Showing posts from category climate change.
-
Sajeda Amin on Population Growth, Urbanization, and Gender Rights in Bangladesh
› “One of the reasons why population grows very rapidly in Bangladesh is women get married very early and have children very early,” the Population Council’s Sajeda Amin told ECSP in a recent interview. “So even though they are only having two children, they are having them at an average age of around 20. As demographers would say, women ‘replace’ themselves very rapidly.”
“One of the reasons why population grows very rapidly in Bangladesh is women get married very early and have children very early,” the Population Council’s Sajeda Amin told ECSP in a recent interview. “So even though they are only having two children, they are having them at an average age of around 20. As demographers would say, women ‘replace’ themselves very rapidly.”
Largely through the promotion of contraceptive use, family planning programs implemented over the past 35 years by the Bangladeshi government and a variety of NGOs have helped lower the country’s total fertility rate to 2.7 from 6.5 in the mid-1970s. To build on this progress, the Population Council has joined a consortium of other organizations – including the Bangladesh Legal Aid and Services Trust, Marie Stopes International, and We Can End All Violence Against Women – to launch the Growing Up Safe and Healthy (SAFE) project in Amin’s native Dhaka and other Bangladeshi cities.
Currently nearing the completion of its first year, the four-year initiative has several aims, among them increasing access to reproductive healthcare services for adolescent girls and young women and bolstering social services to protect those populations from (and offer treatment for) gender-based violence. The project also looks to strengthen laws designed to reduce the prevalence of child marriage – a long-standing Bangladeshi institution that keeps population growth rates high while denying many young women the opportunity to pursue economic and educational advancement.
A Focus on Gender and Climate
Amin says the SAFE project boasts several qualities that collectively set the initiative apart from similar-minded programs in Bangladesh dealing with gender and poverty. These include a strong research component incorporating quantitative and qualitative analysis; the holistic nature of the program, which incorporates educational outreach, livelihood development, and legal empowerment; a commitment to working with both male and female populations; and an emphasis on interventions targeting young people, with the hope that such efforts will allow adolescents to make better-informed decisions about future relationships and reproductive health, thus reducing the likelihood of gender-based violence.
Finally, while many existing gender-based programs focus exclusively on rural communities, Amin points out that the SAFE project also stands apart because of its focus on the country’s rapidly expanding urban areas. To date, the initiative is focusing many of its early interventions in a Dhaka slum that has seen an influx of rural migrants in recent years due to climate-change impacts in the country’s low-lying coastal areas.
“A lot of the big problems in Bangladesh now are climate-driven in the sense of creating mass movements out of areas that are particularly vulnerable or have been hit by a major storm,” Amin said. “Usually these are people who, once they lose their homes and their livelihoods, will have no choice but to move to urban areas, and that’s a process that is kind of a big outstanding issue in Bangladesh now.”
By building programming around girls and young women in such communities, the SAFE project is looking to spark change from the bottom up, prioritizing the unmet health and social needs of some of Bangladesh’s most vulnerable populations.
The “Pop Audio” series is also available as podcasts on iTunes.
Sources: Global Post, Ministry of Health and Family Welfare (Bangladesh), Shaikh and Becker (1985). -
Reducing Health Inequities to Better Weather Climate Change
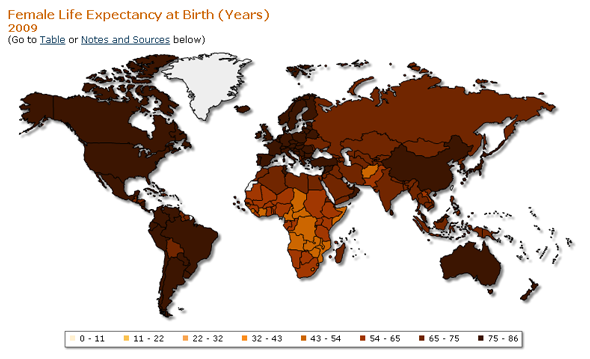
›In an article appearing in the summer issue of Global Health, Dr. Margaret Chan, director-general of the World Health Organization (WHO), brings to light what she calls the starkest statistic in public health: the vast difference in the mortality rates between rich and poor countries. For example, the life expectancy of a girl is doubled if she is born in a developed country rather than in a developing country. Chan writes that efforts to improve health in developing countries now face an additional obstacle: “a climate that has begun to change.”
