-
Top 10 Posts for January 2012
›The event summary from December’s meeting on new climate-conflict research took the top place last month and was joined by several other new comers: Marc Bellemare’s post about his food prices research, new Sahel vulnerability maps from UNEP, a summary of the water security plenary from NSCE 2012, and new reports on youth demographics from UNICEF and the U.S. Institute of Peace.
1. New Research on Climate and Conflict Links Shows Challenges for the Field
2. Tunisia’s Shot at Democracy: What Demographics and Recent History Tell Us
3. In Search of a New Security Narrative: The National Conversation Series Launches at the Wilson Center
4. Guest Contributor Marc F. Bellemare: Do High Food Prices Cause Social Unrest?
5. In the Rush for Land, Is it All About the Water?
6. UNEP Maps Conflict, Migration, Environmental Vulnerability in the Sahel
7. Peter Gleick: Population Dynamics Key to Sustainable Water Solutions
8. India’s Maoists: South Asia’s “Other” Insurgency
9. Move Beyond “Water Wars” to Fulfill Water’s Peacebuilding Potential, Says NCSE Panel
10. Three New Reports Highlight Ongoing Significance of Youth Demographics in Global Trends -
Is Foreign Aid Worth the Cost?
›“Is foreign aid worth the cost? That’s not really the question unless you’re Ron Paul,” quipped Carol J. Lancaster, dean of the School of Foreign Service at Georgetown University, at the Wilson Center on January 23. “The real questions are: What do we want to accomplish with our foreign aid? Where should it go? And in what form?” [Video Below]
Lancaster noted that following World War II, foreign aid became “a two-pronged instrument – one as an instrument of the Cold War and the other as an extension of American values.” It has been a very “intense marriage” between the two, he said, “with one side up and the other side down at different times, as any marriage tends to be.” Truman convinced Congress to provide aid to Greece and Turkey in 1948 to combat communism, and he was able to gain approval for the Marshall Plan by “scaring the wits out of Congress” about the communist threat.
Aid Under Fire
Congressman Donald Payne (N.J.), who is the ranking Democrat on the House Foreign Affairs Committee’s Subcommittee on Africa, agreed that the Cold War was the principal reason for our foreign aid programs after World War II, as we provided hundreds of billions of dollars in aid to our supporters around the world. But, “It’s different today,” he added. “Since the end of the Cold War, more funds are going for humanitarian and development assistance, but it is still directly linked to our national interests. One in five American jobs are tied to U.S. trade, and the growth of our trading partners is our growth as well.”
Payne cautioned that there is “a new group in the House of Representatives who think we should step out of the world. They’ve told their constituents they are going to cut the budget, and foreign aid is an easy target.” Payne noted that polls show the American people think one-quarter or more of the federal budget goes to foreign aid when it is little more than one percent.
Nevertheless, there has been bipartisan support for former President Bush’s HIV/AIDS initiative in Africa which is showing remarkable results in reducing deaths from the disease. Payne added that aid to Africa is showing results in the number of economies that are doing well despite the global economic downturn.
Payne expressed frustration with the inability to enact a foreign aid authorization bill in the last several Congresses because the measures became weighted down with all manner of policy riders that were both partisan and controversial. Consequently, our foreign relations operations are solely dependent on the annual appropriations bills which tend to become encumbered as well with troublesome riders.
The Dangers of “Nation Building”
Charles O. Flickner, Jr., a 28-year Republican staff member on the Senate Budget Committee and then the Foreign Operations Appropriations Subcommittee in the House, presented a more skeptical view, saying foreign aid is not worth the $35 billion it is costing us each year, even though some of the programs have been successful and should be continued. The biggest problem in recent years, he said, has been the amount of money wasted on projects in Iraq and Afghanistan without adequate planning or execution. Money was being virtually shoveled out the door in amounts the host countries did not have the capacity to absorb, said Flickner, and as a consequence we have witnessed a lot of failed projects and corruption.
