Showing posts from category food security.
-
‘Marketplace’ and ‘NewsHour’ Highlight Population, Health, and Environment Program in the Philippines
›The Danajon reef is the only double barrier reef in the Philippines, “one of the richest marine biodiversity hot spots in the world,” and it’s being devastated as the country’s exploding population depends on its waters for their food and livelihoods, reported Sam Eaton in a recent two-part series on population, health, and environment issues in the Philippines broadcast last month for American Public Media’s Marketplace and the PBS NewsHour.
The report is part of joint project called Food for 9 Billion, with Homelands Productions, the Center for Investigative Reporting, APM, and PBS. Previous reports examined food security in East Africa and Egypt.
The Philippines “import more rice than any other country on the planet,” said Eaton. The “highest population growth rates in all of Southeast Asia” as well as dwindling natural resources – nearly 100 million people live in a land area the size of Arizona – have created a cycle of poverty. The first step to breaking that cycle, he said, is improving access to family planning.
Growing Families, Growing Poverty
The Canayong family, living on the edge of a garbage dump in a Manila slum, offers a vivid example of what poverty means in the Philippines. Clarissa Canayong has had 14 children – 4 died from measles and dengue fever, the remaining 10 spend their days alongside Clarissa, sifting through the dump for things they need and things they can sell. At the end of a good day, the family has earned around $7 to survive on. All in all, Clarissa’s “inability to provide enough food, and to pay for her children’s education, all but guarantees she and her family will remain poor,” said Eaton.
The archipelago adds about two million people every year, putting population on track to double in size sometime around 2080. “And that’s only if something is done to close the birth control gap,” said Eaton, as those projections build in an expectation that growth will slow.
“As cities all across the country expand, the displaced often end up migrating to urban slums,” he said. “Population growth among poor Filipinos is twice the national average,” meaning that once a family enters poverty, they end up in a cycle “that’s nearly impossible to break.”
The Difference Family Planning Can Make
If Clarissa had had access to family planning, she told Eaton, she would have wanted to have only two children. In Humayhumay, where residents have access to a community-based family planning distribution program started by PATH Foundation Philippines, Inc., families have that luxury of choice.
Working through local partners, the PATH Foundation identifies and trains community-based vendors to sell contraception – both pills and condoms, said Dr. Joan Castro, who began the program in Humayhumay. The idea is to make buying contraceptives “as easy as buying soft drinks or matches.”
Both Jason Bostero, a farmer and fisherman in Humayhuay, and his wife, Crisna, grew up in large families – so large, in Crisna’s case, that “sometimes, we would only eat once a day because we were so poor. We couldn’t go to school. I did not finish school because there were just so many of us,” she told Eaton.
Now that they have access to contraceptives, a smaller family size means their income is “just right” to feed everyone three times a day. For the community as a whole, smaller family sizes mean that the nearby fish stocks that provide the community with food and income have a chance to replenish themselves in the absence of overfishing.
“In just six years since the program was first established here,” reported Eaton, “family sizes have plummeted from as many as 12 children to a maximum of about 4 today.”
Exception to the Rule
Humayhumay is an exception to the rule in the Philippines. There is no state funding for birth control in the country, and over the past few years, major international donors like USAID and the United Nations have ended their family planning work in the country. More than a quarter of poor Filipinos have no access to any type of family planning service, and more than half of all pregnancies are unintended, said Eaton.
Family planning has long been a contentious issue in the country. Eaton spoke to Congressman Walden Bello, who has spent more than a decade trying to pass legislation to establish universal access to birth control and improve other family planning and reproductive services. The Catholic Church, said Bello, is a powerful (80 percent of Filipinos are Catholic) and consistent opponent. In October 2010, the Church went so far as to threaten President Benigno Aquino with excommunication after he voiced support for access to contraception.
Rather than limit population growth, the Church argues the country should increase food production. But land is limited, rice imports are already the highest in the world, and, “according to the World Bank, every major species of fish here shows signs of severe overfishing,” said Eaton.
Looking Forward and Abroad
Eaton pointed to the Philippines’ neighbors as examples to emulate: “A long history of government-supported family planning has…paved the way for Thailand to become one of the world’s biggest rice exporters” and helped to cut back poverty in the country, said Eaton.
