Showing posts from category disaster relief.
-
Reform Aid to Pakistan’s Health Sector, Says Former Wilson Center Scholar
›August 5, 2010 // By Wilson Center StaffExcerpt from op-ed by Samia Altaf and Anjum Altaf in Dawn:
WE must state at the outset that we have been wary of, if not actually opposed to, the prospect of further economic assistance to Pakistan because of the callous misuse and abuse of aid that has marked the past across all elected and non-elected regimes.
We are convinced that such aid, driven by political imperatives and deliberately blind to the well-recognised holes in the system, has been a disservice to the Pakistani people by destroying all incentives for self-reliance, good governance and accountability to either the ultimate donors or recipients.
Even without the holes in the system the kind of aid flows being proposed are likely to prove problematic. Over half a century ago, Jane Jacobs, in a brilliant chapter (Gradual and Cataclysmic Money) in a brilliant book (The Death and Life of Great American Cities), showed convincingly how ‘cataclysmic’ money (money that arrives in huge amounts in short periods of time) is a surefire way of destroying all possibilities of improvement. What is needed, she argued, is ‘gradual’ money in the control of the residents themselves. While Jacobs was writing in the context of aid to impoverished communities within the US, she concluded with a remarkably prescient concern: “I hope we disburse foreign aid abroad more intelligently than we disburse it at home.”
Continue reading on Dawn.
For more on U.S. aid to Pakistan, see New Security Beat‘s coverage of the recent U.S.-Pakistani Strategic Dialogue.
Photo Credit: A U.S. Army Soldier with 32nd Infantry Regiment, 10th Mountain Division, hands out medical supplies to Pakistani refugees outside an International Committee of the Red Crescent aid station in Afghanistan’s Kunar province, October 23, 2009. Courtesy of flickr user isafmedia. -
Talk Versus Action
‘Dialogue Television’ on Rebuilding Haiti
›Watch below or on MHz Worldview
In the aftermath of Haiti’s 7.0 earthquake, the world turned its attention to the impoverished and devastated island nation (including the New Security Beat, which covered some its demographic problems). Reporters, relief workers, and volunteers from around the globe rushed to provide coverage and aide. Western leaders announced bold blueprints for building a “new Haiti.” Six months later, only a tiny portion of pledged funds have been delivered, over one million Haitians remain homeless, and much of the country’s infrastructure remains in ruins. This week on dialogue, host John Milewski speaks with Donna Leinwand of USA Today and Sheri Fink, Public Policy Scholar at the Wilson Center, on their experiences working and reporting in Haiti after the devastation. Scheduled for broadcast starting July 21st, 2010 on MHz Worldview channel.
Donna Leinwand is a reporter for the nation’s top-selling newspaper, USA Today. She’s been with the paper since 2000, covering legal issues, major crimes, the Justice Department, terrorism, and natural disasters. She is also a past president of the National Press Club. Sheri Fink is a senior fellow with the Harvard Humanitarian Initiative, a staff reporter for Pro Publica, and is a public policy scholar at the Wilson Center. She was awarded a 2010 Pulitzer Prize for her investigative piece on doctors at a hospital cut off by Hurricane Katrina flood waters.
Note: A QuickTime plug-in may be required to launch the video. -
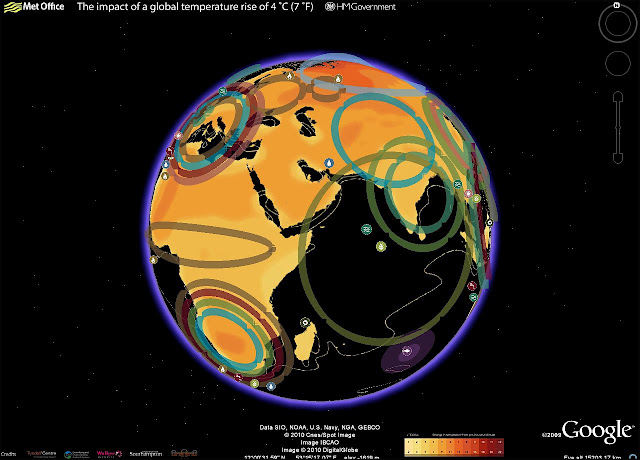
Rear Admiral Morisetti Launches the UK’s “4 Degree Map” on Google Earth
›Having had such success with the original “4 Degree Map” that the United Kingdom launched last October, my colleagues in the UK Foreign and Commonwealth Office have been working on a Google Earth version, which users can now download from the Foreign Office website.
