-
Emmanuel Karagiannis: Mediterranean Oil and Gas Discoveries Could Change Regional Alignments, Global Energy Equation
› “The discovery of gas reserves in the eastern Mediterranean comes at a time when world demand for energy is growing rapidly and many are questioning the reliability of supplies from North Africa and the Middle East,” said Emmanuel Karagiannis, assistant professor of Russian and post-Soviet politics at the University of Macedonia, in an interview at the Wilson Center.The newly-discovered fields contain about 122 trillion cubic feet of recoverable natural gas reserves, 25 trillion of which are located within Israeli territorial waters. “That’s twice the reserves Libya has,” according to Karagiannis. The remaining fields have been claimed by the Republic of Cyprus, the Turkish Republic of Northern Cyprus, Syria, and Lebanon.
“The discovery of gas reserves in the eastern Mediterranean comes at a time when world demand for energy is growing rapidly and many are questioning the reliability of supplies from North Africa and the Middle East,” said Emmanuel Karagiannis, assistant professor of Russian and post-Soviet politics at the University of Macedonia, in an interview at the Wilson Center.The newly-discovered fields contain about 122 trillion cubic feet of recoverable natural gas reserves, 25 trillion of which are located within Israeli territorial waters. “That’s twice the reserves Libya has,” according to Karagiannis. The remaining fields have been claimed by the Republic of Cyprus, the Turkish Republic of Northern Cyprus, Syria, and Lebanon.
Europe currently depends on Russia for most of its gas supplies, so the new fields could provide an “important alternative source for European economies,” said Karagiannis.
The discovery also has the potential to increase stability in the region by serving as an incentive for nations to work together. “For example, Israel and Cyprus have come closer to each other in many respects, including military cooperation,” Karagiannis said. Greece and Israel have also strengthened their relationship, in part due to the historical relationship between Cyprus and Greece but also because the latter could serve as an energy hub to transport gas throughout Europe, he said. “In effect Israel, Greece, and Cyprus could form a new axis of stability in the region.”
“Turkey can also play a significant part in the business of transporting energy resources to Europe,” Karagiannis said, but Syria and Lebanon, the two other countries that lie adjacent to the newly discovered gas reserves, are less likely to benefit in the near future from the find, given their current political circumstances. “It’s very difficult to imagine their participation in the regional energy projects,” he said. Lebanon has tried and failed to sell offshore exploratory licenses twice due to its lack of a state petroleum administration, while the current uprising against President Bashar al-Assad is preventing any progress in Syria.
In part as a result of these political challenges, the gas fields also have the potential to generate conflict in the region. There will be a divide between “haves and have-nots,” explained Karagiannis. According to a report by the Institute for National Strategic Studies, “piping Israeli gas to the RoC [Republic of Cyprus] and then onto Turkey, which could be the gateway to the European market, is unlikely due to current tensions between Ankara, the RoC, and Tel Aviv.” Since the discovery of the fields, “Turkey has already issued military threats against Cyprus in order to stop the gas exploration process that is currently taking place in the Cypriot Exclusive Economic Zone,” Karagiannis said. The Israeli government issued a response to the threat, stating that they are committed to protecting energy infrastructure in the region.
The first new natural gas field in the region is expected to begin full-scale production this year, with two additional fields coming on-line over the next six years.
Keenan Dillard is a cadet at the United States Military Academy at West Point and an intern with the Woodrow Wilson Center’s Environmental Change and Security Program.
Sources: Institute for National Strategic Studies, Noble Energy Inc., Turkish Weekly, U.S. Geological Survey. -
From Youth Bulge to Food and Family Planning, Los Angeles Times’ ‘Beyond 7 Billion’ Series Synthesizes Population Challenges
›Over the next 40 years, the world is set to add 2.3 billion people. Millions more will join the middle class, pushing consumption upwards and further straining the world’s natural resources. Variables like climate change and political instability will exacerbate that strain and complicate efforts to bolster peaceful and stable development. Los Angeles Times correspondent Kenneth Weiss and photographer Rick Loomis examine these numerous and interconnected challenges in a five-part series on population growth and consumption dynamics.
