-
Seven Ways Seven Billion People Affect the Planet
›October 31, 2011 // By Geoffrey D. DabelkoSeven billion people now live on earth, only a dozen years after global population hit six billion. But the seven billion milestone is not about sheer numbers: Demographic trends will significantly impact the planet’s resources and peoples’ security.
Growing populations stress dwindling natural resource supplies while high levels of consumption in both developed countries and emerging economies drive up carbon emissions and deplete the planet’s resources. And neglected “youth bulges” could bolster extremism in fragile states like Somalia and destabilize nascent democracies like Egypt.
Here are seven ways seven billion people affect the planet, according to recent research:
Security: Nearly 90 percent of countries with very young and youthful populations had undemocratic governments at the end of the 20th century. Eighty percent of all new civil conflicts between 1970 and 2007 occurred in countries where at least 60 percent of the population is under age 30, says demographer Elizabeth Leahy Madsen. According to research by demographer Richard Cincotta, these countries may achieve democracy, but are less likely to sustain it.- Richard Cincotta: Tunisia Predicted: Demography and the Probability of Liberal Democracy in the Greater Middle East
- Elizabeth Leahy Madsen: Demographic Security 101
Water: By 2025, 1.8 billion people will be living in countries with water scarcity, and fully two-thirds will be living in conditions of water stress. People are using groundwater faster than it can be naturally replenished, putting us in danger of “peak water,” says MacArthur “Genius” Fellow Peter Gleick. “We cannot talk about water without also understanding the enormously important role of population dynamics and population growth.”- Peter Gleick: Population Dynamics Key to Sustainable Water Solutions
Forests: The growing demand for energy has helped devastate tropical forests, as more than two billion people depend on wood for cooking and heating, particularly in developing countries. Projects in Indonesia, Nepal, and Uganda are fighting deforestation by providing alternative energy and incomes along with health and family planning services.- Indonesia: Health in Harmony
- Nepal: Forests for the Future
- Uganda: Sharing the Forest
Future Growth: By 2050, the UN says global population could range anywhere from 8 billion to 11 billion – and where it ends up depends in large part on the status of women in developing countries. “Even if fertility rates remain constant at current levels (which is unlikely), developing regions would grow from 5.7 billion in 2010 to 9.7 billion in 2050, but the total population of developed countries would remain essentially unchanged,” writes Madsen.- Elizabeth Leahy Madsen: How Did We Arrive at 7 Billion – and Where Do We Go From Here? [Part One] [Part Two]
There are no quick solutions to these seven problems. But meeting the unmet need for contraception of more than 200 million women is an effective and inexpensive way to start.
Sources: Population Action International, UN, World Health Organization.
Image Credit: Used with permission courtesy of Scott Woods, The University of Western Ontario. -
Water and Poverty in a World of 9 Billion, Vulnerable Agriculture in the Niger Basin
› In a two–part Water International special report on water, food, and poverty, examining 10 of the world’s major river basins, a team of researchers say that instead of worrying about having enough water to sustain the world’s growing demand, policymakers should be concerned with understanding how to manage what they already have.
In a two–part Water International special report on water, food, and poverty, examining 10 of the world’s major river basins, a team of researchers say that instead of worrying about having enough water to sustain the world’s growing demand, policymakers should be concerned with understanding how to manage what they already have.
Introducing the special report, Simon Cook, Myles Fisher, Tassilo Tiemann, and Alain Vidal note in “Water, Food and Poverty: Global- and Basin-Scale Analysis” that the vast majority of population growth over the next few decades is expected to happen in developing countries, “where the disjunct between poverty, water and food is particularly acute.” Gaining a better understanding of water – how much we have, who uses it, and how best to use it – is essential to improving development results in the face of this demographic explosion. Water is linked with poverty and development through issues like scarcity, access, and water-related hazards (like drought, flood, and disease). But the authors conclude that water productivity – the ease or difficulty in getting water from its source to agriculture – “is by far the most important water-related constraint to improved food, income and environmental security.”
In “Water, Agriculture and Poverty in the Niger River Basin,” Andrew Ogilvie et al., paint a bleak picture of life in one of West Africa’s most important basins, writing that “[m]uch of the population in the basin suffers from extreme, chronic poverty and remains vulnerable to droughts and malnutrition.” Many of the Niger basin’s 94 million residents rely on subsistence agriculture, and most of that agriculture relies on rainwater rather than groundwater irrigation systems. Over time, the authors write, “there is little doubt that climate change will increase the strain on already-vulnerable agriculture.” Population growth will exacerbate this strain; the basin’s population is expected to increase as much as fourfold by 2050. In spite of this bleak picture, the authors conclude that “[i]mprovements in rainfed agriculture can have an important impact on poverty reduction and food security due to the large population dependent on it.” -
Roger-Mark De Souza, RH Reality Check
Sex and Sustainability: Reflections For My Son Nick
›October 20, 2011 // By Wilson Center StaffThe original version of this article, by Roger-Mark De Souza, appeared on RH Reality Check.