Climate change’s effect on health has increasingly moved into the spotlight over the past year: DARA’s Climate Vulnerability Monitor measures the toll that climate change took in 2010 on human health, estimating some 350,000 people died last year from diseases related to climate change. The majority of these deaths took place in sub-Saharan Africa, where weak health systems already struggle to deal with the disproportionate disease burden found in the region. The loss of “healthy life years” as a result of global environmental change is predicted to be 500 times greater in poor African populations than in European populations, according to The Lancet.
The majority of these deaths are due to climate change exacerbating already-prominent diseases and conditions, including malaria, diarrhea, and malnutrition. Environmental changes affect disease patterns and people’s access to food, water, sanitation, and shelter. The DARA Climate Vulnerability Monitor predicts that these effects will cause the number of deaths related to climate change to rise to 840,000 per year by 2030.
But few of these will be in developed countries. With strong health systems in place, they are not likely to feel the toll of a changing environment on their health. Reducing these inequities can only be achieved by alleviating poverty, which increases the capacity of individuals, their countries, and entire regions to adapt to climate change. It would be in all of our interests to do just this, writes Chan: “A world that is greatly out of balance is neither stable nor secure.”
Sarah Lindsay is a program assistant at the Ministerial Leadership Initiative for Global Health and a Masters candidate at American University.
Sources: DARA, Global Health, The Lancet, World Health Organization.
Image Credit: Henry J. Kaiser Family Foundation and the World Health Organization. -
Lakis Polycarpou, Columbia Earth Institute
The Year of Drought and Flood
›August 1, 2011 // By Wilson Center StaffThe original version of this article, by Lakis Polycarpou, appeared on the Columbia Earth Institute’s State of the Planet blog.
On the horn of Africa, ten million people are now at risk as the region suffers the worst drought in half a century. In China, the Yangtze – the world’s third largest river – is drying up, parching farmers and threatening 40 percent of the nation’s hydropower capacity. In the U.S. drought now spreads across 14 states creating conditions that could rival the dust bowl; in Texas, the cows are so thirsty now that when they finally get water, they drink themselves to death.
And yet this apocalyptic dryness comes even as torrential springtime flooding across much of the United States flows into summer; even as half a million people are evacuated as water rises in the same drought-ridden parts of China.
It seems that this year the world is experiencing a crisis of both too little water and too much. And while these crises often occur simultaneously in different regions, they also happen in the same places as short, fierce bursts of rain punctuate long dry spells.
The Climate Connection
Most climate scientists agree that one of the likely effects of climate will be an acceleration of the global water cycle, resulting in faster evaporation and more precipitation overall. Last year, the Proceedings from the National Academy of Sciences published a study which suggested that such changes may already be underway: According to the paper, annual fresh water flowing from rivers into oceans had increased by 18 percent from 1994 to 2006. It’s not hard to see how increases in precipitation could lead to greater flood risk.
At the same time, many studies make the case that much of the world will be dramatically drier in a climate-altered future, including the Mediterranean basin, much of Southwest and Southeast Asia, Latin America, the western two-thirds of the United States among other places.
Continue reading on State of the Planet.
Sources: Associated Press, The New York Times, Proceedings from the National Academy of Sciences, Reuters, Science Magazine, University Corporation for Atmospheric Research.
Photo Credit: “Drought in SW China,” courtesy of flickr user Bert van Dijk. -
Cynthia Brady, USAID
The Specter of “Climate Wars”
›July 29, 2011 // By Wilson Center StaffThe original version of this article, by Cynthia Brady, appeared in the June/July 2011 edition of USAID’s Frontlines.
In 2007, many in the advocacy community rushed to categorize the conflict in the Darfur region of Sudan as a “climate war” in the wake of a compelling United Nations report that emphasized the ways climate change and environmental degradation can drive conflict.
In 2009, international media focused significant attention on an academic study that analyzed historical linkages between civil war and temperatures in sub-Saharan Africa and suggested there would be a 54-percent increase in armed conflicts by 2030. [Video Below]
In both cases, subsequent research and analyses conducted by prominent scholars countered those original claims of such direct climate and conflict connections, at least based on existing evidence. Those studies are two examples of the recent spate of analyses on the subject and serve as cautionary tales against alarmism and overly simplistic assumptions about specific connections between climate change and stability.