Speaking to demographic and health experts (including a number of New Security Beat regulars, like Richard Cincotta, Jon Foley, and Dr. Joan Castro), Weiss provides a thorough, astute, and compelling assessment of population dynamics in a rapidly changing world. The series starts with a basic introduction to population, climate, and consumption dynamics and progresses through to discuss political demography, global food security, and detailed looks at two important case studies, China and the Philippines.
Part One: A Population Primer
Population growth alone poses a number of challenges as cities become more crowded and demand for basic resources like water and food outpaces supply. Climate change and the unpredictable and sometimes extreme weather that is its hallmark “will make all of these challenges more daunting,” writes Weiss. And “population will rise most rapidly in places least able to handle it.” Africa, the Middle East, and South Asia, already expected to bear the brunt of climate change with rising sea levels, shorter growing seasons, and increasingly variable weather patterns, will also have to support the bulk of the world’s population growth by mid-century. Populations in Europe, North America, and East Asia are expected to stay stable or decline in numbers.
The magnitude of growth in Africa, the Middle East, and South Asia, however, is uncertain. What happens from here “hinges on the cumulative decisions of hundreds of millions of young people around the globe,” Weiss writes. And yet, “population growth has all but vanished from public discourse.” Family planning in particular remains hamstrung by “erratic funding and unpredictable crosscurrents.” The result, he writes, is that even “under the best conditions, it’s hard to get contraceptives into the hands of impoverished women who want them.”
Part Two: The Arc of Instability
Drawing on work from demographer Richard Cincotta, George Mason University’s Jack Goldstone, Population Action International, and others, part two of Weiss’ series examines youth bulges and the so-called “arc of instability,” stretching across the disproportionately youthful countries of Africa, the Middle East, and South Asia.
When a large youth population is mixed with other societal conditions, like “religious and ethnic friction, political rivalries, economic disparities, or food shortages,” youth can be “the kindling” for a spark that ignites simmering tensions, writes Weiss. Afghanistan is a case in point, where unemployed young men are often turning to the Taliban not out of extremist fervor, but out of a desperate need to support themselves and their families. “It’s too hard to employ this many people and too easy to recruit them into violence,” Cincotta told Weiss.
And Afghanistan is just the beginning, according to Goldstone. “We are literally going to see one billion young people come into the populations in the arc of instability over the next two decades,” he said. “We can’t fight them. We have to figure a better way to help them.”
Part Three: Feeding a Growing Population
As the world’s population continues to grow, and as more families join the middle class, world food production will have to double by mid-century in order to meet future demand. “What that actually means,” says World Wildlife Fund’s Jason Clay, an agriculture specialist, “is that in the next 40 years we need to produce as much food as we have in the last 8,000.”Jon Foley on how to feed nine billion and keep the planet
Weiss presents the Horn of Africa and Punjab as microcosms of the problems facing global food production in the 21st century. Desertification and urbanization are eating away at potential cropland, while harmful farming techniques leech essential nutrients from soil, rendering it useless for future use. Insufficient infrastructure means that food spoils as it’s shipped from where it’s produced to where it’s needed, while extreme and widespread poverty means that those most in need can’t afford enough to feed their families.
Stuck between growing demand and restricted supply, the University of Minnesota’s Jonathan Foley said the challenge of the century is straightforward: “How will we feed nine billion people without destroying the planet?”
Part Four: Population and Consumption in China
China has “a greater collective appetite – and a greater ecological impact – than any other country,” writes Weiss, making it a prime example of “how rising consumption and even modest rates of population growth magnify each other’s impact on the planet.”
The country’s one-child policy slowed population growth rapidly, cutting fertility almost in half in less than a decade. Over time, a large working-age cohort with few dependents emerged, and helped China reap a demographic dividend. The resulting economic prosperity has come at a cost, however, as rising incomes and increasing consumption, spread across 1.3 billion people, have wreaked havoc on the country’s environment on a scale not seen anywhere else in the world.
