-
Demographics, Depleted Resources, and Al Qaeda Inflame Tensions in Yemen
›July 21, 2010 // By Schuyler NullA second spectacular Al Qaeda attack on Yemeni government security buildings in less than a month is a worrisome sign that the terrorist group may be trying to take advantage of a country splitting at the seams. U.S. officials are concerned that Yemen, like neighboring Somalia, may become a failed state due to a myriad of challenges, including a separatist movement in the south, tensions over government corruption charges, competition for dwindling natural resources, and one of the fastest growing populations in the world.
Wells Running Dry
Water shortages have become commonplace in Yemen. Last year, the Sunday Times reported that Yemen could become the first modern state to run out of water, “providing a taste of the conflict and mass movement of populations that may spread across the world if population growth outstrips natural resources.”
Earlier this year, government forces came to blows with locals over a disputed water well license in the south. Twenty homes were damaged and two people were killed during the resulting eight day stand-off, according to Reuters.
The heavily populated highlands, home to the capital city of Sanaa, face particularly staggering scarcity. Wells serving the two million people in the capital must now stretch 2,600 – 3,200 feet below the surface to reach an aquifer and many have simply dried up, according to reports.
Yemeni Water and Environment Minister Abdul-Rahman al-Iryani told a Reuters reporter that the country’s burgeoning water crisis is “almost inevitable because of the geography and climate of Yemen, coupled with uncontrolled population growth and very low capacity for managing resources.”
Nineteen of Yemen’s 21 aquifers are being drained faster than they can recover, due to diesel subsidies that encourage excessive pumping, loose government enforcement of existing drilling laws, and growing population demand. Qat farmers in particular represent an excessive portion of water consumption; growing the popular narcotic accounts for 37 percent of agricultural water consumption. Meanwhile, according to a study by the World Food Programme this year, 32.1 percent of the population is food insecure and the country has become reliant on imported wheat.
Yemen’s other wells – the oil variety – have long been the country’s sole source of significant income. According to ASPO, oil has historically represented 70-75 percent of the government’s revenue. But recent exploration efforts have failed to uncover significant additions to Yemen’s reserves, and as a result oil exports have declined 56 percent since 2001. The steep decline has pushed Yemeni authorities to look to other natural resources, such as rare minerals and natural gas, but the infrastructure to support such projects will take significant time and money to develop.
The Fastest Growing Population in the Middle East
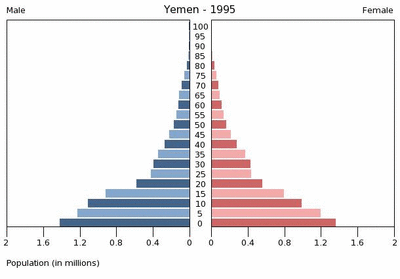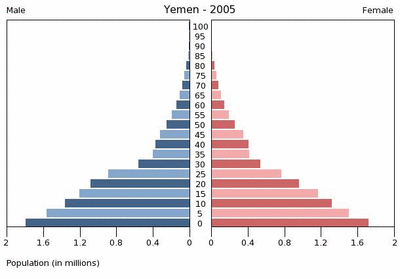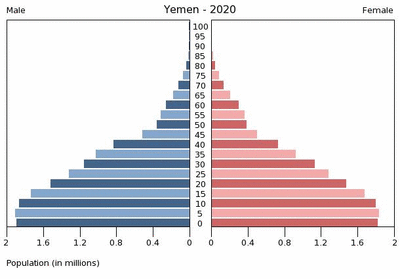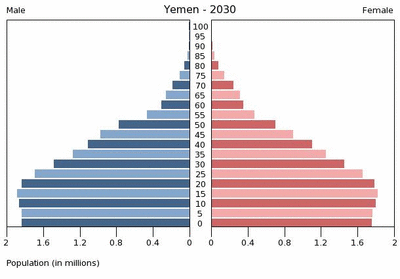
Despite the country’s limited resources, Yemen’s population of 22.8 million people is growing faster than any other country in the Middle East. According to projections from the Population Reference Bureau, by 2050, Yemen’s burgeoning population is expected to rival that of Spain.
Fully 45 percent of the current population is under the age of 15 – a troubling ratio that is expected to grow in the near future. The charts from the U.S. Census Bureau embedded below illustrate the dramatic growth of the country’s youth bulge from 1995 through 2030.