“Are we going to talk about sex again?!” screamed my 12-year old son, Nick, as he ran down the stairs, away from me. That was five years ago and I had just sat down with him to have one of our father-son talks, this time about sex and sustainability.
Now Nick, a rising senior, is preparing for college at the same time as the global community is preparing for an important landmark of its own: the United Nations predicts that by October 31, world population will reach 7 billion.
The confluence of these two events gives me reason to think about the world Nick is inheriting from my generation, and makes me consider what I can say to him as he heads off to college.
This World of 7 Billion
I try to get my head around it. It’s a world of 7 billion people. With greater connectivity than I could have ever dreamed possible. A world of widening disparities and growing environmental degradation. A world with a changing climate. A world of crashing economic markets and changing debt ceilings.
It’s also a world of finite resources and growing demand.
Continue reading on RH Reality Check.
Photo Credit: David Hawxhurst/Wilson Center. -
PHE Is One Great Idea That Won’t Be On the Rio Agenda, Says Roger-Mark De Souza
›October 17, 2011 // By Sean Peoples“I am now serving as an example to other women in the community because I am not having any more children. I have received training in sustainable agricultural practices, I’m generating income, and I’m educating others,” said Berhane Ferkade, an Ethiopian farmer, to Population Action International’s Roger-Mark De Souza earlier this year. The 39-year-old mother of 11 become one of the community’s model farmers after working with LEM Ethiopia – a local population, health, and environment (PHE) development organization.
-
Watch: Dennis Taenzler on Four Key Steps for REDD+ to Avoid Becoming a Source of Conflict
›The UN Program on Reducing Emissions from Deforestation and Forest Degradation (REDD) provides financial incentives to developing countries to conserve their forests and invest in low-carbon pathways to sustainable development. However, it may also be a potential new source of conflict, says Dennis Taenzler, a senior project manager at adelphi in Berlin, who works on climate and energy policies as well as peace and conflict issues.
-
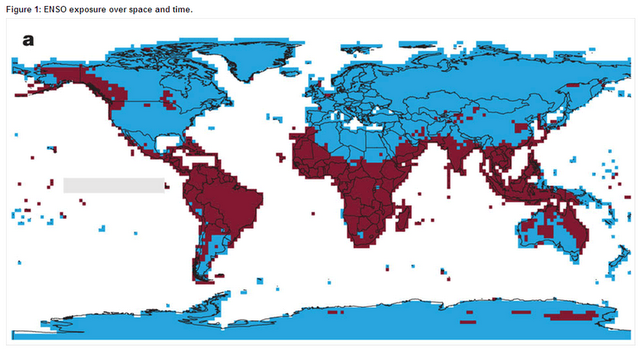
El Niño, Conflict, and Environmental Determinism: Assessing Climate’s Links to Instability
›October 5, 2011 // By Schuyler NullA recent Nature article on climate’s impact on conflict has generated controversy in the environmental security community for its bold conclusions about links between the global El Niño/La Niña cycle and the probability of intrastate conflict.
-
Weathering Change: New Film Links Climate Adaptation and Family Planning
›“Our planet is changing. Our population is growing. Each one of us is impacting the environment…but not equally. Each one of us will be affected…but not equally,” asserts the new documentary, Weathering Change, launched at the Wilson Center on September 22. The film, produced by Population Action International (PAI), explores the devastating impacts of climate change on the lives of women in developing countries through personal stories from Ethiopia, Nepal, and Peru. Family planning, argue the filmmakers, is part of the solution.
-
SXSW Eco Panel: Three Great Ideas That Won’t Be On the Rio+20 Agenda
›September 30, 2011 // By Schuyler Null South by Southwest (SXSW) – the popular music, film, and alternative showcase – is moving into the green space with its first ever “eco” conference, kicking off next week, October 4, with more than 50 panels on “solutions for a sustainable world.” There’s one in particular though you should tune into: “Three Great Ideas that Won’t Be On the Rio Agenda,” featuring Geoff Dabelko, director of the Wilson Center’s Environmental Change and Security Program; Roger-Mark De Souza, vice president of research and director of the climate program at Population Action International; and Aimee Christensen, CEO of Christensen Global Strategies.
South by Southwest (SXSW) – the popular music, film, and alternative showcase – is moving into the green space with its first ever “eco” conference, kicking off next week, October 4, with more than 50 panels on “solutions for a sustainable world.” There’s one in particular though you should tune into: “Three Great Ideas that Won’t Be On the Rio Agenda,” featuring Geoff Dabelko, director of the Wilson Center’s Environmental Change and Security Program; Roger-Mark De Souza, vice president of research and director of the climate program at Population Action International; and Aimee Christensen, CEO of Christensen Global Strategies.
The panel will feature discussion on three issues that will likely not be on the table at the Rio+20 UN Conference on Sustainable Development next year: integrated population, health, and environment development programs, climate adaptation as a path to peacebuilding, and how to get the private sector better involved in helping cope with climate change.
If you’re traveling down to Austin, “Three Great Ideas” is scheduled for Thursday, October 6 at 10am CST; if not, stay tuned for webcast information!
Showing posts from category climate change.