-
How Maternal Mortality and Morbidity Impact Economic Development
›“Investing in women and girls is the right thing to do,” says Mayra Buvinic, sector director of the World Bank’s gender and development group. “It is not only fair for gender equality, but it is smart economics.” But while it may be smart economics, many developing countries fail to address the underlying social causes that impact economic growth, such as poverty and gender inequality. Buvinic was joined by Dr. Nomonde Xundu, health attaché at the Embassy of South Africa in Washington, D.C., and Mary Ellen Stanton, senior maternal health advisor at the U.S. Agency for International Development (USAID), at the sixth meeting of the Advancing Policy Dialogue on Maternal Health Series, which addressed the economic impact of maternal mortality and provided evidence for the need for increased investment in maternal health.
-
Flooded With Food Insecurity in Pakistan
›The floods sweeping across Pakistan have caused widespread destruction, ruined livelihoods, displaced millions, and sparked a food crisis. Food prices have skyrocketed across the country as miles of farmland succumb to the deluge, including 1.5 million hectares in Punjab province, Pakistan’s breadbasket and agricultural heartland.
Food insecurity is now rife across the country — yet even before the floods, millions of Pakistanis struggled to access food. Back in 2008, the UN estimated that 77 million Pakistanis were hungry and 45 million malnourished. And while many developing nations have begun to recover from the global food crisis of 2007-08, Pakistan’s food fortunes have remained miserable. Throughout 2010, Pakistan’s two chief food staples, rice and wheat, have cost 30 to 50 percent times more than they did before the global food crisis. Drought, rampant water shortages, and conflict have intensified food insecurity in Pakistan in recent months.
A new edited book volume published by the Wilson Center’s Asia Program, Hunger Pains: Pakistan’s Food Insecurity, examines the country’s food insecurity. The book has already been the subject of a news story and an editorial in the Pakistani newspaper Dawn. The book, edited by Michael Kugelman and Robert M. Hathaway, is based on the 2009 Wilson Center conference of the same name. It assesses food supply challenges, access issues, governance constraints, social and structural dimensions, gender and regional disparities, and international responses.
The book makes a range of recommendations. These include:- Declare hunger a national security issue. Since some of Pakistan’s most food-insecure regions lie in militant hotbeds, hunger should be linked to defense, and food provision projects should be given ample public funding.
- Diversify the crop mix so that Pakistan’s agricultural economy revolves around more than wheat and rice. The country should accord more resources to crops that are less water-intensive and more nutritious.
- Give schools a central focus in food aid and food distribution. Using schools as a venue for food distribution gives parents powerful incentives to send their children to school.
- Tackle the structural dimensions. Strengthening agricultural institutions, improving infrastructure and storage facilities, and injecting capital into a stagnant farming sector are all key to making Pakistan more food-secure. Yet unless Pakistan deals with poverty, landlessness, and entrenched political interests in agriculture, food insecurity will remain.
Michael Kugelman is program associate with the Asia Program at the Woodrow Wilson International Center for Scholars.
Photo Credit: “Chitarl, Pakistan” where floods damaged the way over Lawari pass and killed five in August 2006. Courtesy of flickr user groundreporter -
Boosting the U.S. Role in the Global Health Arena
›A new video from the Commission on Smart Global Health Policy, which was established by the Center for Strategic & International Studies, reviews the commission’s progress towards its goal of encouraging the U.S. government to embrace global health as a pillar of U.S. foreign policy.
The video reviews the recommendations from the commission’s March 2010 report, A Healthier, Safer and More Prosperous World: 1) Maintain robust U.S. support for the fight against HIV/AIDS, malaria, and tuberculosis; 2) Prioritize maternal and child health, especially in sub-Saharan Africa and South Asia; 3) Help other nations improve their capacity to prevent and respond to outbreaks of contagious disease; 4) Expand U.S. capacity to fund future global health initiatives by securing long-term investments for such efforts; and 5) Step up U.S. funding for multilaterals engaged in the global health field, including the World Health Organization, Global Fund, UNICEF, the World Bank, and the GAVI Alliance.