A poor record on women’s rights and a highly rural, traditional society contribute to these rapid growth scenarios. According to Population Action International’s Elizabeth Leahy Madsen, only 41 percent of Yemeni women are literate and their total fertility rate is well over the global average. A recent survey from Social Watch ranking education, economic, and political empowerment rated Yemen last in the world in gender equity. Yemeni scholar Sultana Al-Jeham pointed out during her Wilson Center presentation, “Yemeni Women: Challenges and Little Hope,” that there is only one woman in a national parliament of 301 members and that ambitious political women routinely face systematic marginalization.
A contributing factor is that 70 percent of Yemen’s population live outside of cities – far more than any other country in the region – making access to education and healthcare difficult, especially in the large swaths of land not controlled by the government.
External migration from war-torn east Africa adds to Yemen’s demographic strains. According to IRIN, approximately 700,000 Somali refugees currently reside in country, and that number may grow as the situation in Somalia continues to escalate. Within Yemen’s own borders, another 320,000 internally displaced people have fled conflict-ridden areas, further disrupting the country’s internal dynamics.
Corruption and Rebellion
Competition over resources, perceived corruption, and Al Qaeda activity have put considerable pressure on the Saleh regime in Sanaa. The government faces serious dissidence in both the north and the south, and the Los Angeles Times reports that talk of rebellion is both widespread and loud:Much of southern and eastern Yemen are almost entirely beyond the central government’s control. Many Yemeni soldiers say they won’t wear their uniforms outside the southern port city of Aden for fear of being killed. In recent months, officials have been attacked after trying to raise the Yemeni flag over government offices in the south.
USAID rates Yemen’s effective governance amongst the lowest in the world (below the 25th percentile), reflecting Sanaa’s poor control and high levels of corruption. Some reports claim that up to a third of Yemen’s 100,000-man army is made up of “ghost soldiers” who do not actually exist but whose commanders collect their salaries and equipment to sell on the open market.
The West and Al Qaeda
In testimony before Congress earlier this year, Assistant Secretary of State Jeffrey Feltman called on the Yemeni government to take a comprehensive approach to “address the security, political, and economic challenges that it faces,” including its natural resource and demographic challenges.
The Yemeni government is poised to receive $150 million in bilateral military assistance from the United States. But some experts are critical of that approach: Dr. Mustafa Alani of the Dubai-based Gulf Research Center told UN Dispatch that, “you are not going to solve the terrorist problem in Yemen by killing terrorists,” calling instead for investing in economic development.
USAID has budgeted $67 million for development assistance, economic support, and training programs in Yemen for FY 2010 and has requested $106 million for FY 2011 (although about a third is designated for foreign military financing).
While Yemen’s Al Qaeda presence continues to captivate Western governments, it is the country’s other problems – resource scarcity, corruption, and demographic issues – that make it vulnerable to begin with and arguably represent the greater threat to its long-term stability. The United States and other developed countries should address these cascading problems in constructive ways, before the country devolves into a more dangerous state like Somalia or Afghanistan. In keeping with the tenets of the Obama administration’s National Security Strategy, an exercise in American soft power in Yemen might pay great dividends in hard power gains.
Sources: Association for the Study of Peak Oil – USA, Central Intelligence Agency, Congressional Research Service, Guardian, IRIN, Los Angeles Times, New York Times, Population Action International, Population Reference Bureau, ReliefWeb, Reuters, Social Watch, Sunday Times, U.S. Census Bureau, U.S. Department of State, UN Dispatch, USA Today, USAID, World Food Programme.