This interactive map shows some of the possible impacts of a global temperature rise of 4 degrees Celsius (7° F). It underlines why the UK government and other countries believe we must keep global warming to below 2 degrees Celsius, compared to pre-industrial times; beyond that, the impacts will be increasingly disruptive to our global prosperity and security.
In my role as the UK’s Climate and Energy Security Envoy I have spoken to many colleagues in the international defense and security community about the threat climate change poses to our security. We need to understand how the impacts, as described in this map, will interact with other drivers of instability and global trends. Once we have this understanding we can then plan what needs to be done to mitigate the risks.
The map includes videos from the contributing scientists, who are led by the Met Office Hadley Centre. For example, if you click on the impact icon showing an increase in extreme weather events in the Gulf of Mexico region, up pops a video clip of the contributing scientist Dr Joanne Camp, talking about her research. It also includes examples of what the UK Foreign and Commonwealth Office and British Council are doing to increase people’s awareness of the risks climate change poses to our national security and prosperity, thus illustrating the FCO’s ongoing work on climate change and the low-carbon transition.
Rear Admiral Neil Morisetti is the United Kingdom’s Climate and Energy Security Envoy. -
Deepwater Horizon Prompts DOD Relief Efforts, Questions About Energy Security
›May 6, 2010 // By Schuyler NullAs the crippled Deepwater Horizon oil rig continues to spew an estimated 210,000 gallons of crude oil a day into the Gulf of Mexico, the Department of Defense has been asked to bring its considerable resources to bear on what has become an increasingly more common mission – disaster relief.
British Petroleum has requested specialized military imaging software and remote operating systems that are unavailable on the commercial market in order to help track and contain the spill.
In addition, the Coast Guard has been coordinating efforts to burn off oil collecting on the ocean’s surface and thousands of National Guard units have been ordered to the Gulf coast to help erect barriers in a bid to halt what President Obama called “a massive and potentially unprecedented environmental disaster,” as the oil slick creeps towards the coast.
As shown by these calls and the ongoing earthquake relief effort in Haiti, the military’s ability to respond to large-scale, catastrophic natural (and manmade) disasters is currently considered unmatched. The first Air National Guard aircraft was on the ground in Haiti 23 hours after the earthquake first struck, and DOD’s Transportation Command was able to begin supporting USAID relief efforts almost immediately. The Department of Defense also spearheaded American relief efforts after the 2004 tsunami and played a critical role in providing aid and security in New Orleans after Hurricane Katrina.
The Pentagon’s four-year strategic doctrine, the Quadrennial Defense Review (QDR), released earlier this year, predicts that such humanitarian missions will become a more common occurrence for America’s military, as the world grapples with the destabilizing effects of climate change, population growth, and competition over finite energy resources. Some experts see this expansion of the military’s portfolio as an essential part of a “hearts and minds” strategy, while others are critical of the military’s ability to navigate the difficulties of long-term reconstruction.
The QDR also highlights DOD’s efforts to reduce the need for oil – and thus deepwater oil rigs – in the first place.
The DOD as a whole is the largest consumer of energy in the United States, consuming a million gallons of petroleum every three days. In accordance with the QDR, Pentagon leaders have set an ambitious goal of procuring at least 25 percent of the military’s non-tactical energy requirement from renewable sources by 2025. The Air Force – by far the Pentagon’s largest consumer of petroleum – would like to acquire half of its domestic jet fuel requirement from alternative fuels by 2016 and successfully flight-tested a F/A-18 “Green Hornet” on Earth Day, using a blend of camelina oil and jet fuel.
At a speech at Andrews Air Force Base in March, President Obama lauded these efforts as key steps to moving beyond a petroleum-dependant economy. However, at the same event, he announced the expansion of off-shore drilling, in what some saw as a political bone thrown to conservatives. Since the Deepwater Horizon incident, the administration announced a temporary moratorium until the causes of the rig explosion and wellhead collapse have been investigated.
Cleo Paskal, associate fellow for the Energy, Environment, and Development Programme at Chatham House, warns that without paying adequate attention to the potential effects of a changing environment on energy infrastructure projects of the future – like the kind of off-shore drilling proposed for the Gulf and Eastern seaboard – such disasters may occur more frequently.
In an interview with ECSP last fall, Paskal pointed out that off-shore oil and gas platforms in the Gulf of Mexico were a prime example of how a changing environment – such as increased storm frequency and strength – can impact existing infrastructure. “Katrina and Rita destroyed over 400 platforms, as well as refining capacity onshore. That creates a global spike in energy prices apart from having to rebuild the infrastructure.”
The Department of Defense has demonstrated – in policy, with the QDR, and in action – that it can marshal its considerable resources in the service of renewable energy and disaster relief. But given the scope of today’s climate and energy challenges, it will take much more to solve these problems.