Because of that scale, what happens in China will have global repercussions. Climate scientists “say that in order to avoid a potentially catastrophic rise in global temperatures, worldwide carbon dioxide emissions must be cut in half by 2050,” Weiss writes. “For that to happen, China’s emissions would have to peak by 2020” – 15 years earlier than official government projections. The government remains opposed to further limits on emissions, arguing that such limits would “cripple” economic growth – an unfair impediment considering that developed countries were able to “pollute their way to prosperity, their argument goes.”
Part Five: Family Planning in the Philippines
Weiss ends the series with an in-depth look at family planning in the Philippines – a country at the forefront of the global debate over access to contraception. Lawmakers in the 80-percent-Catholic country have steadfastly refused to fund family planning services, while support from the international community all but vanished when USAID, “the major donor of contraceptives to the Philippines,” said in 2008 that it would end its contraceptive program.
Today, half of all pregnancies in the Philippines are unintended. Lawmakers are considering a “reproductive health bill…call[ing] for public education about contraceptives and government subsidies to make them available to everyone,” but a powerful opposition, including Church leadership, has stalled the bill for 14 years, Weiss writes.Joan Castro on population-environment programing in the Philippines
Public officials, including the former Manila mayor who ended the city’s contraceptive program 12 years ago, portray unbridled population growth as an economic asset, saying that “when you have more people, you have a bigger labor force.” For the millions of Filipinos who live in poverty, however, the lack of affordable family planning services leaves them with little control over family size and puts the Philippines on track to grow from 96.4 million people today to 154.9 million by mid-century. At that rate, the Philippines would be Asia’s third fastest growing country, behind Timor Leste and Afghanistan.
Not everything in the series is dire – there are side columns highlighting population, health, and environment programming in Uganda, Iran’s successful family planning program, and Dr. Joan Castro’s family planning and marine conservation work in the Philippines. But Weiss is not naïve about the challenges ahead. Under any of the United Nation’s population projections, “living conditions are likely to be bleak for much of humanity,” he writes. “Water, food, and arable land will be more scarce, cities more crowded, and hunger more widespread.”
“Even under optimistic assumptions, the toll on people and the planet will be severe.”
But while the population challenges facing the world are many, Weiss, like many before him, makes one argument clear: providing family planning services to the 222 million women who want to control the number of children they have but cannot would go a long way towards minimizing future strain.
Be sure to check out the photo and video features accompanying the “Beyond 7 Billion” series on the feature site.
Note: The sentence beginning with “When a large youth population…” was corrected.
Sources: Los Angeles Times, UN Population Division.
Video Credit: “The Challenge Ahead,” used with permission courtesy of the Los Angeles Times; Photo: “Dharavi,” used with permission courtesy of Rick Loomis/Los Angeles Times; Jon Foley video: TEDx. -
Michael Kugelman, Sustainable Security
The Global Land Rush: Catalyst for Resource-Driven Conflict?
›July 31, 2012 // By Wilson Center StaffThe original version of this article, by Michael Kugelman, appeared on SustainableSecurity.org.
On May 11, the UN approved new international rules to govern how land is acquired abroad. These Voluntary Guidelines (VGs), the outcome of several years of protracted negotiations, are a response to growing global concern that nations and private investors are seizing large swaths of overseas agricultural land owned or used by small farmers and local communities for food, medicinal, or livelihood purposes. FAO head Jose Graziano da Silva describes the VGs as “a starting point that will help improve the often dire situation of the hungry and poor.”
It’s hard to quibble with the intent of the guidelines. They call for, among other things, protecting the land rights of local communities; promoting gender equality in land title acquisition; and offering legal assistance during land disputes.
Unfortunately, however, any utility deriving from the VGs will be strictly normative. As their name states explicitly, they are purely optional. A toothless set of non-obligatory rules will prove no match for a strategy that is striking both for its scale and for the tremendous power of its executioners.
Oxfam estimates that nearly 230 million hectares of land (an area equivalent to the size of Western Europe) have been sold or leased since 2001 (with most of these transactions occurring since 2008). According to GRAIN, a global land rights NGO, more than two million hectares were subjected to transactions during the first four months of 2012 alone. One of the largest proposed deals – an attempt by South Korea’s Daewoo corporation to acquire 1.3 million hectares of farmland in Madagascar – failed back in 2009. Still, even larger investments are being planned today, including a Brazilian effort to acquire a whopping six million hectares of land in Mozambique to produce corn and soy (Mozambique offered a concession last year).
