelkugelman.
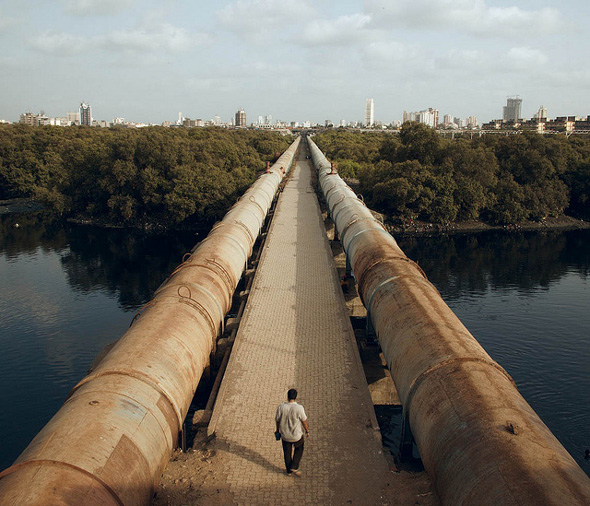
Photo Credit: Mumbai pipes, courtesy of flickr user lenskap. -
Poor Land Tenure: A Key Component to Why Nations Fail
›The murder of five land rights campaigners during the last two months – one in Colombia, three in Brazil, and one in Cambodia – have not captured many headlines, but they are a reminder of the central role land tenure plays not just in rural economic development but also in sparking broadly distributed economic gains throughout a society.
Showing posts from category land.