The reality is far more complicated.
The science and practice of analyzing the interaction of climate change risk and conflict risk is new and still evolving. As a result, there is little certainty over exactly how climatic change will manifest in specific locations and what the consequences will be for economic development, political stability, and peace and security.
Around the world, climate change likely will create both risks and opportunities, making it critical that development and relief organizations like USAID consider climate change not as a monolithic threat but rather as an important influence within a complex web of environmental and social factors.
Responding to climate change effectively means taking action to reduce the threats. It also means harnessing opportunities by helping people and institutions to effectively cope with and adapt to change – environmental or otherwise. Climate-focused interventions, if conducted strategically and with sensitivity to local context, can produce outcomes for conflict prevention and sustainable development as well.
For example, recent USAID-funded research in the conflict-prone Karamoja region of northeastern Uganda found that engaging local communities in the design and implementation of climate change adaptation activities – for example, promoting shared grazing areas and creating small-scale irrigation systems – holds considerable potential to reduce conflict by building social cohesion and addressing feelings of marginalization and disempowerment among local community members.
Since 2008, USAID has invested in research to better understand how specific climate factors contribute to the risk of conflict and affect the resilience of social structures and institutions. The goal is to build a deeper understanding that will enable the agency and its partners to respond most effectively to climate-related stress, reduce the risk of violent outcomes, and maximize the potential for U.S. foreign assistance to prevent conflict and promote stability.
This knowledge also will help USAID make wise investments as part of meeting U.S. Government commitments under the Global Climate Change Initiative as described in President Barack Obama’s September 2010 Presidential Policy Directive on Global Development.
Climate Change and Conflict Prevention
The research thus far points to climate change as an exacerbating factor in situations where political, economic, and social stresses already exist. The risk of conflict is greatest where there is poor governance and low institutional capacity.
The agency, through its Office of Conflict Management and Mitigation (CMM), has identified two basic scenarios under which climate change could combine with other variables and potentially lead to conflict.
First, climate change could intensify existing environmental or resource problems. For example, a series of droughts could reduce the available local water supply, aggravating competition between farmers and pastoralists in already arid regions. Second, climate change could create new environmental or resource problems that contribute to instability. Changing rainfall patterns, for instance, could damage agricultural production in formerly fertile areas, decimating local livelihoods and causing food insecurity.
There is a third area of potential risk for USAID and other donors as well: namely, that climate-related financing, policies, and programs which have not adequately considered local conflict dynamics and context could produce serious unintended negative consequences.
Climate change-related interventions such as incentive payments to stop deforestation – particularly in fragile states and conflict-affected areas – must recognize that both the money and the power to allocate benefits may inadvertently reinforce the social status quo, shift local power balances, or expose governance failures.
In her field work in Nepal, Janani Vivekananda, a researcher with USAID partner International Alert, recently illustrated how certain types of assistance might inadvertently do harm. She explained how a now-defunct village water tap installed in an effort to mitigate the effects of climate variability, did not appropriately consider the local social, political, and conflict context or even basic environmental parameters. In the end, it contributed to local grievance.
The community had requested the tap to be installed during a period of water stress and three consecutive years of drought. The Government of Nepal sponsored the project just before the elections.
Vivekananda explained: “These people are hand-to-mouth farmers. They didn’t know and they wouldn’t know that ground water levels were falling. They wouldn’t know the negative impacts of uncontrolled surface water extraction and so they chased about this tap, and within three months it ran dry. That was the only cash that was injected into the community for development purposes, and it had no impact whatsoever apart from being a stark reminder that the government itself isn’t doing what it ought to.”
This story highlights the reality that local context will define the outcome of peace or conflict and, thus, as CMM’s discussion paper “Climate Change, Adaptation, and Conflict: A Preliminary Review of the Issues” noted, there remains a pressing need for a more robust, fine-grained understanding of the interaction between climate change and the political, social, and economic realities of conflict-prone areas.
To help fill this information gap, USAID is supporting field-based climate change and conflict research in Peru, Uganda, Ethiopia, and the Niger River Basin in West Africa. At the global level, the agency is improving its ability to integrate climate change considerations into conflict early warning models. It is also establishing academic and practitioner partnerships that explore a wide range of environment and security issues.