Indonesia too, he pointed out, has largely avoided the population growth-resource depletion-poverty cycle, thanks in part to a state- and faith-backed family planning program. (As Elizabeth Leahy Madsen wrote in a recent New Security Beat post, the decision of Indonesia’s religious leaders to throw their support behind family planning in the 1960s was a key factor in success there.)
Considering the obstacles, the Philippines face an uphill battle before family planning services become similarly universal. But the political tides may already be turning: last April, the President said he would support the reproductive health legislation even if it meant excommunication.
Meanwhile, PATH Foundation’s Castro is hopeful that Humayhumay’s success story will lay the seeds for widespread public support for family planning. “The vision of the project is in this community you see more children educated who are able to become leaders and speak out for themselves in the future and be able to become stewards of their own sexuality and the future environment,” said Castro. “This is the legacy.”
Sources: BBC, Bloomberg News, Catholic News Agency, The Guardian, Population Reference Bureau, TIME Magazine, US Agency for International Development, U.S. Catholic. -
Kim Lovell, Sierra Club
Pop at COP: Population and Family Planning at the UN Climate Negotiations
›February 8, 2012 // By Wilson Center StaffThe original version of this article, by Kim Lovell, appeared on the Sierra Club’s activist network.
“Population, development, and climate should be a single discussion,” explained Jacques van Zuydam of South Africa’s National Population Unit. Van Zuydam, speaking to a sparsely filled room at the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC) in Durban last month, centers his work around the concept that climate matters because people matter.
Given the focus on the Green Climate Fund, climate change adaptation, and the effects of sea-level rise and changing weather patterns on some of the world’s most vulnerable populations, it would have made sense for discussions about population to play a central role at the 17th Conference of Parties (COP-17). Yet despite these obvious links – and lead negotiator Jonathan Pershing’s admission to the U.S. youth delegation that population plays a central role when discussing climate impacts – the issue gained little traction in the formal negotiations.
Pershing said he considers population “too controversial” to play a role in the international climate talks, and recommended raising the issue elsewhere. But where better to talk about the need for increased access to voluntary family planning services than among a group of world leaders considering solutions to mitigate and adapt to climate change?
As Brian O’Neill and his colleagues at the National Center for Atmospheric Research explained in a 2010 paper, meeting the unmet need for contraceptive services worldwide could reduce emissions in 2050 by 1.4 to 2.5 billion tons of carbon per year, or 16 to 29 percent of the emissions reductions necessary to avoid dangerous changes to our climate. And beyond the potential effects on carbon, increasing access to education and family planning resources will have a huge impact on the ability of women and families to adapt to the effects of climate change that are already altering weather patterns, water availability, and agricultural production around the globe.
Continue reading at Sierra Club.
Sources: Amplify.
Image Credit: UNFCCC/Climate Change Information Center of Armenia. -
Ryan Britton: Addressing Population in Science Media for ‘EarthSky’
›“What we do is educate the general public and advocate on behalf of science to the general public,” said EarthSky Managing Partner Ryan Britton in this interview with ECSP. “Ultimately we try to bring science to people who don’t normally get science information.”
Part of that effort is addressing population dynamics – growth, aging, youth, food security, etc. – which is often a challenging subject. EarthSky’s coverage over the last year included a series of radio shows on global food security and the “year of seven billion,” which won them a second Global Media Award from the Population Institute in January (alongside New Security Beat!).
EarthSky productions appear on television, radio, online, and in multiple languages. “For us, it’s about getting science out to the general public as best we can,” said Britton.
In terms of population-related issues, he said, allocation of resources, how growing population is affecting ecology and biodiversity, and the effects of climate change are all topics on their radar. “But we do it within the lens of talking about humanity and our continued prosperity,” Britton said. “That’s important for people to hear – what are the solutions, how are we going to get through this, how are we going to be OK? And so those are the questions we’ll keep asking.” -
Water and Population: Limits to Growth?
›February 3, 2012 // By Laurie Mazur
Water – essential, finite, and increasingly scarce – has been dubbed “the new oil.” Experts debate whether human societies are approaching “peak water,” beyond which lies a bleak future of diminishing supplies and soaring demand. Others observe that, for many, the water crisis has already arrived.
