-
Updates to African Conflict Database Give Researchers Access to Comprehensive, Near Real-Time Information
›Despite the end of Cold War-era civil wars, political violence rates in Africa remain remarkably high. However, this broad statement hides an important qualification: the types of violence that have persisted in recent years have changed significantly, shifting from rebel and government activity towards violence against civilians, riots, protests, and battles by armed groups other than rebels.
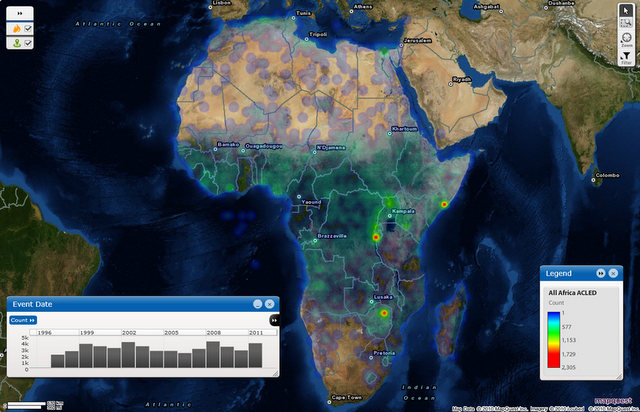
The only way researchers can track this activity is through political violence data disaggregated by type, location, and time. The Armed Conflict Location and Event Dataset (ACLED) project aims to provide that service. We recently released updated information on political violence across Africa from January 1997 to December 2011 (see above for a hotspot map and timeline of violence over this period).
New to the ACLED project are real time data and trend reports on monthly conflict patterns throughout the continent. It is now perhaps the comprehensive and representative depiction of political violence as it occurs throughout Africa.
The data captures an array of actions including battles, looting, rioting, protesting, violence against civilians, and non-violent activity (such as arrests, recruitment drives, troop movements) by a variety of actors such as governments, rebels, militias, rioters and protestors.
Each event is geo-referenced by location and time-stamped by day. In our recently released version, we also included fatalities by event; distinguished conflict groups by their type (government, rebel, political militia, communal militia, rioters, protesters, civilians etc.); and specified the type of interaction between actors (e.g. government-rebel battle; rebel-civilian attack). These changes make ACLED data flexible for multiple uses.
Several new findings on conflict patterns are found using ACLED data:- Violence against civilians accounts for approximately half of all conflict events.
- Generally, where they occur, civil wars intensely affect 19 percent of a state’s territory, yet rebel actions have drastically decreased since 2005.
- Militia activity has significantly increased since 2005 and is especially high during election periods in new democracies.
- Communal violence patterns are more widespread but affect fewer people than civil war violence.
- Civil war patterns are not strongly affected by climate changes, but communal conflict decreases during periods of local scarcity and increases on the cusp of rainy seasons.
- Political violence increases in the period from peace talk announcements to negotiations. This violence is directed towards overtaking territory and civilians are frequently the main victims.
Fine-grained data on the range of political violence in the developing world is important as it provides the opportunity to ask and potentially answer certain questions about a range of issues related to governance, economic development, and conflict dynamics themselves.
For example, ACLED data shows that violence is increasingly occurring in villages, towns, and cities across Africa. In other words, political violence may be “urbanizing.” This has important implications for how we understand the practice of politics, the geography of marginalization, and the role of trigger patterns in explaining conflict. But there are many competing theories that could explain this trend.
Using data that disaggregates by violence type allows us to probe deeper: If the environmental security framework is correct, political violence in towns may be a response to high in-migration from rural areas to cities. Violence therefore is due to competition between urban people and migrant populations.
An alternative explanation is that the poor conditions of African urban life, high rates of informal employment, and under-representation of urban communities in government might explain an increase in violence. In this case, violence is a populist response, in that civilians riot and protest in favor of government reform.
Finally, the advantages of densely populated urban areas – easier access to resources, recruits, infrastructure, and power – may attract more organized groups to contest these spaces. If this explanation were correct, we would expect higher rates of rebel activity against government forces in cities, with a clear drive to overtaking the capital.
We have not been able to address these questions before with credible and comprehensive data, but now we can. Indeed, such data is crucial for interrogating the climate-security debate.
For example, Clionadh recently co-authored an article in the Journal of Peace Research’s special issue on climate and conflict, which used ACLED data for East Africa. In that piece, she and her co-author argued that different conflict groups use their environment in accordance with their overall goals. While much of the conflict activity studied had an environmental signal, the climate signal was much weaker.
We hope that these studies and other work with disaggregated data spur more theories and explanations of conflict patterns in developing states, and that the breadth and form of the data allows for new directions within conflict research.
Clionadh Raleigh is an assistant professor in the Department of Geography at Trinity College, Dublin, external researcher at the Peace Research Institute Oslo (PRIO), and director of the ACLED project. Caitriona Dowd of Trinity College and Andrew Linke of the University of Colorado are senior researchers for ACLED.