In the months ahead, commission members will be participating in public forums throughout the United States to discuss and promote the recommendations included in the report, before gathering in January to review the Obama administration’s progress on global health as the administration begins its third year. To date, the centerpiece of the administration’s health outreach efforts has been the six-year, $63 billion Global Health Initiative, designed to promote an enhanced U.S. role in addressing public health issues overseas.
The CSIS Global Health Policy Center will also be launching a year-long debate series called “Fault Lines in Global Health,” focusing on controversial topics in the global health field. The series’ kick-off event will center on U.S. AIDS funding, and is scheduled for Friday, August 6, 2010, from 9:30-11:00 a.m. -
Top 10 Posts for July 2010
›The new conflict minerals law, Yemen, and the “4 Degree” map top the list this month:
1. DRC’s Conflict Minerals: Can U.S. Law Impact the Violence?
2. Demographics, Depleted Resources, and Al Qaeda Inflame Tensions in Yemen
3. Eye on Environmental Security: Guest Contributor Rear Admiral Morisetti Launches the UK’s “4 Degree Map” on Google Earth
4. Time to Give a Dam: Alternative Energy as Source of Cooperation or Conflict?
5. Copper in Afghanistan: Chinese Investment In Aynak
6. India’s Maoists: South Asia’s “Other” Insurgency
7. A Backdraft Video: Stacy VanDeveer: Will Using Less Oil Affect Petro State Stability?
8. VIDEO: Peter Gleick on Peak Water
9. Is the Third Pole the Next Site for Water Crisis?
10. Interview: Educate Girls, Boys, To Meet the Population Challenge, Say Pakistan’s Leading Demographers -
PRB Maps the PHE World
›The Population Reference Bureau (PRB) has created an interactive Google map that highlights population, health, and environmental programs in Africa, Asia, and Latin America. The Population, Health, and Environment (PHE) Map shows the locations of projects that combine improved health services, sustainable natural resource management, and ecosystem conservation.
According to PRB’s Maura Graff and Jason Bremner, “the map aims to give viewers both a sense of the scale of current PHE integration efforts, and specific information about individual organizations, projects, and their location.”
Clicking on a marker will reveal the title of a PHE program, a short description of its goals and outcomes, a link to its website, and the occasional picture of the project in action. A list on the left alphabetically catalogs all the projects based on region.
The map also provides the opportunity for those working on PHE projects in the field to find nearby projects in order to share experiences. For example, in Ethiopia, Population Media Center and DSW’s Youth to Youth could share lessons learned about disseminating information on the reduction of female genital mutilation, the importance of providing family planning services to young married couples, and the linkage between reduced family size and enhanced stewardship of social and natural resources.
Communities that understand how population, health, and environment are intertwined are more engaged and energized to make a difference. In a video interview with ECSP, Roger-Mark De Souza, director of foundation and corporate relations at the Sierra Club, explains that PHE projects are so effective because solutions to a community’s liked problems demand this logical integration. For example, while learning about the health benefits of birth spacing, father and mothers also learn how their family planning decisions can improve the economic and environmental prospects of the community.
Just like PHE projects themselves, the map is a work in progress; PRB is seeking to add PHE projects that are still active or ended after 2005. Please contact Maura Graff if you would like to add a project.
Josephine Kim is a cadet at the United States Military Academy at West Point, and an intern with the Woodrow Wilson Center’s Environmental Change and Security Program. -
Talk Versus Action
‘Dialogue Television’ on Rebuilding Haiti
›Watch below or on MHz Worldview
In the aftermath of Haiti’s 7.0 earthquake, the world turned its attention to the impoverished and devastated island nation (including the New Security Beat, which covered some its demographic problems). Reporters, relief workers, and volunteers from around the globe rushed to provide coverage and aide. Western leaders announced bold blueprints for building a “new Haiti.” Six months later, only a tiny portion of pledged funds have been delivered, over one million Haitians remain homeless, and much of the country’s infrastructure remains in ruins. This week on dialogue, host John Milewski speaks with Donna Leinwand of USA Today and Sheri Fink, Public Policy Scholar at the Wilson Center, on their experiences working and reporting in Haiti after the devastation. Scheduled for broadcast starting July 21st, 2010 on MHz Worldview channel.