Continue reading on SustainableSecurity.org.
Sources: BBC, Food and Agriculture Organization, GRAIN, MercoPress, Oxfam, Reuters.
Photo Credit: “Garde armé,” courtesy of flickr user Planète à vendre. -
PBS ‘NewsHour’ Reports on Reasons for Optimism Amid Niger’s Cyclical Food Crises
›Set in the middle of the arid region between the Sahara desert and the equatorial savannas of Africa known as the Sahel, Niger is no stranger to drought. In recent years, however, droughts have hit more often, started earlier in the season, and lasted longer, creating a cycle of food insecurity that is becoming more difficult to break.
-
Chaotic Climate Change and Adaptation in Fragile States
›In “Chaotic Climate Change and Security,” published in the June issue of International Political Sociology, Maximilian Mayer traces the transformation of climate change from a long-term problem to something that has taken on a new urgency in recent years. Understanding the non-linear nature of climate change – the “abrupt changes” that can come as environmental thresholds are crossed – has led to the securitization of the environment, writes Mayer. Unfortunately, the “doomsday rhetoric of scientists and campaigners about ‘tipping points’ has apparently failed to spur governments toward negotiating a meaningful agreement.” Climate change skepticism still exists, he points out, and even those who are convinced of the potential negative impacts of environmental change on state security have failed to reverse detrimental actions, choosing instead to focus on ameliorating the effects of change on their individual states. As a replacement for these failed frameworks, Mayer suggests that actor-network theory should be used as it better accounts for the interconnected nature of climate change.