-
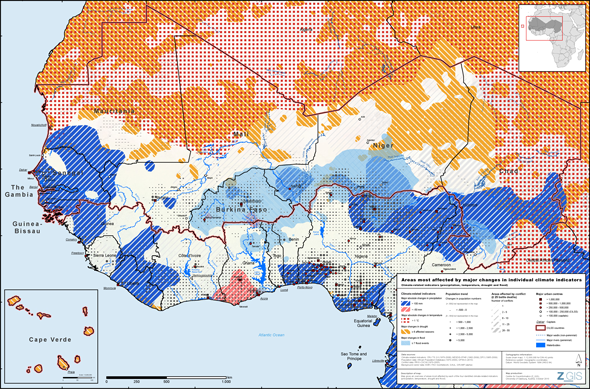
UNEP Maps Conflict, Migration, Environmental Vulnerability in the Sahel
›A new set of maps from the United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP) identifies “climate hotspots” – areas vulnerable to instability exacerbated by climate change – in 17 sub-Saharan countries in and bordering the Sahel region. The maps reflect the fact that, more often than not, the impact of climate change on local populations is compounded by changes in migration, conflict, or both. According to Livelihood Security: Climate Change, Migration and Conflict in the Sahel, the UNEP report accompanying the maps, understanding “the exacerbating effect of changes in climate on population dynamics and conflict in the region” will be essential to developing successful adaptation strategies throughout the region.
UNEP’s maps analyze 40 years of data to pinpoint where the region’s most at-risk populations are located based on environmental, population, and conflict trends dating back to 1970. In a single map pinpointing the Sahel’s 19 hotspots, UNEP synthesizes subnational data from four environmental indicators over time – rainfall (from 1970 to 2006), temperature changes (1970 to 2006), drought (1982 to 2009), and flooding (1985 to 2009) – which are then layered on top of population trends (1970 to 2010) and conflict data (1970 to 2005) in order to identify the region’s most insecure areas.
Composite Vulnerability
At first glance, the map can appear hard to decipher; it is flooded with different colors and symbols, each indicating something different about the extent of climate change, migration, and conflict in the region. A Google Earth version of the map (available for download here) makes all this information easier to process by allowing users to select which indicators they want to see mapped out, cutting back on the number of lines, dots, colors, and pie charts the user has to decode.
Given the vast amount of the information being condensed into these maps, the report is a helpful and worthwhile read. For instance, eight hotspots are in places with growing populations and another seven are located in places that have experienced conflict; altogether, 4 of the 19 hotspots have both past conflict and growing populations. The report digs deeper into the confluence of climate, conflict, and migration by discussing case studies that highlight how the three intersect in local communities (at the same time, the report is careful to avoid suggesting that there is a causal relationship between the three issues.). In Niger, Nigeria, and Chad, for example, tensions have been mounting between northern pastoralists and southern farmers as each group has moved further and further afield in search of water and arable land to sustain their livelihoods.
Holes In the Data
While the hotspot maps include a wealth of information, the report makes clear that it is by no means exhaustive. Rising sea levels are, for instance, a major impending threat to coastal populations in the Sahel, but only the downloadable Google Earth map – not the hotspot map in the report or the Google Earth map as presented online – incorporates this factor. Compounded with a skyrocketing population in the coastal areas – the coast between Accra and the Niger delta is expected to be “an urban megalopolis of 50 million people” by 2020, according to the report – an increase in sea levels could have a huge impact on the region’s stability.
The report also readily admits that the datasets for population trends and conflict have shortcomings. Population data is largely based on censuses, which both the report and its data sources (UNEP’s African Population Database and the Gridded Population of the World, version 3) acknowledge can be inconsistent in their accuracy. Additionally, after 2000, population data is based on projections rather than estimates, which, as last year’s update from the UN Population Division showed, have often proven inaccurate, particularly in sub-Saharan Africa.
Regarding conflict, the UNEP report is straightforward in admitting its limits. The report lacks data on small-scale conflict (fewer than 25 battle deaths, following the Uppsala Conflict Data Program’s threshold that separates conflicts from lower-level violence), even as it acknowledges that such conflict is “often the first to occur” when climate change threatens communities’ access to resources and livelihoods.