Today, close to 60 percent of the State Department’s and USAID’s foreign assistance goes to 50 countries that are in the midst of, recovering from, or trying to prevent conflict or state failure. A significant amount of that assistance is slated for Global Climate Change mitigation and adaptation programming. Yet, as CMM’s conflict early warning specialist, Kirby Reiling, observed, “much of that money could be a lost investment if those countries fall into armed conflict.”
With conflict-sensitive development assistance and with smart climate change policies and programs, vulnerable countries will have enhanced opportunities to build stronger societies and more resilient institutions for sustainable development, peace, and security.
Cynthia Brady is a senior conflict advisor in USAID’s Office of Conflict Management and Mitigation.
Photo Credit: Afghan farmers plow a field guarded by U.S. Marines, courtesy of flickr user isafmedia. -
Edward Carr, Open the Echo Chamber
Drought Does Not Equal Famine
›July 27, 2011 // By Wilson Center StaffThe original version of this article, by Edward Carr, appeared on Open the Echo Chamber.
After reading a lot of news and blog posts on the situation in the Horn of Africa, I feel the need to make something clear: The drought in the Horn of Africa is not the cause of the famine we are seeing take shape in southern Somalia. We are being pounded by a narrative of this famine that more or less points to the failure of seasonal rains as its cause…which I see as a horrible abdication of responsibility for the human causes of this tragedy.
First, I recommend that anyone interested in this situation – or indeed in food security and famine more generally, to read Mike Davis’ book Late Victorian Holocausts. It is a very readable account of massive famines in the Victorian era that lays out the necessary intersection of weather, markets, and politics to create tragedy – and also makes clear the point that rainfall alone is poorly correlated to famine. For those who want a deeper dive, have a look at the lit review (pages 15-18) of my article “Postmodern Conceptualizations, Modernist Applications: Rethinking the Role of Society in Food Security” to get a sense of where we are in contemporary thinking on food security. The long and short of it is that food insecurity is rarely about absolute supplies of food – mostly it is about access and entitlements to existing food supplies. The Horn of Africa situation does actually invoke outright scarcity, but that scarcity can be traced not just to weather – it is also about access to local and regional markets (weak at best) and politics/the state (Somalia lacks a sovereign state, and the patchy, ad hoc governance provided by Al Shabaab does little to ensure either access or entitlement to food and livelihoods for the population).
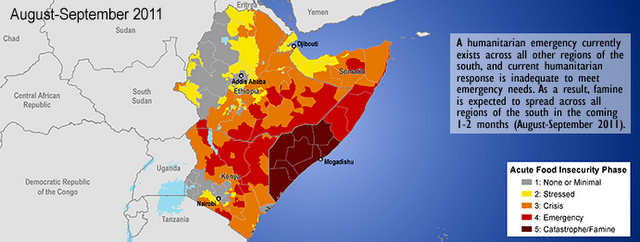
For those who doubt this, look at the Famine Early Warning System Network (FEWS NET) maps I put in previous posts here and here (Editor: also above). Famine stops at the Somali border. I assure you this is not a political manipulation of the data – it is the data we have. Basically, the people without a functional state and collapsing markets are being hit much harder than their counterparts in Ethiopia and Kenya, even though everyone is affected by the same bad rains, and the livelihoods of those in Somalia are not all that different than those across the borders in Ethiopia and Kenya. Rainfall is not the controlling variable for this differential outcome, because rainfall is not really variable across these borders where Ethiopia, Kenya, and Somalia meet.
Continue reading on Open the Echo Chamber.
Image Credit: FEWS NET and Edward Carr. -
Eddie Walsh, The Diplomat
Indonesia’s Military and Climate Change
›July 22, 2011 // By Wilson Center StaffThe original version of this article, by Eddie Walsh, appeared on The Diplomat’s ASEAN Beat blog.
With more than 17,000 islands and 80,000 kilometers of coastline, Indonesia is extremely vulnerable to climate change. Analysts believe that rising temperatures will almost certainly have a negative impact on human security in Indonesia, which in turn will increase the probability of domestic instability and introduce new regional security concerns. With this in mind, it’s important that Indonesia’s armed forces take a range of measures to prioritize environmental security, including procuring new equipment, strengthening bilateral and multilateral relations, and undertaking training for new roles and missions.