Katherine Houghton discusses the relationship between climate change and resilience in her article “Climate Change in Fragile States: Adaptation as Reinforcement of the Fabric of the State,” published in a collection of articles written by members of the United Nations University Summer Academy. Houghton writes that in fragile states, environmental issues can be “compounded by armed conflict and institutional failure,” which further destabilizes the country. She mentions cases in which the state lacks the authority to properly assist its citizens following natural disasters, like the flooding of the Indus Valley in Pakistan’s Federally Administered Tribal Areas. In these cases, failure of the government to meet citizens’ needs “fuels instability and fragility rather than fosters resilience.” Any action to reduce the effects of climate change on residents of vulnerable areas must thus begin with the state, she writes. “Without effective action to strengthen the state and thereby enable adaptation, climate-induced adverse effects and extreme events may lead to the further destabilization of already fragile states.” -
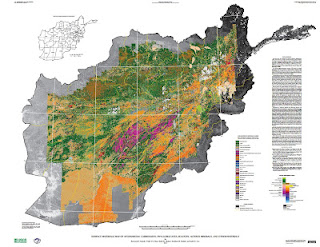
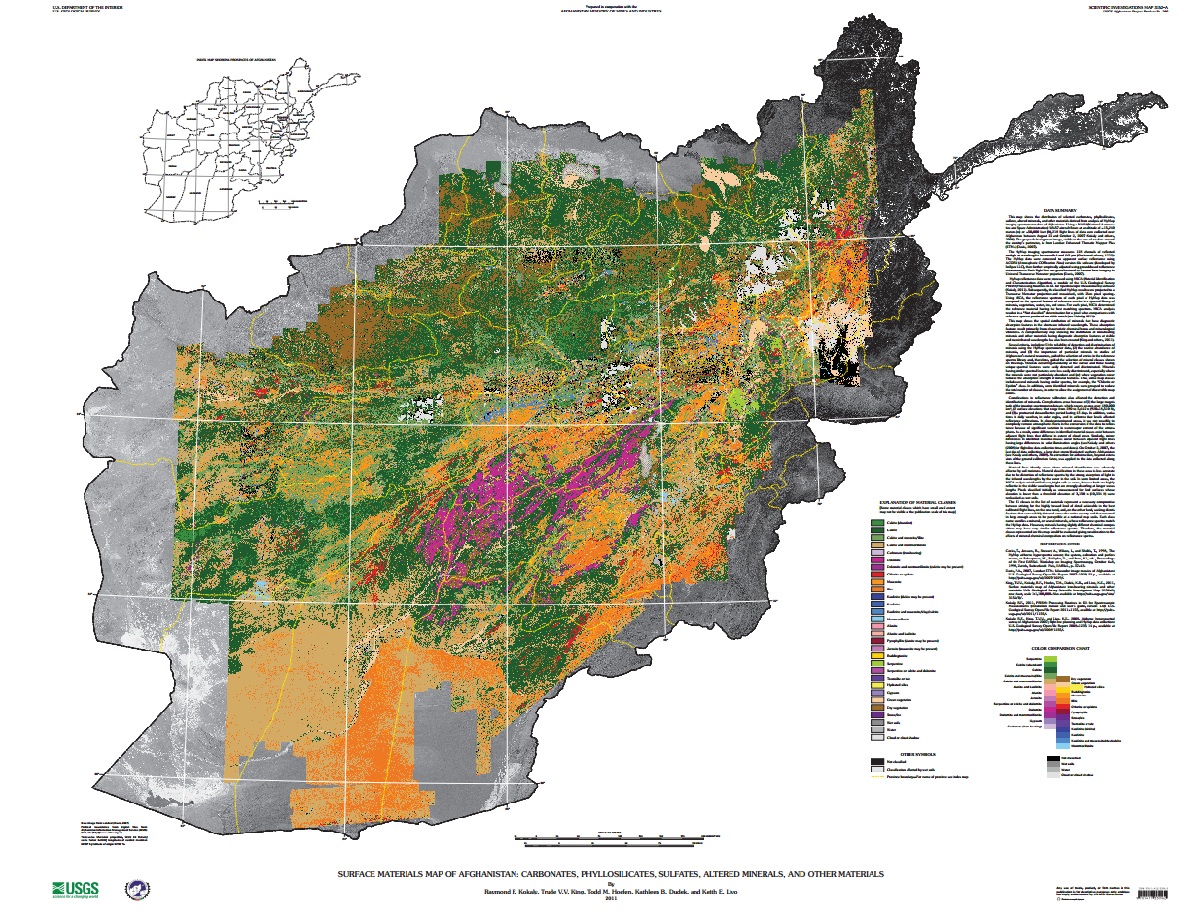
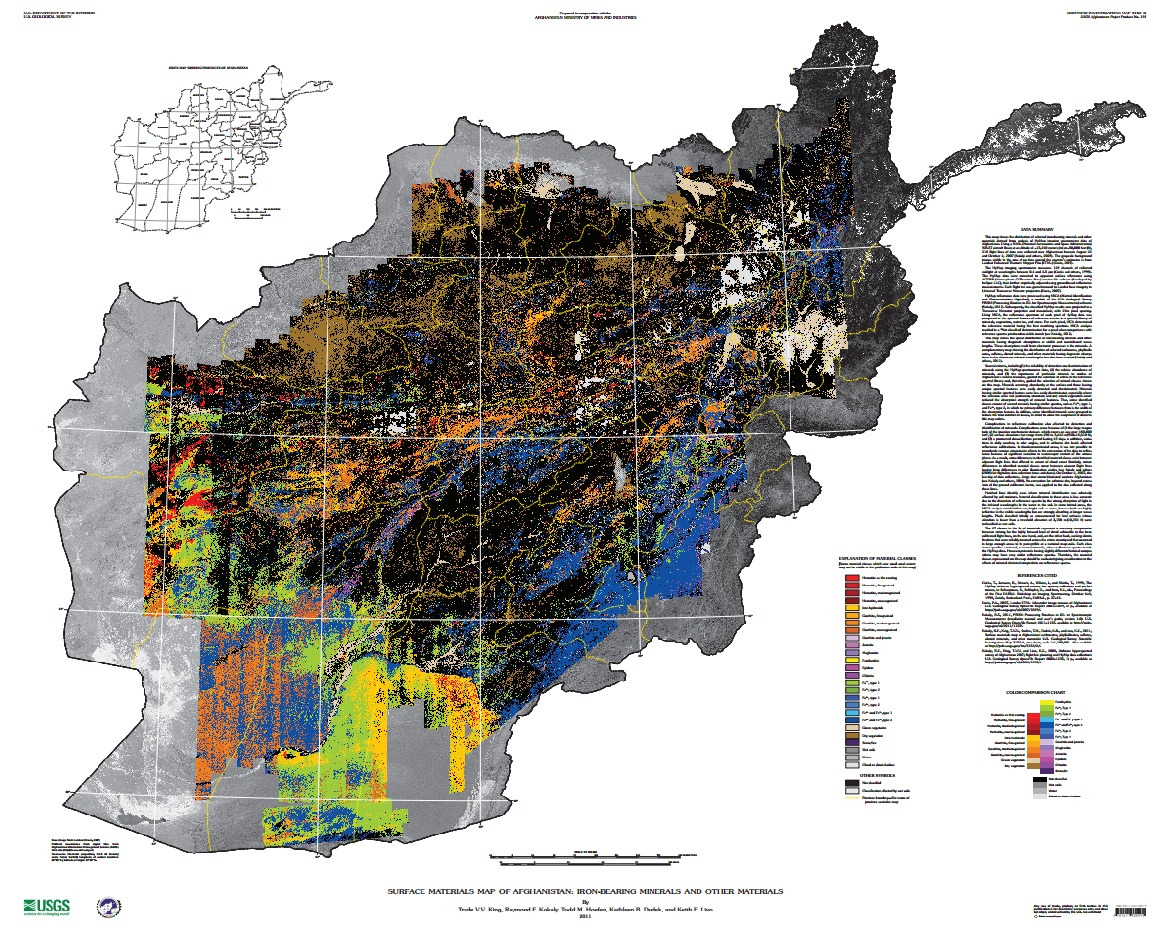
New USGS Report and Maps Highlight Afghanistan’s Mineral Potential, But Obstacles Remain
›Two maps released to the public for the first time this month illustrate the vast wealth of mineral deposits in the war-torn nation of Afghanistan. The maps, created through a joint effort from the U.S. Geological Survey and Department of Defense Task Force for Business and Stability Operations, are the first of their kind to provide large-scale coverage of a country using a technology called hyperspectral imaging, which measures the reflectance of material on the Earth’s surface simultaneously across a continuous band of wavelengths broken up into 10 to 20 nanometer intervals. More than 800 million individual pixels of data were collected during a period of 43 days in 2007 by a NASA aircraft. Each data point was then “compared to reference spectrum entries in a spectral library of minerals, vegetation, water, ice, and snow in order to characterize surface materials across the Afghan landscape.”


