-
The Global Impact of COVID-19 on Women and Girls
›
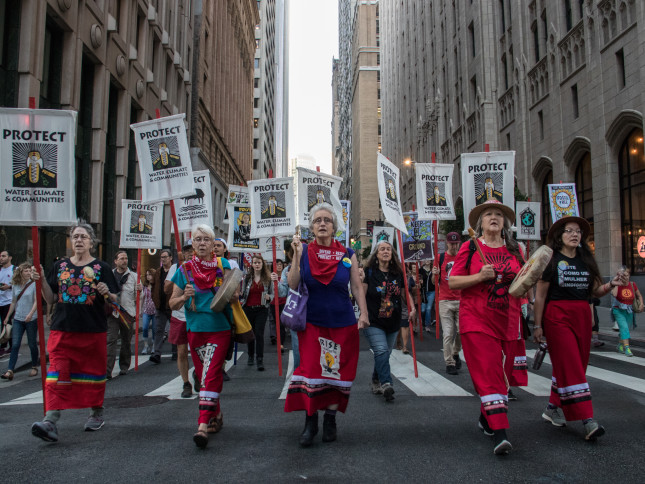
“As we face a global pandemic that has taken the lives of more than 800,000 people as of right now around the world, we certainly have to recognize the particular impacts that that has had on women and girls and their lives,” said Rep. Chrissy Houlahan (D-PA), at a recent event hosted by CARE and UNFPA about the global impact of COVID-19 on women and girls. While women make up 70-80 percent of frontline healthcare workers globally, they have also been disproportionately affected during the pandemic by increased rates of gender-based violence, lack of access to sexual and reproductive healthcare, and economic and food insecurity.
-
Divesting Won’t be Enough to Achieve Climate Justice
›
A quiet disruption to the established financial order is underway: Around the world, institutions are pulling their investments out of fossil fuels. Climate activists campaigning for divestment suggest that such economic rearrangements might keep oil, gas, and coal in the ground, curbing carbon emissions. In parallel, some high-profile advocates call for reinvestment in renewable energy. But can the financial sector really drive the structural changes needed to address climate change—and, more fundamentally, climate justice?
-
Improve Biodiversity Conservation, Enhance Public Health and Food Security
›
Our collective development objectives will not be achieved if they come at the expense of biodiversity and natural resource management, said Jeff Haeni, Acting Deputy Assistant Administrator in the Bureau for Economic Growth, Education, and Environment at USAID. He spoke at a recent Wilson Center virtual event, co-hosted with USAID, that explored the links between conservation and public health with examples from USAID’s BRIDGE project, which aims to build the evidence base for integrating biodiversity conservation considerations into policy discussions and decision-making across sectors. “The ability of societies around the world to develop and thrive is dependent on the health of the forests, fisheries, and natural systems around them,” he said.
-
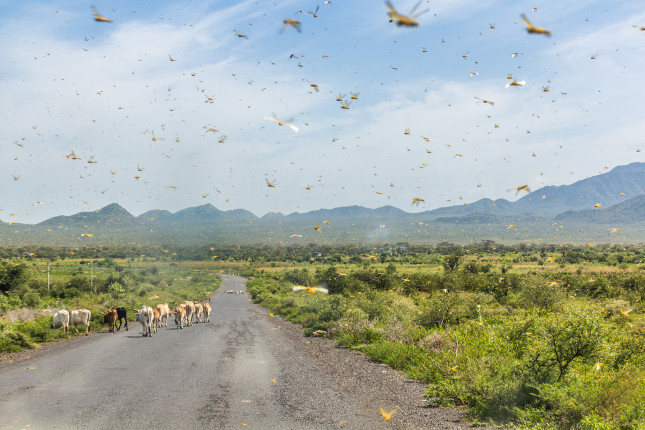
A Plague of Ravenous Locusts Descends on East Africa, Jeopardizes Food Security
›May 18, 2020 // By Wania Yad
Weeks before most of the world began to take the spread of COVID-19 seriously, Africa was already threatened by another plague, the biggest locust outbreak in the last 70 years. Locusts swarmed into Ethiopia, Kenya, Somalia, Uganda, and South Sudan in January and February this year. Those hordes of voracious locusts laid eggs, and now the second wave, 20 times the size of the first group, is arriving. According to Locust Watch, “The current situation in East Africa remains extremely alarming as more swarms form and mature in northern and central Kenya, southern Ethiopia, and probably in Somalia.”