Indonesians are expected to experience warmer temperatures, increased precipitation (in the northern islands), decreased precipitation (in the southern islands), and changes in the seasonality of precipitation and the timing of monsoons. These phenomena could increase the risk of either droughts or flooding, depending on the location, and could also reduce biodiversity, lead to more frequent forest fires and other natural disasters, and increase diseases such as malaria and dengue, as well incidences of diarrhea.
The political, economic, and social impact of this will be significant for an archipelago-based country with decentralized governance, poor infrastructure, and a history of separatist and radical conflict. According to a World Bank report, the greatest concern for Indonesia will be decreased food security, with some estimates projecting variance in crop yields of between -22 percent and +28 percent by the end of the century. Rising sea levels also threaten key Indonesian cities, including Jakarta and Surabaya, which could stimulate ‘disruptive internal migration’ and result in serious economic losses. Unsurprisingly, the poor likely will be disproportionately impacted by all of this.
Continue reading on The Diplomat.
Sources: World Bank.
Photo Credit: “Post tsunami wreckage Banda Aceh, Sumatra, Indonesia,” courtesy of flickr user simminch. -
UN Security Council Debates Climate Change
› Today the UN Security Council is debating climate change and its links to peace and international security. In this short video, ECSP Director Geoff Dabelko outlines his hopes for today’s session and its follow-on activities. He suggests it is time to move from problem identification to problem solving by developing practical steps to respond to climate-security links.
Today the UN Security Council is debating climate change and its links to peace and international security. In this short video, ECSP Director Geoff Dabelko outlines his hopes for today’s session and its follow-on activities. He suggests it is time to move from problem identification to problem solving by developing practical steps to respond to climate-security links.
This Security Council debate was held at the instigation of the German government, chair of the Security Council this month. But it is not the first time this body has debated climate and security. In 2007, the United Kingdom used its prerogative as chair to introduce the topic in the security forum. Opinions from member states diverged on whether the Security Council was the appropriate venue for climate change.
Largely at the instigation of the Alliance of Small Island States, the UN General Assembly tackled climate and security links in 2009. The resulting resolution also spurred the UN Secretary-General to produce a summary report on the range of climate and security links.
Sources: Reuters, UN. -
Life on the Edge: Climate Change and Reproductive Health in the Philippines
›July 18, 2011 // By Hannah MarquseeHigh population growth and population density have placed serious stress on natural resources in the Philippines. No one lives far from the coast in the 7,150-island archipelago, making the population extremely dependent on marine resources and vulnerable to sea-level rise, flooding, and other effects of climate change. The coastal megacity of Manila – one of the most densely populated in the world – is beset by poor urban planning, lack of infrastructure, and a large population living in lowland slums, making it particularly vulnerable to increased flooding and natural disasters. [Video Below]
The Philippines is now home to 93 million people and by 2050 is expected to reach 155 million, according to the UN’s medium fertility variant projections. Development programs in the country have made great strides towards increasing access to family planning and reproductive health services as well as improving management of marine resources, but the underlying trends remain troubling.
The Battle Over Reproductive Health
Since 1970, the government’s Commission on Population has been addressing population growth, reproductive health, and family planning. “The impact of the high rate of population growth is intricately linked to the welfare and sustainable development for a country like the Philippines, where poverty drives millions of people to overexploit their resource base,” wrote the commission. As a result of these efforts and others, total fertility rate has dropped from 6.0 children per woman in 1970, to the present 3.2.
The Philippines has also made great gains towards achieving Millennium Development Goal targets, “particularly in the alleviation of extreme poverty; child mortality; incidences of HIV/AIDS, tuberculosis, and malaria; gender equality in education; household dietary intake; and access to safe drinking water,” according to the United Nations Development Program (UNDP). Yet, “glaring disparities across regions persist,” UNDP states.
One of the poorest regions in the country, the Autonomous Region of Muslim Mindanao, is also home to a violent separatist movement. With limited access to health services, fertility and population growth rates are the highest in the country. Women in Mindanao average 4.2 children per woman; one in four married women has an unmet need for contraception; and 45 percent of households live in poverty (compared to 24 percent nationally).
Nationally, “serious challenges and threats remain with regard to targets on maternal health, access to reproductive health services, nutrition, primary education, and environmental sustainability,” according to UNDP–in particular, indicators on maternal health are “disturbing” and of all the MDGs, are labeled “least likely to be achieved.”