Smaller projects, which the U.S. government and private aid donors are better at, have a greater chance for success because they do not overwhelm the capacities of host countries. He cited some of the scholarships and technical training programs available for foreign nationals as being among the most worthwhile in building internal leadership capacity for the future in developing countries.
Rajiv Chandrasekaran agreed on the amount of wasted aid dollars being spent in Iraq and Afghanistan, which he has covered as a foreign correspondent for The Washington Post. He told the story of a small, dirt-poor town in Afghanistan he visited in where the bazaar was bustling with new shops and goods, and people were freely spending money on modern electronics, motor bikes, and clothes. The town was the beneficiary of a massive U.S. aid program that provided seed money for farmers to grow crops and created day labor jobs for the residents of the area. A contractor was authorized to spend $30 million on the economic development of the town during the U.S. counterinsurgency surge and that came to roughly $300 per person. It was clear to the USAID official on the ground and to the reporter that the experiment would not be sustainable over the long-term, even though there was a temporary sense of economic activity and prosperity.
Future Vulnerabilities
The panel seemed to agree that it was unfair to blame USAID for these failures since they were thrown into situations overnight they were not prepared to manage in countries that were not capable of absorbing the assistance being directed at them – all in the midst of ongoing conflict. The real test of whether the new directions being charted by the Obama Administration will work will be on the smaller, more manageable projects in which the host countries have a greater role in shaping and implementing.
Lancaster listed four vulnerabilities in the future course of U.S. foreign aid that should be avoided, including trying to merge our various interests through the State and Defense Departments with our aid programs in countries like Pakistan, where the institutions are weak and corrupt; the danger of creating an entitlement dependency through funding of HIV/AIDS drugs, where we will be guilty of causing deaths if we reduce funding; the danger of attempting to undertake too many initiatives at once, such as food aid, global health, climate change, and science and technology innovations, while simultaneously trying to reform the infrastructure of USAID; and trying too hard to demonstrate results from aid given the difficulty of disentangling causes and effects and gauging success over too short a time frame.
Event Resources:
Don Wolfensberger is director of the Congress Project at the Wilson Center. -
Richard Black: Future Climate-Migration Interactions Will Stress Cities, “Trap” Vulnerable Populations
›“In a 50-year time span, climate change, in particular, is likely to have a quite a strong impact on the drivers of migration,” said Richard Black, professor of human geography at University of Sussex and lead author of Migration and Global Environmental Change: Future Challenges and Opportunities. “But in a way that is different to what has been understood until now.”
-
Call for Papers: Reducing Urban Poverty
›The Woodrow Wilson Center’s Comparative Urban Studies Project, USAID, the International Housing Coalition, the World Bank, and Cities Alliance are teaming up a third time to co-sponsor an academic paper competition for graduate- and PhD-level students focused on challenges facing urban centers in the developing world.
The themes of this year’s competition are land markets, global climate change, and youth.
Land Markets: The absence of efficient land and housing markets and lack of secure tenure for both renters and owners are impediments to urban and economic development in developing cities. Papers on this topic should explore strategies and approaches that would enable property markets to function better and would provide increased security of tenure and strengthened property ownership rights.
Global Climate Change: Papers should examine how urban populations, especially the poor, are coping with the impacts of climate change, and provide strategic policy analysis to better understand how cities can become more resilient to climate change impacts.
Youth: Most of the youth of the developing world are now or will soon be living in urban areas. Unfortunately, they are often growing up in the poorest urban areas – informal settlements and slum communities where their opportunities for advancement are limited by a variety of negative factors. Papers focused on youth should explore ways to build capacity so that you can develop knowledge and skills, find gainful employment, and participate more fully in society to advance economic growth and social development.
Winning papers from each category will be published and the authors invited to Washington, D.C. in the fall of 2012 for a policy workshop with subject matter experts. Additionally, one grand prize winner will be asked to present his or her work at the World Urban Forum (WUF). WUF was established by the United Nations to examine rapid urbanization and its impact on communities, cities, economies, climate change, and policies. The sixth WUF will be held from September 1-7, 2012 in Naples, Italy and will be focused on “The Urban Future.” In addition to the Washington conference and publication of his or her paper, the grand-prize winner will be invited to present his or her winning paper on a panel at the World Urban Youth Assembly at WUF on September 1st and 2nd.