Donna Leinwand is a reporter for the nation’s top-selling newspaper, USA Today. She’s been with the paper since 2000, covering legal issues, major crimes, the Justice Department, terrorism, and natural disasters. She is also a past president of the National Press Club. Sheri Fink is a senior fellow with the Harvard Humanitarian Initiative, a staff reporter for Pro Publica, and is a public policy scholar at the Wilson Center. She was awarded a 2010 Pulitzer Prize for her investigative piece on doctors at a hospital cut off by Hurricane Katrina flood waters.
Note: A QuickTime plug-in may be required to launch the video. -
Stephanie Hanson Reports on PHE in Agricultural Development and Rwanda’s ‘One Acre Fund’
›Driving from Kigali into rural Rwanda, the hills that flank either side of the paved road are covered with bananas, maize, coffee, and beans under cultivation. Most Rwandans are farmers, using any bit of available land to feed their families and generate income. In this country—the most densely populated in Africa—little arable land is left untended.
My organization, One Acre Fund, offers loans and education to smallholder farmers in Kenya and Rwanda. We work with 18,000 farmers in three districts in the southwestern and western part of Rwanda, where we are know as Tubura, which means “multiply” in Kinyarwanda.
Though One Acre Fund is not a traditional population, health, and environment (PHE) project, agricultural development work inherently is PHE work, particularly in Rwanda, which faces significant population and environment challenges.
Our farmers have small plots of land because Rwanda’s population density is so high—375 people per square kilometer, higher than Japan—leaving only .13 hectares of arable land per person. They struggle to grow enough food because it’s difficult to support a big family on a small piece of land, especially without access to high-quality seed and fertilizer.
When farmers don’t grow enough to ensure basic food security for their families, their children are malnourished, which makes them more susceptible to illness.
Finally, agriculture both depends on and affects the environment. Farmers need favorable growing conditions—good soil and adequate rainfall—for a good harvest. Sustainable agriculture practices, such as composting and preventing soil erosion, ensure the environment remains healthy to support future farming.One Acre Fund is acutely aware of the challenges that our farmers face due to high population density, food insecurity, and environmental degradation. We offer a service model that addresses all the needs of a smallholder farmer: financing, farm inputs, education, and market access.
When a farmer enrolls with One Acre Fund in Rwanda, she joins as part of a group of 6-15 farmers. She receives an in-kind loan of seed and fertilizer, which is guaranteed by her group members. One Acre Fund delivers this seed and fertilizer to a market point within two kilometers of where she lives. A field officer provides in-field training on composting, techniques to prevent soil erosion, land preparation, planting, fertilizer application, and weeding.
Over the course of the season, the field officer monitors the farmer’s fields. At the end of the season, he trains her on how to harvest and store her crop. One Acre Fund also offers a harvest buyback program that farmers can choose to participate in.
On average, One Acre Fund farmers double their farm income per acre in one growing season. Ninety-eight percent of our farmers repay their loans, which are due several weeks after harvest.
With their increased harvests, One Acre Fund farmers are able to feed their children, which reduces malnutrition. Anecdotally, we also know that One Acre Fund children experience less illness; this year, we are working to incorporate health indicators into our monitoring and evaluation work.
At a harvest buyback last month, I met many farmers who had benefited from One Acre Fund’s services. One woman, Tamar, had sold 400 kilograms (880 pounds) of beans at the previous season’s buyback, which earned her roughly 132,000 Rwandan francs ($235 USD). She told me that she was using the money to build a bigger home for the six of her ten children who lived at home.
However, Tamar really wanted to buy a cow, but she knew that she would not earn enough money this year to afford one. With so many children, she struggled to earn enough money to invest in something that might generate additional income for her and her family.
Another woman, Medeatrice, had also made $235 USD from the sale of her beans. With that income, she had opened a small shop with her husband in a nearby market. Unusually for Rwanda, where the average woman has 5.5 children, Medeatrice only had one, a three-year old boy named Prince. I asked her if she planned to have more children.
“I only want one more child,” she told me. “If I only have two children, it is easy to educate and to take care of them.”