Image Credit: ACLED. -
Women’s Rights and Voices Belong at Rio+20
›This summer, world leaders will gather in Rio de Janeiro for the 20th anniversary of the first UN Earth Summit to hammer out a new set of agreements on what sustainable development means and, more importantly, how both rich and developing nations can get there before it’s too late. However, for the scores of women who will be attending (and just importantly for those who aren’t), there are glaring omissions: reproductive health, gender equality, and girls education are nowhere to be found on the Rio+20 agenda.
Women offer many of the most promising levers for the transformation to sustainable development. My experience with the Global Fund for Women tells me that women are full of creative and strategic solutions to the problems facing their communities around the world. Their voices must be included in critical decisions affecting our world. And the fact is, sustainable development isn’t sustainable if it doesn’t include empowering women to plan their families, educate themselves, and their children, and have a voice in government at all levels. Rio+20 must have human rights – and women’s rights – at its core. Earth summit planners haven’t yet done that, but women can make it happen.
Women are 51 percent of the world’s population, yet own only one percent of its assets, are two-thirds of the world’s workers but earn a mere 10 percent of wages. Rio+20 must not become another forum in which women’s issues are not heard. Instead, the summit must demonstrate that women’s voices are integral to all development. Environmental sustainability simply can’t happen without women’s inclusion.
For example, in West Africa, women make up 70 percent of workers in agriculture. In Burkina Faso, deforestation, water scarcity, and soil erosion show us that climate change is already impacting women farmers. Women tend to “sacrifice themselves” in order to care for their families – feeding themselves last. And women are most likely to suffer and die in environmental disasters – particularly in the Asian countries most at risk from climate change.
So how do we support women while supporting the environment that sustains us all?
Simply meeting women’s needs for family planning is one inexpensive and powerful development strategy with a host of environmental benefits. Over 200 million women around the world want the ability to choose the spacing and number of children but don’t have access to, or accurate information about, basic contraceptives like condoms, pills, and IUDs. One-hundred and seventy-nine nations already agree that meeting this need is a top priority, and the Millennium Development Goals (MDGs) reflect a goal of universal access to family planning as well.
Satisfying this demand would dramatically reduce maternal and child mortality and enhance human rights. What’s more, two recent studies show that a reduction of 8 to 15 percent of essential carbon emissions can be obtained by meeting women’s needs for family planning. This reduction would be equivalent to stopping all deforestation or increasing the world’s use of wind power fortyfold.
The Earth Summit presents a major opportunity to ensure that women’s needs and rights are given top priority in plans for sustainable development. In a time of multiple, interlinked human and environmental crises and a very tight funding environment, investing in women is a clear winner.
A greater understanding of the impact of environmental degradation, pollution, and climate change on women, coupled with solid public policy that respects and protects women’s reproductive rights, is essential to the “Sustainable Development Goals” that many believe will emerge from Rio+20 to replace the MDGs, which expire in 2015.
As the summit approaches, it’s time to reflect on why women’s full participation and inclusion is so important and call for world leaders to harness the power of women as we launch the era of sustainable development.
Musimbi Kanyoro is president and CEO of the Global Fund for Women, which advances women’s human rights by investing in women-led organizations worldwide.
Sources: Food and Agriculture Organization, Guttmacher Institute, Moreland et al. (2010), O’Neill et al. (2010), Princeton Environmental Institute, UN, UNEP, World Bank, World Health Organization.
Photo Credit: “Reokadia Nakaweesa Nalongo,” courtesy of Jason Taylor/Friends of Earth International. -
Responses to JPR Climate and Conflict Special Issue: John O’Loughlin, Andrew M. Linke, Frank Witmer (University of Colorado, Boulder)
›
Complexity, in terms of economic, cultural, institutional, and ecological characteristics, weighs heavily on contemporary attempts to unravel the climate change/variability and conflict nexus. The view that local-level complexity can be “controlled away” by technical fixes or adding variables in quantitative analysis does not sit well with many geographers (though some do try to adopt a middle ground position).
-
A New Land Security Agenda to Enable Sustainable, Equitable Development
›The recent news that overseas investors have acquired over 10 percent of Australia’s farmland and 9 percent of water entitlements in its agriculture sector has struck a political chord in the country. Large grain-producing nations like Brazil and Argentina have passed laws to restrict the foreign ownership of land. In other global grain hubs, like Ukraine and Russia, compromised harvests due to droughts could result in export restrictions. In a globalized economy, the combination of scarcity, market and population pressures, and weather volatility will make fertile land an increasingly precious resource.
A shift is underway in global financial markets, where global investors perceive that owning what grows on the land – or better still, owning the land itself – may be a hedge against the risks of more volatile financial markets. A surge in farmland investments is expected to grow over the next decade is due to a number of combined pressures: a growing global demand for commodities, rising commodity prices, ecological limits, and the fact that farmland is a “real asset” that offers diversification to the portfolios of investors at a time of market volatility.
The need to increase food production against the backdrop of resource limits, social vulnerability, and population growth, puts the question of land at the center of a new security agenda.
In sub-Saharan Africa large-scale acquisitions of land that neglect local livelihoods and resource scarcity, commonly referred to as “land grabs,” put the region’s future in the balance. Not all land investments have negative consequences, but given the lower levels of land tenure by communities and the fragility of human security in sub-Saharan Africa, regulating land investments with foresight is an urgent issue. Population growth and climate change underpin this agenda. A worse-than-average drought, exacerbated by climate change, may be all that is needed in certain places to realize the political, humanitarian, and ecological risks that are slowly building momentum.