The deadline for the submission of abstracts is February 20, 2012.
For detailed competition guidelines and requirements, and further information on the sub-topics, please see the full call for papers.
Image Credit: “Split by yelowcap,” courtesy of flickr user yelowcap (Vladimir Kaštier). -
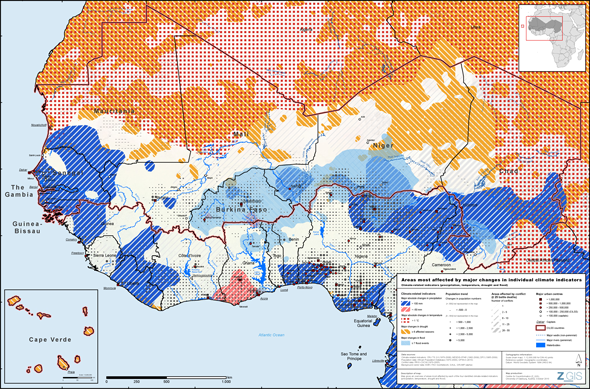
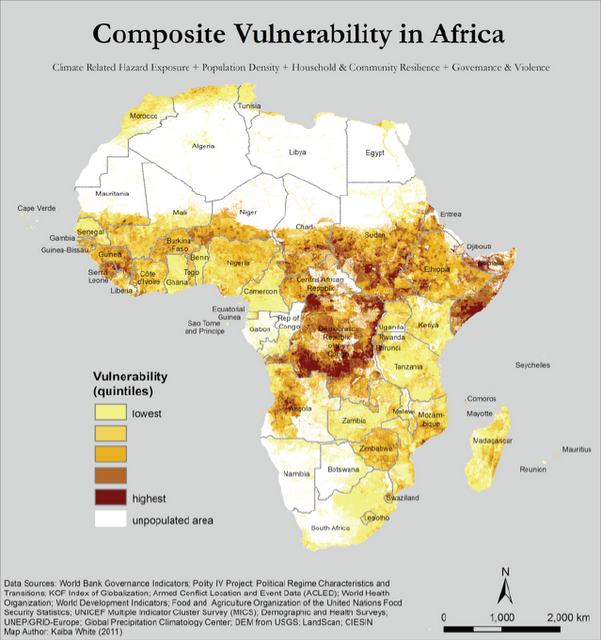
UNEP Maps Conflict, Migration, Environmental Vulnerability in the Sahel
›A new set of maps from the United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP) identifies “climate hotspots” – areas vulnerable to instability exacerbated by climate change – in 17 sub-Saharan countries in and bordering the Sahel region. The maps reflect the fact that, more often than not, the impact of climate change on local populations is compounded by changes in migration, conflict, or both. According to Livelihood Security: Climate Change, Migration and Conflict in the Sahel, the UNEP report accompanying the maps, understanding “the exacerbating effect of changes in climate on population dynamics and conflict in the region” will be essential to developing successful adaptation strategies throughout the region.
UNEP’s maps analyze 40 years of data to pinpoint where the region’s most at-risk populations are located based on environmental, population, and conflict trends dating back to 1970. In a single map pinpointing the Sahel’s 19 hotspots, UNEP synthesizes subnational data from four environmental indicators over time – rainfall (from 1970 to 2006), temperature changes (1970 to 2006), drought (1982 to 2009), and flooding (1985 to 2009) – which are then layered on top of population trends (1970 to 2010) and conflict data (1970 to 2005) in order to identify the region’s most insecure areas.
Composite Vulnerability
At first glance, the map can appear hard to decipher; it is flooded with different colors and symbols, each indicating something different about the extent of climate change, migration, and conflict in the region. A Google Earth version of the map (available for download here) makes all this information easier to process by allowing users to select which indicators they want to see mapped out, cutting back on the number of lines, dots, colors, and pie charts the user has to decode.