Out of three million pregnancies that occur every year, half were unplanned and one-third of these end in abortions, according to a 2006 report of the Allan Guttmacher Institute conducted in the Philippines. Induced abortion was the fourth leading cause of maternal deaths, and young women accounted for 17 percent of induced abortions. Over half of births occurred at home and one-third of them were assisted by traditional birth attendants. Around 75 percent of the poorest quintile did not have access to skilled birth attendants compared to only 20 percent of the richest quintile.
The politically influential Catholic Church recently blocked passage of a reproductive health bill, despite support by President Benigno Aquino and a majority of Filipinos. The bill seeks to provide universal access to contraception and would make sex education required from fifth grade onwards, a provision that has angered Church officials.
Manila Under Water
The Philippines’ combination of high population growth and limited land area (nearly all of which is near the coast) makes the country extremely vulnerable to the effects of climate change. Sixty-five percent of Filipinos live in coastal areas and 49 percent live in urban areas. Paul Hutchcroft, in Climate Change and Natural Security, writes that “even in the best of times, the frequency of typhoons, floods, earthquakes, and volcanic eruptions makes the Philippines one of the most disaster-prone countries in the world” (p. 45).
Population growth, climate change, and deforestation will only increase the severity of these disasters, he concludes. Hutchcroft points out that by 2080, projected temperature increases of between 1.2 to 3.9 degrees Celsius could raise sea levels by an estimated 0.19 to 1.04 meters – a scary thought for the 15 million living within a one-meter elevation zone (p. 46).
In 2009, metropolitan Manila, currently home to 11 million people (18,650 per square kilometer) and projected to grow to 19 million by 2050, was hit by tropical storms that caused devastating flooding – at their peak, waters reached nearly seven meters, according to a World Bank report. “More than 80 percent of the city was underwater,” write the authors, “causing immense damage to housing and infrastructure and displacing around 280,000-300,000 people.”
“Even if current flood infrastructure plans are implemented, the area flooded in 2050 will increase by 42 percent in the event of a 1-in-100-year flood,” says the World Bank report. Climate change could also increase the cost of flooding as much as $650 million, or 6 percent of GDP. Only by considering climate-related risks in urban planning can the Philippines hope to mitigate the effects of climate change, the report concludes.
Integrated Development: One Piece of the Puzzle?
Population, health, and environment (PHE) programs that integrate family planning and natural resource management are one way to help the majority of Filipinos that live in densely populated and resource-stressed coastal areas.
In ECSP’s FOCUS Issue 15, “Fishing for Families: Reproductive Health and Integrated Coastal Management in the Philippines,” Joan Castro and Leona D’Agnes explain how Path Foundation Philippines, Inc.’s IPOPCORM project – which ran from 2000 to 2006 – helped “improve reproductive health and coastal resource management more than programs that focused exclusively on reproductive health or the environment – and at a lower total cost.” A recent peer-reviewed study, co-authored by Castro and D’Agnes and published in Environmental Conservation, proved the same point with rigorous analysis.
“When we started IPOPCORM, there was really nothing about integrating population, health, and environment,” said Castro in an interview with ECSP. IPOPCORM provided some of the first evidenced-based results showing there is value added to implementing coastal resource management and family planning in tandem rather than separately. In part due to the success of the IPOPCORM, the Philippines have become one of the major PHE development implementers in the world.
Creating sustainably managed marine sanctuaries while improving access to family planning provides a way forward for many coastal communities. However, the Philippines’ urban woes – 44 percent of urban dwellers live in slums, according to the Population Reference Bureau – internal divisions, and natural vulnerability will likely make it difficult to dodge considerable climate-related effects in the near future. Already the archipelago’s vast biodiversity is in crisis, according to studies over two thirds of native plant and animal species are endemic to the islands and nearly half of them are threatened; only seven percent of its original old-growth less than 10 percent of the islands’ original vegetation remains; and 70 percent of nearly 27,000 square kilometers of coral reefs are in poor condition.
Sources: CIA, Conservation International, Field Museum, The Guardian, The Huffington Post, Philippines National Statistics Office, Population Reference Bureau, United Nations, U.S. Census Bureau, World Bank, World Wildlife Fund.
Photo Credit: “Climate Risk and Resilience: Securing the Region’s Future” courtesy of Flickr user Asian Development Bank.