-
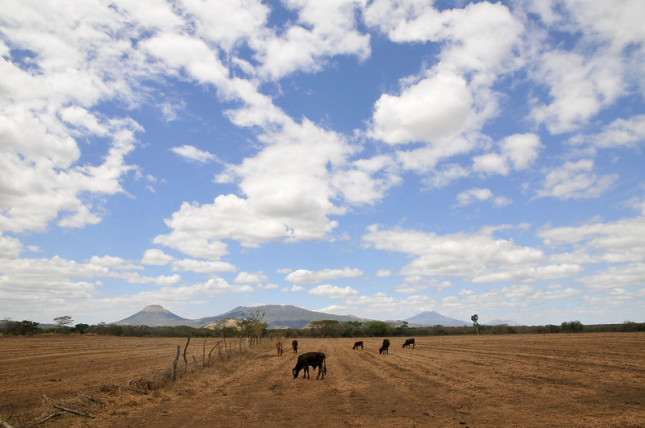
Local Solutions Needed to Stem Humanitarian Crisis in Central America’s Dry Zone
›
As the humanitarian community responds to the Covid-19 pandemic, other long-term pressing priorities persist and require innovative solutions. The dry zone which extends across Central America encompassing parts of Guatemala, Honduras, El Salvador, and Nicaragua and a 10-year drought has left 1.4 million people in urgent need of food assistance. The impact of climate change, which includes extreme drought, poses an ever-increasing risk across Central America and contributes not only to food insecurity but also to migration issues that have plagued the continent in recent years.
-
How Gum Acacia Trees Could Help Build Peace in the Sahel
›
A special type of tree could facilitate peacebuilding in the Sahel. A stretch of semi-arid land south of the Sahara that runs from the Red Sea to the Atlantic Ocean through 10 countries (Eritrea, Sudan, Chad, Niger, Nigeria, Burkina Faso, Mali, Algeria, Mauritania, and Senegal). But the western subregion covering the Lake Chad area (the intersection of Chad, Cameroon, Nigeria, and Niger) and Liptako-Gourma (the tri-border zone of Burkina Faso, Mali, and Niger) in the Sahel has been the scene of a growing humanitarian crisis. Armed groups are terrorizing local populations. Rampant insecurity has forced 1 million people to flee their homes. People have been cut off from their livelihoods. Food insecurity is worsening. Casualties continue to mount. And climate change will likely exacerbate conditions, forcing more people to compete for depleted forest resources and land. More food shortages and instability will surely follow.
-
How Natural Resources Could Help Build Peace in Afghanistan
›
Potential water wars due to plans for multiple dams, violent opium cartels supporting world heroin markets, and many conflict-financing minerals including everyday talc used for baby powder. These are the types of natural resources stories that usually make front page news about Afghanistan. But natural resources have a significant role to play in stabilizing Afghanistan. Instead of being a source of conflict, they may help with peacebuilding by creating livelihoods and creating opportunities for ex-combatants.
-
Glass Half Full? Innovative Technologies Could Increase Global Water Security
›
By 2050, the UN estimates that 52 percent of the world’s population will be at risk for water insecurity. Climate change is threatening water availability through increased temperatures and drought, unpredictable rain, and the growing threat of more pollution. Globally, most wastewater reenters the water cycle without being treated, introducing dangerous unseen particles including pharmaceuticals, diseases, and larger waste products such as plastics.
Showing posts from category food security.