Photo Credit: “Deepwater Horizon,” courtesy of flickr user U.S. Coast Guard. U.S. Air Force Tech. Sgt. Joe Torba of the 910th Aircraft Maintenance Squadron, which specializes in aerial spray, prepares to dispatch aircraft to a Gulf staging area. -
Family Planning in Fragile States
›
“Conflict-affected countries have some of the worst reproductive health indicators,” said Saundra Krause of the Women’s Refugee Commission at a recent Wilson Center event. “Pregnant women may deliver on the roadside or in makeshift shelters, no longer able to access whatever delivery plans they had. People fleeing their homes may have forgotten or left behind condoms and birth control methods.”
-
Shape of Things to Come: A Demographic Perspective of Haiti’s Reconstruction
›Last month, the International Donors’ Conference Towards a New Future for Haiti sought to lay the groundwork for Haiti’s long-term recovery by pledging an impressive $9.9 billion over the next decade. A large portion of the money will fund health, education, and employment efforts that are crucial to meeting the needs of Haiti’s people—particularly its youth. In a new case study of Haiti’s demography and development, Population Action International (PAI) argues that the country’s age structure should play a central role in any reconstruction strategy.
In Haiti, almost 70 percent of the population is under the age of 30, and this very youthful population affects every aspect of the country’s development prospects, from economic opportunities to security issues, political stability, gender equality, and climate change adaptation.
Haiti is at a demographic crossroads. If sound policies are in place, youthful age structures can translate into an economic asset for the country. The combination of decreasing fertility levels and a growing working-age population may open a window of opportunity for economic growth. To seize it, large-scale education and employment policies and programs should seek to raise employment rates for both male and female youth.
For Haiti to reap the benefits of this “demographic dividend,” access to reproductive health services is equally important. According to the most recent Demographic and Health Survey (2005-2006), if all unintended births were avoided, the average fertility level in the country would be 2.4 children instead of four.
But if instead, Haiti ignores the needs of its youth, the country will remain vulnerable to a variety of political and economic challenges. Youth unemployment is twice that of the rest of the population, which could have a negative impact on the country’s political stability and security situation.
The PAI report The Shape of Things to Come shows that countries with very young age structures are less likely than others to sustain democratic regimes and that age structure impacts political stability. To be an effective partner in its reconstruction, the Haitian government needs stable governance. By prioritizing education, health, and employment for young people, Haiti may reduce the risk of urban violence, help attract private investors, and speed its recovery.
Addressing demographic factors will also help Haiti achieve broader development goals. Decades of high population growth and the use of charcoal as the main source of energy have deforested 97 percent of the country, increasing Haiti’s inherent vulnerability to environmental disasters and climate change. Denuded landscapes contribute to devastating floods, especially in urban coastal zones. The lack of tree cover reduces the country’s ability to absorb carbon and causes wide variations in temperature. Due to soil erosion, Haiti’s agricultural industry is one of the least productive in the world, leading to widespread poverty and food insecurity.
The integration of demographic factors into development strategies constitutes one of the most compelling ways for Haiti to facilitate not only its reconstruction, but also address the challenges of climate change and make its population more resilient and prosperous.
Three new case studies from Population Action International on Haiti, Yemen and Uganda examine the challenges specific to countries with very young age structures and recommend policy solutions.
Béatrice Daumerie is a research fellow at Population Action International (PAI).
Photo: Haitian youth. Courtesy Flickr user NewsHour -
SOUTHCOM Takes Disaster Response to Google
›United States Southern Command (SOUTHCOM) has publicly released a Google Earth-based mapping system, 3D User Defined Operational Pictures (UDOP) (Google Earth plug-in required), aiming to help emergency personnel and donors better respond to humanitarian crises.
Currently, UDOP maps are available for responses in Haiti and Chile. Data layers uploaded by SOUTHCOM and others can be toggled on and off and depict an array of information, from earthquake intensity maps to a 3D model of Haiti’s collapsed presidential palace. Other layers mark:
Although intriguing, the mapping system currently has major shortcomings: much of the information provided is out of date rather than in real time, and while some maps include information such as the structural integrity of buildings, patient capacities of hospitals, and brief status updates on site activities, others offer little more than approximate locations and names.- Locations and statuses of hospitals;
- Collapsed or blockaded sections of major roadways;
- Helipads and airstrips;
- Food and water distribution centers;
- IDP shelters; and
- Areas of gang activity.