Two maps released to the public for the first time this month illustrate the vast wealth of mineral deposits in the war-torn nation of Afghanistan. The maps, created through a joint effort from the U.S. Geological Survey and Department of Defense Task Force for Business and Stability Operations, are the first of their kind to provide large-scale coverage of a country using a technology called hyperspectral imaging, which measures the reflectance of material on the Earth’s surface simultaneously across a continuous band of wavelengths broken up into 10 to 20 nanometer intervals. More than 800 million individual pixels of data were collected during a period of 43 days in 2007 by a NASA aircraft. Each data point was then “compared to reference spectrum entries in a spectral library of minerals, vegetation, water, ice, and snow in order to characterize surface materials across the Afghan landscape.”
Accompanying the release of the maps is a USGS study, completed in September of 2011, that largely confirms earlier reports from the DOD and USGS on the size of Afghanistan’s untapped mineral resources. The first reports received widespread media coverage last year, and updated estimates indicate that upwards of $900 billion worth of mineral reserves are present in a number of different forms including copper, iron, gold, and, most notably, more than one million metric tons of rare earth elements.
Scientists involved with the project believe that there may be even more reserves awaiting discovery. “I fully expect that our estimates are conservative,” said Robert Tucker from the USGS in an interview with Scientific American. “With more time, and with more people doing proper exploration, it could become a major, major discovery.”
Over the course of the study, scientists from the USGS and Afghan Geological Survey combined the newly-created spectral data with existing maps to identify 24 areas of interest (AOIs) that warranted hands-on investigation.