Ultimately, however, these maps give valuable data on specific locations that are uniquely vulnerable to trends in population, climate, migration, and conflict. They add focus to the conventional wisdom that climate change will impact the region’s stability, and, taken together, the maps and the report provide a valuable resource for scholars and policymakers attempting to craft adaptation policies that take into consideration these complex links.
Sources: Socioeconomic Data and Applications Center at Columbia University’s Earth Institute, UNEP, Uppsala Conflict Data Program.
Image Credit: UNEP. -
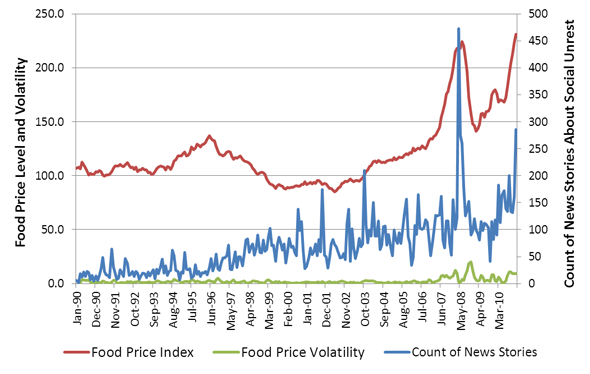
Do High Food Prices Cause Social Unrest?
›In March 2011, a senior Brookings Institution official wrote that “the crux of the food price challenge is about price volatility, rather than high prices per se” and that “[i]t is the rapid and unpredictable changes in food prices that wreak havoc on markets, politics, and social stability.”
-
Ambassador Melanne Verveer, U.S. Department of State
Ambassador-at-Large for Global Women’s Issues on Durban and the Role of Women in Combating Climate Change
›December 23, 2011 // By Wilson Center StaffThe original version of this article, by Ambassador Melanne Verveer, appeared on the White House Council on Environmental Quality blog.
Last week I traveled to Durban, South Africa to participate in the Conference of the Parties to the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change to highlight the critical and largely untapped potential of women to combat climate change. Studies have shown that it is often women who are on the frontlines of, and suffer disproportionately from, the impacts of climate change. This is certainly important. But we must remember that women are also a powerful force for finding solutions to climate change across the board, including in areas such as agriculture, sustainable forest management, and energy access.
Agriculture, which accounts for approximately 14 percent of global greenhouse gas emissions and is a sector that can be particularly sensitive to climate variability and change, is one key area where women can play a major role. A recent FAO report shows that women, in many places, are the main producers of the world’s staple crops, particularly in developing countries and regions likely to be adversely affected by climate change impacts. However, globally, only a small minority of women farmers have access to land tenure. This is a problem for many reasons – including that it limits women’s potential to combat climate change. Studies have shown that women with the right to property are significantly more capable of investing in climate-smart agricultural productivity; we have a lot of work to do to unlock women’s potential in this area.
Women also have untapped potential for increasing energy access, which directly relates to climate change. For example, nearly three billion people globally still rely on traditional cookstoves and open fires to prepare food for their families. In most instances, women are responsible for cooking – not to mention also spending many hours per week collecting fuel, which often puts women at risk of gender based violence. The resulting smoke exposure causes an estimated two million premature deaths annually, with women and young children the most affected. Cookstoves also impact the climate through emissions of greenhouse gases and short-lived particles such as black carbon. Engaging women is critical to tackling this problem. As we work to build a global market for clean cookstoves, integrating women into the cookstoves supply chain will help increase clean cookstove adoption rates while also creating new economic development opportunities. And as Secretary Clinton has noted, women create a multiplier effect in local communities because they disproportionately spend more of their earned income on food, healthcare, home improvement, and schooling.
The United States recognizes the power of women’s potential in these areas and many others, and is investing in major initiatives including Feed the Future and the Global Alliance for Clean Cookstoves, where women’s role in generating transformative change is front and center.