Haiti and Chile, however, were only the first tests of the UDOP system. Given that the distinction between real-time and frozen data is blurred during days immediately following a disaster (the period for which UDOP is designed and most needed) and that the donor and humanitarian assistance communities will likely develop greater familiarity and comfort with the system over time, UDOP’s current flaws may simply reflect the system’s recent adoption.
For more on Google’s contributions to environmental work and human security, check out our previous post on educational climate change “tours” in Google Earth. -
‘Wilson Center on the Hill:’ Haiti’s Long Road Ahead
›March 25, 2010 // By Wilson Center StaffNearly two months after the devastating 7.0 magnitude earthquake in Port-au Prince, Haiti, the country still needs assistance to provide basic healthcare and shelter, in addition to rebuilding Haiti’s economy, government, and institutions. As the international community and NGOs make the transition from emergency disaster relief to long-term reconstruction and capacity-building efforts, donor coordination and long-term commitment are crucial. Recently, on Capitol Hill, a panel of experts organized by Wilson Center on the Hill and the Wilson Center’s Latin American Program discussed Haiti’s continuing problems and challenges.
Patience Necessary
Johanna Mendelson Forman, a senior associate for the Americas Program at the Center for Strategic and International Studies, stressed that progress in Haiti will take time—perhaps five years to rebuild and 10 years to see positive economic growth. This timeline is often frustrating for donors—including Congress and U.S. citizens—who want to see immediate results, she noted. Nevertheless, Mendelson Forman discounted the myth that “because Haiti is a weak state it is not a sovereign state,” and emphasized that developing and strengthening the Haitian government remains necessary.
She observed that the post-earthquake efforts in Haiti have been different from previous United Nations interventions, particularly in terms of the Latin American community’s involvement. Brazil, for example, is leading relief operations. Other Latin American countries—including Haiti’s neighbor, the Dominican Republic—have committed to promoting a stable and secure Haiti. Here Mendelson Forman noted a new partnership initiated by the Dominican and Haitian governments. “[Dominican officials] understand that they are doomed if Haiti is doomed,” she said. “As members of the international community, it is our job to foster that reconciliation.”
Costs Are Rising
Andrew Philip Powell, a regional economic advisor in the Caribbean Country Department at the Inter-American Development Bank (IDB), said that while the IDB initially estimated damage from the earthquake at about $8 billion, the complete destruction of the government and commerce centered in Port-au-Prince could push that number much higher. The IDB and partner organizations are currently conducting a Post-Disaster Needs Assessment that will ultimately identify the official damages and ballpark the cost of reconstruction.
Powell stated that Haiti is “not starting from a blank slate,” citing a development strategy agreed upon in April 2009 by the Haitian government and international donors. In keeping with the strategy, he emphasized the need for effective coordination between donors and the Haitian government. At the same time, he said it is vital to encourage population dispersion by shifting government agencies and private-sector jobs to other parts of the country. Haiti needs roads and communication networks outside of the capital area, as well as export processing zones in outlying regions, to increase the economic opportunities outside of Port-au-Prince, he said.
However, with the large amounts of aid flowing into the country, Powell warned donors and Haitian officials to remain on the lookout for “Dutch disease”—a decline in the manufacturing sector following a sharp increase in natural resource prices, foreign assistance, or foreign direct investment. Its occurrence could increase Haiti’s dependency on aid in the future.
Challenges for Healthcare
Sheri Fink, a public policy scholar at the Woodrow Wilson Center and senior fellow at the Harvard Humanitarian Initiative, offered her perspective on Haiti’s continuing health crisis based on two trips to the country in the earthquake’s aftermath. There are signs of hope, including some normalcy and commerce returning to the camps, she noted, but problems in the health sector as a whole are increasing. As field hospitals put in place after the earthquake close, “there is a fear among Haitians that attention is starting to turn elsewhere,” she said.
According to Fink, “the work is far from done” in Haiti, a sentiment she said is shared by many departing health workers. The hospitals left standing are not prepared to deal with the influx of patients arriving at their doors following the closure of field hospitals, and government health workers are currently working without pay.
Fink also pointed out the risk of long-term earthquake-related health problems, including injuries suffered during aftershocks or from falling debris, inflamed chronic diseases, horrible conditions and lack of basic health services in camps, and the “looming nightmare” of infectious disease epidemics.
Fink called for more international involvement to avert a widening of the health crisis. “We’ve made a big commitment and to follow-up on the investment, to make it mean something; let’s not be satisfied with just bringing things back to where they were,” she said.
By Sarah Huston and David Klaus of Wilson Center on the Hill at the Woodrow Wilson International Center for Scholars.
Photo: Courtesy Flickr user United Nations Development Programme