The two hyperspectral maps illustrate different parts of the electromagnetic spectrum. Shortwave infrared wavelengths reveal carbonates, phyllosilicates, and sulfates, while visible and near-infrared wavelengths show iron-bearing minerals, which yield products ranging from copper to rare earth elements and uranium. Each map classifies 31 different types of materials by color.
Although the hyperspectral maps only show mineral deposits on the surface, geologists were able to estimate what lies beneath by combining new data with samples previously taken from trenches, drill holes, or underground workings at the AOIs by Soviet and Afghan scientists. According to the USGS, “A number of the AOIs were field checked by USGS and DOD geologists between 2009 and 2011, and the previous geologic interpretations and concepts were confirmed.”
Actual Extraction: Not Easy
Afghanistan has been “scouring the globe for investors to develop its mines in an attempt to lift one of the world’s poorest nations out of misery through investment,” according to The Wall Street Journal. Contracts have already been awarded to China and India to develop copper and iron mines, respectively, and another round of bidding is currently in progress for four unexploited sites that are being closely eyed by countries such as the United States, Australia, and Turkey.
But significant hurdles remain in the quest to turn Afghanistan’s buried minerals into a steady source of income for the government and the Afghan people. Security is still a major concern and United States will pull out a vast majority of its combat troops by 2014. The government has established a Mines Protection Unit to guard sites where ground has already been broken, and plans to increase the size of the unit as necessary to provide security for all mining projects nationwide. For now the Afghan Ministry of Mines is only taking bids for projects in the more secure northern part of the country, where deposits of copper and gold are located. As the nation develops and stabilizes, massive resources of rare earth elements located in the notoriously volatile Helmand Province will open for bids.
Security isn’t the only factor affecting the country’s mining prospects. “If you want to do mineral resource development, there are two things you need to pay attention to: water and energy resources. Where is the power going to come from? You can’t develop these large mineral deposits without energy,” said director of the USGS program in Afghanistan, Jack Medlin, in an interview with EARTH magazine.
There are also the traditional pitfalls of developing extractive industries, especially in poor and conflict-prone countries, including corruption, inequity, land disputes, and environmental degradation. And the fact that Afghanistan is landlocked, making supply lines in an out of the country difficult (as the United States has discovered).
Despite the many hurdles, there is plenty of optimism for an Afghan future brightened by mineral wealth. The new data shows that previous reports of substantial resources were not far off, and the Afghan economy, which for years has relied on opium as its biggest export, could certainly use the help. “The prognosis is extremely encouraging and could play a significant role in recovery from decades of war,” USAID advisor Wayne Pennington told EARTH.
For the full resolution versions of the hyperspectral imaging maps (~90MB each) see here and here.
Keenan Dillard is a cadet at the United States Military Academy at West Point and an intern with the Woodrow Wilson Center’s Environmental Change and Security Program.
Sources: Afghan Geological Survey, Afghan Ministry of Mines, Christian Science Monitor, U.S. Department of Defense, EARTH, The New York Times, Scientific American, U.S. Geological Survey, The Wall Street Journal, World Bank.
Image Credit: USGS.
-
Urbanization and the Global Climate Dilemma
›
Urbanization and climate change may be the two most important trends to shape global development in the decades ahead. On the one hand, urban cities have the potential to serve as engines of change, driving economic growth in some of the world’s least developed countries and pulling more people out of poverty than at any other time in history. On the other hand, climate change could undercut all of this by exacerbating resource scarcity and putting vulnerable communities at risk from sea level rise and more frequent and intense storms.
-
Linking Water, Sanitation, and Biodiversity Conservation in Sub-Saharan Africa
›July 25, 2012 // By Kate DiamondWater, poverty, and the environment are “intrinsically connected,” and the development programs targeting them should be as well, writes David Bonnardeaux in Linking Biodiversity Conservation and Water, Sanitation, and Hygiene: Experiences From sub-Saharan Africa, a new Africa Biodiversity Collaborative Group briefing. In a review of 43 programs across sub-Saharan Africa, including four in-depth case studies, Bonnardeaux finds that natural synergies between water, sanitation, and hygiene (WASH) programming and conservation work provide opportunities for greater effectiveness in addressing both.