Photo Credit: “Yemen pol 2002” via Wikimedia Commons courtesy of the U.S. Federal Government and “Yemen youth bulge animation” arranged by Schuyler Null using images courtesy of the U.S. Census Bureau’s International Data Base. -
Local Case Studies of Population-Environment Connections
›“The role of intergenerational transfers, land, and education in fertility transition in rural Kenya: the case of Nyeri district” in Population & Environment by Karina M. Shreffler and F. Nii-Amoo Dodoo, explores the reasons for a dramatic and unexpected decline in fertility in rural Kenya. In one province, total fertility rate (TFR) declined from 8.4 to 3.7, from 1978 to 1998. The study found numerous contributing factors for this decline, which occurred more quickly and earlier than demographers expected, but land productivity seemed to be the primary motivator. A growing population and the tradition of dividing family land among sons made continuing to have large families unrealistic for these Kenyan families. “Family planning is, therefore, not the primary causal explanation for limiting the number of children, but rather serves to help families attain their ideal family sizes,” the authors conclude. Also in Population & Environment, “Impacts of population change on vulnerability and the capacity to adapt to climate change and variability: a typology based on lessons from ‘a hard country,’” by Robert McLeman, explores the potential for human communities to adapt to climate change. The article centers on a region in Ontario that is experiencing changes in both local climatic conditions and demographics. The study finds that demographic change can have both an adverse and positive effect on the ability of a community to successfully adapt to climate change and highlights the importance of social networks and social capital to a community’s resilience or vulnerability. McLeman also presents a new typology that he hopes will “serve the purpose of drawing greater attention to the degree to which adaptive capacity is responsive to population and demographic change.”
Also in Population & Environment, “Impacts of population change on vulnerability and the capacity to adapt to climate change and variability: a typology based on lessons from ‘a hard country,’” by Robert McLeman, explores the potential for human communities to adapt to climate change. The article centers on a region in Ontario that is experiencing changes in both local climatic conditions and demographics. The study finds that demographic change can have both an adverse and positive effect on the ability of a community to successfully adapt to climate change and highlights the importance of social networks and social capital to a community’s resilience or vulnerability. McLeman also presents a new typology that he hopes will “serve the purpose of drawing greater attention to the degree to which adaptive capacity is responsive to population and demographic change.”
SpringerLink offers free access to both these articles through August 15. -
‘Dialogue Television’ Interviews Paul Collier
›Watch below or on MHz Worldview
According to last week’s guest on Dialogue, restoring environmental order and eradicating global poverty have become the two defining challenges of our era. The environmental horror unfolding in the Gulf of Mexico illustrates just how difficult it is to balance economic progress and protection of the planet. It provides an alarming example of how the search for resources and profit can lead to the plunder of nature. Host John Milewski speaks with Oxford University economist Paul Collier on his latest book, The Plundered Planet: Why We Must and How We Can Manage Nature for Global Prosperity. Scheduled for broadcast starting June 30th, 2010 on MHz Worldview channel.
Paul Collier is professor of economics and director of the Center for the Study of African Economies at Oxford University. Formerly, he served as director of development research at the World Bank. He is the author of several books, including the award-winning The Bottom Billion.
Note: A QuickTime plug-in may be required to launch the video. -
Stacy VanDeveer: Will Using Less Oil Affect Petrostate Stability?
›July 12, 2010 // By Schuyler NullIf we were to actually use less fossil fuel, what would happen to today’s petrostates? “If the oil revenues dry up or even decline a little bit you might have a real serious crisis,” said Stacy VanDeveer of the University of New Hampshire, during an interview with ECSP. We spoke to VanDeveer following his presentation at the Wilson Center event, “Backdraft: The Conflict Potential of Climate Mitigation and Adaptation.”
-
The United States and China: Clean Energy Friends or Foes?
›July 7, 2010 // By Joshua Nickell As the world moves toward clean energy alternatives, companies in the United States and China are working to develop new, more cost-efficient manufacturing processes and increase their shares of the domestic and export markets for new renewable energy technologies. Controlling production lines and growing market share will certainly have important economic implications for both countries. But over the long term, a broader perspective suggests that cooperative initiatives to increase the capacity and reduce the cost of renewable energy technologies may produce benefits on both sides of the Pacific.
As the world moves toward clean energy alternatives, companies in the United States and China are working to develop new, more cost-efficient manufacturing processes and increase their shares of the domestic and export markets for new renewable energy technologies. Controlling production lines and growing market share will certainly have important economic implications for both countries. But over the long term, a broader perspective suggests that cooperative initiatives to increase the capacity and reduce the cost of renewable energy technologies may produce benefits on both sides of the Pacific.
At an event co-hosted by the Wilson Center on the Hill and the China Environment Forum last month, John Romankiewicz, a senior analyst for China Clean Energy and Carbon Markets at Bloomberg New Energy Finance, and Ethan Zindler, head of North American Research at Bloomberg New Energy Finance, considered the big picture implications for U.S.-China clean energy cooperation and development.