I went to Durban to highlight the critical role of women in combating climate change. While there, I worked with U.S. negotiators on the Durban texts and participated in public engagement events. Our efforts to build on the gender equality and women’s empowerment language in the Cancun agreements are reflected in several crucial institutional developments, including language on gender balance related to the composition of the board of the new Green Climate Fund, the Standing Committee, and the Adaptation Committee. We also worked to reflect gender considerations in the mission of the Climate Technology Center and Network. USAID Assistant Administrator Eric Postel and I solicited input during a meeting with leading non-governmental organizations working on gender and climate issues, and I hosted a high-level side event at the U.S. Center focused on unlocking women’s potential to combat climate change. The level of enthusiasm among my fellow panelists and the audience at the event was inspirational.
We made progress in Durban, but we can’t stop here. To achieve the future we all seek, we must do more. As the late Wangari Maathai, founder of the Green Belt Movement and ground-breaking advocate on women and the environment said, “We must not tire, we must not give up, we must persist.” The future of not only women, but our planet, depends on it.
Ambassador Melanne Verveer is U.S. Ambassador-at-Large for Global Women’s Issues.
Sources: Food and Agriculture Organization, Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, The White House.
Photo Credit: “Melanne S. Verveer,” courtesy of the U.S. Embassy, Kabul. -
In Somalia, Beyond the Immediate Crises, Demography Reveals a Long-Term Challenge
›December 21, 2011 // By Elizabeth Leahy MadsenIn the nearly 20 years since the infamous intervention that resulted in the deaths of dozens of American and UN peacekeeping soldiers on the streets of Mogadishu, Somalia has become the epitome of a “failed state.” Neighboring countries, global bodies, and aid agencies are rushing to respond to the country’s rapidly evolving political, security and humanitarian crises.
Diplomatic attention has focused on decentralized, weak governance that is divided among the Al Shabab insurgency, clan warlords, and a hamstrung and largely ineffective Transitional Federal Government, whose control does not extend beyond the capital. Foreign militaries have had to devote naval resources to curtailing daring and far-reaching acts of piracy against civilian and military vessels from networks based in Somalia. Aid groups have been stymied in their efforts to stem famine as access to populations in the hardest-hit areas has been cut off by Al Shabab and food aid has been stolen. Most recently, Kenyan and, reportedly, Ethiopian forces have crossed the border, extending the reach of the country’s political crisis. Hundreds of thousands of have fled conditions of hunger, illness, and violence into neighboring countries.
Perhaps the deepest woe of a “failed state” is that its problems are deep-seated and cannot be solved during the brief span of a UN meeting or the news cycle following the latest terrorist attack. Amid the extraordinary efforts to battle the country’s crises, one of the most important underlying structural factors is often overlooked: the country’s unusual demographic picture.
A Demographic Outlier
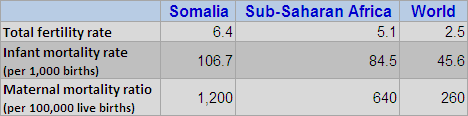
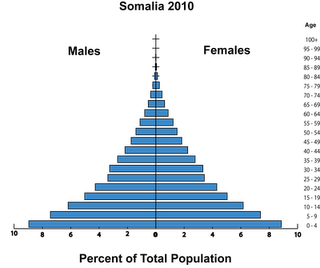
Somalia is a global outlier in demographic terms, with rates of fertility (6.4 children per woman), infant mortality (107 deaths per 1,000 births), and maternal mortality (1,200 deaths per 100,000 live births) all above the already-high averages for sub-Saharan Africa. These demographic indicators are both a reflection of the abysmal state of health care in the country and a warning that its economic and security challenges are unlikely to be easily resolved.Research shows that where at least 60 percent of the population is younger than 30 years old, countries are more prone to outbreaks of civil conflict, and the risk increases as the proportional size of the “youth bulge” grows. In Somalia, 70 percent of the population is younger than 30, a level comparable to Iraq and the Palestinian Territories. With little to no improvements in health care, Somalia’s age structure has remained unchanged over the past 40 years. Unlike dozens of other countries where fertility has declined significantly in recent decades, Somali women have nearly as many children on average today as they did in the 1970s. The current total fertility rate of 6.4 children per woman is only a 12 percent decline from the 1970 rate.