Integrating WASH and Conservation: A Natural Match
“WASH interventions are generally reliant on natural resources and processes, whether indirectly or directly,” he writes, and “WASH services produce outputs that are potentially detrimental to the environment if not managed properly.” At the same time, poor ecosystem management can “threaten biodiversity and jeopardize the vital services that these ecosystems in turn provide to humanity, in the form of regulation of stream flow, erosion prevention, water filtration, aquifer recharge, carbon sequestration, wildlife habitat, outdoor recreation, and flood abatement.”
Given the connections between the two, WASH and conservation efforts would benefit from programmatic integration, according to Bonnardeaux. To bring the two closer together, he recommends three tools for policymakers and development programmers: integrated river basin management and basin planning; payments for watershed services (also known as payments for environmental services); and population, health, and environment (PHE) programming.
A Whole-of-Basin Perspective
“The causal link between WASH and ecosystem health and integrity is most accentuated when
dealing with freshwater ecosystems,” writes Bonnardeaux.
In Tanzania’s Pangani River Basin, one of his in-depth case studies, a growing reliance on hydropower, urbanization, and increased agricultural demand is altering a valuable ecosystem marked by endemism and iconic landscapes, including Mount Kilimanjaro.
In response, the government and international organizations are partnering through the Pangani River Basin Management Project to developing a greater understanding of the basin’s hydrology and ecosystem, how local populations interact with that ecosystem, and how potential development scenarios could impact the basin in the future. That knowledge, paired with an intensive training program for local water officials, is enabling stronger integrated resource management, which in turn could lay the groundwork for integrating WASH and conservation interventions, writes Bonnardeaux.
Economic incentives – in this case, payments for watershed services – offer another valuable tool for building support for conservation efforts, especially when upstream communities bear a disproportionate burden of safeguarding watersheds.
In South Africa, another case study country, “increased economic development and urbanization have taken its toll on” the country’s wetlands, while unemployment and poverty have remained a persistent problem in slum areas, writes Bonnardeaux. Through the government-run Working for Wetlands program, both the environmental and socioeconomic problems of development are being targeted for improvement. The program hires “the most marginalized from society” to clear wetlands of invasive plants in order to improve its natural filtration capabilities and, in turn, improves the quality of water feeding the burgeoning urban areas.
Although Working for Wetlands, now 17 years old, has been “hugely successful,” Bonnardeaux warns that such economic incentive programs are, more often than not, extremely difficult to carry out effectively. “While there is great potential for this incentive-based conservation approach,” Bonnardeaux notes, “the reality is there are many barriers to its effective implementation.”
Building Long-Term Support for Conservation With Near-Term PHE Successes
Building support for conservation can be a difficult task. The impacts of conservation programming are “often undervalued,” Bonnardeaux writes, in part because results tend to become apparent only over the longer term. By pairing conservation efforts with nearer-term programming, like PHE efforts targeting immediate health needs, development workers can foster the kind of local support that is essential for pursuing long term goals.
The Jane Goodall Institute’s Lake Tanganyika Catchment Reforestation and Education Project (TACARE), in northwest Tanzania, offers a case in point. Established in 1994, TACARE began as a conservation program meant to protect the areas around Gombe National Park, where Goodall first began her chimpanzee research in the 1960s. Local communities, however, were more interested in better health, “with an emphasis on clear water and reduction in water-borne diseases like cholera,” writes Bonnardeaux.
By adopting local health and poverty priorities, he writes, TACARE was able to establish trust and goodwill with the communities it served, which in turn enabled it to pursue longer-term conservation goals aimed at protecting the region’s natural biodiversity.
Bonnardeaux’s work shows that regardless of how policymakers choose to combine WASH and conservation goals, well-implemented integration can yield immense benefits for practitioners, funders, and local communities.
“Linking various sectors such as WASH, forestry, agriculture, population, and community development,” he writes, “can result in cost and effort sharing which in turn can increase the effectiveness of the project including improved conservation and improved livelihoods and health.”
Sources: Bonnardeaux 2012.
Photo Credit: “Intaka Island towards Table Mountain,” courtesy of flickr user Ian Junor.
Showing posts from category environment.