From Land Grabs to Land Stewardship
Progress now depends on moving from a land grabs debate to land stewardship solutions. This shift, which the Earth Security Initiative summarized in a report published this month, The Land Security Agenda: How Investor Risks in Farmland Create Opportunities for Sustainability, requires an improved understanding by investors and political leaders of three priorities: managing land degradation, protecting human rights by focusing on food security and land ownership, and keeping economies within ecological – especially water – limits.
The agenda we have developed discusses why these issues form part of a new risk management agenda for investors as well as for countries seeking to attract foreign capital, whose economic competitiveness and political stability may be compromised by these trends. But managing these risks, we argue, will require making human rights and ecological limits a central feature of a new investment paradigm.
A range of international investors is already searching for solutions to engage practically with this debate. Among those with whom we have engaged throughout the study are individual investment funds, people seeking change within the financial sector, and investor networks such as the UN-backed Principles of Responsible Investment. Recently, governments, international organizations and civil society groups have also agreed on a set of voluntary guidelines for land governance under the auspices of the Committee on World Food Security. These developments are positive steps, but their voluntary nature remains problematic. The focus must now be placed on operationalizing their recommendations to ensure real accountability and creating political incentives in host countries to regulate their land to ensure long-term and equitable prosperity.
A Call to Action
In The Land Security Agenda we call on investors to turn their attention to their land and commodities portfolios, as well as the investments currently under due diligence, and begin to ask how soil resilience, the prosperity of local people, and freshwater limits are being considered. We recommend beginning to assess the risks of countries according to how well their governments are managing these issues.
We similarly call on heads of state in countries seeking to attract large investments in land to become more aware that these risks may undermine their country’s wealth, their stability, and economic competitiveness. Political leadership is needed to champion and enforce regulations that will encourage investments and modernization while protecting a country’s social and natural capital.
Some of the recommendations we have developed, which would help set the tone for investors and governments to move from voluntary principles to action, include:- Define land security parameters: Establish a set of verifiable measures that allows stakeholders to distinguish those land investments that advance equitable and sustainable prosperity from those that do not. Based on these criteria, which we suggest must consider people, water, and soil, it is possible to advance their integration into three important areas of the investment cycle: the identification of investment opportunities that build positive value, the due diligence process, and the performance reviews of fund managers.
- Build better country risk profiles: If the population of a given country is dependent on agriculture for livelihoods, shouldn’t issues like soil erosion, water availability and lack of recognition for people’s land rights increase that country’s sovereign risk? We think so and now seek to develop a “land security index” to help investors and host country governments assimilate these trends into their decisions as well as increase the advocacy capacity of local civil society.
- Advance the formal recognition of land rights on a large scale: The universal call for the prior and informed consent of communities must be supported, but will be of little practical value if communities do not hold the legal rights to their land or are not well informed about their rights and the commercial opportunities available to them. Civil society groups working to advance good governance, land titling, and capacity building – many of whom we have spoken to during this study – are in a position to help create a “land security partnership” that builds technical and political momentum for the formal recognition of land rights on a large scale, as well as the resourcing and oversight that government agencies will require to implement them.
Alejandro Litovsky is the founder and director of the Earth Security Initiative and lead author of the report. The Land Security Agenda can be downloaded here.
Sources: DGC Asset Management, Land Commodities Asset Management, Telegraph.
Image Credit: Cover of the The Land Security Agenda. -
Responses to JPR Climate and Conflict Special Issue: Steve Lonergan (University of Victoria)
›
The relationship between climate change and conflict has been discussed for over two decades but most of the evidence of the link between the two has been anecdotal, drawing on extreme climate scenarios. The authors featured in the January special issue of the Journal of Peace Research devoted to climate change and conflict are therefore to be commended for their detailed investigations into a possible causal relationship between the two.
-
Responses to JPR Climate and Conflict Special Issue: François Gemenne (Sciences Po)
›
If you want a government to address something, make it a defense issue. No need to hold a PhD in political science to know that governments tend to give the highest priority to issues that involve national security interests – one can complain and whine about it, but that’s the way it is.
-
Responses to JPR Climate and Conflict Special Issue: Solomon Hsiang (Princeton University) and Todd G. Smith (University of Texas, Austin)
›
A January special issue of the Journal of Peace Research brings together a new collection of evidence on a subject that has been a mainstay of the environmental security agenda: the links between climate and conflict.
-
Much Ado About Conflict? Climate’s Links to Violence Reexamined
›
Violence is on the wane in human affairs, even if slowly and irregularly. Could climate change reverse this trend? Pundits and politicians have raised the specter of havoc caused by rising temperature, erratic patterns of rainfall, and rising sea levels. In this way, so the story goes, climate change will produce famine and mass migration that threatens political stability and provokes violence. However, to date there is little evidence that the meteorological or agricultural conditions associated with climate change are actually a major source of violence.
Showing posts from category Guest Contributor.