Given the vast amount of the information being condensed into these maps, the report is a helpful and worthwhile read. For instance, eight hotspots are in places with growing populations and another seven are located in places that have experienced conflict; altogether, 4 of the 19 hotspots have both past conflict and growing populations. The report digs deeper into the confluence of climate, conflict, and migration by discussing case studies that highlight how the three intersect in local communities (at the same time, the report is careful to avoid suggesting that there is a causal relationship between the three issues.). In Niger, Nigeria, and Chad, for example, tensions have been mounting between northern pastoralists and southern farmers as each group has moved further and further afield in search of water and arable land to sustain their livelihoods.
Holes In the Data
While the hotspot maps include a wealth of information, the report makes clear that it is by no means exhaustive. Rising sea levels are, for instance, a major impending threat to coastal populations in the Sahel, but only the downloadable Google Earth map – not the hotspot map in the report or the Google Earth map as presented online – incorporates this factor. Compounded with a skyrocketing population in the coastal areas – the coast between Accra and the Niger delta is expected to be “an urban megalopolis of 50 million people” by 2020, according to the report – an increase in sea levels could have a huge impact on the region’s stability.
The report also readily admits that the datasets for population trends and conflict have shortcomings. Population data is largely based on censuses, which both the report and its data sources (UNEP’s African Population Database and the Gridded Population of the World, version 3) acknowledge can be inconsistent in their accuracy. Additionally, after 2000, population data is based on projections rather than estimates, which, as last year’s update from the UN Population Division showed, have often proven inaccurate, particularly in sub-Saharan Africa.
Regarding conflict, the UNEP report is straightforward in admitting its limits. The report lacks data on small-scale conflict (fewer than 25 battle deaths, following the Uppsala Conflict Data Program’s threshold that separates conflicts from lower-level violence), even as it acknowledges that such conflict is “often the first to occur” when climate change threatens communities’ access to resources and livelihoods.
Ultimately, however, these maps give valuable data on specific locations that are uniquely vulnerable to trends in population, climate, migration, and conflict. They add focus to the conventional wisdom that climate change will impact the region’s stability, and, taken together, the maps and the report provide a valuable resource for scholars and policymakers attempting to craft adaptation policies that take into consideration these complex links.
Sources: Socioeconomic Data and Applications Center at Columbia University’s Earth Institute, UNEP, Uppsala Conflict Data Program.
Image Credit: UNEP. -
Delivering Solutions: Advancing Dialogue to Improve Maternal Health
›“Throughout the 2009-2011 Advancing Dialogue on Maternal Health lecture series, we always heard the same good news: we know how to save the lives of women and girls. But more political will is needed,” said Calyn Ostrowksi, program associate for the Wilson Center’s Global Health Initiative on December 15 for the launch of the series’ culminating report, Delivering Solutions: Advancing Dialogue To Improve Maternal Health.
Joining Ostrowski were co-author Margaret Greene, director of GreeneWorks; Luc de Bernis, senior advisor on maternal health at the UN Population Fund; Tim Thomas, interim director for the Maternal Health Task Force; and Chaacha Mwita, director of communications at the African Population and Health Research Center.
One of the few forums dedicated to maternal health, the series brought together senior-level policymakers, academic researchers, members of the media, and NGO workers from the United States and abroad. The series consisted of 21 separate events, with hundreds of experts sharing their experiences and thousands of participants and stakeholders providing their expertise. The final report captures, analyzes, and synthesizes the strategies and recommendations that emerged from the series.
Promoting Social Change
Unlike other health issues, said Green during her presentation on the findings of Delivering Solutions, the field of maternal health requires a holistic and multi-faceted approach; that is, an approach that looks not only at health systems, but also at underlying social factors. The report divides maternal health into three broad categories: social, economic, and cultural factors; health systems factors; and research/data demands.