Coming from an investment background, Zindler said that he looks at clean energy development “not as a social project, but as an industry.” The end goal, he asserted, is to produce clean energy more cheaply than fossil fuels. Zindler argued that if clean energy remains prohibitively expensive and uncompetitive without subsidies, it will be more difficult to implement and less likely to produce the desired environmental benefits.
Romankiewicz discussed China’s current supply of and growing demand for energy, pointing out that China’s power grid has grown by more than 70 gigawatts per year during each of the past 5 years, and that “at some point next year, the total installed capacity of China’s grid will surpass that of the United States.”
While coal and hydropower continue to play a significant role in meeting this growing demand, Romankiewicz noted that China also has set ambitious investment targets for wind farms, solar farms, biomass power plants, and other renewable energy sources.
China Looks to Go Global With Renewables
China is investing in clean energy not only to serve growing domestic energy demands, but also to become a major force in the international market, Romankiewicz asserted. Already, China has made impressive advances in clean energy industries: Of the top 15 wind turbine producers, four are Chinese and only two are American. Of the top 10 crystalline-silicon solar cell producers, six are Chinese.
But how will the United States impact China’s drive to become a major player in exporting clean energy technologies? Romankiewicz argued that breaking into the American market could prove exceedingly difficult for Chinese companies given the stiff competition from U.S. companies and other foreign firms.
The speakers also emphasized the importance of understanding the complex global economic implications of clean energy development. “If the Chinese are helping to drive down the cost… then they make solar less expensive,” said Zindler, “which means you can create more jobs in California or New Jersey.” Romankiewicz cautioned against reading too much into the “Made in China” label on clean energy technologies, as the supply chain could include parts from all over the world.
Though he maintained that focusing on the long-term benefits of clean energy investment in the United States would prove beneficial, Zindler advocated for a modicum of urgency. “I think a lot of opportunity would be missed potentially because there is innovation that doesn’t just come from a lab but comes from building newer and newer assembly lines,” Zindler remarked. But in the end, he characterized the U.S.-China battle for influence in the world’s renewable energy market as “a marathon, not a sprint,” asserting that “we’ve got a long way to go to determine who the winner will be in the clean energy race here.”
Joshua Nickell is a staff intern with the Program on America & the Global Economy at the Woodrow Wilson Center.
Photo Credit: <Wind Turbine Manufacture (in China),” courtesy of flickr user ANR2008. -
India’s Maoists: South Asia’s “Other” Insurgency
›July 7, 2010 // By Schuyler Null
The Indian government’s battle with Maoist and tribal rebels – which affects 22 of India’s 35 states and territories, according to Foreign Policy and in 2009 killed more people than any year since 1971 – has been largely ignored in the West. That should change, as South Asia’s “other” insurgency, fomenting in the world’s largest democracy and a key U.S. partner, offers valuable lessons about the role of resource management and stable development in preventing conflict.
-
Interview With Wilson Center Scholar Jill Shankleman: Could Transparency Initiatives Mitigate the Resource Curse in Afghanistan?
›June 25, 2010 // By Schuyler Null
In the wake of The New York Times article detailing a potential mineral bonanza in Afghanistan, Senators Ben Cardin and Dick Lugar earlier this week published an op-ed in support of a bill that would create “an international standard for transparency in law” by requiring oil, gas, and mining industries to report amounts paid for drilling/mining rights in their SEC filings. A similar program, albeit a voluntary one, already exists – the Extractive Industries Transparency Initiative (EITI). The senators, however, raised questions about the ability of EITI to ensure transparency and accountability of payments for future mining rights to Afghanistan’s government. Joining EITI was a “good first step,” they say, “but too many countries and companies remain outside this system.”
-
Backdraft: The Conflict Potential of Climate Mitigation and Adaptation
›The European Union’s biofuel goal for 2020 “is a good example of setting a target…without really thinking through [the] secondary, third, or fourth order consequences,” said Alexander Carius, co-founder and managing director of Adelphi Research and Adelphi Consult. While the 2007-2008 global food crisis demonstrated that the growth of crops for fuels has “tremendous effects” in the developing world, analysis of these threats are underdeveloped and are not incorporated into climate change policies, he said. [Video Below]
Showing posts from category economics.