The Rwandan government has invested in educating its population on family planning, but it will take time for birth rates to drop. For now, families with five, six, or nine children are not uncommon.
However, research shows that when women have increased access to economic opportunities, birth rates drop. One Acre Fund is focused on helping Rwanda’s families increase their harvests so that they not only have enough to eat, but they can start investing in their futures.
Guest Contributor Stephanie Hanson is the director of policy and outreach at One Acre Fund.
Photo Credit: Rwanda’s hills and Medeatrice, courtesy of Stephanie Hanson. -
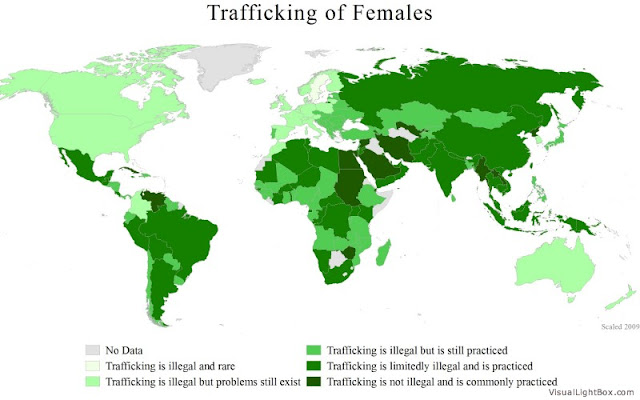
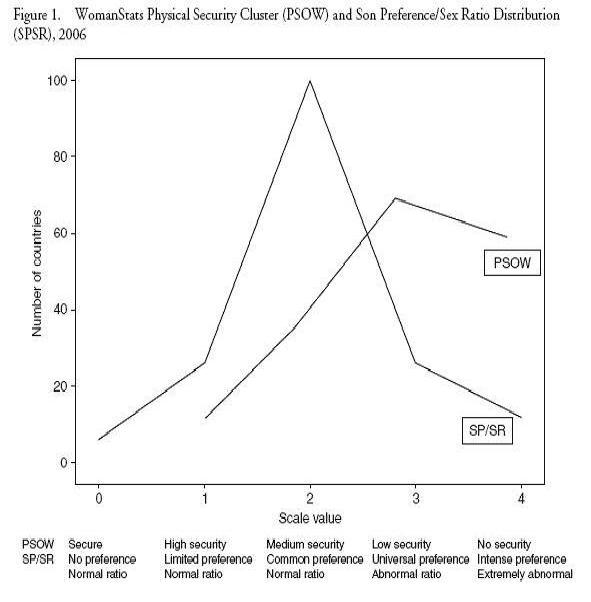
WomanStats Maps Gender-Linked Security Issues
›The WomanStats Project has published an array of maps depicting the challenges and conditions facing women worldwide today. The maps, which serve as a visual representation of the project’s database, cover gender-linked security issues such as: son preference and sex ratio, physical security, inequity in family law, human trafficking, polygamy, maternal mortality, discrepancy in education, government participation, intermingling between the sexes in public, and required dress codes.
These maps help researchers visually see correlations between two or more map themes. For example, Women’s Physical Security is moderately correlated to fertility rate, while Sex Ratio/Son Preference is not highly correlated to any other measures tested, such as women in the labor force, democracy, political rights, and economic rights. In addition to maps, the WomanStats Project’s database was used to create graphs that compare the scale values of Physical Security Clusters and Son Preference/Sex Ratio Distributions to the number of countries the scale level affected.
Some of the maps would benefit from additional functionality. For example, the “Women’s Physical Security” map broadly categorizes states based on high, medium, and low levels of security, but the legend is not linked to the definitions of these classifications. Another useful addition would be data tables that rank the countries for each theme. Such enhancements would better enable the viewer to perform empirical and spatial analysis of the status of women.
Overall, the WomanStats Project maps offer the viewer engaging visual depictions of how women’s lives vary across the world, and how countries compare to each other in terms of women’s security.
Josephine Kim is a cadet at the United States Military Academy at West Point and an intern with the Woodrow Wilson Center’s Environmental Change and Security Program.
Map and graph used courtesy of the WomanStats Project.
Showing posts from category *Blog Columns.