Looking first at the social, cultural, and economic issues, Greene highlighted the need to improve nutrition and educational opportunities for young women in developing countries. Policymakers must be convinced that investing in women is not just good for women but good for families and children, she said. The participation of male partners and other male family members is also needed to increase access to maternal health services, such as family planning, and promote gender equality. The report pointed to a number of recommendations to promote male engagement:- Target interventions that educate men about danger signs and pregnancy complications.
- Address pressures that many young married men feel to prove their fertility.
- Inform men about sexual rights and how they relate to the health and wellbeing of their partners.
Health systems and medical resources play an equally pivotal role in reducing maternal mortality as social factors. The report highlights several key areas for strengthening the health system including the expansion of healthcare workers, health finance schemes, technology, and commodity distribution.
One key recommendation is to integrate reproductive health and maternal health supply chains. Four key medicines, oxytocin misoprostol, magnesium sulfate, and manual vacuum aspirators, target the three leading causes of maternal mortality (post-partum hemorrhage, obstructed labor, and unsafe abortion). Efforts to improve the distribution of these commodities should be more widely dispersed in developing countries and supported by community-based interventions. Women in urban slums, for example, face unique challenges that are not being adequately addressed.
Additionally, new technologies should be more creatively and effectively used, in particular the use of mobile phones in rural communities.
Many of the policy recommendations offered by the report, as Greene pointed out, are low-cost and highly effective. Yet three significant challenges remain for the field in general:- Six countries – Afghanistan, Democratic Republic of Congo, Ethiopia, India, Nigeria, and Pakistan – account for over half of the maternal deaths worldwide. The unique problems of each of these countries must be addressed and solved.
- Integration of maternal health with existing health services along with an over-reliance on community health workers can overburden weak infrastructure.
- Unnecessary cesarean births are on the rise as more women deliver in private sector facilities. These births cost 2 to 18 times as much as vaginal births and create unnecessary risks for mothers.
Chaacha Mwita of the African Population and Health Research Center (APHRC), located in Nairobi has seen firsthand the result of an overburdened and inadequate maternal health system in both his personal and professional life. Mwita endorsed the findings of the series report, emphasizing in particular the focus on transportation systems, male involvement, stakeholder dialogue, and education.
Mwita said that collaboration at all levels is the key to improving maternal health. Policymakers must communicate with researchers, who, in turn, must communicate with doctors, nurses, and hospital administrators in the field. The collaborative in-country dialogue series between the Wilson Center and APHRC, he believes, was a highly useful and easily replicable way of encouraging dialogue among relevant stakeholders in the field.
The Big Picture
”Our hope is that we’ve been able to seed discussions,” said Tim Thomas of the Maternal Health Task Force, one of the co-sponsors of the maternal health series. “We hope those seeds will take root and flourish.” Luc de Bernis, senior maternal health advisor of UNFPA, echoed Thomas’ sentiments, emphasizing the need for continued dialogue.
While maternal health has drawn increased international attention, creating political agreement among policymakers is a complex and often difficult process. There has been marked, though uneven, progress in improving maternal health across the globe, but more must be done. The Delivering Solutions report provides a state of the field assessment as well recommendations for existing, easy-to-implement solutions.
Event Resources: -
New Research on Climate and Conflict Links Shows Challenges for the Field
›
“We know that there will be more conflicts in the future as a result of climate change than there would have been in a hypothetic world without climate change,” said Marc Levy, deputy director of the Center for International Earth Science Information Network (CIESIN) at Columbia University’s Earth Institute, although existing data and methodologies cannot predict how many additional conflicts there will be, or which causal factors will matter most. [Video Below]
-
Jon Barnett: Should Climate Change Be Addressed by the UN Security Council?
›For a small island state like Tuvalu, climate change is an enormous security issue and they have told the UN Security Council as much, said Jon Barnett, professor of resource management and geography at the University of Melbourne, in an interview with ECSP. But, despite debate in 2007 and 2011, the Council has been unable to reach agreement on whether climate change is an international security issue or not.
Showing posts from category *Blog Columns.