Despite high infant mortality – more than 10 percent of children die before turning one – this sustained high fertility rate has generated rapid population growth, with each successive generation larger than the next. Somalia’s population has almost tripled since 1970, from 3.6 to 9.3 million, although population density remains low (one-third the world average). If the fertility rate remains constant at the current level – not an unreasonable projection considering how stagnant it has been over past decades – Somalia would be home to 33 million people by 2050. Even if the fertility rate drops to near four children per woman, as projected in the UN’s medium variant, the population would still triple to 28 million by mid-century given the demographic momentum of decades of high fertility.
The fertility decline built into the UN’s medium variant projection – which would still place Somalia among the highest total fertility rates in the world by 2050 – is unlikely without steady and major improvements in the country’s health system, particularly women’s health. But with decades of conflict, weak governance and little investment, the environment for reproductive health services is dire.
A recent World Health Organization assessment described “unacceptable levels of unmet need, extreme inequities in access…slow progress…[and] underinvestment and poorly coordinated actions.” Pregnancy and childbirth are major risks to women’s well-being. Somali women have a one in 14 chance of dying from maternal causes over their lifetimes, the second-highest risk in the world. Funding to improve reproductive and maternal health care remains too low to meet demand. The United Nations Population Fund reports that donors spent about $6 million on population and reproductive health programs in 2008, about one-third as much as was spent in Benin and Burundi, which have smaller populations.
The Future for Youth
Instability and violence have become entrenched in Somalia; according to the Armed Conflict Dataset, civil conflict occurred in 12 of the past 20 years. The direct causes of the conflict are typically recorded as struggles for power and resources among competing clans. But in considering the underlying causes of conflict, demographic security scholars have suggested that very young age structures such as Somalia’s can create both motive and opportunity for recruitment into a violent uprising. As ever-growing numbers of young people face adulthood with few prospects for employment, hopelessness or desperation can make them vulnerable to the promise of well-being and identity offered by a political faction or rebel group.
There are 1.7 million people between the ages of 15 and 24 in Somalia today, with another 2.5 million following in the next ten-year age cohort. With opportunities for education, jobs, and equitable participation in society, these youth would represent a promising future for their country. Unfortunately, such opportunities are not afforded to most of them. A United Nations survey found that the secondary school enrollment rate is just six percent, with poverty and early marriage keeping many young people out of school. World Bank data from 2002 show that two-thirds of urban working-age adults and 41 percent of those in rural areas were unemployed. Nearly half of the population lives on less than $1 per day.
Youth Education, Economic Opportunities Could Increase Stability
While global attention centers on the government’s commitment to a new roadmap for peace and the efforts of the African Union’s peacekeeping forces to drive Al Shabab out of Mogadishu, development agencies have recognized demographic security as an important component of Somalia’s future.
The United Nations Children’s Fund is supporting schools for displaced children in Mogadishu, saying in a press release that “providing them with learning opportunities in a safe environment is critical for the country’s long-term stability and growth.”
The U.S. Agency for International Development (USAID) has announced plans for a new program called the Somali Youth Leaders Initiative, which aims to improve young people’s access to secondary education and economic opportunities and to increase their civic participation. In designing the program, USAID noted “the recruitment of boys and men by extremist organizations and piracy networks” and “the common perception that an increasing youth population is a potentially destabilizing force.”
As the October 4 bombing at the Education Ministry in Mogadishu showed, young people are often the victims of the country’s instability. Programs such as those of UNICEF and USAID that empower young people to capitalize on their potential should be a greater focus among initiatives to address Somalia’s long-term future as well as its immediate crises.
Elizabeth Leahy Madsen is a consultant on political demography for the Wilson Center’s Environmental Change and Security Program and former senior research associate at Population Action International.
Sources: BBC, Population Action International, The New York Times, UCDP/PRIO, UNICEF, UNESCO, UN Population Division, UN Population Fund, Urdal (2006), USAID, World Bank, World Health Organization.
Image Credit: “Somalia Suffers from Worst Drought in Century,” courtesy of flickr user United Nations Photo/Stuart Price; charts arranged by Elizabeth Leahy Madsen, data from the UN Population Division and World Health Organization.